280:
55:
37:
214:
261:
173:
484:
382:
152:
Flares are sudden, severe and without warning. Diet does not appear to cause flares. Overexertion of any exercise, standing too long, shopping, stressful or loud environments, can or may lead to severe flares, which can last from one hour to months. Although, in some patient interviews, alcohol
248:
within the affected joint, indicating a substantial amount of calcium crystal deposition within the cartilage or ligaments. Ultrasound is a reliable method to diagnose CPPD. Using ultrasound, chondrocalcinosis may be depicted as echogenic foci with no acoustic shadow within the hyaline cartilage or
823:
Zhang W, Doherty M, Bardin T, Barskova V, Guerne PA, Jansen TL, Leeb BF, Perez-Ruiz F, Pimentao J, Punzi L, Richette P, Sivera F, Uhlig T, Watt I, Pascual E. European League
Against Rheumatism recommendations for calcium pyrophosphate deposition. Part I: terminology and diagnosis. Ann Rheum Dis.
349:
NSAIDs, Colchicine, and methotrexate may provide initial relief. There is currently no treatment for non-invasive removal of these crystals once they are deposited. Attempts to dissolve crystals in situ using enzymes turned up to be a "clinical failure". New, innovative methods using catalytic
145:
The symptoms can be monoarticular (involving a single joint) or polyarticular (involving several joints). Symptoms usually last for days to weeks, and often recur. Although any joint may be affected, the knees, wrists, and hips are most common.
310:
on polarized light microscopy, and this method remains the most reliable method of identifying the crystals under the microscope. However, even this method has poor sensitivity, specificity, and inter-operator agreement.
1267:
1248:
1233:
399:
361:
CPPD is estimated to affect 4% to 7% of the adult populations of Europe and the United States. Previous studies have overestimated the prevalence by simply estimating the prevalence of
210:
The disease is defined by presence of joint inflammation and the presence of CPPD crystals within the joint. The crystals are usually detected by imaging and/or joint fluid analysis.
186:(ATP; the molecule used as energy currency in all living things), which results in increased pyrophosphate levels in joints, is thought to be one reason why crystals may develop.
338:. In general, NSAIDs are administered in low doses to help prevent CPPD. However, if an acute attack is already occurring, higher doses are administered. If nothing else works,
294:, or removing synovial fluid from the affected joint, is performed to test the synovial fluid for the calcium pyrophosphate crystals that are present in CPPD. When stained with
1389:
326:
Because any medication that could reduce the inflammation of CPPD bears a risk of causing organ damage, treatment is not advised if the condition is not causing pain. For
446:
418:
1174:
425:
504:
432:
156:
X-ray, CT, or other imaging usually shows accumulation of calcium within the joint cartilage, known as chondrocalcinosis. There can also be findings of
1382:
414:
368:
It may cause considerable pain, but it is never fatal. Women are at a slightly higher risk than men, with an estimated ratio of occurrence of 1.4:1.
942:
561:
or radiographic findings are most prominent. A task force of the
European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) made recommendations on preferred
149:
CPPD crystals appear as shattered glass under the microscope. When released into the synovial fluid, it causes unbearable pain to the patient.
1375:
929:
1121:"A Phage Display-Identified Short Peptide Capable of Hydrolyzing Calcium Pyrophosphate Crystals-The Etiological Factor of Chondrocalcinosis"
1591:
346:
may provide relief. Research into surgical removal of calcifications is underway, however, this still remains an experimental procedure.
202:
Chrondocalcinosis may be extremely common in the population. CPPD flares may also be triggered by joint trauma from previous surgeries.
439:
880:"Ultrasound in the diagnosis of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate deposition disease. A systematic literature review and a meta-analysis"
928:
Arend CF. Ultrasound of the
Shoulder. Master Medical Books, 2013. Free chapter on acromioclavicular chondrocalcinosis is available at
314:
These two modalities currently define CPPD disease, but lack diagnostic accuracy. Thus, the diagnosis of CPPD disease is potentially
569:(CPPD) is an umbrella term for the various clinical subsets, whose naming reflects an emphasis on particular features. For example,
1683:
279:
1204:
331:
1693:
1281:
1688:
526:
465:
1519:
778:
Tsui FW (April 2012). "Genetics and mechanisms of crystal deposition in calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease".
