114:. For a given CPU, the clock rates are determined at the end of the manufacturing process through testing of each processor. Chip manufacturers publish a "maximum clock rate" specification, and they test chips before selling them to make sure they meet that specification, even when executing the most complicated instructions with the data patterns that take the longest to settle (testing at the temperature and voltage that gives the lowest performance). Processors successfully tested for compliance with a given set of standards may be labeled with a higher clock rate, e.g., 3.50 GHz, while those that fail the standards of the higher clock rate yet pass the standards of a lower clock rate may be labeled with the lower clock rate, e.g., 3.3 GHz, and sold at a lower price.
27:
103:
357:
microarchitectures. Further, a "cumulative clock rate" measure is sometimes assumed by taking the total cores and multiplying by the total clock rate (e.g. a dual-core 2.8 GHz processor running at a cumulative 5.6 GHz). There are many other factors to consider when comparing the performance of CPUs, like the width of the CPU's
173:
After each clock pulse, the signal lines inside the CPU need time to settle to their new state. That is, every signal line must finish transitioning from 0 to 1, or from 1 to 0. If the next clock pulse comes before that, the results will be incorrect. In the process of transitioning, some energy is
356:
running at 50 MHz will be about twice as fast (internally only) as one with the same CPU and memory running at 25 MHz, while the same will not be true for MIPS R4000 running at the same clock rate as the two are different processors that implement different architectures and
307:
Engineers continue to find new ways to design CPUs that settle a little more quickly or use slightly less energy per transition, pushing back those limits, producing new CPUs that can run at slightly higher clock rates. The ultimate limits to energy per transition are explored in
498:"Overclocking" early processors was as simple – and as limited – as changing the discrete clock crystal ... The advent of adjustable clock generators has allowed "overclocking" to be done without changing parts such as the clock crystal.
376:
processors can execute more than one instruction per cycle (on average), yet it is not uncommon for them to do "less" in a clock cycle. In addition, subscalar CPUs or use of parallelism can also affect the performance of the computer regardless of clock rate.
348:
The clock rate of a CPU is most useful for providing comparisons between CPUs in the same family. The clock rate is only one of several factors that can influence performance when comparing processors in different families. For example, an IBM PC with an
477:
174:
wasted as heat (mostly inside the driving transistors). When executing complicated instructions that cause many transitions, the higher the clock rate the more heat produced. Transistors may be damaged by excessive heat.
457:
30:
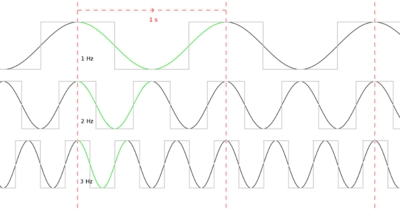
Microprocessor clock speed measures the number of pulses per second generated by an oscillator that sets the tempo for the processor. It is measured in hertz (pulses per second).
322:(cycles or clock cycles per instruction) count, although they may run at the same or a lower clock rate as older CPUs. This is achieved through architectural techniques such as
212:(c. 1981) had a clock rate of 4.77 MHz (4,772,727 cycles per second). In 1992, both Hewlett-Packard and Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) exceeded 100 MHz with
85:
is commonly advertised in gigahertz (GHz). This metric is most useful when comparing processors within the same family, holding constant other features that may affect
525:
1803:
315:
The first fully reversible CPU, the
Pendulum, was implemented using standard CMOS transistors in the late 1990s at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
242:
per cycle). Since then, the clock rate of production processors has increased more slowly, with performance improvements coming from other design changes.
166:
produced by the CPU. Conversely, some people try to increase performance of a CPU by replacing the oscillator crystal with a higher frequency crystal ("
775:
510:
1914:
1097:
1616:
894:
657:
372:
are more useful. Clock rates can sometimes be misleading since the amount of work different CPUs can do in one cycle varies. For example,
1773:
1339:
1156:
368:
The clock rate alone is generally considered to be an inaccurate measure of performance when comparing different CPUs families. Software
318:
Engineers also continue to find new ways to design CPUs so that they complete more instructions per clock cycle, thus achieving a lower
81:(PCs) to arrive throughout the 1970s and 1980s had clock rates measured in megahertz (MHz), and in the 21st century the speed of modern
2127:
110:
Manufacturers of modern processors typically charge higher prices for processors that operate at higher clock rates, a practice called
170:"). However, the amount of overclocking is limited by the time for the CPU to settle after each pulse, and by the extra heat created.
1119:
284:, achieved in November 2012. It is also surpassed by the slightly slower AMD FX-8370 overclocked to 8.72 GHz which tops off the
1768:
1840:
285:
564:
2122:
1593:
238:
model was introduced as the first CPU with a clock rate of 3 GHz (three billion cycles per second corresponding to ~ 0.33
201:, used a 100 kHz clock in its cycling unit. As each instruction took 20 cycles, it had an instruction rate of 5 kHz.
