258:
pointing the chairs more or less toward the performance, being able to see the conductor in the pit, being able to see other patrons, being able to see actors on elevated scenery, and not being obstructed by a wall, railing, column, ceiling overhang, loudspeaker cluster, or any other obstruction. The design of sightlines includes considerations of how much of the stage and scenery each patron can see. For example, can each patron see the top of the scenery or not, and can each patron see the whole stage floor or not? Design of sightlines is divided into two related exercises, vertical sightlines and horizontal sightlines. Design of proper sightlines includes resolving both technical and aesthetic issues. At issue is the emotional response of the audience: whether a performer can hold the audience's attention or not; whether the patron feels they had a "good" seat and their ticket was fairly priced or not; whether the audience gets the emotional impact of the performance or not; and whether the patron wants to come back and see another performance in that theater or not. Building codes restrict the maximum and minimum rise per row, limit the minimum width per row, limit the maximum deviation in the size of steps from row to row to achieve the curvature of the rake, and limit other aspects of sightline design.
238:
329:
from the touch lines and five metres behind the centre of the goal lines. FIFA ticketing carry out an assessment of all seats and those seats that have an obstructed view of the game will be classed obstructed view seats and will not be sold. Quite often these are the first few seats adjacent to the pitch with their view partially blocked by the advertising hoardings. This is an especially big problem with football stadiums that have running tracks around them. These seats are either covered with a fabric and not occupied during the game or the tickets are issued to non-paying spectators.
303:
286:
play. This is an annoyance to others and can lead to fights and in the context of large crowds this can be a serious safety threat. The maximum step height between terraces or rows is usually limited to 540mm. If this is exceeded then a continuous guardrail is required as protection against falling. Even with a 540mm terrace step many spectators become uncomfortable and start to feel the impact of vertigo. An ideal maximum terrace step height that will avoid most people feeling insecure is 450mm.
295:
36:
312:
their view from one of their eyes blocked by the head of the adjacent spectator. During exciting play this can lead to spectators jumping up out of their seats to get a better view. A clear view for both eyes for all front row spectators can be achieved by the use of curved stands in plan. It can also be argued that with play that is already a long distance away a better view of the game is available on the big video screen.
278:
354:
an algorithm to derive actual sight area in the early design stage of theater without producing a 3D model. The algorithm uses plan and cross sectional drawings to analyze view of audiences to resolve to address errors of the "sight area rate" algorithm which does not account for sightlines being blocked by the front-row seats in a theater.
209:
impractical to make different step heights for every single row. In practice the riser height is the same for a set of 4 or 5 rows at the bottom of the bowl with the number of rows in each same height set increasing for higher up rows. The uppermost tier could have only 2 or even 1 different step heights.
328:
There should be a clear view of the playing field from all seats. Roof supports should be eliminated entirely from the seating area. In calculating the sight lines it should be appreciated that advertising boards of 90–100 cm in height may be erected around the field at a distance of five metres
257:
in
Cincinnati; alternate row sightlines where each patron sees between the heads of patrons in the row in front and over the heads of patrons in the second row in front; next row sightlines where each patron sees over the heads of patrons in the row immediately in front; and basic considerations like
353:
The audience's sightline is an important aspect of the design of viewing venues. For theaters, an algorithm is used to check the sightline from a seat to determine if it is blocked. The development of better methods is the subject of continuing research. In 2011, Yeonhee Kim and Ghang Lee presented
311:
The C-Value considers the sightlines in the vertical plane. The sightlines in the horizontal plane need to be considered for the front row spectators in the instance where they look acutely sideways, typically adjacent far end corner flag. At the extreme end of the front row, spectators could have
285:
This is done with careful modelling utilizing the C-Value to ensure the ideal rake or curvature of the seating bowl. C-values are improved with a steeper slope or moving the seating rows away from the focus point. Inadequate views result in spectators jumping up for a better view during exciting
208:
in section. The curvature will be greatest closest to the pitch and will become an increasingly flatter curve as it moves to the upper rows. As a general rule the rake or curve of the seating bowl will flatten as the first row of seats move away from the side-line for a constant C-value. It is
196:
Good sightlines allow spectators to see all areas of a venue stage or field of play. To ensure this designers utilize the C-value, defined as the vertical distance from a spectator's eyes to sightline of the spectator directly behind. The C-value is determined in part by the
212:
It is the lowest rows of seats that are the most sensitive to the impact of the C-value because of the very flat view angle to the touch line. The higher seats can have a reduced C-value without impacting as seriously on the clear view of the field of play.
