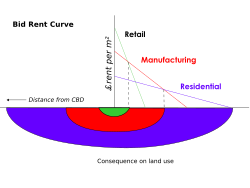
191:. This theory states that the concentric circles are based on the amount that people will pay for the land. This value is based on the profits that are obtainable from maintaining a business on that land. The center of the town will have the highest number of customers so it is profitable for retail activities. Manufacturing will pay slightly less for the land as they are only interested in the accessibility for workers, 'goods in' and 'goods out'. Residential land use will take the surrounding land.
20:
1118:
178:
199:
The model has been challenged by many contemporary urban geographers. First, the model does not work well with cities outside the United States, in particular with those developed under different historical contexts. Even in the United States, because of changes such as advancement in transportation
377:
707:
222:
Physical features – land may restrict growth of certain sectors; hills and water features may make some locations unusually desirable for residential purposes.
409:
347:
428:
117:(or CBD) was in the middle of the model, and the city is expanded in rings with different land uses. It is effectively an urban version of
929:
922:
577:
934:
939:
802:
200:
and information technology and transformation in global economy, cities are no longer organized with clear "zones" (see:
315:
390:
174:-mid-uptown divide by which downtown is the CBD, uptown the affluent residential outer ring, and midtown in between.
166:
zone, high-class homes on outskirts of outer suburbs - homeowner can afford to commute to central business district.
463:
1053:
652:
376:
Park, Robert E.; Burgess, Ernest W. (1925). "The Growth of the City: An
Introduction to a Research Project".
325:
118:
429:
https://cpb-us-e1.wpmucdn.com/cobblearning.net/dist/0/1338/files/2015/12/Concentric-Zone-Model-1dw14xo.pdf
1142:
797:
1018:
792:
702:
114:
62:
406:
355:
82:, is one of the earliest theoretical models to explain urban social structures. It was created by
1043:
712:
1028:
917:
889:
774:
1068:
859:
834:
692:
634:
300:
129:
121:
regional land use model developed a century earlier. It influenced the later development of
1058:
1033:
456:
295:
8:
1098:
717:
997:
280:
201:
143:
47:
1083:
992:
864:
817:
812:
602:
557:
386:
234:
1103:
1048:
1002:
972:
909:
879:
659:
310:
285:
227:
262:
982:
894:
684:
669:
587:
480:
449:
413:
320:
188:
181:
113:. This concentric ring model depicts urban land usage in concentric rings: the
1078:
1038:
784:
764:
592:
525:
290:
266:
251:
241:
86:
1136:
1122:
1093:
1063:
987:
977:
967:
962:
807:
759:
535:
255:
244:– more expensive property can be found in formerly 'low class' housing areas.
98:
160:
Better quality middle-class homes (outer suburbs) or zone of better housing,
1073:
957:
854:
839:
732:
674:
647:
624:
582:
305:
125:
106:
899:
884:
769:
737:
722:
697:
642:
619:
572:
552:
545:
540:
520:
493:
150:
83:
1088:
1023:
874:
824:
664:
597:
562:
488:
209:
154:
122:
110:
247:
Many new housing estates were built on the edges of cities in
Britain.
844:
752:
614:
609:
530:
515:
142:
The transition zone of mixed residential and commercial uses or the
949:
869:
742:
567:
498:
171:
163:
102:
19:
829:
727:
505:
219:
It assumes an isotropic plane – an even, unchanging landscape.
213:
105:, it was the first to give the explanation of distribution of
510:
177:
747:
472:
230:
defy the theory, being a distant part of the commuter zone.
441:
208:
It describes the peculiar
American geography, where the
233:
Decentralization of shops, manufacturing industry (see
1134:
170:The model is more detailed than the traditional
385:. University of Chicago Press. pp. 47–62.
216:are wealthy; the inverse is the norm elsewhere.
153:homes (inner suburbs), in later decades called
139:The center with the central business district,
457:
375:
464:
450:
157:or zone of independent working men's home,
176:
18:
1135:
101:theory done by Burgess and applied on
445:
202:Los Angeles School of Urban Analysis
803:Technical aspects of urban planning
187:Burgess's work helped generate the
13:
348:"The Burgess Urban Land Use Model"
14:
1154:
437:
418:Urban Land Use and Transportation
1116:
578:Cities with the most skyscrapers
28: Commuter zone (outer ring)
1054:Sustainable Development Goal 11
935:Most populous national capitals
316:Tobler's first law of geography
128:(1939) and Harris and Ullman's
940:Most populous satellite cities
422:
399:
369:
340:
1:
930:Most densely populated cities
333:
194:
92:
23:Key (from outside to inside)
16:Urban social structure model
7:
273:
135:The zones identified are:
10:
1159:
798:Theories of urban planning
471:
326:Johann Heinrich von Thünen
250:It does not address local
1112:
1011:
948:
908:
793:History of urban planning
783:
703:Central business district
683:
633:
479:
306:Sector model (Hoyt model)
115:Central Business District
63:Central business district
40: Working class zone
1044:Million Tree Initiative
261:The model does not fit
240:Urban regeneration and
1029:Ecological engineering
918:World's largest cities
890:Cycling infrastructure
775:Peri-urban agriculture
184:
72:concentric zone model
67:
34: Residential zone
1069:Urban forest inequity
860:Multiple nuclei model
850:Concentric zone model
835:Mixed-use development
708:Most expensive cities
693:World's cities by GDP
407:Urban Land Use Models
301:Multiple nuclei model
237:), and entertainment.
