2256:
2503:
2523:
2513:
144:
The definition given initially by
Quillen was that of a closed model category, the assumptions of which seemed strong at the time, motivating others to weaken some of the assumptions to define a model category. In practice the distinction has not proven significant and most recent authors (e.g., Mark
1143:
Cofibrations can be characterized as the maps which have the left lifting property with respect to acyclic fibrations, and acyclic cofibrations are characterized as the maps which have the left lifting property with respect to fibrations. Similarly, fibrations can be characterized as the maps which
1172:
with respect to the class of weak equivalences. This definition of homotopy category does not depend on the choice of fibrations and cofibrations. However, the classes of fibrations and cofibrations are useful in describing the homotopy category in a different way and in particular avoiding
1124:. In general, not all objects are fibrant or cofibrant, though this is sometimes the case. For example, all objects are cofibrant in the standard model category of simplicial sets and all objects are fibrant for the standard model category structure given above for topological spaces.
148:
The definition has been separated to that of a model structure on a category and then further categorical conditions on that category, the necessity of which may seem unmotivated at first but becomes important later. The following definition follows that given by Hovey.
913:-modules admit natural model structures. This follows because there is an adjunction between simplicial sets and simplicial commutative rings (given by the forgetful and free functors), and in nice cases one can lift model structures under an adjunction.
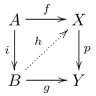
386:: acyclic cofibrations have the left lifting property with respect to fibrations, and cofibrations have the left lifting property with respect to acyclic fibrations. Explicitly, if the outer square of the following diagram commutes, where
959:
candidates for distinct model structures: in one, the so-called projective model structure, fibrations and weak equivalences are those maps of functors which are fibrations and weak equivalences when evaluated at each object of
756:, but rather the narrower class of maps that have the left lifting property with respect to the acyclic Serre fibrations. Equivalently, they are the retracts of the relative cell complexes, as explained for example in Hovey's
98:: the category of topological spaces is a model category, with the homotopy corresponding to the usual theory. Similarly, objects that are thought of as spaces often admit a model category structure, such as the category of
964:. Dually, the injective model structure is similar with cofibrations and weak equivalences instead. In both cases the third class of morphisms is given by a lifting condition (see below). In some cases, when the category
1438:
1181:
which are both fibrant and cofibrant, and whose morphisms are left homotopy classes of maps (equivalently, right homotopy classes of maps) as defined above. (See for instance Model
Categories by Hovey, Thm 1.2.10)
1135:. These notions coincide when the domain is cofibrant and the codomain is fibrant. In that case, homotopy defines an equivalence relation on the hom sets in the model category giving rise to homotopy classes.
1337:
354:
411:
760:. This structure is not unique; in general there can be many model category structures on a given category. For the category of topological spaces, another such structure is given by
1451:
are not equivalent, but their homotopy categories are. Therefore, simplicial sets are often used as models for topological spaces because of this equivalence of homotopy categories.
1239:
725:
848:-modules can be computed by either resolving the source projectively or the target injectively. These are cofibrant or fibrant replacements in the respective model structures.
234:
202:
650:
604:
1173:
set-theoretic issues arising in general localizations of categories. More precisely, the "fundamental theorem of model categories" states that the homotopy category of
501:
456:
727:
also admits a model structure so that weak equivalences correspond to their opposites, fibrations opposites of cofibrations and cofibrations opposites of fibrations.
132:, one of the first major applications of the theory. Because of the above example regarding homology, the study of closed model categories is sometimes thought of as
319:
1260:
preserves cofibrations and acyclic cofibrations or, equivalently by the closed model axioms, such that G preserves fibrations and acyclic fibrations. In this case
672:
1148:
with respect to acyclic cofibrations, and acyclic fibrations are characterized as the maps which have the right lifting property with respect to cofibrations.
990:
Denis-Charles
Cisinski has developed a general theory of model structures on presheaf categories (generalizing simplicial sets, which are presheaves on the
1185:
Applying this to the category of topological spaces with the model structure given above, the resulting homotopy category is equivalent to the category of
969:
683:
The axioms imply that any two of the three classes of maps determine the third (e.g., cofibrations and weak equivalences determine fibrations).
975:
The process of forcing certain maps to become weak equivalences in a new model category structure on the same underlying category is known as
1367:
1544:
Barnea, Ilan; Schlank, Tomer M. (2016), "A projective model structure on pro-simplicial sheaves, and the relative étale homotopy type",
1900:
1521:
Cisinski, Denis-Charles. Les préfaisceaux comme modèles des types d'homotopie. (French) Astérisque No. 308 (2006), xxiv+390 pp.
