1240:
1250:
1274:
20:
149:
As oxystat bioreactors are expensive to buy and run, lower-cost solutions have been devised. For example, the Micro-Oxygenated
Culture Device (MOCD) is a system involving ordinary flasks, oxygen-permeable tubes, sensors, and water pumps. Aeration is done by pumping the culture medium through the
145:
Newer oxystat bioreactor methods allow for more precise control of gas levels in the microaerobic environment, using a probe to measure the oxygen concentration or redox potential in real time. Ways to control oxygen intake include gas-generating packs and gas exchange.
49:
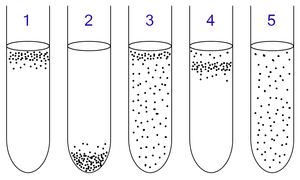
can grow with or without oxygen because they can metabolise energy aerobically or anaerobically. They gather mostly at the top because aerobic respiration generates more ATP than either fermentation or anaerobic respiration.
56:
need oxygen because they cannot ferment or respire anaerobically. However, they are poisoned by high concentrations of oxygen. They gather in the upper part of the test tube but not the very top.
62:
do not require oxygen as they metabolise energy anaerobically. Unlike obligate anaerobes however, they are not poisoned by oxygen. They can be found evenly spread throughout the test tube.
158:
A wide variety of microaerobic conditions exist in the world: in human bodies, underwater, etc. Many bacteria from these sources are microaerobes, some of which are also microaerophiles.
481:
Liu, Chen-Guang; Xue, Chuang; Lin, Yen-Han; Bai, Feng-Wu (March 2013). "Redox potential control and applications in microaerobic and anaerobic fermentations".
90:) for optimal growth. A more restrictive interpretation requires the microorganism to be obligate in this requirement. Many microaerophiles are also
37:
need oxygen because they cannot ferment or respire anaerobically. They gather at the top of the tube where the oxygen concentration is highest.
222:
1315:
1334:
142:
lid. The candle's flame burns until extinguished by oxygen deprivation, creating a carbon dioxide-rich, oxygen-poor atmosphere.
581:
420:
212:) are microaerophiles. As facultative anaerobes, they do survive anaerobic conditions, but grow better with a little oxygen.
1179:
946:
686:
659:
118:
has been criticized for being too restrictive and not accurate enough compared to similar categories. The broader term
382:
357:
216:
1308:
936:
863:
1060:
791:
250:
43:
are poisoned by oxygen, so they gather at the bottom of the tube where the oxygen concentration is lowest.
297:
Fuduche, Maxime; Davidson, Sylvain; Boileau, Céline; Wu, Long-Fei; Combet-Blanc, Yannick (19 March 2019).
134:
Microaerophiles are traditionally cultivated in candle jars. Candle jars are containers into which a lit
1339:
270:
1301:
901:
518:"The isolation and nature of campylobacters (microaerophilic vibrios) from laboratory and wild rodents"
1253:
1055:
978:
941:
737:
412:
1131:
1050:
1029:
679:
227:
59:
660:
Characterization of an unclassified microaerophilic bacterium associated with gastroenteritis.
1171:
813:
245:
79:
46:
557:
Cover TL (2012). "Perspectives on
Methodology for in Vitro Culture of Helicobacter pylori".
404:
1011:
886:
869:
707:
126:
to respire oxygen "within microoxic environments by using high-affinity terminal oxidase".
28:
8:
1136:
1021:
1016:
909:
879:
732:
717:
405:
240:
230:. The formation of magnetite in such bacteria in general require microaerobic conditions.
178:
1289:
1166:
1065:
874:
786:
779:
592:
325:
298:
1243:
1106:
1072:
1039:
896:
891:
849:
796:
672:
638:
597:
577:
539:
498:
494:
463:
416:
378:
353:
330:
265:
163:
40:
958:
834:
769:
628:
587:
569:
529:
490:
453:
320:
310:
209:
187:
1184:
1083:
968:
844:
774:
727:
260:
34:
617:"Lactobacillus Species: Taxonomic Complexity and Controversial Susceptibilities"
573:
16:
Microorganism requiring lower levels of oxygen than normally found in atmosphere
1285:
839:
95:
534:
517:
1328:
1193:
1078:
1034:
1006:
997:
987:
963:
859:
458:
437:
315:
299:"A Novel Highly Efficient Device for Growing Micro-Aerophilic Microorganisms"
204:
170:
104:
71:
1281:
1223:
1208:
1088:
829:
747:
695:
642:
615:
Goldstein, Ellie J. C.; Tyrrell, Kerin L.; Citron, Diane M. (15 May 2015).
