1561:
31:
1571:
1581:
851:, such as CASCADE (forwards a change/delete in the referenced table to the referencing tables), NO ACTION (if the specific row is referenced, changing the key is not allowed) or SET NULL / SET DEFAULT (a changed/deleted key in the referenced table results in setting the referencing values to NULL or to the DEFAULT value if one is specified).
948:: Referential integrity is a database concept that ensures that relationships between tables remain consistent. When one table has a foreign key to another table, the concept of referential integrity states that you may not add a record to the table that contains the foreign key unless there is a corresponding record in the linked table.
115:
performs, 'referring' to a linked column in another table. In simple terms, 'referential integrity' guarantees that the target 'referred' to will be found. A lack of referential integrity in a database can lead relational databases to return incomplete data, usually with no indication of an error.
672:
104:(RDBMS) can enforce referential integrity, normally either by deleting the foreign key rows as well to maintain integrity, or by returning an error and not performing the delete. Which method is used may be determined by a referential integrity constraint defined in a
100:. In other words, when a foreign key value is used it must reference a valid, existing primary key in the parent table. For instance, deleting a record that contains a value referred to by a foreign key in another table would break referential integrity. Some
528:
863:
the term DRI also applies to the assigning of permissions to users on a database object. Giving DRI permission to a database user allows them to add foreign key constraints on a table.
492:
420:
274:
701:
328:
301:
761:
741:
721:
512:
440:
368:
348:
166:
146:
1171:
843:(RDBMS) checks if the entered key value exists in the referenced table. If not, no insert is possible. It is also possible to specify DRI actions on
1154:
1166:
823:
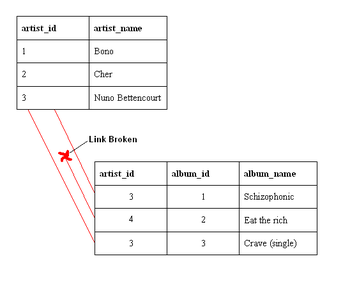
A table (called the referencing table) can refer to a column (or a group of columns) in another table (the referenced table) by using a
1098:
81:(table) references a value of another attribute (either in the same or a different relation), then the referenced value must exist.
667:{\displaystyle \forall {\vec {x}},{\vec {y}}.(R({\vec {x}},{\vec {y}})\rightarrow \exists {\vec {z}}.S({\vec {x}},{\vec {z}}))}
964:
840:
101:
1605:
1564:
17:
1237:
1126:
1584:
1290:
1541:
1188:
1480:
977:
63:
787:
1475:
1032:"Error message 1785 occurs when you create a FOREIGN KEY constraint that may cause multiple cascade paths"
1506:
1225:
518:
1429:
1419:
1195:
1516:
1249:
912:
445:
373:
1070:
766:
Logical implication between inclusion dependencies can be axiomatized by inference rules and can be
779:
933:
171:
66:" referred to this artist. With referential integrity enforced, this would not have been possible.
1465:
1119:
783:
827:. The referenced column(s) in the referenced table must be under a unique constraint, such as a
677:
1546:
1501:
1178:
902:
887:
872:
1610:
1275:
897:
42:) value in the album table that references a non-existent artist — in other words there is a
1574:
1511:
1393:
1363:
1232:
1183:
860:
306:
279:
782:. However, logical implication between dependencies that can be inclusion dependencies or
8:
1531:
1424:
1409:
1336:
1161:
1094:
831:. Also, self-references are possible (not fully implemented in MS SQL Server though). On
78:
74:
1526:
1470:
1439:
1388:
1280:
1220:
1112:
767:
746:
726:
706:
497:
425:
353:
333:
151:
131:
50:
value in the referenced table. What happened here was that there was an artist called "
1346:
1200:
960:
522:
763:, and no variable appears multiple times neither in the TGD's body nor in its head.