2185:
1806:
1770:
1727:
1526:
1443:
involving the geometric realization of a simplicial set and the singular chains in some topological space. The categories
1274:
161:
40:
1037:
by cocompleteness, since these objects are the limit and colimit, respectively, of the empty diagram. Given an object
886:
Other examples of categories admitting model structures include the category of all small categories, the category of
541:
The above definition can be succinctly phrased by the following equivalent definition: a model category is a category
1694:
1679:
1664:
1639:
121:. Homology can then be viewed as a type of homotopy, allowing generalizations of homology to other objects, such as
921:
741:
1893:
1206:
2097:
2052:
752:
and with weak equivalences as weak homotopy equivalences. The cofibrations are not the usual notion found
1342:
between the homotopy categories. There is also an explicit criterion for the latter to be an equivalence (
526:
2526:
2466:
906:
696:
2175:
2516:
2302:
2166:
2074:
1165:
860:
784:-modules carries at least two model structures, which both feature prominently in homological algebra:
207:
145:
Hovey and Philip
Hirschhorn) work with closed model categories and simply drop the adjective 'closed'.
175:
2475:
2119:
2057:
1980:
607:
287:
2552:
2547:
2506:
2462:
2067:
1886:
830:
2062:
2044:
1546:
617:
571:
522:
2269:
2035:
2015:
1938:
1145:
976:
480:
435:
2151:
1990:
1872:
1470:
1963:
1958:
1816:
1780:
1737:
1649:
1616:
1612:
1587:
1565:
1532:
297:
905:
Simplicial objects in a category are a frequent source of model categories; for instance,
236:
subject to the following axioms. A fibration that is also a weak equivalence is called an
8:
2307:
2255:
2181:
1985:
1138:
980:
891:
133:
126:
122:
118:
1569:
765:
2161:
2156:
2138:
2020:
1995:
1820:
1631:
1555:
1460:
1253:
761:
657:
83:
75:
2470:
2407:
2395:
2297:
2222:
2217:
2171:
1953:
1948:
1848:
1824:
1802:
1766:
1723:
1690:
1675:
1660:
1635:
1604:
1522:
895:
691:
530:
52:
2431:
2317:
2292:
2227:
2212:
2207:
2146:
1975:
1943:
1794:
1758:
1715:
1627:
1573:
1465:
991:
899:
898:, the category of topological spectra, and the categories of simplicial spectra or
160:
consists of three distinguished classes of morphisms (equivalently subcategories):
74:
In recent decades, the language of model categories has been used in some parts of
60:
972:, there is a third model structure lying in between the projective and injective.
2343:
1909:
1812:
1776:
1754:
1733:
1645:
1583:
1529:
1198:
1132:
1030:
95:
32:
24:
983:
can be obtained as a
Bousfield localization of the model category of simplicial
2380:
2375:
2359:
2322:
2232:
1860:
1746:
1358:
1128:
1034:
887:
99:
64:
51:' satisfying certain axioms relating them. These abstract from the category of
1798:
1578:
1488:
Some readers find the term "trivial" ambiguous and so prefer to use "acyclic".
2541:
2370:
2202:
2079:
2005:
1719:
777:
106:
56:
2124:
2025:
1186:
837:
796:
380:
is defined and any two of these are weak equivalences then so is the third.
325:
belongs to the same distinguished class. Explicitly, the requirement that
2385:
2365:
2237:
2107:
924:
with a model structure that is compatible with the simplicial structure.
866:
cofibrations are monomorphisms that are split as morphisms of underlying
826:
819:
807:
789:
753:
410:
353:
169:
48:
20:
16:
Mathematical category with weak equivalences, fibrations and cofibrations
1753:, Lecture Notes in Mathematics, No. 43, vol. 43, Berlin, New York:
2417:
2355:
1968:
1762:
1433:{\displaystyle |-|:\mathbf {sSet} \leftrightarrows \mathbf {Top} :Sing}
1006:
1139:
Characterizations of fibrations and cofibrations by lifting properties
873:
fibrations are epimorphisms that are split as morphisms of underlying
764:
and standard cofibrations, and the weak equivalences are the (strong)
2411:
2102:
1510:
749:
165:
44:
1041:
in the model category, if the unique map from the initial object to
2480:
2112:
2010:
1837:
984:
800:
36:
1878:
1842:
1560:
2450:
2440:
2089:
2000:
936:
282:
is a morphism belonging to one of the distinguished classes, and
1017:) can also be constructed by imposing a weaker set of axioms to
2445:
1177:
is equivalent to the category whose objects are the objects of
248:
and a cofibration that is also a weak equivalence is called an
2327:
1543:
748:, admits a standard model category structure with the usual
536:
1864:
86:, where homotopy-theoretic approaches led to deep results.