972:
493:
54:
1615:
403:
1586:
1552:
950:
1097:
44:
Polarized light microscopy of CPPD, showing rhombus-shaped calcium pyrophosphate crystals with positive
237:
582:
93:
is most commonly affected. The disease is metabolic in origin and its treatment remains symptomatic.
36:
1542:
1295:
878:
Filippou G, Adinolfi A, Iagnocco A, Filippucci E, Cimmino MA, Bertoldi I, et al. (June 2016).
330:
pseudogout, treatments include intra-articular corticosteroid injection, systemic corticosteroids,
217:
192:
forms are rare. One genetic study found an association between CPPD and a region of chromosome 8q.
1175:"Clinical manifestations and diagnosis of calcium pyrophosphate crystal deposition (CPPD) disease"
392:
1610:
1537:
497:
250:
183:
1335:
1242:
547:
176:
86:
1598:
755:
681:
508:
8:
1650:
1603:
1532:
1490:
1271:
268:
233:
199:
is involved in crystal-related inflammatory reactions and inorganic phosphate transport.
1678:
1645:
1565:
1527:
1276:
1147:
1120:
1027:
1002:
852:
835:
803:
650:
625:
339:
284:
241:
1498:
1306:
1200:
1152:
1078:
1032:
911:
857:
795:
711:
655:
586:
362:
245:
221:
101:
When symptomatic, the disease classically begins with symptoms that are similar to a
836:"Linkage of early-onset osteoarthritis and chondrocalcinosis to human chromosome 8q"
807:
58:
Artistic depiction of pseudogout crystals (calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals)
1475:
1467:
1352:
1346:
1142:
1132:
1068:
1022:
1014:
901:
891:
847:
834:
Baldwin CT, Farrer LA, Adair R, Dharmavaram R, Jimenez S, Anderson L (March 1995).
787:
645:
637:
327:
161:
1448:
1300:
626:"Calcium pyrophosphate crystal deposition is not always 'wear and tear' or aging"
1570:
1355:
1349:
1057:"Crystal arthritis: calcium pyrophosphate deposition-nothing 'pseudo' about it!"
213:
1640:
1422:
1311:
896:
879:
598:
594:
291:
157:
1261:
1257:
1137:
791:
1672:
1427:
1417:
589:, on the other hand, refers to the radiographic evidence of calcification in
307:
249:
fibrocartilage. By x-ray, CPPD can appear similar to other diseases such as
45:
1073:
1056:
973:"Calcium Pyrophosphate Dihydrate Deposition Disease: Synovial Biopsy, Wrist"
539:
CPPD crystal deposition disease was originally described over 50 years ago.
1635:
1480:
1458:
1156:
1082:
1036:
915:
799:
715:
699:
343:
315:
295:
272:
82:
1225:
861:
659:
641:
1398:
1330:
1119:
Piast RW, Wieczorek RM, Marzec N, Garstka M, Misicka A (September 2021).
1018:
906:
562:
229:
283:
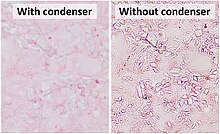
CPPD crystals are more clearly visualized on light microscopy without a
260:
172:
1655:
1443:
406: in this section. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
335:
299:
264:
1412:
1367:
1341:
574:
129:
85:
disease which is thought to be secondary to abnormal accumulation of
754:
Rothschild BM, Bruno MA (9 April 2021). Coombs BD, Keats TE (eds.).
381:
1179:
680:
Rothschild BM, Bruno MA (7 June 2022). Coombs BD, Keats TE (eds.).
554:
303:
189:
877:
590:
558:
557:, which have been given various names, based upon which clinical
550:
1289:
1286:
1252:
1237:
1194:
833:
597:. "Osteoarthritis (OA) with CPPD" reflects a situation where
182:
The cause of CPPD disease is unknown. Increased breakdown of
415:"Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition disease"
1509:
1118:
578:
254:
196:
102:
90:
302:"). However, CPP crystals are much better known for their
1560:
756:"Calcium Pyrophosphate Deposition Disease (rheumatology)"
1195:
Longmore M, Wilkinson I, Turmezei T, Cheung CK (2007).
298:, calcium pyrophosphate crystals appears deeply blue ("
682:"Calcium Pyrophosphate Deposition Disease (radiology)"
573:
refers to the acute symptoms of joint inflammation or
135:
inability to walk or perform everyday tasks or hobbies
1215:
577:: red, tender, and swollen joints that may resemble
365:, which is found in many other conditions as well.