632:
2537:
1661:
924:
768:
438:
234:
demonstrated passing the 1 GHz milestone a few days ahead of Intel shipping 1 GHz in systems. In 2002, an Intel
2547:
1688:
193:, operated at 1 Hz (cycle per second) clock frequency and the first electromechanical general purpose computer, the
815:
63:
529:
288:
frequency rankings. These records were broken in late 2022 when an Intel Core i9-13900K was overclocked to 9.008 GHz.
1855:
1683:
1656:
1035:
2670:
2233:
1126:
1092:
1087:
1006:
971:
2645:
2542:
1943:
1850:
1651:
872:
761:
744:
1671:
1390:
825:
475:, "Method and apparatus for optimizing production yield and operational performance of integrated circuits"
387:
277:
208:(by MITS), used an Intel 8080 CPU with a clock rate of 2 MHz (2 million cycles per second). The original
158:. With any particular CPU, replacing the crystal with another crystal that oscillates at half the frequency ("
66:
the operations of its components, and is used as an indicator of the processor's speed. It is measured in the
1845:
1693:
1666:
1527:
1141:
1102:
959:
331:
254:
67:
2282:
2044:
1520:
1481:
1136:
1131:
1065:
877:
493:
1909:
1606:
1304:
1001:
745:"Theory, Synthesis, and Application of Adiabatic and Reversible Logic Circuits For Security Applications"
605:
151:
77:
The clock rate of the first generation of computers was measured in hertz or kilohertz (kHz), the first
2559:
2206:
1623:
1114:
1082:
852:
840:
820:
143:
2650:
2613:
2603:
991:
292:
197:, operated at a frequency of about 5–10 Hz. The first electronic general purpose computer, the
2665:
2072:
2008:
1985:
1835:
1797:
1633:
1583:
1578:
1055:
949:
857:
19:"Clocking" redirects here. For the practice of tampering with odometers to read less mileage, see
2711:
2618:
2401:
2295:
2259:
2176:
2160:
2002:
1791:
1750:
1738:
1601:
1515:
1436:
1201:
862:
805:
407:
353:
82:
526:"AMD Breaks 8 GHz Overclock with Upcoming FX Processor, Sets World Record with AMD FX 8350"
2424:
2396:
2306:
2271:
2020:
2014:
1996:
1730:
1724:
1628:
1532:
1423:
1362:
1224:
867:
327:
323:
319:
231:
224:
579:
2706:
2598:
2507:
2253:
1965:
1783:
1542:
1510:
1468:
1380:
1181:
996:
986:
976:
966:
936:
919:
784:
369:
246:
209:
2628:
2564:
2150:
1872:
1762:
1709:
1241:
954:
810:
792:
309:
86:
707:
8:
2675:
2660:
2480:
2331:
2313:
2277:
2265:
1919:
1866:
1643:
1559:
1441:
1296:
1191:
1050:
2532:
2524:
2376:
2351:
2155:
2030:
1554:
1495:
1375:
1107:
835:
127:
2485:
2452:
2368:
2300:
2201:
2191:
2181:
2112:
2107:
2102:
2025:
1954:
1860:
1820:
1453:
1403:
1353:
1329:
1211:
1151:
1146:
1028:
944:
221:
78:
2655:
2588:
2574:
2429:
2336:
2290:
2097:
2092:
2087:
2082:
2077:
2067:
1937:
1904:
1815:
1810:
1719:
1571:
1566:
1549:
1537:
1476:
1040:
1018:
904:
882:
800:
392:
26:
2569:
2554:
2502:
2406:
2381:
2218:
2211:
2062:
2057:
2052:
1991:
1899:
1889:
1611:
1446:
1398:
1161:
1045:
1013:
914:
909:
830:
358:
281:
262:
227:
111:
51:
580:"AMD's Ryzen rules overclocking world records… but can't beat a 5 year-old chip"
565:"8.79GHz FX-8350 is the Fastest Ever CPU | ROG – Republic of Gamers Global"
2680:
2514:
2497:
2490:
2386:
2243:
1980:
1894:
1825:
1408:
1370:
1319:
1314:
1309:
1023:
847:
494:"Overclocking Guide Part 1: Risks, Choices and Benefits : Who Overclocks?"