73:
is a property of data stating that all its references are valid. In the context of
1536:
1383:
1373:
1341:
892:
877:
85:
1444:
1414:
1368:
1149:
1006:
775:
521:(TGD) where in both the sides of the rule there is only one relational atom. In
105:
84:
For referential integrity to hold in a relational database, any column in a base
1496:
1434:
1378:
1351:
1244:
1205:
1031:
882:
836:
30:
1104:
1599:
1315:
1300:
907:
97:
1010:
848:
844:
832:
1305:
1285:
828:
824:
818:
112:
93:
89:
47:
43:
1051:
ANSI/ISO/IEC 9075-1:2003, Information technology—Database languages—SQL
1449:
1358:
1320:
1295:
51:
92:
can only contain either null values or values from a parent table's
1310:
1265:
1135:
959:
Coronel et al. (2013). Database
Systems 10th ed. Cengage Learning,
983:. University of California Santa Cruz & IBM Research - Almaden
791:
1014:
1215:
771:
62:, which was deleted from the artist table. However, the album "
1210:
77:, it requires that if a value of one attribute (column) of a
370:. It implies that the tuples of values appearing in columns
1270:
806:
809:
database programming language to ensure data integrity.
111:
The adjective 'referential' describes the action that a
749:
729:
709:
680:
531:
500:
448:
428:
376:
356:
336:
309:
282:
174:
154:
134:
797:
1005:
755:
735:
715:
695:
666:
506:
486:
434:
414:
362:
342:
322:
295:
268:
160:
140:
1029:
442:must also appear as a tuple of values in columns
1597:
1001:
999:
997:
1134:
778:by reduction from the acceptance problem for a
34:An example of a database that has not enforced
1120:
994:
854:
38:. In this example, there is a foreign key (
1127:
1113:
1071:"Managing Users Permissions on SQL Server"
774:algorithm. The problem can be shown to be
330:are distinct attributes (column names) of
128:over two (possibly identical) predicates
517:Such constraint is a particular form of
29:
1068:
14:
1598:
805:(DRI) is one of the techniques in the
102:relational database management systems
1108:
978:"A Tutorial on Database Dependencies"
841:relational database management system
786:is undecidable by reduction from the
975:
1580:
1057:Part 2: Foundation (SQL/Foundation)
1019:. Addison-Wesley. pp. 192–199.
1013:(1994). "9. Inclusion Dependency".
931:
27:Where all data references are valid
24:
607:
532:
25:
1622:
1088:
1069:Chigrik, Alexander (2003-08-13).
1054:Part 1: Framework (SQL/Framework)
812:
803:Declarative referential integrity
798:Declarative referential integrity
1579:
1569:
1560:
1559:
1030:Microsoft Support (2007-02-11).
839:into the referencing table, the
119:
1570:
487:{\displaystyle B_{1},...,B_{n}}
415:{\displaystyle A_{1},...,A_{n}}
1062:
1045:
1023:
969:
953:
925:
687:
661:
658:
652:
637:
628:
616:
604:
601:
595:
580:
571:
565:
556:
541:
263:
225:
216:
178:
13:
1:
918:
703:is the vector (whose size is
269:{\displaystyle R\subseteq S}
46:value with no corresponding
7:
1606:Database management systems
1136:Database management systems
866:
519:tuple-generating dependency
10:
1627:
1542:Object–relational database
873:Null pointer dereferencing
816:
696:{\displaystyle {\vec {x}}}
1555:
1517:Federated database system
1489:
1458:
1402:
1329:
1258:
1250:Blockchain-based database
1142:
913:Slowly changing dimension
723:) of variables shared by
168:from a schema is written
1016:Foundations of Databases
855:Product-specific meaning
780:linear bounded automaton
934:"Referential Integrity"
784:functional dependencies
1547:Transaction processing
1502:Database normalization
1445:Query rewriting system
903:Propagation constraint
888:Domain/key normal form
757:
737:
717:
697:
668:
508:
488:
436:
416:
364:
344:
324:
297:
270:
162:
142:
67:
1522:Referential integrity
976:Kolaitis, Phokion G.