89:dihydrate crystals within joint soft tissues. The
1670:
1050:
1048:
1046:
873:
871:
753:
697:
679:
1003:"Identification of crystals in synovial fluid"
358:The condition is more common in older adults.
1383:
1095:
1054:
1043:
749:
747:
745:
623:
1592:Systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis
1188:
868:
743:
741:
739:
737:
735:
733:
731:
729:
727:
725:
700:"Update on calcium pyrophosphate deposition"
675:
673:
671:
669:
619:
617:
1168:
1166:
819:
817:
1390:
1376:
1000:
934:
827:
773:
771:
769:
507:. Please do not remove this message until
1172:
1146:
1136:
1072:
1026:
996:
994:
905:
895:
851:
722:
666:
649:
614:
527:Learn how and when to remove this message
466:Learn how and when to remove this message
1163:
814:
581:arthritis (a similar condition in which
553:are associated with a range of clinical
503:Relevant discussion may be found on the
278:
259:
212:
171:
138:gnawing/chewing sensations in the joints
53:
766:
605:refers to several of these situations.
22:Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate disease
1671:
1397:
1185:This topic last updated: Jul 24, 2018.
991:
704:Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology
1371:
624:Wright GD, Doherty M (October 1997).
334:(NSAIDs), or, on occasion, high-dose
332:non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
96:
1197:Oxford Handbook of Clinical Medicine
1173:Rosenthal AK (2021). Post TW (ed.).
777:
693:
691:
477:
404:adding citations to reliable sources
375:
1102:Journal of Musculoskeletal Medicine
13:
1055:Rosenthal AK, Ryan LM (May 2011).
979:. American College of Rheumatology
940:
840:American Journal of Human Genetics
585:are deposited within the joints).
14:
1705:
688:
267:showing crystal deposition in an
1007:Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases
630:Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases
601:features are the most apparent.
567:calcium pyrophosphate deposition
482:
380:
35:
1112:
1098:"All about gout and pseudogout"
1089:
965:
548:Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate
391:needs additional citations for
353:
228:Medical imaging, consisting of
63:Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate
1684:Inflammatory polyarthropathies
1096:Emkey GR, Reginato AM (2009).
922:
698:Abhishek A, Doherty M (2016).
542:
119:swelling of one or more joints
1:
1587:Juvenile idiopathic arthritis
1001:Dieppe P, Swan A (May 1999).
608:
350:peptides are in development.
1061:Nature Reviews. Rheumatology
884:Osteoarthritis and Cartilage
780:Current Rheumatology Reports
321:
205:
7:
1694:Crystal deposition diseases
1616:Adult-onset Still's disease
1553:Connective tissue disorders
943:"calcinosis_cutis_2_060122"
509:conditions to do so are met
10:
1710:
897:10.1016/j.joca.2016.01.136
371:
71:crystal deposition disease
1689:Musculoskeletal disorders
1628:
1579:
1551:
1518:
1489:
1466:
1457:
1436:
1405:
1321:
1219:
1138:10.3390/molecules26195777
792:10.1007/s11926-011-0230-6
603:Pyrophosphate arthropathy
583:monosodium urate crystals
105:attack (thus the moniker
79:pyrophosphate arthropathy
43:
34:
26:
21:
1543:Enteropathic arthropathy
1183:. Waltham, MA: UpToDate.
306:shape and weak positive
167:
153:may be a known trigger.
1199:. Oxford. p. 841.
1074:10.1038/nrrheum.2011.50
977:Rheumatology Image Bank
164:count is often raised.
1611:Palindromic rheumatism
1538:Ankylosing spondylitis
1481:Tuberculosis arthritis
288:
276:
251:ankylosing spondylitis
225:
184:adenosine triphosphate
179:
128:feeling of malaise or
59:
710:(4 Suppl 98): 32–38.