412:
397:
343:
139:
55:
20:
276:
record for the highest CPU clock rate at 8.79433 GHz with an AMD FX-8350
102:
2700:
2475:
2391:
1431:
1413:
1206:
899:
682:
633:"Overclockers surpassed the elusive 9GHz clock speed. Here's how they did it"
258:
194:
190:
159:
155:
138:
at the same frequency for digital electronics applications (or, when using a
134:—the frequency reference signal. Electronic circuitry translates that into a
1334:
230:
chip ran at 100 MHz (100 million cycles per second). On March 6, 2000,
2685:
2623:
2439:
2416:
2228:
1949:
887:
731:
472:
452:
273:
250:
167:
147:
59:
2470:
2434:
2145:
2117:
1975:
1830:
753:
373:
350:
296:
266:
205:
178:
135:
2356:
2346:
2341:
2323:
2196:
1458:
1291:
1261:
981:
402:
239:
163:
162:") will generally make the CPU run at half the performance and reduce
2447:
2444:
2186:
1256:
1234:
362:
235:
217:
131:
123:
47:
35:
550:
2462:
1281:
1271:
1229:
732:"Reversible Computing: A Requirement for Extreme Supercomputing"
1286:
1251:
1216:
142:, some fixed multiple of the crystal reference frequency). The
177:
There is also a lower limit of the clock rate, unless a fully
1744:
1276:
1246:
270:
198:
71:
184:
2608:
1756:
1676:
1266:
433:
249:
for the highest CPU clock rate is 8.42938 GHz with an
213:
299:, clocked at 6.2 GHz, which was released in Q1 2024.
1196:
1186:
511:"Highest clock frequency achieved by a silicon processor"
154:
has a "clock" pin driven by a similar system to set the
683:"The Reversible and Quantum Computing Group (Revcomp)"
122:
The clock rate of a CPU is normally determined by the
130:. Typically a crystal oscillator produces a fixed
16:Frequency at which a CPU chip or core is operating
2698:
189:The first fully mechanical analog computer, the
455:, "Optimization of die placement on wafers"
106:Representation of a clock signal and clock rate
769:
1774:Computer performance by orders of magnitude
783:
776:
762:
598:
523:
491:
185:Historical milestones and current records
216:techniques in the PA-7100 and AXP 21064
101:
25:
524:Chiappetta, Marco (23 September 2011).
492:Soderstrom, Thomas (11 December 2006).
2699:
705:
295:rate on a production processor is the
92:
757:
630:
624:
577:
361:, the latency of the memory, and the
1745:Floating-point operations per second
631:White, Monica J (22 December 2022).
571:
439:Free On-line Dictionary of Computing
13:
150:to all the parts that need it. An
14:
2723:
680:
551:"CPU-Z Validator – World Records"
2671:Semiconductor device fabrication
578:James, Dave (16 December 2019).
2646:History of general-purpose CPUs
873:Nondeterministic Turing machine
737:
724:
699:
674:
658:"Products formerly Raptor Lake"
650:
826:Deterministic finite automaton
557:
543:
517:
503:
485:
465:
445:
426:
388:Crystal oscillator frequencies
117:
1:
1617:Simultaneous and heterogenous
606:"CPU Frequency: Hall of Fame"
528:. HotHardware. Archived from
419:
332:instruction level parallelism
204:The first commercial PC, the
2301:Integrated memory controller
2283:Translation lookaside buffer
1482:Memory dependence prediction
925:Random-access stored program
878:Probabilistic Turing machine
337:
146:inside the CPU carries that
7:
1757:Synaptic updates per second
380:
302:
269:. This is surpassed by the
10:
2730:
2161:Heterogeneous architecture
1083:Orthogonal instruction set
853:Alternating Turing machine
841:Quantum cellular automaton
341:
330:which attempts to exploit
144:clock distribution network
97:
18:
2651:Microprocessor chronology
2638:
2614:Dynamic frequency scaling
2587:
2523:
2461:
2415:
2367:
2322:
2242:
2169:
2138:
2043:
1964:
1928:
1882:
1782:
1769:Cache performance metrics
1708:
1642:
1592:
1503:
1494:
1467:
1422:
1389:
1361:
1352:
1172:
1075:
1064:
935:
791:
743:Matthew Arthur Morrison.
2666:Hardware security module
2009:Digital signal processor
1986:Graphics processing unit
1798:Graphics processing unit
708:"Backward to the Future"
706:Swaine, Michael (2004).
46:typically refers to the
2619:Dynamic voltage scaling
2402:Memory address register
2296:Branch target predictor
2260:Address generation unit
2003:Physics processing unit
1792:Central processing unit
1751:Transactions per second
1739:Instructions per second
1662:Array processing (SIMT)
806:Stored-program computer
408:Instructions per second
220:respectively. In 1995,
2425:Hardwired control unit
2307:Memory management unit
2272:Memory management unit
2021:Secure cryptoprocessor
2015:Tensor Processing Unit
1997:Vision processing unit
1731:Cycles per instruction
1725:Instructions per cycle
1672:Associative processing
1363:Instruction pipelining
785:Processor technologies
328:out-of-order execution
324:instruction pipelining
280:-based chip bathed in
107:
31:
2508:Sum-addressed decoder
2254:Arithmetic logic unit
1381:Classic RISC pipeline
1335:Epiphany architecture
1182:Motorola 68000 series
265:cryobath, 5 GHz
247:Guinness World Record
105:
29:
2629:Performance per watt
2207:replacement policies
1873:Package on a package
1763:Performance per watt
1667:Pipelined processing
1437:Tomasulo's algorithm
1242:Clipper architecture
1098:Application-specific
811:Finite-state machine
310:reversible computing
62:, which are used to
2661:Digital electronics
2314:Instruction decoder
2266:Floating-point unit
1920:Soft microprocessor
1867:System in a package
1442:Reservation station
972:Transport-triggered
93:Determining factors
2533:Integrated circuit
2377:Processor register
2031:Baseband processor
1376:Operand forwarding
836:Cellular automaton
730:Michael P. Frank.
