43:
100:
292:. A labeled vertex is a vertex that is associated with extra information that enables it to be distinguished from other labeled vertices; two graphs can be considered isomorphic only if the correspondence between their vertices pairs up vertices with equal labels. An unlabeled vertex is one that can be substituted for any other vertex based only on its
397:. Collection Universitaire de Mathématiques, II Dunod, Paris 1958, viii+277 pp. (English edition, Wiley 1961; Methuen & Co, New York 1962; Russian, Moscow 1961; Spanish, Mexico 1962; Roumanian, Bucharest 1969; Chinese, Shanghai 1963; Second printing of the 1962 first English edition. Dover, New York 2001)
139:
consists of a set of vertices and a set of arcs (ordered pairs of vertices). In a diagram of a graph, a vertex is usually represented by a circle with a label, and an edge is represented by a line or arrow extending from one vertex to another.
195:
307:
of a polyhedron forms a graph, the vertices of which are the vertices of the polyhedron, but polyhedron vertices have additional structure (their geometric location) that is not assumed to be present in graph theory. The
218:) is a vertex with degree one. In a directed graph, one can distinguish the outdegree (number of outgoing edges), denoted 𝛿(v), from the indegree (number of incoming edges), denoted 𝛿(v); a
210:
is a vertex with degree zero; that is, a vertex that is not an endpoint of any edge (the example image illustrates one isolated vertex). A
154:
The two vertices forming an edge are said to be the endpoints of this edge, and the edge is said to be incident to the vertices. A vertex
147:, although they may have additional structure depending on the application from which the graph arises; for instance, a
479:
460:
438:
417:
86:
64:
57:
103:
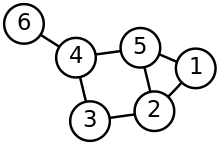
A graph with 6 vertices and 7 edges where the vertex number 6 on the far-left is a leaf vertex or a pendant vertex
128:
17:
258:
249:
is a collection of vertices the removal of which would disconnect the remaining graph into small pieces. A
428:
171:
269:
of a graph is a vector space having a set of basis vectors corresponding with the graph's vertices.
331:
293:
250:
51:
321:
273:
31:
350:
68:
524:
231:
203:
143:
From the point of view of graph theory, vertices are treated as featureless and indivisible
108:
8:
304:
144:
132:
265:
is a set of vertices that includes at least one endpoint of each edge in the graph. The
406:
379:
497:
475:
456:
434:
413:
312:
of a vertex in a polyhedron is analogous to the neighborhood of a vertex in a graph.
300:
281:
277:
383:
371:
246:
235:
179:
148:
500:
276:
if it has symmetries that map any vertex to any other vertex. In the context of
206:
of a vertex, denoted 𝛿(v) in a graph is the number of edges incident to it. An
401:
136:
518:
309:
448:
390:
326:
266:
262:
151:
is a graph in which the vertices represent concepts or classes of objects.
112:
426:
245:
is a vertex the removal of which would disconnect the remaining graph; a
198:
Example network with 8 vertices (of which one is isolated) and 10 edges.
375:
362:
Gallo, Giorgio; Pallotino, Stefano (1988). "Shortest path algorithms".
242:
505:
238:
is a vertex that is adjacent to every other vertex in the graph.
194:
469:
299:
Vertices in graphs are analogous to, but not the same as,
296:
in the graph and not based on any additional information.
99:
353:; example image of a network with 8 vertices and 10 edges
261:
is a set of vertices no two of which are adjacent, and a
257:
vertices always leaves the remaining graph connected. An
127:
is the fundamental unit of which graphs are formed: an
427:
Biggs, Norman; Lloyd, E. H.; Wilson, Robin J. (1986).
182:
of the graph, formed by all vertices adjacent to
495:
405:
516:
361:
455:. Reading, Mass.: Addison-Wesley Publishing.
131:consists of a set of vertices and a set of
27:Fundamental unit of which graphs are formed
400:
158:is said to be adjacent to another vertex
87:Learn how and when to remove this message
470:Harary, Frank; Palmer, Edgar M. (1973).
253:is a graph in which removing fewer than
222:is a vertex with indegree zero, while a
193:
98:
50:This article includes a list of general
395:Théorie des graphes et ses applications
284:it is important to distinguish between
135:(unordered pairs of vertices), while a
14:
517:
447:
234:: every two neighbors are adjacent. A
496:
189:
36:
226:is a vertex with outdegree zero. A
24:
56:it lacks sufficient corresponding
25:
536:
489:
41:
162:if the graph contains an edge (
344:
230:is one whose neighbors form a
13:
1:
364:Annals of Operations Research
337:
474:. New York, Academic Press.