642:10.1136/ard.56.10.586
282:
263:
216:
177:Calcium pyrophosphate
175:
87:calcium pyrophosphate
57:
1599:Rheumatoid arthritis
1019:10.1136/ard.58.5.261
400:improve this article
1533:Psoriatic arthritis
496:of this section is
316:epiphenomenological
269:intervertebral disc
1566:systemic sclerosis
1528:Reactive arthritis
1399:Diseases of joints
1322:External resources
953:on 5 February 2007
340:hydroxychloroquine
289:
277:
226:
180:
109:). These include:
97:Signs and symptoms
60:
1666:
1665:
1624:
1623:
1499:Chondrocalcinosis
1365:
1364:
1206:978-0-19-856837-7
587:Chondrocalcinosis
537:
536:
529:
476:
475:
468:
450:
363:chondrocalcinosis
246:chondrocalcinosis
222:chondrocalcinosis
52:
51:
16:Medical condition
1701:
1651:Bouchard's nodes
1604:Felty's syndrome
1476:Septic arthritis
1464:
1463:
1392:
1385:
1378:
1369:
1368:
1217:
1216:
1211:
1210:
1192:
1186:
1184:
1170:
1161:
1160:
1150:
1140:
1116:
1110:
1109:
1093:
1087:
1086:
1076:
1052:
1041:
1040:
1030:
998:
989:
988:
986:
984:
969:
963:
962:
960:
958:
949:. Archived from
938:
932:
926:
920:
919:
909:
899:
875:
866:
865:
855:
831:
825:
821:
812:
811:
775:
764:
763:
751:
720:
719:
695:
686:
685:
677:
664:
663:
653:
621:
565:. Accordingly,
532:
525:
521:
518:
512:
486:
485:
478:
471:
464:
460:
457:
451:
449:
408:
384:
376:
162:white blood cell
73:, also known as
39:
19:
18:
1709:
1708:
1704:
1703:
1702:
1700:
1699:
1698:
1669:
1668:
1667:
1662:
1646:Heberden's node
1629:Noninflammatory
1620:
1575:
1547:
1514:
1485:
1453:
1449:Joint stiffness
1432:
1401:
1396:
1366:
1361:
1360:
1317:
1316:
1228:
1214:
1207:
1193:
1189:
1171:
1164:
1117:
1113:
1094:
1090:
1053:
1044:
999:
992:
982:
980:
971:
970:
966:
956:
954:
939:
935:
927:
923:
876:
869:
832:
828:
824:2011;70(4):563.
822:
815:
776:
767:
752:
723:
696:
689:
678:
667:
636:(10): 586–588.
622:
615:
611:
545:
533:
522:
516:
513:
502:
487:
483:
472:
461:
455:
452:
409:
407:
397:
385:
374:
356:
324:
220:of a knee with
208:
170:
99:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1707:
1697:
1696:
1691:
1686:
1681:
1664:
1663:
1661:
1660:
1659:
1658:
1653:
1648:
1641:Osteoarthritis
1638:
1632:
1630:
1626:
1625:
1622:
1621:
1619:
1618:
1613:
1608:
1607:
1606:
1596:
1595:
1594:
1583:
1581:
1577:
1576:
1574:
1573:
1568:
1563:
1557:
1555:
1549:
1548:
1546:
1545:
1540:
1535:
1530:
1524:
1522:
1516:
1515:
1513:
1512:
1507:
1501:
1495:
1493:
1487:
1486:
1484:
1483:
1478:
1472:
1470:
1461:
1455:
1454:
1452:
1451:
1446:
1440:
1438:
1434:
1433:
1431:
1430:
1425:
1423:Oligoarthritis
1420:
1415:
1409:
1407:
1403:
1402:
1395:
1394:
1387:
1380:
1372:
1363:
1362:
1359:
1358:
1338:
1326:
1325:
1323:
1319:
1318:
1315:
1314:
1303:
1292:
1278:
1264:
1245:
1229:
1224:
1223:
1221:
1220:Classification
1213:
1212:
1205:
1187:
1162:
1111:
1088:
1067:(5): 257–258.
1042:
1013:(5): 261–263.
990:
964:
933:
930:ShoulderUS.com
921:
890:(6): 973–981.
867:
846:(3): 692–697.
826:
813:
786:(2): 155–160.