257:-based chip in an
128:oscillator crystal
108:
79:personal computers
70:unit of frequency
32:
2694:
2693:
2583:
2582:
2202:Instruction cache
2192:Scratchpad memory
2039:
2038:
2026:Network processor
1955:Network on a chip
1910:Ultra-low-voltage
1861:Multi-chip module
1704:
1703:
1490:
1489:
1477:Branch prediction
1454:Register renaming
1348:
1347:
1330:VISC architecture
1152:Quantum computing
1147:VISC architecture
1029:Secondary storage
945:Microarchitecture
905:Register machines
245:Set in 2011, the
2719:
2656:Processor design
2548:Power management
2430:Instruction unit
2291:Branch predictor
2240:
2239:
1938:System on a chip
1880:
1879:
1720:Transistor count
1644:Flynn's taxonomy
1501:
1500:
1359:
1358:
1162:Addressing modes
1073:
1072:
1019:Memory hierarchy
883:Hypercomputation
801:Abstract machine
778:
771:
764:
755:
754:
748:
741:
735:
728:
722:
721:
719:
718:
703:
697:
696:
694:
693:
687:www.cise.ufl.edu
681:Frank, Michael.
678:
672:
671:
669:
668:
654:
648:
647:
645:
643:
628:
622:
621:
619:
617:
602:
596:
594:
592:
590:
575:
569:
568:
561:
555:
554:
547:
541:
540:
538:
537:
521:
515:
514:
507:
501:
500:
489:
483:
481:
480:
476:
469:
463:
461:
460:
456:
449:
443:
442:
430:
393:Double data rate
2729:
2728:
2722:
2721:
2720:
2718:
2717:
2716:
2697:
2696:
2695:
2690:
2676:Tick–tock model
2634:
2590:
2579:
2519:
2503:Address decoder
2457:
2411:
2407:Program counter
2382:Status register
2363:
2318:
2278:Load–store unit
2245:
2238:
2165:
2134:
2035:
1992:Image processor
1967:
1960:
1930:
1924:
1900:Microcontroller
1890:Embedded system
1878:
1778:
1711:
1700:
1638:
1588:
1486:
1463:
1447:Re-order buffer
1418:
1399:Data dependency
1385:
1344:
1174:
1168:
1067:
1066:Instruction set
1060:
1046:Multiprocessing
1014:Cache hierarchy
1007:Register/memory
931:
831:Queue automaton
787:
782:
752:
751:
742:
738:
729:
725:
716:
714:
704:
700:
691:
689:
679:
675:
666:
664:
656:
655:
651:
641:
639:
629:
625:
615:
613:
604:
603:
599:
588:
586:
576:
572:
563:
562:
558:
549:
548:
544:
535:
533:
522:
518:
509:
508:
504:
490:
486:
478:
471:
470:
466:
458:
451:
450:
446:
432:
431:
427:
422:
417:
383:
346:
340:
305:
187:
120:
100:
95:
52:clock generator
24:
17:
12:
11:
5:
2727:
2726:
2715:
2714:
2712:Temporal rates
2709:
2692:
2691:
2689:
2688:
2683:
2681:Pin grid array
2678:
2673:
2668:
2663:
2658:
2653:
2648:
2642:
2640:
2636:
2635:
2633:
2632:
2626:
2621:
2616:
2611:
2606:
2601:
2595:
2593:
2585:
2584:
2581:
2580:
2578:
2577:
2572:
2567:
2562:
2557:
2552:
2551:
2550:
2545:
2540:
2529:
2527:
2521:
2520:
2518:
2517:
2515:Barrel shifter
2512:
2511:
2510:
2505:
2498:Binary decoder
2495:
2494:
2493:
2483:
2478:
2473:
2467:
2465:
2459:
2458:
2456:
2455:
2450:
2442:
2437:
2432:
2427:
2421:
2419:
2413:
2412:
2410:
2409:
2404:
2399:
2394:
2389:
2387:Stack register
2384:
2379:
2373:
2371:
2365:
2364:
2362:
2361:
2360:
2359:
2354:
2344:
2339:
2334:
2328:
2326:
2320:
2319:
2317:
2316:
2311:
2310:
2309:
2298:
2293:
2288:
2287:
2286:
2280:
2269:
2263:
2257:
2250:
2248:
2237:
2236:
2231:
2226:
2221:
2216:
2215:
2214:
2209:
2204:
2199:
2194:
2189:
2179:
2173:
2171:
2167:
2166:
2164:
2163:
2158:
2153:
2148:
2142:
2140:
2136:
2135:
2133:
2132:
2131:
2130:
2120:
2115:
2110:
2105:
2100:
2095:
2090:
2085:
2080:
2075:
2070:
2065:
2060:
2055:
2049:
2047:
2041:
2040:
2037:
2036:
2034:
2033:
2028:
2023:
2018:
2012:
2006:
2000:
1994:
1989:
1983:
1981:AI accelerator
1978:
1972:
1970:
1962:
1961:
1959:
1958:
1952:
1947:
1944:Multiprocessor
1941:
1934:
1932:
1926:
1925:
1923:
1922:
1917:
1912:
1907:
1902:
1897:
1895:Microprocessor
1892:
1886:
1884:
1883:By application
1877:
1876:
1870:
1864:
1858:
1853:
1848:
1843:
1838:
1833:
1828:
1826:Tile processor
1823:
1818:
1813:
1808:
1807:
1806:
1795:
1788:
1786:
1780:
1779:
1777:
1776:
1771:
1766:
1760:
1754:
1748:
1742:
1736:
1735:
1734:
1722:
1716:
1714:
1706:
1705:
1702:
1701:
1699:
1698:
1697:
1696:
1686:
1681:
1680:
1679:
1674:
1669:
1664:
1654:
1648:
1646:
1640:
1639:
1637:
1636:
1631:
1626:
1621:
1620:
1619:
1614:
1612:Hyperthreading
1604:
1598:
1596:
1594:Multithreading
1590:
1589:
1587:
1586:
1581:
1576:
1575:
1574:
1564:
1563:
1562:
1557:
1547:
1546:
1545:
1540:
1530:
1525:
1524:
1523:
1518:
1507:
1505:
1498:
1492:
1491:
1488:
1487:
1485:
1484:
1479:
1473:
1471:
1465:
1464:
1462:
1461:
1456:
1451:
1450:
1449:
1444:
1434:
1428:
1426:
1420:
1419:
1417:
1416:
1411:
1406:
1401:
1395:
1393:
1387:
1386:
1384:
1383:
1378:
1373:
1371:Pipeline stall
1367:
1365:
1356:
1350:
1349:
1346:
1345:
1343:
1342:
1337:
1332:
1327:
1324:
1323:
1322:
1320:z/Architecture
1317:
1312:
1307:
1299:
1294:
1289:
1284:
1279:
1274:
1269:
1264:
1259:
1254:
1249:
1244:
1239:
1238:
1237:
1232:
1227:
1219:
1214:
1209:
1204:
1199:
1194:
1189:
1184:
1178:
1176:
1170:
1169:
1167:
1166:
1165:
1164:
1154:
1149:
1144:
1139:
1134:
1129:
1124:
1123:
1122:
1112:
1111:
1110:
1100:
1095:
1090:
1085:
1079:
1077:
1070:
1062:
1061:
1059:
1058:
1053:
1048:
1043:
1038:
1033:
1032:
1031:
1026:
1024:Virtual memory
1016:
1011:
1010:
1009:
1004:
999:
994:
984:
979:
974:
969:
964:
963:
962:
952:
947:
941:
939:
933:
932:
930:
929:
928:
927:
922:
917:
912:
902:
897:
892:
891:
890:
885:
880:
875:
870:
865:
860:
855:
848:Turing machine
845:
844:
843:
838:
833:
828:
823:
818:
808:
803:
797:
795:
789:
788:
781:
780:
773:
766:
758:
750:
749:
736:
723:
698:
673:
649:
623:
597:
570:
556:
542:
516:
502:
484:
464:
444:
424:
423:
421:
418:
416:
415:
410:
405:
400:
398:Quad data rate
395:
390:
384:
382:
379:
365:architecture.