1189:
and homotopy classes of continuous maps, whence the name.
521:
is a category that has a model structure and all (small)
1843:"(infinity,1)-categories directly from model categories"
678:
955:) is also a model category. In fact, there are always
1605:
Les préfaisceaux commes modèles des types d'homotopie
1370:
1357:
A typical example is the standard adjunction between
1277:
1209:
1151:
699:
660:
620:
574:
483:
438:
300:
210:
178:
1793:, Algebra and Applications, vol. 27, Springer,
545:and three classes of (so-called) weak equivalences
94:Model categories can provide a natural setting for
1432:
1331:
1233:
1080:is cofibrant and there is a weak equivalence from
855:-modules has a model structure that is defined by
719:
666:
644:
598:
495:
450:
313:
228:
196:
1332:{\displaystyle LF:Ho(C)\leftrightarrows Ho(D):RG}
1001:is a model category, then so is the category Pro(
935:, under certain extra hypothesis the category of
2539:
1104:is fibrant and there is a weak equivalence from
1611:
1131:and right homotopy is defined with respect to
321:, where 2 is the 2-element ordered set), then
1894:
1626:, Amsterdam: North-Holland, pp. 73–126,
851:The category of arbitrary chain-complexes of
1687:Abstract homotopy and simple homotopy theory
349:, such that the following diagram commutes:
1057:to the terminal object is a fibration then
2522:
2512:
2268:
1901:
1887:
1076:are objects of a model category such that
979:. For example, the category of simplicial
105:Another model category is the category of
1702:La théorie de l'homotopie de Grothendieck
1577:
1559:
1127:Left homotopy is defined with respect to
537:Definition via weak factorization systems
1657:Model Categories and Their Localizations
1617:"Homotopy theories and model categories"
1849:Model Categories and Simplicial Methods
1788:
1745:
1685:Klaus Heiner Kamps and Timothy Porter:
1234:{\displaystyle F:C\leftrightarrows D:G}
818:weak equivalences are maps that induce
788:weak equivalences are maps that induce
776:The category of (nonnegatively graded)
68:
63:theory). The concept was introduced by
2540:
1847:Paul Goerss and Kristen Schemmerhorn,
1608:, Astérisque, (308) 2006, xxiv+392 pp.
1192:
1053:. Analogously, if the unique map from
686:Also, the definition is self-dual: if
2267:
1920:
1882:
1709:
1497:
1024:
735:
117:. Homotopy theory in this context is
1838:"Do we still need model categories?"
1704:. Astérisque, (301) 2005, vi+140 pp.
1013:. However, a model structure on Pro(
679:First consequences of the definition
172:, and two functorial factorizations
139:
1908:
881:
720:{\displaystyle {\mathcal {C}}^{op}}
13:
1831:
1152:Homotopy and the homotopy category
1029:Every closed model category has a
771:
703:
294:(as objects in the arrow category
14:
2564:
1854:
229:{\displaystyle (\gamma ,\delta )}
2521:
2511:
2502:
2501:
2254:
1921:
1632:10.1016/B978-044481779-2/50003-1
1411:
1408:
1405:
1397:
1394:
1391:
1388:
900:presheaves of simplicial spectra
844:This explains why Ext-groups of
531:complete and cocomplete category
409:
352:
197:{\displaystyle (\alpha ,\beta )}
113:-modules for a commutative ring
836:cofibrations are maps that are
799:in each degree with projective
795:cofibrations are maps that are
1791:A Handbook of Model Categories
1714:, Cambridge University Press,
1624:Handbook of algebraic topology
1537:
1515:
1503:
1491:
1482:
1401:
1380:
1372:
1317:
1311:
1302:
1299:
1293:
1219:
902:on a small Grothendieck site.
829:in each degree with injective
742:category of topological spaces
690:is a model category, then its
674:satisfies the 2 of 3 property.
652:is a weak factorization system
639:
621:
593:
575:
402:is acyclic, then there exists
223:
211:
191:
179:
35:with distinguished classes of
1:
1596:
1244:between two model categories
825:fibrations are maps that are
806:fibrations are maps that are
89:
907:simplicial commutative rings
564:has all limits and colimits,
7:
2196:Constructions on categories
1712:Categorical homotopy theory
1454:
861:chain homotopy equivalences
730:
645:{\displaystyle (C,F\cap W)}
599:{\displaystyle (C\cap W,F)}
462:and an acyclic cofibration
10:
2569:
2303:Higher-dimensional algebra
1689:, 1997, World Scientific,
2497:
2430:
2394:
2342:
2335:
2286:
2276:
2263:
2252:
2195:
2137:
2088:
2043:
2034:
1931:
1927:
1916:
1799:10.1007/978-3-030-75035-0
1615:; Spaliński, Jan (1995),
1579:10.1016/j.aim.2015.11.014
918:simplicial model category
608:weak factorization system
503:for an acyclic fibration
1720:10.1017/CBO9781107261457
1602:Denis-Charles Cisinski:
1476:
1361:and topological spaces:
533:with a model structure.