180:
130:multiple nuclei model
22:
1059:Sustainable urbanism
1034:Green infrastructure
405:Jean-Paul Rodrigue,
296:Friction of distance
74:, also known as the
1099:Urban reforestation
718:Most livable cities
1143:City layout models
998:Urban homesteading
923:throughout history
412:2011-03-20 at the
352:people.hofstra.edu
281:100 percent corner
263:polycentric cities
185:
144:zone of transition
68:
55: Factory zone
48:Zone of transition
1130:
1129:
1123:Cities portal
1084:Urban heat island
993:Urban exploration
865:Linear settlement
813:Public open space
653:direct-controlled
603:Abandoned village
558:Metropolitan area
235:Industrial suburb
228:Commuter villages
1150:
1121:
1120:
1119:
1104:Zero-carbon city
1049:Sustainable city
1003:Unitary urbanism
973:Urban morphology
910:Urban population
880:Bicycle-friendly
660:Independent city
635:Urban government
593:Shrinking cities
466:
459:
452:
443:
442:
431:
426:
420:
403:
397:
396:
384:
373:
367:
366:
364:
363:
354:. Archived from
344:
311:Transect (urban)
286:Core frame model
60:
54:
45:
39:
33:
27:
1158:
1157:
1153:
1152:
1151:
1149:
1148:
1147:
1133:
1132:
1131:
1126:
1117:
1115:
1108:
1007:
983:Urban sociology
944:
904:
895:Pedestrian zone
779:
713:Cheapest cities
685:Urban economics
679:
670:Autonomous city
629:
588:Suburbanization
481:Urban geography
475:
470:
440:
435:
434:
427:
423:
414:Wayback Machine
404:
400:
393:
382:
374:
370:
361:
359:
346:
345:
341:
336:
331:
321:Urban structure
276:
197:
95:
66:
58:
56:
52:
50:
43:
41:
37:
35:
31:
29:
25:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1156:
1146:
1145:
1128:
1127:
1113:
1110:
1109:
1107:
1106:
1101:
1096:
1091:
1086:
1081:
1079:Urban forestry
1076:
1071:
1066:
1061:
1056:
1051:
1046:
1041:
1039:Green urbanism
1036:
1031:
1026:
1021:
1019:Climate change
1015:
1013:
1009:
1008:
1006:
1005:
1000:
995:
990:
985:
980:
975:
970:
965:
960:
954:
952:
946:
945:
943:
942:
937:
932:
927:
926:
925:
914:
912:
906:
905:
903:
902:
897:
892:
887:
882:
877:
872:
867:
862:
857:
852:
847:
842:
837:
832:
827:
822:
821:
820:
810:
808:Urban planners
805:
800:
795:
789:
787:
785:Urban planning
781:
780:
778:
777:
772:
767:
765:Municipal bond
762:
757:
756:
755:
750:
745:
740:
735:
730:
720:
715:
710:
705:
700:
695:
689:
687:
681:
680:
678:
677:
672:
667:
662:
657:
656:
655:
645:
639:
637:
631:
630:
628:
627:
622:
617:
612:
607:
606:
605:
595:
590:
585:
580:
575:
570:
565:
560:
555:
550:
549:
548:
538:
533:
528:
526:Satellite city
523:
518:
513:
508:
503:
502:
501:
491:
485:
483:
477:
476:
469:
468:
461:
454:
446:
439:
438:External links
436:
433:
432:
421:
398:
391:
368:
338:
337:
335:
332:
330:
329:
323:
318:
313:
308:
303:
298:
293:
291:Distance decay
288:
283:
277:
275:
272:
271:
270:
267:Stoke-on-Trent
265:, for example
259:
254:and forces of
252:urban politics
248:
245:
242:gentrification
238:
231:
225:
224:
223:
217:
212:is poor while
196:
193:
189:bid rent curve
182:Bid rent curve
168:
167:
161:
158:
149:Working class
147:
140:
94:
91:
87:Ernest Burgess
57:
51:
42:
36:
30:
24:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1155:
1144:
1141:
1140:
1138:
1125:
1124:
1111:
1105:
1102:
1100:
1097:
1095:
1094:Urban prairie
1092:
1090:
1087:
1085:
1082:
1080:
1077:
1075:
1072:
1070:
1067:
1065:
1064:Urban ecology
1062:
1060:
1057:
1055:
1052:
1050:
1047:
1045:
1042:
1040:
1037:
1035:
1032:
1030:
1027:
1025:
1022:
1020:
1017:
1016:
1014:
1010:
1004:
1001:
999:
996:
994:
991:
989:
988:Anti-urbanism
986:
984:
981:
979:
978:Urban culture
976:
974:
971:
969:
968:Urban studies
966:
964:
963:Urban warfare
961:
959:
956:
955:
953:
951:
947:
941:
938:
936:
933:
931:
928:
924:
921:
920:
919:
916:
915:
913:
911:
907:
901:
898:
896:
893:
891:
888:
886:
883:
881:
878:
876:
873:
871:
868:
866:
863:
861:
858:
856:
853:
851:
848:
846:
843:
841:
838:
836:
833:
831:
828:
826:
823:
819:
816:
815:
814:
811:
809:
806:
804:
801:
799:
796:
794:
791:
790:
788:
786:
782:
776:
773:
771:
768:
766:
763:
761:
760:Urban renewal
758:
754:
751:
749:
746:
744:
741:
739:
736:
734:
731:
729:
726:
725:
724:
721:
719:
716:
714:
711:
709:
706:
704:
701:
699:
696:
694:
691:
690:
688:
686:
682:
676:
673:
671:
668:
666:
663:
661:
658:
654:
651:
650:
649:
646:
644:
641:
640:
638:
636:
632:
626:
623:
621:
618:
616:
613:
611:
608:
604:
601:
600:
599:
596:
594:
591:
589:
586:
584:
581:
579:
576:
574:
571:
569:
566:
564:
561:
559:
556:
554:
551:
547:
544:
543:
542:
539:
537:
536:Commuter town
534:
532:
529:
527:
524:
522:
519:
517:
514:
512:
509:
507:
504:
500:
497:
496:
495:
492:
490:
487:
486:
484:
482:
478:
474:
467:
462:
460:
455:
453:
448:
447:
444:
430:
425:
419:
415:
411:
408:
402:
394:
392:9780226148199
388:
381:
380:
372:
358:on 2011-06-29
357:
353:
349:
343:
339:
328:'s ring model
327:
324:
322:
319:
317:
314:
312:
309:
307:
304:
302:
299:
297:
294:
292:
289:
287:
284:
282:
279:
278:
268:
264:
260:
257:
256:globalization
253:
249:
246:
243:
239:
236:
232:
229:
226:
221:
220:
218:
215:
211:
207:
206:
205:
203:
192:
190:
183:
179:
175:
173:
165:
162:
159:
156:
152:
148:
145:
141:
138:
137:
136:
133:
131:
127:
124:
120:
116:
112:
108:
107:social groups
104:
100:
99:human ecology
90:
88:
85:
81:
77:
76:Burgess model
73:
64:
49:
21:
1114:
1074:Urban forest
958:New Urbanism
855:Sector model
849:
840:Urban design
733:Modern ruins
675:Capital city
648:Municipality
625:College town
583:Urbanization
424:
417:
401:
378:
371:
360:. Retrieved
356:the original
351:
342:
198:
186:
169:
134:
126:sector model
123:Homer Hoyt's
119:Von Thünen's
96:
79:
75:
71:
69:
1012:Environment
900:Walkability
885:Cyclability
818:Green space
770:Habitat III
738:Shanty town
723:Urban decay
698:Global city
643:City status
620:Closed city
573:Megalopolis
553:Conurbation
541:City proper
521:Twin cities
494:City centre
151:residential
111:urban areas
84:sociologist
1089:Urban park
1024:Eco-cities
875:Smart city
825:Urban wild
665:City-state
598:Ghost town
563:Metropolis
489:Urban area
362:2016-09-26
334:References
210:inner city
195:Criticisms
155:inner city
845:Grid plan
753:Squatting
615:Tent city
610:Lost city
531:Edge city
516:Core city
97:Based on
93:The model
89:in 1925.
80:CCD model
1137:Category
950:Urbanism
870:Land use
743:Skid row
568:Megacity
499:Downtown
410:Archived
379:The City
274:See also
164:Commuter
132:(1945).
65:(center)
214:suburbs
109:within
103:Chicago
78:or the
830:Zoning
728:Ghetto
546:limits
506:Suburb
473:Cities
389:
61:
59:
53:
46:
44:
38:
32:
26:
511:Exurb
383:(PDF)
748:Slum
387:ISBN
172:down
70:The
416:in
204:).
1139::
350:.
465:e
458:t
451:v
395:.
365:.
269:.
258:.
146:,
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.