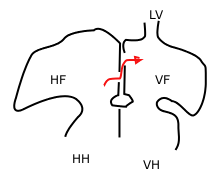
382:. Oxygenated blood from the placenta travels through the umbilical cord to the right atrium of the fetal heart. As the fetal lungs are non-functional at this time, the blood bypasses them through two cardiac shunts. The first is the foramen ovale (the valve present between them called eustachian valve) which shunts blood from the right atrium to the left atrium. The second is the
57:
44:
Sketch showing foramen ovale in a fetal heart. Red arrow shows blood from the inferior cava traveling to the right atrium and then to the left atrium. HF: right atrium, VF: left atrium. HH and VH: right and left ventricle. The heart still has a common
343:, grows over the ostium secundum in the right atrium. Blood then passes from the right to left atrium only by way of a small passageway in the septum secundum and then through the ostium secundum. This passageway is called the foramen ovale
560:
354:
The foramen ovale often closes at birth. At birth, when the lungs become functional, the pulmonary vascular pressure decreases and the left atrial pressure exceeds that of the right. This forces the
695:
40:
688:
142:
681:
386:
which shunts blood from the pulmonary artery (which, after birth, carries blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs) to the descending aorta.
339:
The ostium secundum provides communication between the atria after the ostium primum closes completely. Subsequently, a second wall of tissue, the
427:
is considered the most accurate investigation to demonstrate a patent foramen ovale. A patent foramen ovale may also be an incidental finding.
118:
1074:
316:, as a small passageway between the septum secundum and the ostium secundum. Initially the atria are separated from one another by the
837:
362:, functionally closing the foramen ovale. In time the septa eventually fuse, leaving a remnant of the foramen ovale, the
938:
502:
656:
573:
324:. As the septum primum grows, the ostium primum narrows and eventually closes. Before it does so, bloodflow from the
769:
565:
401:
424:
137:
804:
420:
666:
404:. In most of these individuals, the PFO causes no problems and remains undetected throughout life.
303:
101:
899:
832:
513:
894:
784:
149:
125:
113:
904:
333:
283:
89:
24:
774:
408:
400:
In about 25% of adults the foramen ovale does not close completely, but remains as a small
395:
363:
291:
8:
1084:
1079:
1069:
954:
740:
673:
1048:
1012:
779:
730:
705:
625:
590:
325:
607:
1024:
992:
914:
713:
652:
630:
612:
569:
456:
436:
383:
279:
378:
receives oxygen not from its lungs, but from the mother's oxygen-rich blood via the
1032:
1020:
972:
799:
745:
620:
602:
475:
177:
1043:
809:
480:
461:
359:
340:
329:
106:
77:
20:
1008:
1004:
1000:
886:
536:
309:
287:
271:
46:
332:. Some embryologists postulate that the ostium secundum may be formed through
1063:
962:
871:
794:
750:
735:
722:
616:
355:
321:
317:
290:. In most individuals, the foramen ovale closes at birth. It later forms the
275:
130:
531:
415:
that travels from the venous side to the arterial side). This may lead to a
282:(which allows blood that still escapes to the right ventricle to bypass the
866:
858:
634:
517:
84:
922:
876:
72:
155:
313:
61:
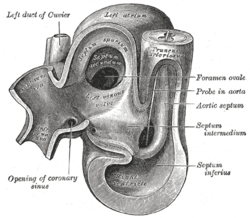
Heart of human embryo of about thirty-five days, opened on left side.
1039:
982:
977:
412:
379:
967:
39:
507:
416:
198:
1028:
1016:
375:
242:
167:
254:
227:
218:
203:
192:
183:
56:
703:
212:
328:
wears down a portion of the septum primum, forming the
230:
180:
312: 'oval hole') forms in the late fourth week of
251:
239:
215:
209:
189:
248:
236:
224:
206:
195:
186:
286:). Another similar adaptation in the fetus is the
407:PFO has long been studied because of its role in
320:except for a small opening below the septum, the
1061:
16:Passageway between the atria of the human heart
646:
274:from the right atrium. It is one of two fetal
689:
696:
682:
649:Human Embryology And Developmental Biology
55:
38:
624:
606:
582:
389:
838:Protein signalling in heart development
1062:
561:Langman's Essential Medical Embryology
557:
677:
588:
304:Interatrial septum § Development
1075:Embryology of cardiovascular system
13:
939:Vascular remodelling in the embryo
14:
1096:
608:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.524371
591:"Patent Foramen Ovale and Stroke"
566:Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
270:, allows blood to enter the left
770:Primary interventricular foramen
651:(3rd ed.). Elsevier Mosby.