496:{\displaystyle p\circ i}
451:{\displaystyle p\circ i}
406:completing the diagram.
260:(or sometimes called an
2113:Cokernels and quotients
2036:Universal constructions
1789:Balchin, Scott (2021),
1547:Advances in Mathematics
1045:is a cofibration, then
1033:by completeness and an
840:in each nonzero degree.
333:means that there exist
2270:Higher category theory
2016:Natural transformation
1700:Georges Maltsiniotis:
1655:Philip S. Hirschhorn:
1434:
1333:
1235:
1146:right lifting property
977:Bousfield localization
859:weak equivalences are
810:in each nonzero degree
721:
668:
646:
600:
497:
452:
315:
230:
198:
1710:Riehl, Emily (2014),
1471:Stable model category
1435:
1334:
1268:induce an adjunction
1236:
1094:cofibrant replacement
931:and a model category
892:simplicial presheaves
766:homotopy equivalences
722:
669:
647:
601:
498:
453:
390:is a cofibration and
316:
314:{\displaystyle C^{2}}
231:
199:
65:Daniel G. Quillen
2139:Algebraic categories
1368:
1275:
1207:
1160:of a model category
697:
658:
618:
572:
481:
436:
394:is a fibration, and
298:
208:
176:
2308:Homotopy hypothesis
1986:Commutative diagram
1751:Homotopical algebra
1570:2011arXiv1109.5477B
1509:Definition 2.1. of
1352:Quillen equivalence
1193:Quillen adjunctions
1118:fibrant replacement
927:Given any category
922:simplicial category
863:of chain-complexes;
762:Hurewicz fibrations
134:homotopical algebra
119:homological algebra
39:('arrows') called '
2021:Universal property
1763:10.1007/BFb0097438
1747:Quillen, Daniel G.
1430:
1329:
1254:Quillen adjunction
1231:
1133:path space objects
1025:Some constructions
750:(Serre) fibrations
736:Topological spaces
717:
664:
642:
596:
507:and a cofibration
493:
477:can be written as
448:
432:can be written as
311:
226:
194:
84:algebraic geometry
53:topological spaces
23:, particularly in
2535:
2534:
2493:
2492:
2489:
2488:
2471:monoidal category
2426:
2425:
2298:Enriched category
2250:
2249:
2246:
2245:
2223:Quotient category
2218:Opposite category
2133:
2132:
1875:in Joyal's catlab
1808:978-3-030-75034-3
1772:978-3-540-03914-3
1729:978-1-107-04845-4
1613:Dwyer, William G.
1527:978-2-85629-225-9
1158:homotopy category
896:Grothendieck site
692:opposite category
667:{\displaystyle W}
553:and cofibrations
162:weak equivalences
140:Formal definition
41:weak equivalences
2560:
2525:
2524:
2515:
2514:
2505:
2504:
2340:
2339:
2318:Simplex category
2293:Categorification
2284:
2283:
2265:
2264:
2258:
2228:Product category
2213:Kleisli category
2208:Functor category
2053:Terminal objects
2041:
2040:
1976:Adjoint functors
1929:
1928:
1918:
1917:
1903:
1896:
1889:
1880:
1879:
1827:
1783:
1740:
1672:Model Categories
1652:
1621:
1591:
1590:
1581:
1563:
1541:
1535:
1519:
1513:
1507:
1501:
1495:
1489:
1486:
1466:Cocycle category
1439:
1437:
1436:
1431:
1414:
1400:
1383:
1375:
1338:
1336:
1335:
1330:
1240:
1238:
1237:
1232:
1199:adjoint functors
1129:cylinder objects
1116:is said to be a
1100:. Similarly, if
1092:is said to be a
992:simplex category
882:Further examples
758:Model Categories
726:
724:
723:
718:
716:
715:
707:
706:
673:
671:
670:
665:
651:
649:
648:
643:
605:
603:
602:
597:
502:
500:
499:
494:
458:for a fibration
457:
455:
454:
449:
413:
356:
329:is a retract of
320:
318:
317:
312:
310:
309:
262:anodyne morphism
235:
233:
232:
227:
203:
201:
200:
195:
61:derived category
2568:
2567:
2563:
2562:
2561:
2559:
2558:
2557:
2553:Category theory
2548:Homotopy theory
2538:
2537:
2536:
2531:
2485:
2455:
2422:
2399:
2390:
2347:
2331:
2282:
2272:
2259:
2242:
2191:
2129:
2098:Initial objects
2084:
2030:
1923:
1912:
1910:Category theory
1907:
1857:
1834:
1832:Further reading
1809:
1773:
1755:Springer-Verlag
1730:
1642:
1619:
1599:
1594:
1542:
1538:
1520:
1516:
1508:
1504:
1496:
1492:
1487:
1483:
1479:
1457:
1404:
1387:
1379:
1371:
1369:
1366:
1365:
1359:simplicial sets
1276:
1273:
1272:
1208:
1205:
1204:
1195:
1154:
1141:
1031:terminal object
1027:
947:) (also called
888:simplicial sets
884:
778:chain complexes
774:
772:Chain complexes
738:
733:
708:
702:
701:
700:
698:
695:
694:
681:
659:
656:
655:
619:
616:
615:
573:
570:
569:
539:
482:
479:
478:
469:every morphism
437:
434:
433:
424:every morphism
305:
301:
299:
296:
295:
209:
206:
205:
177:
174:
173:
154:model structure
142:
107:chain complexes
100:simplicial sets
96:homotopy theory
92:
57:chain complexes
25:homotopy theory
17:
12:
11:
5:
2566:
2556:
2555:
2550:
2533:
2532:
2530:
2529:
2519:
2509:
2498:
2495:
2494:
2491:
2490:
2487:
2486:
2484:
2483:
2478:
2473:
2459:
2453:
2448:
2443:
2437:
2435:
2428:
2427:
2424:
2423:
2421:
2420:
2415:
2404:
2402:
2397:
2392:
2391:
2389:
2388:
2383:
2378:
2373:
2368:
2363:
2352:
2350:
2345:
2337:
2333:
2332:
2330:
2325:
2323:String diagram
2320:
2315:
2313:Model category
2310:
2305:
2300:
2295:
2290:
2288:
2281:
2280:
2277:
2274:
2273:
2261:
2260:
2253:
2251:
2248:
2247:
2244:
2243:
2241:
2240:
2235:
2233:Comma category
2230:
2225:
2220:
2215:
2210:
2205:
2199:
2197:
2193:
2192:
2190:
2189:
2179:
2169:
2167:Abelian groups
2164:
2159:
2154:
2149:
2143:
2141:
2135:
2134:
2131:
2130:
2128:
2127:
2122:
2117:
2116:
2115:
2105:
2100:
2094:
2092:
2086:
2085:
2083:
2082:
2077:
2072:
2071:
2070:
2060:
2055:
2049:
2047:
2038:
2032:
2031:
2029:
2028:
2023:
2018:
2013:
2008:
2003:
1998:
1993:
1988:
1983:
1978:
1973:
1972:
1971:
1966:
1961:
1956:
1951:
1946:
1935:
1933:
1925:
1924:
1914:
1913:
1906:
1905:
1898:
1891:
1883:
1877:
1876:
1873:Model category
1870:
1861:Model category
1856:
1855:External links
1853:
1852:
1851:
1845:
1840:
1833:
1830:
1829:
1828:
1807:
1785:
1784:
1771:
1742:
1741:
1728:
1706:
1705:
1698:
1683:
1668:
1653:
1640:
1609:
1598:
1595:
1593:
1592:
1536:
1514:
1502:
1490:
1480:
1478:
1475:
1474:
1473:
1468:
1463:
1461:(∞,1)-category
1456:
1453:
1441:
1440:
1429:
1426:
1423:
1420:
1417:
1413:
1410:
1407:
1403:
1399:
1396:
1393:
1390:
1386:
1382:
1378:
1374:
1340:
1339:
1328:
1325:
1322:
1319:
1316:
1313:
1310:
1307:
1304:
1301:
1298:
1295:
1292:
1289:
1286:
1283:
1280:
1242:
1241:
1230:
1227:
1224:
1221:
1218:
1215:
1212:
1194:
1191:
1153:
1150:
1140:
1137:
1061:is said to be
1049:is said to be
1035:initial object
1026:
1023:
970:Reedy category
909:or simplicial
883:
880:
879:
878:
871:
864:
842:
841:
834:
823:
812:
811:
804:
793:
773:
770:
737:
734:
732:
729:
714:
711:
705:
680:
677:
676:
675:
663:
653:
641:
638:
635:
632:
629:
626:
623:
612:
611:
595:
592:
589:
586:
583:
580:
577:
566:
565:
538:
535:
519:model category
515:
514:
513:
512:
492:
489:
486:
467:
447:
444:
441:
416:
415:
414:
381:
359:
358:
357:
308:
304:
272:
271:
269:
225:
222:
219:
216:
213:
193:
190:
187:
184:
181:
156:on a category
141:
138:
91:
88:
29:model category
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2565:
2554:
2551:
2549:
2546:
2545:
2543:
2528:
2520:
2518:
2510:
2508:
2500:
2499:
2496:
2482:
2479:
2477:
2474:
2472:
2468:
2464:
2460:
2458:
2456:
2449:
2447:
2444:
2442:
2439:
2438:
2436:
2433:
2429:
2419:
2416:
2413:
2409:
2406:
2405:
2403:
2401:
2393:
2387:
2384:
2382:
2379:
2377:
2374:
2372:
2371:Tetracategory
2369:
2367:
2364:
2361:
2360:pseudofunctor
2357:
2354:
2353:
2351:
2349:
2341:
2338:
2334:
2329:
2326:
2324:
2321:
2319:
2316:
2314:
2311:
2309:
2306:
2304:
2301:
2299:
2296:
2294:
2291:
2289:
2285:
2279:
2278:
2275:
2271:
2266:
2262:
2257:
2239:
2236:
2234:
2231:
2229:
2226:
2224:
2221:
2219:
2216:
2214:
2211:
2209:
2206:
2204:
2203:Free category
2201:
2200:
2198:
2194:
2187:
2186:Vector spaces
2183:
2180:
2177:
2173:
2170:
2168:
2165:
2163:
2160:
2158:
2155:
2153:
2150:
2148:
2145:
2144:
2142:
2140:
2136:
2126:
2123:
2121:
2118:
2114:
2111:
2110:
2109:
2106:
2104:
2101:
2099:
2096:
2095:
2093:
2091:
2087:
2081:
2080:Inverse limit
2078:
2076:
2073:
2069:
2066:
2065:
2064:
2061:
2059:
2056:
2054:
2051:
2050:
2048:
2046:
2042:
2039:
2037:
2033:
2027:
2024:
2022:
2019:
2017:
2014:
2012:
2009:
2007:
2006:Kan extension
2004:
2002:
1999:
1997:
1994:
1992:
1989:
1987:
1984:
1982:
1979:
1977:
1974:
1970:
1967:
1965:
1962:
1960:
1957:
1955:
1952:
1950:
1947:
1945:
1942:
1941:
1940:
1937:
1936:
1934:
1930:
1926:
1919:
1915:
1911:
1904:
1899:
1897:
1892:
1890:
1885:
1884:
1881:
1874:
1871:
1869:
1867:
1862:
1859:
1858:
1850:
1846:
1844:
1841:
1839:
1836:
1835:
1826:
1822:
1818:
1814:
1810:
1804:
1800:
1796:
1792:
1787:
1786:
1782:
1778:
1774:
1768:
1764:
1760:
1756:
1752:
1748:
1744:
1743:
1739:
1735:
1731:
1725:
1721:
1717:
1713:
1708:
1707:
1703:
1699:
1696:
1695:981-02-1602-5
1692:
1688:
1684:
1681:
1680:0-8218-1359-5
1677:
1673:
1669:
1666:
1665:0-8218-3279-4
1662:
1658:
1654:
1651:
1647:
1643:
1641:9780444817792
1637:
1633:
1629:
1625:
1618:
1614:
1610:
1607:
1606:
1601:
1600:
1589:
1585:
1580:
1575:
1571:
1567:
1562:
1557:
1553:
1549:
1548:
1540:
1534:
1531:
1528:
1524:
1518:
1511:
1506:
1499:
1494:
1485:
1481:
1472:
1469:
1467:
1464:
1462:
1459:
1458:
1452:
1450:
1446:
1427:
1424:
1421:
1418:
1415:
1384:
1376:
1364:
1363:
1362:
1360:
1355:
1353:
1350:are called a
1349:
1345:
1326:
1323:
1320:
1314:
1308:
1305:
1296:
1290:
1287:
1284:
1281:
1278:
1271:
1270:
1269:
1267:
1263:
1259:
1255:
1251:
1247:
1228:
1225:
1222:
1216:
1213:
1210:
1203:
1202:
1201:
1200:
1190:
1188:
1183:
1180:
1176:
1171:
1167:
1163:
1159:
1149:
1147:
1136:
1134:
1130:
1125:
1123:
1119:
1115:
1111:
1107:
1103:
1099:
1095:
1091:
1087:
1083:
1079:
1075:
1071:
1066:
1064:
1060:
1056:
1052:
1048:
1044:
1040:
1036:
1032:
1022:
1020:
1016:
1012:
1008:
1004:
1000:
995:
993:
988:
986:
982:
978:
973:
971:
967:
963:
958:
954:
951:-diagrams in
950:
946:
942:
938:
934:
930:
925:
923:
919:
914:
912:
908:
903:
901:
897:
894:on any small
893:
889:
876:
872:
870:-modules; and
869:
865:
862:
858:
857:
856:
854:
849:
847:
839:
838:monomorphisms
835:
832:
828:
824:
821:
817:
816:
815:
809:
805:
802:
798:
797:monomorphisms
794:
791:
787:
786:
785:
783:
779:
769:
767:
763:
759:
755:
751:
747:
743:
728:
712:
709:
693:
689:
684:
661:
654:
636:
633:
630:
627:
624:
614:
613:
609:
590:
587:
584:
581:
578:
568:
567:
563:
560:
559:
558:
556:
552:
549:, fibrations
548:
544:
534:
532:
528:
524:
520:
510:
506:
490:
487:
484:
476:
472:
468:
465:
461:
445:
442:
439:
431:
427:
423:
422:
420:
419:Factorization
417:
412:
408:
407:
405:
401:
397:
393:
389:
385:
382:
379:
375:
371:
367:
363:
360:
355:
351:
350:
348:
344:
340:
336:
332:
328:
324:
306:
302:
293:
289:
285:
281:
277:
274:
273:
270:
267:
266:
265:
263:
259:
255:
251:
247:
243:
239:
220:
217:
214:
188:
185:
182:
171:
167:
163:
159:
155:
150:
146:
137:
135:
131:
129:
124:
120:
116:
112:
108:
103:
101:
97:
87:
85:
81:
79:
72:
70:
66:
62:
58:
54:
50:
46:
42:
38:
34:
30:
26:
22:
2451:
2432:Categorified
2336:n-categories
2312:
2287:Key concepts
2125:Direct limit
2108:Coequalizers
2026:Yoneda lemma
1932:Key concepts
1922:Key concepts
1865:
1790:
1750:
1711:
1701:
1686:
1671:
1670:Mark Hovey:
1656:
1623:
1603:
1551:
1545:
1539:
1517:
1505:
1493:
1484:
1448:
1444:
1442:
1356:
1351:
1347:
1343:
1341:
1265:
1261:
1257:
1252:is called a
1249:
1245:
1243:
1196:
1187:CW complexes
1184:
1178:
1174:
1169:
1166:localization
1161:
1157:
1155:
1142:
1126:
1121:
1117:
1113:
1109:
1105:
1101:
1097:
1093:
1089:
1085:
1081:
1077:
1073:
1069:
1067:
1062:
1058:
1054:
1050:
1046:
1042:
1038:
1028:
1018:
1014:
1010:
1002:
998:
996:
989:
974:
965:
961:
956:
952:
948:
944:
940:
932:
928:
926:
917:
915:
910:
904:
885:
874:
867:
852:
850:
845:
843:
827:epimorphisms
822:in homology;
820:isomorphisms
813:
808:epimorphisms
792:in homology;
790:isomorphisms
781:
775:
757:
745:
739:
687:
685:
682:
561:
554:
550:
546:
542:
540:
518:
516:
508:
504:
474:
470:
463:
459:
429:
425:
418:
403:
399:
395:
391:
387:
383:
377:
373:
372:are maps in
369:
365:
361:
346:
342:
338:
334:
330:
326:
322:
291:
283:
279:
275:
261:
257:
253:
249:
245:
241:
237:
170:cofibrations
157:
153:
151:
147:
143:
127:
114:
110:
104:
93:
77:
73:
49:cofibrations
28:
18:
2400:-categories
2376:Kan complex
2366:Tricategory
2348:-categories
2238:Subcategory
1996:Exponential
1964:Preadditive
1959:Pre-abelian
1554:: 784–858,
1498:Riehl (2014
1007:pro-objects
258:cofibration
21:mathematics
2542:Categories
2418:3-category
2408:2-category
2381:∞-groupoid
2356:Bicategory
2103:Coproducts
2063:Equalizers
1969:Bicategory
1597:References
1197:A pair of
985:presheaves
529:, i.e., a
376:such that
166:fibrations
90:Motivation
76:algebraic
45:fibrations
2467:Symmetric
2412:2-functor
2152:Relations
2075:Pullbacks
1825:240268465
1561:1109.5477
1402:⇆
1377:−
1303:⇆
1220:⇆
1144:have the
1051:cofibrant
877:-modules.