765:
721:
687:
665:
612:
610:
607:
599:osteoarthritis
595:fibrocartilage
544:
541:
535:
534:
490:
488:
481:
474:
473:
388:
386:
379:
373:
370:
355:
352:
323:
320:
292:Arthrocentesis
207:
204:
169:
166:
158:osteoarthritis
143:
142:
139:
136:
133:
132:-like symptoms
126:
123:
122:severe fatigue
120:
117:
114:
98:
95:
50:
49:
41:
40:
32:
31:
28:
24:
23:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1706:
1695:
1692:
1690:
1687:
1685:
1682:
1680:
1677:
1676:
1674:
1657:
1654:
1652:
1649:
1647:
1644:
1643:
1642:
1639:
1637:
1634:
1633:
1631:
1627:
1617:
1614:
1612:
1609:
1605:
1602:
1601:
1600:
1597:
1593:
1590:
1589:
1588:
1585:
1584:
1582:
1578:
1572:
1569:
1567:
1564:
1562:
1559:
1558:
1556:
1554:
1550:
1544:
1541:
1539:
1536:
1534:
1531:
1529:
1526:
1525:
1523:
1521:
1517:
1511:
1508:
1505:
1502:
1500:
1497:
1496:
1494:
1492:
1488:
1482:
1479:
1477:
1474:
1473:
1471:
1469:
1465:
1462:
1460:
1456:
1450:
1447:
1445:
1442:
1441:
1439:
1435:
1429:
1428:Polyarthritis
1426:
1424:
1421:
1419:
1418:Monoarthritis
1416:
1414:
1411:
1410:
1408:
1404:
1400:
1393:
1388:
1386:
1381:
1379:
1374:
1373:
1370:
1357:
1354:
1351:
1348:
1344:
1343:
1339:
1337:
1333:
1332:
1328:
1327:
1324:
1320:
1313:
1309:
1308:
1304:
1302:
1298:
1297:
1293:
1291:
1288:
1284:
1283:
1279:
1274:
1273:
1269:
1265:
1263:
1259:
1255:
1254:
1250:
1246:
1244:
1240:
1239:
1235:
1231:
1230:
1227:
1222:
1218:
1208:
1202:
1198:
1191:
1182:
1181:
1176:
1169:
1167:
1158:
1154:
1149:
1144:
1139:
1134:
1130:
1126:
1122:
1115:
1107:
1103:
1099:
1092:
1084:
1080:
1075:
1070:
1066:
1062:
1058:
1051:
1049:
1047:
1038:
1034:
1029:
1024:
1020:
1016:
1012:
1008:
1004:
997:
995:
978:
974:
968:
952:
948:
944:
937:
931:
925:
917:
913:
908:
907:11392/2365664
903:
898:
893:
889:
885:
881:
874:
872:
863:
859:
854:
849:
845:
841:
837:
830:
820:
818:
809:
805:
801:
797:
793:
789:
785:
781:
774:
772:
770:
761:
757:
750:
748:
746:
744:
742:
740:
738:
736:
734:
732:
730:
728:
726:
717:
713:
709:
705:
701:
694:
692:
683:
676:
674:
672:
670:
661:
657:
652:
647:
643:
639:
635:
631:
627:
620:
618:
613:
606:
604:
600:
596:
592:
588:
584:
580:
576:
572:
568:
564:
560:
556:
552:
549:
540:
531:
528:
520:
510:
506:
500:
499:
495:
489:
480:
479:
470:
467:
459:
448:
445:
441:
438:
434:
431:
427:
424:
420:
417: –
416:
412:
411:Find sources:
405:
401:
395:
394:
389:This section
387:
383:
378:
377:
369:
366:
364:
359:
351:
347:
345:
341:
337:
333:
329:
319:
317:
312:
309:
308:birefringence
305:
301:
297:
296:H&E stain
293:
286:
281:
274:
273:H&E stain
270:
266:
262:
258:
256:
252:
247:
243:
239:
235:
231:
223:
219:
215:
211:
203:
200:
198:
193:
191:
187:
185:
178:
174:
165:
163:
159:
154:
150:
147:
140:
137:
134:
131:
127:
124:
121:
118:
115:
112:
111:
110:
108:
104:
94:
92:
88:
84:
83:rheumatologic
80:
76:
72:
68:
64:
56:
47:
46:birefringence
42:
38:
33:
29:
25:
20:
1636:Hemarthrosis
1520:Seronegative
1506:(Pseudogout)
1503:
1459:Inflammatory
1353:orthoped/382
1340:
1329:
1305:
1294:
1280:
1266:
1247:
1232:
1196:
1190:
1178:
1131:(19): 5777.