601:
502:
467:
334:
255:
191:
1111:
664:
633:
616:
543:
91:
1218:
1203:
1121:
854:
1213:
1044:
1002:
914:
808:
195:
722:
699:
139:
75:
24:
1152:
1116:
752:
108:
1198:
953:
135:
1273:
1126:
19:
377:(3rd ed.). Wm. C. Brown Publishers. pp. 130–131.
296:
402:
614:
74:
that requires environments containing lower levels of
407:
Jawetz, Melnick & Adelberg's
Medical Microbiology
568:. Methods Mol Biol. Vol. 921. pp. 11–15.
372:
27:can be identified by growing them in test tubes of
403:Brooks GF, Carroll KC, Butel JS, Morse SA (2007).
435:
1326:
1309:
680:
138:is introduced before sealing the container's
480:
436:Salim SM, Mandal J, Parija SC (March 2014).
550:
429:
1316:
1302:
694:
687:
673:
515:
632:
591:
533:
509:
457:
373:Prescott LM, Harley JP, Klein DA (1996).
324:
314:
292:
290:
288:
286:
94:, requiring an elevated concentration of
556:
352:(1st ed.). Wiley. pp. 91–107.
347:
18:
411:(24th ed.). McGraw Hill. pp.
1327:
283:
668:
398:
396:
394:
226:sp. QH-2 are aquatic microaerophilic
122:has been coined to describe microbes
1268:
1249:
341:
13:
516:Fernie DS, Park RW (August 1977).
391:
366:
14:
1351:
653:
1272:
1248:
1239:
1238:
559:Perspectives on methodology for
495:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2012.11.005
217:Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense
937:Bacterial cellular morphologies
1335:Microbial growth and nutrition
608:
474:
1:
276:
114:The original definition of a
78:than that are present in the
1288:. You can help Knowledge by
621:Clinical Infectious Diseases
182:(previously identified as a
174:species are microaerophilic.
7:
574:10.1007/978-1-62703-005-2_3
271:Oxygenation (environmental)
234:
153:
10:
1356:
1267:
1180:Bacteria (classifications)
902:Primary nutritional groups
129:
1234:
1165:
1145:
1097:
986:
977:
929:
822:
760:
746:
706:
535:10.1099/00222615-10-3-325
442:from human stool samples"
303:Frontiers in Microbiology
1056:Bacterial outer membrane
459:10.4103/0255-0857.124294
316:10.3389/fmicb.2019.00534
190:that has been linked to
1284:-related article is a
1051:Gram-negative bacteria
1030:Gram-positive bacteria
483:Biotechnology Advances
446:Indian J Med Microbiol
350:Essential Microbiology
228:magnetotactic bacteria
63:
60:Aerotolerant organisms
906:Substrate preference
627:(suppl_2): S98–S107.
246:Anaerobic respiration
166:are microaerophilic:
47:Facultative anaerobes
22:
887:Microbial metabolism
251:Facultative anaerobe
29:thioglycollate broth
1137:Non-motile bacteria
733:Pathogenic bacteria
565:Helicobacter pylori
241:Aerobic respiration
179:Helicobacter pylori
86:; typically 2–10% O
1340:Microbiology stubs
1066:Lipopolysaccharide
634:10.1093/cid/civ072
194:and some types of
64:
41:Obligate anaerobes
1297:
1296:
1262:
1261:
1161:
1160:
1107:Bacterial capsule
1073:Periplasmic space
1040:Lipoteichoic acid
925:
924:
897:Microbial ecology
892:Nitrogen fixation
583:978-1-62703-004-5
522:J. Med. Microbiol
422:978-0-07-128735-7
348:Hogg, S. (2005).