273:
The spectator view in modern stadia is optimised very carefully to balance the uninterrupted clear view to the field for every seat whilst not making the seating terraces any higher than necessary to satisfy structure, cost and safety considerations.
306:
The illustration indicates the partially obstructed view of the front row spectators looking at the far corner flag of the adjacent touchline. One eye can see the action on the field whilst vision to the second eye is
264:
It is recommended that a spectator's eye height must not be lower than 800 mm above the stage. However, in larger theatres it is acceptable to locate the eye height of the first row on the level of the stage.
229:. It is United Kingdom Government-funded guidance book on spectator safety at sports grounds. On Page 109 Green Guide Fifth Edition, the graphic reference does show the C-Value location.
184:
Subjects that have a line of sight with one another are said to be intervisible, where intervisibility is the ability of viewers at separate places to see each other without any
370:
237:
544:
508:
221:
The existing sightline formula in the Green Guide (Guide to Safety at Sports
Grounds) can be traced back to the sightline section of the
378:
100:
53:
440:
72:
298:
The C-value is the vertical distance from the spectator eye to where it intersects the sightline of the spectator directly behind.
79:
518:
86:
567:
403:
393:
119:
68:
581:
17:
57:
608:
603:
524:
320:
The touch-line (or side-line) and the goal-line are considered the C-Value focus point in stadiums.
93:
46:
8:
250:
155:
142:
are a particularly important consideration in the design of civic structures, such as a
573:
246:
563:
514:
409:
399:
577:
555:
302:
163:
143:
198:
167:
413:
245:
Sightline criteria in theaters can include: the "isacoustic curve" defined by
597:
559:
254:
27:
Unobstructed line between an observer and a subject of interest in a building
204:
The stadium bowl rake if based on consistent C-values will follow half of a
175:
135:
226:
222:
294:
35:
205:
185:
179:
178:
within sightlines is restricted to protect the key views of famous
151:
277:
545:"A Study of Sight Area Rate Analysis Algorithm on Theater Design"
472:
The
Architectural Press, London, Second Edition, 1987, pp. 26–30.
261:
Books on theater planning that discuss the design of sightlines.
159:
374:
171:
147:
513:. Dept of Culture, Media and Sport. 2008. p. 117.
154:. They determine the configuration of such items as
457:
The
Planning and Construction of American Theatres.
60:. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
510:The Green Guide – Guide to safety at sports ground
595:
216:
542:
201:, that is, the upward slope of the seating.
459:John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1907, p. 90.
430:Edinburgh new philosophical Journal 27, 1838.
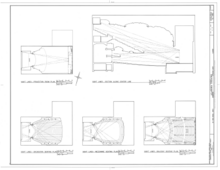
281:Typical Architectural Section of a stadium.
371:"London View Management Framework (LVMF)"
332:
268:
232:
120:Learn how and when to remove this message
323:
301:
293:
276:
241:Plans of a Movie theater with sightlines
236:
14:
596:
538:
536:
534:
391:
398:( ed.). Spon Press. p. 47.
289:
58:adding citations to reliable sources
29:
531:
24:
25:
620:
498:The MIT Press, 1985, pp. 235–242.
442:Journal of the Franklin Institute
223:Guide to Safety at Sports Grounds
34:
485:McGraw-Hill, 1977, pp. 579–599.
45:needs additional citations for
552:Computing in Civil Engineering
543:Kim, Y. & Lee, G. (2011).
501:
488:
475:
462:
449:
433:
420:
385:
363:
315:
13:
1:
357:
341:9 cm recommended minimum
217:Green Guide Sightline Formula
69:"Sightline" architecture
7:
348:
249:in 1838 and applied at the
10:
625:
338:6 cm absolute minimum
191:
445:. Pergamon Press. 1843.
428:Treatise on Sightlines.
377:. 2009. Archived from
333:FIFA C-Value standards
308:
299:
282:
269:Sightlines in stadiums
242:
233:Sightlines in theatres
455:Birkmire, William H.
426:Russell, John Scott.