425:Transesophageal echocardiography
176:
551:
524:
495:
481:Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary
462:Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary
449:
297:
1:
442:
667:"Congenital Heart Disorders"
402:patent foramen ovale ("PFO")
308:The foramen ovale (from
7:
805:Primary interatrial foramen
430:
369:
10:
1101:
558:Sadler, Thomas W. (2004).
393:
349:
301:
18:
991:
951:
931:
913:
885:
857:
850:
825:
759:
721:
712:
537:Dictionary.com Unabridged
421:transient ischemic attack
148:
136:
124:
112:
100:
95:
83:
71:
66:
54:
37:
32:
19:Not to be confused with
900:Posterior cardinal vein
833:Aorticopulmonary septum
647:Carlson, Bruce (2004).
514:Oxford University Press
268:ostium secundum of Born
895:Anterior cardinal vein
785:Atrioventricular canal
278:, the other being the
150:Anatomical terminology
49:(LV), instead of four.
905:Common cardinal veins
510:UK English Dictionary
390:Clinical significance
334:programmed cell death
284:pulmonary circulation
90:Cardiovascular system
33:Foramen ovale (heart)
25:foramen ovale (skull)
775:Endocardial cushions
409:paradoxical embolism
396:Patent foramen ovale
741:Primitive ventricle
704:Development of the
669:. Cleveland Clinic.
1049:Vitelline arteries
1013:Inferior vena cava
780:Septum intermedium
731:Truncus arteriosus
706:circulatory system
589:Homma, S. (2005).
326:inferior vena cava
1057:
1056:
1025:Ductus arteriosus
993:Fetal circulation
947:
946:
846:
845:
766:Atrioventricular
760:Chamber formation
484:. Merriam-Webster
465:. Merriam-Webster
437:Coronary arteries
384:ductus arteriosus
280:ductus arteriosus
164:
163:
159:
1092:
1033:Umbilical artery
1021:Pulmonary artery
973:Connecting stalk
855:
854:
800:Foramen secundum
746:Primitive atrium
719:
718:
698:
691:
684:
675:
674:
670:
662:
639:
638:
628:
610:
601:(7): 1063–1072.
586:
580:
579:
555:
549:
548:
546:
545:
528:
522:
521:
516:. Archived from
499:
493:
492:
490:
489:
473:
471:
470:
453:
261:
260:
257:
256:
253:
250:
245:
244:
241:
238:
233:
232:
229:
226:
221:
220:
217:
214:
211:
208:
205:
201:
200:
197:
194:
191:
188:
185:
182:
156:edit on Wikidata
153:
59:
42:
30:
29:
1100:
1099:
1095:
1094:
1093:
1091:
1090:
1089:
1060:
1059:
1058:
1053:
1044:Vitelline veins
987:
955:hemangiogenesis
953:
943:
927:
909:
881:
842:
821:
810:Septum secundum
755:
708:
702:
665:
659:
643:
642:
587:
583:
576:
556:
552:
543:
541:
530:
529:
525:
501:
500:
496:
487:
485:
474:
468:
466:
455:
454:
450:
445:
433:
398:
392:
372:
360:septum secundum
352:
341:septum secundum
330:ostium secundum
306:
300:
264:foramen Botalli
247:
235:
223:
202:
179:
175:
160:
78:Septum secundum
62:
50:
28:
21:ostium secundum
17:
12:
11:
5:
1098:
1088:
1087:
1082:
1077:
1072:
1055:
1054:
1052:
1051:
1046:
1036:
1035:
1009:Ductus venosus
1005:Umbilical vein
1001:umbilical cord
997:
995:
989:
988:
986:
985:
980:
975:
970:
965:
959:
957:
952:Extraembryonic
949:
948:
945:
944:
942:
941:
935:
933:
929:
928:
926:
925:
919:
917:
911:
910:
908:
907:
902:
897:
891:
889:
883:
882:
880:
879:
874:
869:
863:
861:
852:
848:
847:
844:
843:
841:
840:
835:
829:
827:
823:
822:
820:
819:
818:
817:
812:
807:
802:
797:
789:
788:
787:
782:
777:
772:
763:
761:
757:
756:
754:
753:
748:
743:
738:
733:
727:
725:
716:
710:
709:
701:
700:
693:
686:
678:
672:
671:
663:
657:
641:
640:
581:
574:
550:
523:
520:on 2020-09-30.