1128:
1124:
1114:
1105:
1101:
1091:
1064:
1060:
1010:
1006:
981:. Retrieved
976:
967:
955:. Retrieved
951:the original
946:
936:
924:
887:
883:
843:
839:
829:
783:
779:
759:
707:
703:
633:
629:
602:
570:
566:
546:
538:
523:
517:October 2023
514:
492:
462:
456:October 2023
453:
443:
436:
429:
422:
410:
398:Please help
393:verification
390:
367:
360:
357:
354:Epidemiology
348:
344:methotrexate
325:
313:
290:
227:
209:
201:
194:
188:
181:
155:
151:
148:
144:
106:
100:
78:
74:
70:
66:
62:
61:
1331:MedlinePlus
563:terminology
543:Terminology
244:may detect
113:severe pain
27:Other names
1673:Categories
1656:Osteophyte
1468:Infectious
1444:Joint pain
1307:DiseasesDB
947:Derm Atlas
941:Hosler G.
609:References
571:pseudogout
494:neutrality
426:newspapers
336:colchicine
300:basophilic
265:Micrograph
242:ultrasound
107:pseudogout
91:knee joint
75:pseudogout
30:Pseudogout
1679:Arthritis
1571:Sjögren's
1413:Arthritis
1356:emerg/221
1350:radio/125
1342:eMedicine
1125:Molecules
575:synovitis
555:syndromes
505:talk page
322:Treatment
285:condenser
206:Diagnosis
195:The gene
1437:Symptoms
1347:med/1938
1180:UpToDate
1157:34641321
1083:21532639
1037:10225806
983:13 March
957:13 March
916:26826301
808:41336263
800:22198832
760:Medscape
716:27586801
559:symptoms
551:crystals
498:disputed
304:rhomboid
190:Familial
1491:Crystal
1406:General
1301:D002805
1148:8510196
1028:1752883
862:7887424
853:1801178
660:9389218
651:1752269
593:and/or
591:hyaline
440:scholar
372:History
160:. The
141:burning
81:, is a
1336:000421
1290:118600
1287:600668
1243:FA26.0
1203:
1155:
1145:
1081:
1035:
1025:
914:
860:
850:
806:
798:
714:
658:
648:
442:
435:
428:
421:
413:
116:warmth
1580:Other
1312:10832
1262:M11.2
1258:M11.1
1108:(10).
804:S2CID
579:gouty
447:JSTOR
433:books
328:acute
240:, or
230:x-ray
218:X-ray
168:Cause
125:fever
1510:Gout
1504:CPPD
1296:MeSH
1282:OMIM
1272:9-CM
1201:ISBN
1153:PMID
1079:PMID
1033:PMID
985:2012
959:2012
912:PMID
858:PMID
796:PMID
712:PMID
656:PMID
491:The
419:news
255:gout
253:and
197:ANKH
103:gout
77:and
67:CPPD
1561:SLE
1268:ICD
1249:ICD
1234:ICD
1143:PMC
1133:doi
1069:doi
1023:PMC
1015:doi
902:hdl
892:doi
848:PMC
788:doi
646:PMC
638:doi
402:by
342:or
238:MRI
130:flu
1675::
1345::
1334::
1310::
1299::
1285::
1275::
1260:,
1256::
1253:10
1241::
1238:11
1177:.
1165:^
1151:.
1141:.
1129:26
1127:.
1123:.
1106:26
1104:.
1100:.
1077:.
1063:.
1059:.
1045:^
1031:.
1021:.
1011:58
1009:.
1005:.
993:^
975:.
945:.
910:.
900:.
888:24
886:.
882:.
870:^
856:.
844:56
842:.
838:.
816:^
802:.
794:.
784:14
782:.
768:^
758:.
724:^
708:34
706:.
702:.
690:^
668:^
654:.
644:.
634:56
632:.
628:.
616:^
318:.
271:.
257:.
236:,
234:CT
232:,
69:)
1391:e
1384:t
1377:v
1277:]
1270:-
1251:-
1236:-
1226:D
1209:.
1159:.
1135::
1085:.
1071::
1065:7
1039:.
1017::
987:.
961:.
918:.
904::
894::
864:.
810:.
790::
762:.
718:.
684:.
662:.
640::
530:)
524:(
519:)
515:(
511:.
501:.
469:)
463:(
458:)
454:(
444:·
437:·
430:·
423:·
396:.
287:.
275:.
224:.
65:(
48:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.