898:Functional dependency
758:
738:
718:
698:
669:
525:it is expressible as
509:
489:
437:
417:
365:
345:
325:
323:{\displaystyle B_{i}}
298:
296:{\displaystyle A_{i}}
271:
163:
143:
71:Referential integrity
36:referential integrity
33:
1512:Distributed database
1009:; Hull, Richard B.;
861:Microsoft SQL Server
747:
727:
707:
678:
529:
498:
446:
426:
374:
354:
334:
307:
280:
172:
152:
132:
126:inclusion dependency
75:relational databases
18:Inclusion dependency
1532:Relational calculus
1410:Concurrency control
1095:DRI versus Triggers
88:that is declared a
1527:Relational algebra
1471:Query optimization
1276:Armstrong's axioms
1073:. Database Journal
753:
733:
713:
693:
664:
504:
484:
432:
412:
360:
340:
320:
293:
266:
158:
138:
68:
1593:
1592:
1201:Wide-column store
1196:Document-oriented
965:978-1-111-96960-8
756:{\displaystyle S}
736:{\displaystyle R}
716:{\displaystyle n}
690:
655:
640:
619:
598:
583:
559:
544:
523:first-order logic
507:{\displaystyle S}
494:for some fact of
435:{\displaystyle R}
363:{\displaystyle S}
343:{\displaystyle R}
161:{\displaystyle S}
141:{\displaystyle R}
16:(Redirected from
1618:
1583:
1582:
1573:
1572:
1563:
1562:
1537:Relational model
1507:Database storage
1384:Stored procedure
1129:
1122:
1115:
1106:
1105:
1082:
1081:
1079:
1078:
1066:
1060:
1049:
1043:
1042:
1040:
1039:
1027:
1021:
1020:
1007:Abiteboul, Serge
1003:
992:
991:
989:
988:
982:
973:
967:
957:
951:
950:
942:
941:
929:
893:Entity integrity
878:Dangling pointer
762:
760:
759:
754:
742:
740:
739:
734:
722:
720:
719:
714:
702:
700:
699:
694:
692:
691:
683:
673:
671:
670:
665:
657:
656:
648:
642:
641:
633:
621:
620:
612:
600:
599:
591:
585:
584:
576:
561:
560:
552:
546:
545:
537:
513:
511:
510:
505:
493:
491:
490:
485:
483:
482:
458:
457:
441:
439:
438:
433:
421:
419:
418:
413:
411:
410:
386:
385:
369:
367:
366:
361:
349:
347:
346:
341:
329:
327:
326:
321:
319:
318:
302:
300:
299:
294:
292:
291:
275:
273:
272:
267:
262:
261:
237:
236:
215:
214:
190:
189:
167:
165:
164:
159:
147:
145:
144:
139:
61:
57:
41:
21:
1626:
1625:
1621:
1620:
1619:
1617:
1616:
1615:
1596:
1595:
1594:
1589:
1551:
1497:Database models
1485:
1454:
1440:Query optimizer
1415:Data dictionary
1398:
1369:Transaction log
1325:
1281:Codd's 12 rules
1254:
1184:Column-oriented
1150:Object-oriented
1138:
1133:
1091:
1086:
1085:
1076:
1074:
1067:
1063:
1050:
1046:
1037:
1035:
1034:. microsoft.com
1028:
1024:
1004:
995:
986:
984:
980:
974:
970:
958:
954:
939:
937:
932:Chapple, Mike.