344:Megahertz myth
342:Main article:
339:
336:
304:
301:
186:
183:
140:CPU multiplier
119:
116:
99:
96:
94:
91:
21:Odometer fraud
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2725:
2724:
2713:
2710:
2708:
2705:
2704:
2702:
2687:
2684:
2682:
2679:
2677:
2674:
2672:
2669:
2667:
2664:
2662:
2659:
2657:
2654:
2652:
2649:
2647:
2644:
2643:
2641:
2637:
2630:
2627:
2625:
2622:
2620:
2617:
2615:
2612:
2610:
2607:
2605:
2602:
2600:
2597:
2596:
2594:
2592:
2586:
2576:
2573:
2571:
2568:
2566:
2563:
2561:
2558:
2556:
2553:
2549:
2546:
2544:
2541:
2539:
2536:
2535:
2534:
2531:
2530:
2528:
2526:
2522:
2516:
2513:
2509:
2506:
2504:
2501:
2500:
2499:
2496:
2492:
2489:
2488:
2487:
2484:
2482:
2479:
2477:
2476:Demultiplexer
2474:
2472:
2469:
2468:
2466:
2464:
2460:
2454:
2451:
2449:
2446:
2443:
2441:
2438:
2436:
2433:
2431:
2428:
2426:
2423:
2422:
2420:
2418:
2414:
2408:
2405:
2403:
2400:
2398:
2397:Memory buffer
2395:
2393:
2392:Register file
2390:
2388:
2385:
2383:
2380:
2378:
2375:
2374:
2372:
2370:
2366:
2358:
2355:
2353:
2350:
2349:
2348:
2345:
2343:
2340:
2338:
2335:
2333:
2332:Combinational
2330:
2329:
2327:
2325:
2321:
2315:
2312:
2308:
2305:
2304:
2302:
2299:
2297:
2294:
2292:
2289:
2284:
2281:
2279:
2276:
2275:
2273:
2270:
2267:
2264:
2261:
2258:
2255:
2252:
2251:
2249:
2247:
2241:
2235:
2232:
2230:
2227:
2225:
2222:
2220:
2217:
2213:
2210:
2208:
2205:
2203:
2200:
2198:
2195:
2193:
2190:
2188:
2185:
2184:
2183:
2180:
2178:
2175:
2174:
2172:
2168:
2162:
2159:
2157:
2154:
2152:
2149:
2147:
2144:
2143:
2141:
2137:
2129:
2126:
2125:
2124:
2121:
2119:
2116:
2114:
2111:
2109:
2106:
2104:
2101:
2099:
2096:
2094:
2091:
2089:
2086:
2084:
2081:
2079:
2076:
2074:
2071:
2069:
2066:
2064:
2061:
2059:
2056:
2054:
2051:
2050:
2048:
2046:
2042:
2032:
2029:
2027:
2024:
2022:
2019:
2016:
2013:
2010:
2007:
2004:
2001:
1998:
1995:
1993:
1990:
1987:
1984:
1982:
1979:
1977:
1974:
1973:
1971:
1969:
1963:
1956:
1953:
1951:
1948:
1945:
1942:
1939:
1936:
1935:
1933:
1927:
1921:
1918:
1916:
1913:
1911:
1908:
1906:
1903:
1901:
1898:
1896:
1893:
1891:
1888:
1887:
1885:
1881:
1874:
1871:
1868:
1865:
1862:
1859:
1857:
1854:
1852:
1849:
1847:
1844:
1842:
1839:
1837:
1834:
1832:
1829:
1827:
1824:
1822:
1819:
1817:
1814:
1812:
1809:
1805:
1802:
1801:
1799:
1796:
1793:
1790:
1789:
1787:
1785:
1781:
1775:
1772:
1770:
1767:
1764:
1761:
1758:
1755:
1752:
1749:
1746:
1743:
1740:
1737:
1732:
1729:
1728:
1726:
1723:
1721:
1718:
1717:
1715:
1713:
1707:
1695:
1692:
1691:
1690:
1687:
1685:
1682:
1678:
1675:
1673:
1670:
1668:
1665:
1663:
1660:
1659:
1658:
1655:
1653:
1650:
1649:
1647:
1645:
1641:
1635:
1632:
1630:
1627:
1625:
1622:
1618:
1615:
1613:
1610:
1609:
1608:
1605:
1603:
1600:
1599:
1597:
1595:
1591:
1585:
1582:
1580:
1577:
1573:
1570:
1569:
1568:
1565:
1561:
1558:
1556:
1553:
1552:
1551:
1548:
1544:
1541:
1539:
1536:
1535:
1534:
1531:
1529:
1526:
1522:
1519:
1517:
1514:
1513:
1512:
1509:
1508:
1506:
1502:
1499:
1497:
1493:
1483:
1480:
1478:
1475:
1474:
1472:
1470:
1466:
1460:
1457:
1455:
1452:
1448:
1445:
1443:
1440:
1439:
1438:
1435:
1433:
1432:Scoreboarding
1430:
1429:
1427:
1425:
1421:
1415:
1414:False sharing
1412:
1410:
1407:
1405:
1402:
1400:
1397:
1396:
1394:
1392:
1388:
1382:
1379:
1377:
1374:
1372:
1369:
1368:
1366:
1364:
1360:
1357:
1355:
1351:
1341:
1338:
1336:
1333:
1331:
1328:
1325:
1321:
1318:
1316:
1313:
1311:
1308:
1306:
1303:
1302:
1300:
1298:
1295:
1293:
1290:
1288:
1285:
1283:
1280:
1278:
1275:
1273:
1270:
1268:
1265:
1263:
1260:
1258:
1255:
1253:
1250:
1248:
1245:
1243:
1240:
1236:
1233:
1231:
1228:
1226:
1223:
1222:
1220:
1218:
1215:
1213:
1210:
1208:
1207:Stanford MIPS
1205:
1203:
1200:
1198:
1195:
1193:
1190:
1188:
1185:
1183:
1180:
1179:
1177:
1171:
1163:
1160:
1159:
1158:
1155:
1153:
1150:
1148:
1145:
1143:
1140:
1138:
1135:
1133:
1130:
1128:
1125:
1121:
1118:
1117:
1116:
1113:
1109:
1106:
1105:
1104:
1101:
1099:
1096:
1094:
1091:
1089:
1086:
1084:
1081:
1080:
1078:
1074:
1071:
1069:
1068:architectures
1063:
1057:
1054:
1052:
1049:
1047:
1044:
1042:
1039:
1037:
1036:Heterogeneous
1034:
1030:
1027:
1025:
1022:
1021:
1020:
1017:
1015:
1012:
1008:
1005:
1003:
1000:
998:
995:
993:
990:
989:
988:
987:Memory access
985:
983:
980:
978:
975:
973:
970:
968:
965:
961:
958:
957:
956:
953:
951:
948:
946:
943:
942:
940:
938:
934:
926:
923:
921:
920:Random-access
918:
916:
913:
911:
908:
907:
906:
903:
901:
900:Stack machine
898:
896:
893:
889:
886:
884:
881:
879:
876:
874:
871:
869:
866:
864:
861:
859:
856:
854:
851:
850:
849:
846:
842:
839:
837:
834:
832:
829:
827:
824:
822:
819:
817:
816:with datapath
814:
813:
812:
809:
807:
804:
802:
799:
798:
796:
794:
790:
786:
779:
774:
772:
767:
765:
760:
759:
756:
746:
740:
733:
727:
713:
709:
702:
688:
684:
677:
663:
662:www.intel.com
659:
653:
638:
637:digitaltrends
634:
627:
611:
607:
601:
585:
581:
574:
566:
560:
552:
546:
532:on 2015-03-10
531:
527:
520:
512:
506:
499:
495:
488:
474:
468:
454:
448:
441:
440:
435:
429:
425:
414:
411:
409:
406:
404:
401:
399:
396:
394:
391:
389:
386:
385:
378:
375:
371:
366:
364:
360:
355:
352:
345:
335:
334:in the code.
333:
329:
325:
321:
316:
313:
311:
300:
298:
294:
289:
287:
283:
279:
275:
272:
268:
264:
260:
256:
252:
248:
243:
241:
237:
233:
229:
226:
223:
219:
215:
211:
207:
202:
200:
196:
192:
182:
180:
175:
171:
169:
165:
161:
160:underclocking
157:
156:sampling rate
153:
152:A/D Converter
149:
145:
141:
137:
133:
129:
125:
115:
113:
104:
90:
88:
84:
80:
75:
73:
69:
65:
61:
58:can generate
57:
53:
50:at which the
49:
45:
41:
37:
28:
22:
2707:Clock signal
2686:Chip carrier
2624:Clock gating
2543:Mixed-signal
2440:Write buffer
2417:Control unit
2229:Clock signal
2223:
1968:accelerators
1950:Cypress PSoC
1607:Simultaneous
1424:Out-of-order
1056:Neuromorphic
937:Architecture
895:Belt machine
888:Zeno machine
821:Hierarchical
739:
726:
715:. Retrieved
711:
701:
690:. Retrieved
686:
676:
665:. Retrieved
661:
652:
640:. Retrieved
636:
626:
614:. Retrieved
609:
600:
587:. Retrieved
583:
573:
559:
545:
534:. Retrieved
530:the original
519:
505:
497:
487:
467:
447:
437:
428:
367:
347:
317:
314:
306:
291:The highest
290:
274:overclocking
253:AMD FX-8150
244:
203:
188:
176:
172:
168:overclocking
148:clock signal
121:
109:
76:
43:
39:
33:
2471:Multiplexer
2435:Data buffer
2146:Single-core
2118:bit slicing
1976:Coprocessor
1831:Coprocessor
1712:performance
1634:Cooperative
1624:Speculative
1584:Distributed
1543:Superscalar
1528:Instruction
1496:Parallelism
1469:Speculative
1301:System/3x0
1173:Instruction
950:Von Neumann
863:Post–Turing
616:23 November
589:23 November
413:Moore's law
374:superscalar
351:Intel 80486
251:overclocked
240:nanoseconds
206:Altair 8800
179:static core
136:square wave
118:Engineering
87:performance
64:synchronize
44:clock speed
2701:Categories
2591:management
2486:Multiplier
2347:Logic gate
2337:Sequential
2244:Functional
2224:Clock rate
2197:Data cache
2170:Components
2151:Multi-core
2139:Core count
1629:Preemptive
1533:Pipelining
1516:Bit-serial
1459:Wide-issue
1404:Structural
1326:Tilera ISA
1292:MicroBlaze
1262:ETRAX CRIS
1157:Comparison
1002:Load–store
982:Endianness
717:2024-03-17
712:Dr. Dobb's
692:2024-03-17
667:2024-07-05
642:20 January
536:2012-04-28
473:US 6694492
453:US 6826738
420:References
403:Pulse wave
370:benchmarks
297:i9-14900KS
293:base clock
278:Piledriver
164:waste heat
40:clock rate
2525:Circuitry
2445:Microcode
2369:Registers
2212:coherence
2187:CPU cache
2045:Word size
1710:Processor
1354:Execution
1257:DEC Alpha
1235:Power ISA
1051:Cognitive
858:Universal
610:hwbot.org
338:Comparing
255:Bulldozer
236:Pentium 4
218:DEC Alpha
181:is used.