266:Obligate anaerobe
164:Campylobacterales
1347:
1318:
1311:
1304:
1276:
1269:
1252:
1251:
1242:
1241:
1190:Former groupings
984:
983:
835:Human microbiome
758:
757:
689:
682:
675:
666:
665:
647:
646:
636:
612:
606:
605:
595:
554:
548:
547:
537:
513:
507:
506:
478:
472:
471:
461:
433:
427:
426:
410:
400:
389:
388:
370:
364:
363:
345:
339:
338:
328:
318:
294:
210:Lactobacillaceae
208:sensu lato (see
202:Many members of
188:Campylobacterota
186:), a species of
162:Some members of
82:(i.e. < 21% O
35:Obligate aerobes
1355:
1354:
1350:
1349:
1348:
1346:
1345:
1344:
1325:
1324:
1323:
1322:
1265:
1263:
1258:
1230:
1185:Bacterial phyla
1169:
1157:
1141:
1099:
1093:
1084:Arabinogalactan
989:
973:
921:
818:
762:
750:
742:
728:Lysogenic cycle
709:
702:
693:
656:
651:
650:
613:
609:
584:
555:
551:
514:
510:
479:
475:
434:
430:
423:
401:
392:
385:
371:
367:
360:
346:
342:
295:
284:
279:
261:Obligate aerobe
237:
156:
132:
102:in the case of
101:
89:
85:
57:
54:Microaerophiles
51:
44:
38:
32:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1353:
1343:
1342:
1337:
1321:
1320:
1313:
1306:
1298:
1295:
1294:
1277:
1260:
1259:
1257:
1256:
1246:
1235:
1232:
1231:
1229:
1228:
1227:
1226:
1221:
1216:
1211:
1201:
1196:
1187:
1182:
1176:
1174:
1163:
1162:
1159:
1158:
1156:
1155:
1149:
1147:
1143:
1142:
1140:
1139:
1134:
1129:
1124:
1119:
1114:
1109:
1103:
1101:
1095:
1094:
1092:
1091:
1086:
1075:
1070:
1069:
1068:
1063:
1047:
1042:
1037:
1026:
1025:
1024:
1019:
1014:
1000:
994:
992:
981:
975:
974:
972:
971:
966:
961:
956:
951:
950:
949:
944:
942:cell structure
933:
931:
927:
926:
923:
922:
920:
919:
918:
917:
915:Saccharophilic
912:
904:
899:
894:
889:
884:
883:
882:
877:
872:
867:
857:
852:
847:
842:
832:
826:
824:
820:
819:
817:
816:
811:
806:
804:Microaerophile
801:
800:
799:
794:
784:
783:
782:
777:
766:
764:
755:
744:
743:
741:
740:
735:
730:
725:
720:
714:
712:
704:
703:
692:
691:
684:
677:
669:
663:
662:
655:
654:External links
652:
649:
648:
607:
582:
549:
508:
489:(2): 257–265.
473:
438:"Isolation of
428:
421:
390:
383:
365:
358:
340:
281:
280:
278:
275:
274:
273:
268:
263:
258:
253:
248:
243:
236:
233:
232:
231:
213:
200:
199:
198:
175:
155:
152:
131:
128:
116:microaerophile
99:
96:carbon dioxide
87:
83:
68:microaerophile
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1352:
1341:
1338:
1336:
1333:
1332:
1330:
1319:
1314:
1312:
1307:
1305:
1300:
1299:
1293:
1291:
1287:
1283:
1278:
1275:
1271:
1270:
1266:
1255:
1247:
1245:
1237:
1236:
1233:
1225:
1222:
1220:
1217:
1215:
1212:
1210:
1207:
1206:
1205:
1202:
1200:
1197:
1195:
1194:Schizomycetes
1191:
1188:
1186:
1183:
1181:
1178:
1177:
1175:
1173:
1168:
1164:
1154:
1151:
1150:
1148:
1144:
1138:
1135:
1133:
1130:
1128:
1125:
1123:
1120:
1118:
1115:
1113:
1110:
1108:
1105:
1104:
1102:
1096:
1090:
1087:
1085:
1082:
1080:
1076:
1074:
1071:
1067:
1064:
1062:
1059:
1058:
1057:
1054:
1052:
1048:
1046:
1043:
1041:
1038:
1036:
1035:Teichoic acid
1033:
1031:
1027:
1023:
1020:
1018:
1015:
1013:
1010:
1009:
1008:
1007:Peptidoglycan
1004:
1001:
999:
998:Cell membrane
996:
995:
993:
991:
985:
982:
980:
976:
970:
967:
965:
962:
960:
957:
955:
952:
948:
945:
943:
940:
939:
938:
935:
934:
932:
928:
916:
913:
911:
908:
907:
905:
903:
900:
898:
895:
893:
890:
888:
885:
881:
878:
876:
873:
871:
868:
865:
861:
858:
856:
853:
851:
848:
846:
843:
841:
838:
837:
836:
833:
831:
828:
827:
825:
821:
815:
812:
810:
807:
805:
802:
798:
795:
793:
790:
789:
788:
785:
781:
778:
776:
773:
772:
771:
768:
767:
765:
759:
756:
754:
749:
745:
739:
736:
734:
731:
729:
726:
724:
721:
719:
716:
715:
713:
711:
705:
701:
697:
690:
685:
683:
678:
676:
671:
670:
667:
661:
658:
657:
644:
640:
635:
630:
626:
622:
618:
611:
603:
599:
594:
589:
585:
579:
575:
571:
567:
564:
560:
553:
545:
541:
536:
531:
527:
523:
519:
512:
504:
500:
496:
492:
488:
484:
477:
469:
465:
460:
455:
451:
447:
443:
441:
440:Campylobacter
432:
424:
418:
414:
409:
408:
399:
397:
395:
386:
384:0-697-29390-4
380:
376:
369:
361:
359:0-471-49754-1
355:
351:
344:
336:
332:
327:
322:
317:
312:
308:
304:
300:
293:
291:
289:
287:
282:
272:
269:
267:
264:
262:
259:
257:
254:
252:
249:
247:
244:
242:
239:
238:
229:
225:
224:
219:
218:
214:
211:
207:
206:
205:Lactobacillus
201:
197:
193:
192:peptic ulcers
189:
185:
184:Campylobacter
181:
180:
176:
173:
172:
171:Campylobacter
168:
167:
165:
161:
160:
159:
151:
147:
143:
141:
137:
127:
125:
121:
117:
112:
110:
107:
106:
105:Campylobacter
97:
93:
81:
77:
73:
72:microorganism
69:
61:
55:
48:
42:
36:
30:
26:
21:
1290:expanding it
1282:microbiology
1279:
1264:
1224:Mendosicutes
1209:Gracilicutes
1189:
1089:Mycolic acid
1079:Mycobacteria
1077:
1049:
1028:
964:Coccobacilli
864:in pregnancy
830:Extremophile
814:Aerotolerant
803:
748:Biochemistry
710:microbiology
696:Microbiology
624:
620:
610:
566:
562:
558:
552:
528:(3): 325–9.
525:
521:
511:
486:
482:
476:
452:(1): 35–38.
449:
445:
439:
431:
406:
375:Microbiology
374:
368:
349:
343:
306:
302:
256:Fermentation
223:Magnetospira
221:
215:
203:
183:
177:
169:
157:
148:
144:
133:
123:
119:
115:
113:
103:
98:(e.g. 10% CO
67:
65:
53:
1112:Slime layer
792:Facultative
780:Facultative
563:culture of
120:microaerobe
92:capnophiles
1329:Categories
1219:Mollicutes
1214:Firmicutes
1204:Prokaryota
1122:Glycocalyx
947:plasticity
910:Lipophilic
763:preference
738:Resistance
277:References
80:atmosphere
23:Anaerobic
1172:evolution
1146:Composite
1045:Endospore
1003:Cell wall
979:Structure
870:Placental
809:Nanaerobe
787:Anaerobic
718:Infection
196:gastritis
1244:Category
1167:Taxonomy
1100:envelope
990:envelope
880:Salivary
797:Obligate
775:Obligate
723:Exotoxin
700:Bacteria
643:25922408
602:23015486
561:in vitro
503:23178703
468:24399385
335:31001208
235:See also
154:Examples
140:airtight
76:dioxygen
25:bacteria
1254:Commons
1153:Biofilm
1132:Fimbria
1117:S-layer
1098:Outside
959:Bacilli
875:Uterine
860:Vaginal
770:Aerobic
753:ecology
708:Medical
593:3921885
326:6434946
309:: 534.
150:tubes.
130:Culture
109:species
1199:Monera
969:Spiral
761:Oxygen
641:
600:
590:
580:
544:330861
542:
501:
466:
419:
415:–275.
381:
356:
333:
323:
136:candle
1280:This
1127:Pilus
1081:only:
1061:Porin
1053:only:
1032:only:
954:Cocci
930:Shape
850:Mouth
823:Other
70:is a
1286:stub
1170:and
988:Cell
855:Skin
845:Lung
751:and
639:PMID
598:PMID
578:ISBN
540:PMID
499:PMID
464:PMID
417:ISBN
379:ISBN
354:ISBN
331:PMID
220:and
124:able
1022:DAP
1017:NAG
1012:NAM
840:Gut
629:doi
588:PMC
570:doi
530:doi
491:doi
454:doi
413:273
321:PMC
311:doi
111:).
58:5:
52:4:
45:3:
39:2:
33:1:
1331::
1192::
1005::
698::
637:.
625:60
623:.
619:.
596:.
586:.
576:.
538:.
526:10
524:.
520:.
497:.
487:31
485:.
462:.
450:32
448:.
444:.
393:^
329:.
319:.
307:10
305:.
301:.
285:^
66:A
31::
1317:e
1310:t
1303:v
1292:.
866:)
862:(
688:e
681:t
674:v
645:.
631::
604:.
572::
546:.
532::
505:.
493::
470:.
456::
425:.
387:.
362:.
337:.
313::
100:2
88:2
84:2
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.