930:
926:
921:
869:
857:
821:
815:
800:
776:PSPACE-complete
748:
745:
744:
728:
725:
724:
708:
705:
704:
682:
681:
679:
676:
675:
647:
646:
632:
631:
611:
610:
590:
589:
575:
574:
551:
550:
536:
535:
530:
527:
526:
499:
496:
495:
478:
474:
453:
449:
447:
444:
443:
427:
424:
423:
406:
402:
381:
377:
375:
372:
371:
355:
352:
351:
335:
332:
331:
314:
310:
308:
305:
304:
287:
283:
281:
278:
277:
257:
253:
232:
228:
210:
206:
185:
181:
173:
170:
169:
153:
150:
149:
133:
130:
129:
122:
106:data dictionary
59:
55:
39:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1624:
1614:
1613:
1608:
1591:
1590:
1588:
1587:
1577:
1567:
1556:
1553:
1552:
1550:
1549:
1544:
1539:
1534:
1529:
1524:
1519:
1514:
1509:
1504:
1499:
1493:
1491:
1490:Related topics
1487:
1486:
1484:
1483:
1478:
1473:
1468:
1466:Administration
1462:
1460:
1456:
1455:
1453:
1452:
1447:
1442:
1437:
1435:Query language
1432:
1427:
1422:
1417:
1412:
1406:
1404:
1400:
1399:
1397:
1396:
1391:
1386:
1381:
1376:
1371:
1366:
1361:
1356:
1355:
1354:
1349:
1344:
1333:
1331:
1327:
1326:
1324:
1323:
1318:
1313:
1308:
1303:
1298:
1293:
1288:
1283:
1278:
1273:
1268:
1262:
1260:
1256:
1255:
1253:
1252:
1247:
1242:
1241:
1240:
1230:
1229:
1228:
1218:
1213:
1208:
1203:
1198:
1193:
1192:
1191:
1181:
1176:
1175:
1174:
1169:
1159:
1158:
1157:
1146:
1144:
1140:
1139:
1132:
1131:
1124:
1117:
1109:
1103:
1102:
1090:
1089:External links
1087:
1084:
1083:
1061:
1059:
1058:
1055:
1044:
1022:
993:
968:
952:
923:
922:
920:
917:
916:
915:
910:
905:
900:
895:
890:
885:
883:Data integrity
880:
875:
868:
865:
856:
853:
817:Main article:
814:
813:Meaning in SQL
811:
799:
796:
752:
732:
712:
689:
686:
663:
660:
654:
651:
645:
639:
636:
630:
627:
624:
618:
615:
609:
606:
603:
597:
594:
588:
582:
579:
573:
570:
567:
564:
558:
555:
549:
543:
540:
534:
503:
481:
477:
473:
470:
467:
464:
461:
456:
452:
431:
409:
405:
401:
398:
395:
392:
389:
384:
380:
359:
339:
317:
313:
290:
286:
265:
260:
256:
252:
249:
246:
243:
240:
235:
231:
227:
224:
221:
218:
213:
209:
205:
202:
199:
196:
193:
188:
184:
180:
177:
157:
137:
121:
118:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1623:
1612:
1609:
1607:
1604:
1603:
1601:
1586:
1578:
1576:
1568:
1566:
1558:
1557:
1554:
1548:
1545:
1543:
1540:
1538:
1535:
1533:
1530:
1528:
1525:
1523:
1520:
1518:
1515:
1513:
1510:
1508:
1505:
1503:
1500:
1498:
1495:
1494:
1492:
1488:
1482:
1479:
1477:
1474:
1472:
1469:
1467:
1464:
1463:
1461:
1457:
1451:
1448:
1446:
1443:
1441:
1438:
1436:
1433:
1431:
1428:
1426:
1423:
1421:
1418:
1416:
1413:
1411:
1408:
1407:
1405:
1401:
1395:
1392:
1390:
1387:
1385:
1382:
1380:
1377:
1375:
1372:
1370:
1367:
1365:
1362:
1360:
1357:
1353:
1350:
1348:
1345:
1343:
1340:
1339:
1338:
1335:
1334:
1332:
1328:
1322:
1319:
1317:
1316:Surrogate key
1314:
1312:
1309:
1307:
1304:
1302:
1301:Candidate key
1299:
1297:
1294:
1292:
1289:
1287:
1284:
1282:
1279:
1277:
1274:
1272:
1269:
1267:
1264:
1263:
1261:
1257:
1251:
1248:
1246:
1243:
1239:
1236:
1235:
1234:
1231:
1227:
1224:
1223:
1222:
1219:
1217:
1214:
1212:
1209:
1207:
1204:
1202:
1199:
1197:
1194:
1190:
1187:
1186:
1185:
1182:
1180:
1177:
1173:
1170:
1168:
1165:
1164:
1163:
1160:
1156:
1153:
1152:
1151:
1148:
1147:
1145:
1141:
1137:
1130:
1125:
1123:
1118:
1116:
1111:
1110:
1107:
1100:
1096:
1093:
1092:
1072:
1065:
1056:
1053:
1052:
1048:
1033:
1026:
1018:
1017:
1012:
1011:Vianu, Victor
1008:
1002:
1000:
998:
979:
972:
966:
962:
956:
949:
947:
935:
928:
924:
914:
911:
909:
908:Surrogate key
906:
904:
901:
899:
896:
894:
891:
889:
886:
884:
881:
879:
876:
874:
871:
870:
864:
862:
852:
850:
846:
842:
838:
834:
830:
826:
820:
810:
808:
804:
795:
793:
789:
785:
781:
777:
773:
769:
764:
750:
730:
710:
684:
649:
643:
634:
625:
622:
613:
592:
586:
577:
568:
562:
553:
547:
538:
524:
520:
515:
501:
479:
475:
471:
468:
465:
462:
459:
454:
450:
429:
422:for facts of
407:
403:
399:
396:
393:
390:
387:
382:
378:
357:
337:
315:
311:
288:
284:
258:
254:
250:
247:
244:
241:
238:
233:
229:
222:
219:
211:
207:
203:
200:
197:
194:
191:
186:
182:
175:
155:
135:
127:
120:Formalization
117:
114:
109:
107:
103:
99:
98:candidate key
95:
91:
87:
82:
80:
76:
72:
65:
53:
49:
45:
37:
32:
19:
1611:Data quality
1521:
1075:. Retrieved
1064:
1047:
1036:. Retrieved
1025:
1015:
985:. Retrieved
971:
955:
945:
944:
938:. Retrieved
927:
858:
822:
802:
801:
788:word problem
765:
516:
276:, where the
125:
123:
110:
83:
70:
69:
64:Eat the Rich
35:
1585:WikiProject
1476:Replication
1364:Transaction
1306:Foreign key
1286:CAP theorem
1233:Multi-model
936:. About.com
829:primary key
825:foreign key
819:Foreign key
113:foreign key
94:primary key
90:foreign key
54:", with an
48:primary key
44:foreign key
1600:Categories
1450:Query plan
1403:Components
1321:Unique key
1238:comparison
1172:comparison
1162:Relational
1155:comparison
1077:2006-12-17
1038:2009-01-24
987:2021-12-10
946:Definition
940:2011-03-20
919:References
1459:Functions
1394:Partition
1221:In-memory
1179:Key–value
833:inserting
688:→
653:→
638:→
617:→
608:∃
605:→
596:→
581:→
557:→
542:→
533:∀
220:⊆
56:artist_id
52:Aerosmith
40:artist_id
1565:Category
1481:Sharding
1337:Relation
1311:Superkey
1266:Database
1259:Concepts
1099:archived
867:See also
674:, where
79:relation
1575:Outline
1374:Trigger
1330:Objects
792:monoids
768:decided
1389:Cursor
1347:column
1216:NewSQL
963:
849:DELETE
845:UPDATE
835:a new
772:PSPACE
1379:Index
1342:table
1245:Cloud
1211:NoSQL
1206:Graph
1143:Types
981:(PDF)
770:by a
96:or a
86:table
1430:ODBC
1420:JDBC
1359:View
1296:Null
1291:CRUD
1271:ACID
1226:list
1189:list
1167:list
961:ISBN
847:and
790:for
743:and
350:and
148:and
1425:XQJ
1352:row
859:In
837:row
807:SQL
124:An
58:of
1602::
996:^
943:.
794:.
514:.
303:,
108:.
1128:e
1121:t
1114:v
1101:)
1097:(
1080:.
1041:.
990:.
751:S
731:R
711:n
685:x
662:)
659:)
650:z
644:,
635:x
629:(
626:S
623:.
614:z
602:)
593:y
587:,
578:x
572:(
569:R
566:(
563:.
554:y
548:,
539:x
502:S
480:n
476:B
472:,
469:.
466:.
463:.
460:,
455:1
451:B
430:R
408:n
404:A
400:,
397:.
394:.
391:.
388:,
383:1
379:A
358:S
338:R
316:i
312:B
289:i
285:A
264:]
259:n
255:B
251:,
248:.
245:.
242:.
239:,
234:1
230:B
226:[
223:S
217:]
212:n
208:A
204:,
201:.
198:.
195:.
192:,
187:1
183:A
179:[
176:R
156:S
136:R
60:4
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.