324:Obstructed view seats
305:
297:
280:
240:
188:blocking their view.
587:on 19 February 2020.
560:10.1061/41182(416)87
496:Buildings for Music.
392:Sheard, Rod (2001).
170:. In cities such as
54:improve this article
494:Forsythe, Michael.
395:Sports architecture
253:in Chicago and the
251:Auditorium Building
609:Parts of a theatre
344:12 cm optimum
309:
300:
290:Sightlines in plan
283:
247:John Scott Russell
243:
604:Stage terminology
520:978-0-11-702074-0
481:Izenour, George.
130:
129:
122:
104:
16:(Redirected from
616:
589:
588:
586:
580:. Archived from
549:
540:
529:
528:
527:on 27 June 2008.
523:. Archived from
505:
499:
492:
486:
479:
473:
466:
460:
453:
447:
446:
437:
431:
424:
418:
417:
389:
383:
382:
381:on 11 July 2011.
367:
225:, also known as
125:
118:
114:
111:
105:
103:
62:
38:
30:
21:
624:
623:
619:
618:
617:
615:
614:
613:
594:
593:
592:
584:
570:
547:
541:
532:
521:
507:
506:
502:
493:
489:
483:Theater Design.
480:
476:
468:Ham, Roderick.
467:
463:
454:
450:
439:
438:
434:
425:
421:
406:
390:
386:
369:
368:
364:
360:
351:
335:
326:
318:
292:
271:
235:
219:
194:
126:
115:
109:
106:
63:
61:
51:
39:
28:
23:
22:
18:Intervisibility
15:
12:
11:
5:
622:
612:
611:
606:
591:
590:
568:
530:
519:
500:
487:
474:
461:
448:
432:
419:
404:
384:
361:
359:
356:
350:
347:
346:
345:
342:
339:
334:
331:
325:
322:
317:
314:
291:
288:
270:
267:
234:
231:
218:
215:
193:
190:
168:urban planning
128:
127:
42:
40:
33:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
621:
610:
607:
605:
602:
601:
599:
583:
579:
575:
571:
569:9780784411827
565:
561:
557:
553:
546:
539:
537:
535:
526:
522:
516:
512:
511:
504:
497:
491:
484:
478:
471:
465:
458:
452:
444:
443:
436:
429:
423:
415:
411:
407:
405:9781138982833
401:
397:
396:
388:
380:
376:
372:
366:
362:
355:
343:
340:
337:
336:
330:
321:
313:
304:
296:
287:
279:
275:
266:
262:
259:
256:
255:Emery Theatre
252:
248:
239:
230:
228:
224:
214:
210:
207:
202:
200:
189:
187:
182:
181:
177:
173:
169:
165:
164:road junction
161:
157:
153:
149:
145:
141:
137:
132:
124:
121:
113:
102:
99:
95:
92:
88:
85:
81:
78:
74:
71: –
70:
66:
65:Find sources:
59:
55:
49:
48:
43:This article
41:
37:
32:
31:
19:
582:the original
551:
525:the original
509:
503:
495:
490:
482:
477:
469:
464:
456:
451:
441:
435:
427:
422:
394:
387:
379:the original
365:
352:
327:
319:
310:
284:
272:
263:
260:
244:
220:
211:
203:
195:
183:
176:construction
139:
136:architecture
133:
131:
116:
107:
97:
90:
83:
76:
64:
52:Please help
47:verification
44:
554:: 706–712.
316:Focus point
227:Green Guide
166:layout and
598:Categories
414:1017768626
358:References
140:sightlines
110:April 2009
80:newspapers
470:Theatres.
180:landmarks
578:73518339
349:Research
307:blocked.
206:parabola
186:landform
162:design,
152:monument
192:C-Value
160:stadium
156:theater
94:scholar
576:
566:
517:
412:
402:
375:London
172:London
96:
89:
82:
75:
67:
585:(PDF)
574:S2CID
548:(PDF)
150:, or
148:arena
144:stage
101:JSTOR
87:books
564:ISBN
515:ISBN
410:OCLC
400:ISBN
199:rake
158:and
73:news
556:doi
134:In
56:by
600::
572:.
562:.
550:.
533:^
408:.
373:.
174:,
146:,
138:,
558::
416:.
123:)
117:(
112:)
108:(
98:·
91:·
84:·
77:·
50:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.