634:∩
582:∩
488:∘
443:∘
246:fibration
221:δ
215:γ
189:β
183:α
130:-algebras
37:morphisms
2527:Glossary
2507:Category
2481:n-monoid
2434:concepts
2090:Colimits
2058:Products
2011:Morphism
1954:Concrete
1949:Additive
1939:Category
1749:(1967),
1674:, 1999,
1659:, 2003,
1500:, §11.3)
1455:See also
937:functors
801:cokernel
731:Examples
557:so that
527:colimits
276:Retracts
33:category
2517:Outline
2476:n-group
2441:2-group
2396:Strict
2386:∞-topos
2182:Modules
2120:Pushout
2068:Kernels
2001:Functor
1944:Abelian
1863:at the
1817:4385504
1781:0223432
1738:3221774
1650:1361887
1588:3459031
1566:Bibcode
1533:2294028
1354:then).
1164:is the
1063:fibrant
981:sheaves
384:Lifting
288:retract
254:trivial
250:acyclic
242:trivial
238:acyclic
80:-theory
67: (
47:' and '
2463:Traced
2446:2-ring
2176:Fields
2162:Groups
2157:Magmas
2045:Limits
1823:
1815:
1805:
1779:
1769:
1736:
1726:
1693:
1678:
1663:
1648:
1638:
1586:
1525:
831:kernel
523:limits
362:2 of 3
345:, and
268:Axioms
168:, and
123:groups
55:or of
2457:-ring
2344:Weak
2328:Topos
2172:Rings
1821:S2CID
1620:(PDF)
1556:arXiv
1477:Notes
1112:then
1088:then
1005:) of
968:is a
939:Fun (
920:is a
833:; and
803:; and
606:is a
364:: if
286:is a
278:: if
31:is a
2147:Sets
1803:ISBN
1767:ISBN
1724:ISBN
1691:ISBN
1676:ISBN
1661:ISBN
1636:ISBN
1523:ISBN
1447:and
1445:sSet
1346:and
1264:and
1248:and
1156:The
1120:for
1096:for
1072:and
754:here
740:The
525:and
368:and
252:(or
240:(or
204:and
125:and
82:and
69:1967
43:', '
27:, a
1991:End
1981:CCC
1868:Lab
1795:doi
1759:doi
1716:doi
1628:doi
1574:doi
1552:291
1449:Top
1256:if
1168:of
1108:to
1084:to
1068:If
1009:in
997:If
994:).
957:two
890:or
814:or
780:of
746:Top
473:in
428:in
398:or
290:of
264:).
109:of
71:).
19:In
2544::
2469:)
2465:)(
1819:,
1813:MR
1811:,
1801:,
1777:MR
1775:,
1765:,
1757:,
1734:MR
1732:,
1722:,
1646:MR
1644:,
1634:,
1622:,
1584:MR
1582:,
1572:,
1564:,
1550:,
1530:MR
1065:.
1021:.
987:.
943:,
916:A
768:.
744:,
517:A
421::
378:gf
341:,
337:,
256:)
244:)
164:,
152:A
136:.
102:.
2461:(
2454:n
2452:E
2414:)
2410:(
2398:n
2362:)
2358:(
2346:n
2188:)
2184:(
2178:)
2174:(
1902:e
1895:t
1888:v
1866:n
1797::
1761::
1718::
1697:.
1682:.
1667:.
1630::
1576::
1568::
1558::
1512:.
1428:g
1425:n
1422:i
1419:S
1416::
1412:p
1409:o
1406:T
1398:t
1395:e
1392:S
1389:s
1385::
1381:|
1373:|
1348:G
1344:F
1327:G
1324:R
1321::
1318:)
1315:D
1312:(
1309:o
1306:H
1300:)
1297:C
1294:(
1291:o
1288:H
1285::
1282:F
1279:L
1266:G
1262:F
1258:F
1250:D
1246:C
1229:G
1226::
1223:D
1217:C
1214::
1211:F
1179:C
1175:C
1170:C
1162:C
1122:X
1114:Z
1110:Z
1106:X
1102:Z
1098:X
1090:Z
1086:X
1082:Z
1078:Z
1074:X
1070:Z
1059:X
1055:X
1047:X
1043:X
1039:X
1019:C
1015:C
1011:C
1003:C
999:C
966:C
962:C
953:M
949:C
945:M
941:C
933:M
929:C
911:R
875:R
868:R
853:R
846:R
782:R
713:p
710:o
704:C
688:C
662:W
640:)
637:W
631:F
628:,
625:C
622:(
610:,
594:)
591:F
588:,
585:W
579:C
576:(
562:C
555:C
551:F
547:W
543:C
511:.
509:i
505:p
491:i
485:p
475:C
471:f
466:;
464:i
460:p
446:i
440:p
430:C
426:f
404:h
400:p
396:i
392:p
388:i
374:C
370:g
366:f
347:s
343:r
339:j
335:i
331:g
327:f
323:f
307:2
303:C
292:g
284:f
280:g
224:)
218:,
212:(
192:)
186:,
180:(
158:C
128:R
115:R
111:R
78:K
59:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.