494:
447:
446:
444:
441:
440:
439:
432:
429:
394:Main article:
391:
388:
371:
368:
351:
348:
302:Main article:
299:
296:
288:ductus venosus
276:cardiac shunts
162:
161:
152:
146:
145:
140:
134:
133:
128:
122:
121:
116:
110:
109:
104:
98:
97:
93:
92:
87:
81:
80:
75:
69:
68:
64:
63:
60:
52:
51:
47:pulmonary vein
43:
35:
34:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1097:
1086:
1083:
1081:
1078:
1076:
1073:
1071:
1068:
1067:
1065:
1050:
1047:
1045:
1041:
1038:
1037:
1034:
1030:
1026:
1022:
1018:
1014:
1010:
1006:
1002:
999:
998:
996:
994:
990:
984:
981:
979:
976:
974:
971:
969:
966:
964:
963:Blood islands
961:
960:
958:
956:
950:
940:
937:
936:
934:
930:
924:
921:
920:
918:
916:
915:Lymph vessels
912:
906:
903:
901:
898:
896:
893:
892:
890:
888:
884:
878:
875:
873:
872:Aortic arches
870:
868:
865:
864:
862:
860:
856:
853:
849:
839:
836:
834:
831:
830:
828:
824:
816:
815:Foramen ovale
813:
811:
808:
806:
803:
801:
798:
796:
795:Septum primum
793:
792:
790:
786:
783:
781:
778:
776:
773:
771:
768:
767:
765:
764:
762:
758:
752:
751:Sinus venosus
749:
747:
744:
742:
739:
737:
736:Bulbus cordis
734:
732:
729:
728:
726:
724:
723:Tubular heart
720:
717:
715:
711:
707:
699:
694:
692:
687:
685:
680:
679:
676:
668:
664:
660:
658:0-323-03649-X
654:
650:
645:
644:
636:
632:
627:
622:
618:
614:
609:
604:
600:
596:
592:
585:
577:
575:0-7817-5571-9
571:
567:
563:
562:
554:
540:(Online). n.d
539:
538:
533:
527:
519:
515:
511:
509:
504:
498:
483:
482:
477:
464:
463:
458:
452:
448:
438:
435:
434:
428:
426:
422:
418:
414:
410:
405:
403:
397:
387:
385:
381:
377:
367:
365:
361:
357:
356:septum primum
347:
346:
342:
337:
335:
331:
327:
323:
322:ostium primum
319:
318:septum primum
315:
311:
305:
295:
293:
289:
285:
281:
277:
273:
269:
265:
259:
173:
172:foramen ovale
169:
166:In the fetal
157:
151:
147:
144:
141:
139:
135:
132:
129:
127:
123:
120:
117:
115:
111:
108:
105:
103:
99:
94:
91:
88:
86:
82:
79:
76:
74:
70:
65:
58:
53:
48:
41:
36:
31:
26:
22:
867:Dorsal aorta
814:
648:
598:
594:
584:
559:
553:
542:. Retrieved
535:
526:
518:the original
506:
497:
486:. Retrieved
479:
467:. Retrieved
460:
451:
406:
399:
373:
364:fossa ovalis
358:against the
353:
344:
338:
307:
292:fossa ovalis
267:
263:
171:
165:
119:A12.1.01.007
595:Circulation
298:Development
96:Identifiers
1085:Pediatrics
1080:Obstetrics
1070:Cardiology
1064:Categories
923:Lymph sacs
877:Aortic sac
544:2016-01-22
488:2016-01-22
469:2016-01-22
443:References
617:0009-7322
532:"foramen"
503:"foramen"
457:"foramen"
314:gestation
73:Precursor
1040:yolk sac
983:Placenta
978:Yolk sac
859:Arteries
635:16103257
431:See also
413:embolism
380:placenta
370:Function
262:), also
968:Chorion
851:Vessels
791:Atrial
626:3723385
476:"ovale"
350:Closure
266:or the
107:D054085
67:Details
655:
633:
623:
615:
572:
508:Lexico
417:stroke
272:atrium
170:, the
85:System
1029:Aorta
1017:Heart
932:Other
887:Veins
826:Other
714:Heart
376:fetus
310:Latin
168:heart
154:[
143:86043
653:ISBN
631:PMID
613:ISSN
570:ISBN
411:(an
131:3967
114:TA98
102:MeSH
621:PMC
603:doi
599:112
419:or
246:-,-
234:-,-
138:FMA
126:TA2
23:or
1066::
1042::
1031:→
1027:→
1023:→
1019:→
1015:→
1011:→
1007:→
1003::
629:.
619:.
611:.
597:.
593:.
568:.
564:.
534:.
512:.
505:.
478:.
459:.
423:.
374:A
366:.
336:.
294:.
258:-/
255:eɪ
243:ɑː
222:,-
204:oʊ
199:ən
193:eɪ
697:e
690:t
683:v
661:.
637:.
605::
578:.
547:.
491:.
472:.
345:.
252:v
249:ˈ
240:v
237:ˈ
231:n
228:ɛ
225:m
219:i
216:l
213:æ
210:v
207:ˈ
196:m
190:r
187:ˈ
184:ə
181:f
178:/
174:(
158:]
27:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.