132:sine wave
124:frequency
56:processor
48:frequency
36:computing
2463:Datapath
2156:Manycore
2128:variable
1966:Hardware
1602:Temporal
1282:OpenRISC
977:Cellular
967:Dataflow
960:modified
584:pcgamesn
381:See also
359:data bus
303:Research
2639:Related
2570:Quantum
2560:Digital
2555:Boolean
2453:Counter
2352:Quantum
2113:512-bit
2108:256-bit
2103:128-bit
1946:(MPSoC)
1931:on chip
1929:Systems
1747:(FLOPS)
1560:Process
1409:Control
1391:Hazards
1277:Itanium
1272:Unicore
1230:PowerPC
955:Harvard
915:Pointer
910:Counter
868:Quantum
747:. 2014.
612:. HWBOT
436:at the
228:Pentium
222:Intel's
112:binning
98:Binning
2575:Switch
2565:Analog
2303:(IMC)
2274:(MMU)
2123:others
2098:64-bit
2093:48-bit
2088:32-bit
2083:24-bit
2078:16-bit
2073:15-bit
2068:12-bit
1905:Mobile
1821:Stream
1816:Barrel
1811:Vector
1800:(GPU)
1759:(SUPS)
1727:(IPC)
1579:Memory
1572:Vector
1555:Thread
1538:Scalar
1340:Others
1287:RISC-V
1252:SuperH
1221:Power
1217:MIPS-X
1192:PDP-11
1041:Fabric
793:Models
595:
479:
459:
267:on air
210:IBM PC
126:of an
74:(Hz).
60:pulses
38:, the
2631:(PPW)
2589:Power
2481:Adder
2357:Array
2324:Logic
2285:(TLB)
2268:(FPU)
2262:(AGU)
2256:(ALU)
2246:units
2182:Cache
2063:8-bit
2058:4-bit
2053:1-bit
2017:(TPU)
2011:(DSP)
2005:(PPU)
1999:(VPU)
1988:(GPU)
1957:(NoC)
1940:(SoC)
1875:(PoP)
1869:(SiP)
1863:(MCM)
1804:GPGPU
1794:(CPU)
1784:Types
1765:(PPW)
1753:(TPS)
1741:(IPS)
1733:(CPI)
1504:Level
1315:S/390
1310:S/370
1305:S/360
1247:SPARC
1225:POWER
1108:TRIPS
1076:Types
434:Clock
363:cache
286:HWBOT
271:CPU-Z
199:ENIAC
72:hertz
54:of a
2609:ACPI
2342:Glue
2234:FIFO
2177:Core
1915:ASIP
1856:CPLD
1851:FPOA
1846:FPGA
1841:ASIC
1694:SPMD
1689:MIMD
1684:MISD
1677:SWAR
1657:SIMD
1652:SISD
1567:Data
1550:Task
1521:Word
1267:M32R
1212:MIPS
1175:sets
1142:ZISC
1137:NISC
1132:OISC
1127:MISC
1120:EPIC
1115:VLIW
1103:EDGE
1093:RISC
1088:CISC
997:HUMA
992:NUMA
644:2023
618:2021
591:2021
326:and
214:RISC
83:CPUs
2604:APM
2599:PMU
2491:CPU
2448:ROM
2219:Bus
1836:PAL
1511:Bit
1297:LMC
1202:ARM
1197:x86
1187:VAX
354:CPU
320:CPI
282:LN2
263:LN2
259:LHe
232:AMD
89:.
42:or
34:In
2703::
2538:3D
710:.
685:.
660:.
635:.
608:.
582:.
496:.
312:.
225:P5
195:Z3
191:Z1
68:SI
777:e
770:t
763:v
734:.
720:.
695:.
670:.
646:.
620:.
593:.
567:.
553:.
539:.
513:.
482:.
462:.
261:/
23:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.