433:. Oxford : Clarendon Press.
7:
315:
111:, and more specifically in
10:
541:
29:
408:Introductory graph theory
332:Glossary of graph theory
251:k-vertex-connected graph
430:Graph theory, 1736-1936
322:Node (computer science)
71:more precise citations.
32:Vertex (disambiguation)
351:File:Small Network.png
199:
104:
472:Graphical enumeration
301:vertices of polyhedra
197:
102:
109:discrete mathematics
30:For other uses, see
412:. New York: Dover.
498:Weisstein, Eric W.
376:10.1007/BF02288320
290:unlabeled vertices
200:
105:
282:graph isomorphism
278:graph enumeration
274:vertex-transitive
228:simplicial vertex
190:Types of vertices
97:
96:
89:
16:(Redirected from
532:
511:
510:
485:
466:
444:
423:
411:
387:
354:
348:
286:labeled vertices
247:vertex separator
236:universal vertex
180:induced subgraph
149:semantic network
129:undirected graph
92:
85:
81:
78:
72:
67:this article by
58:inline citations
45:
44:
37:
21:
540:
539:
535:
534:
533:
531:
530:
529:
515:
514:
492:
482:
463:
441:
420:
402:Chartrand, Gary
358:
357:
349:
345:
340:
318:
259:independent set
208:isolated vertex
192:
93:
82:
76:
73:
63:Please help to
62:
46:
42:
35:
28:
23:
22:
18:Isolated vertex
15:
12:
11:
5:
538:
528:
527:
513:
512:
501:"Graph Vertex"
491:
490:External links
488:
487:
486:
480:
467:
461:
445:
439:
424:
418:
398:
388:
356:
355:
342:
341:
339:
336:
335:
334:
329:
324:
317:
314:
216:pendant vertex
191:
188:
137:directed graph
95:
94:
49:
47:
40:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
537:
526:
523:
522:
520:
508:
507:
502:
499:
494:
493:
483:
481:0-12-324245-2
477:
473:
468:
464:
462:0-201-41033-8
458:
454:
450:
449:Harary, Frank
446:
442:
440:0-19-853916-9
436:
432:
431:
425:
421:
419:0-486-24775-9
415:
410:
409:
403:
399:
396:
392:
391:Berge, Claude
389:
385:
381:
377:
373:
369:
365:
360:
359:
352:
347:
343:
333:
330:
328:
325:
323:
320:
319:
313:
311:
310:vertex figure
306:
302:
297:
295:
291:
287:
283:
279:
275:
270:
268:
264:
260:
256:
252:
248:
244:
239:
237:
233:
229:
225:
221:
220:source vertex
217:
213:
209:
205:
196:
187:
185:
181:
177:
173:
169:
165:
161:
157:
152:
150:
146:
141:
138:
134:
130:
126:
122:
118:
114:
110:
101:
91:
88:
80:
77:February 2014
70:
66:
60:
59:
53:
48:
39:
38:
33:
19:
525:Graph theory
504:
471:
453:Graph theory
452:
429:
407:
394:
367:
363:
346:
327:Graph theory
298:
289:
285:
271:
267:vertex space
263:vertex cover
254:
240:
227:
223:
219:
215:
211:
207:
201:
183:
175:
174:of a vertex
172:neighborhood
167:
163:
159:
155:
153:
142:
124:
120:
116:
113:graph theory
106:
83:
74:
55:
370:(1): 1–79.
294:adjacencies
272:A graph is
224:sink vertex
212:leaf vertex
69:introducing
338:References
243:cut vertex
52:references
506:MathWorld
519:Category
451:(1969).
404:(1985).
384:62752810
316:See also
305:skeleton
121:vertices
119:(plural
170:). The
145:objects
65:improve
478:
459:
437:
416:
382:
303:: the
232:clique
214:(also
204:degree
178:is an
117:vertex
54:, but
380:S2CID
133:edges
123:) or
476:ISBN
457:ISBN
435:ISBN
414:ISBN
288:and
280:and
202:The
125:node
115:, a
372:doi
107:In
521::
503:.
393:,
378:.
368:13
366:.
241:A
186:.
509:.
484:.
465:.
443:.
422:.
386:.
374::
255:k
184:v
176:v
168:w
166:,
164:v
160:v
156:w
90:)
84:(
79:)
75:(
61:.
34:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.