684:
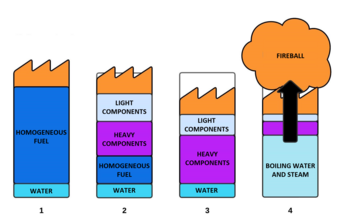
164:, is formed, which becomes progressively richer in higher-boiling-point species. Its temperature, as well as thickness, progressively increase. Its lower boundary moves downwards towards the fuel–water interface at a speed higher than the overall level of fuel decreases due to the fire burning it. As a result, when the hot zone reaches the water layer, a considerable amount of unburnt fuel may still be present above the water. Upon the water contacting the hot zone, some steam forms. The resulting turbulence promotes mixing of the water into the hot fuel. This can result in rapid water vaporization. The violent expansion of the steam bubbles will push out a significant part of the fuel above it, causing a violent overflow of flaming liquid. In these conditions water may be
541:
89:
2139:
675:. In the context of boilovers and slopovers, the fuel is generally lighter than water. At industrial scale, this means that water applied to an open-top tank fire will sink to the bottom of the tank, which can cause boilover at a later stage. At small/domestic scale, assuming the water can find its way down through the fuel, use of water may cause the content of the vessel to spill over and spread the fire. If water does not sink efficiently to the bottom, then a violent slopover may occur. This makes water both inefficient as an extinguishing agent and potentially very hazardous.
449:, often hundreds of meters or in the order of ten tank diameters downwind. Bunding, however, remains an important measure to reduce fire spread. Moreover, since boilover inception is sometimes unpredictable —either in terms of time to onset or whether it will occur at all (because the presence of water in the tank bottom may not be a known factor)— the impact on the firefighters that have intervened to control the fire can be deadly. In some cases, simple bystanders were caught in the blaze and perished.
606:
456:. Failure to appreciate the hazards posed by a water layer underneath the fuel has been a significant contributing cause to the aftermath of boilover accidents, in terms of human and material losses. Uncertainty surrounding the time to boilover onset adds unpredictability that further complicates the efforts of the firefighting services. Mathematical models for boilover have been developed that predict the time necessary for boilover to initiate, among other things.
2808:
586:
1526:, p. 102. "A boil-over is an entirely different phenomenon from a slopover or froth-over. Slop-over involves a minor frothing that occurs when water is sprayed onto the hot surface of a burning oil. Froth-over is not associated with a fire but results when water is present or enters a tank containing hot viscous oil. Upon mixing, the sudden conversion of water to steam causes a portion of the tank contents to overflow."
2820:
1916:
185:
water and the fact that the hot zone composition is different from that of the initial fuel have to be considered. In general, boilover is possible if the fuel mean boiling point (calculated as a geometric mean of its lower and upper boiling points, i.e. the temperatures at which the mixture, respectively, starts to boil and is completely vaporized) is higher than 120 °C (248 °F):
743:
has also been proposed. However, uncertainty regarding the presence and depth of a water or a water–fuel emulsion layer remains, and unpredictability about boilover onset cannot be completely dispelled. Draining the product from the tank may reduce accidental consequences, because less fluid would be
726:
from the distillation curve and the properties of the fuel, with the aid of mathematical formulas, including the ones given above. However, this approach requires knowledge of the depth of the water layer at the bottom of the tank. Further, it does not consider the potential for a layer of water–fuel
718:
during a boilover is considerably higher than during the pool fire that precedes it. Although the event is short-lived, emergency response activities, for which tenable levels of thermal radiations are typically 6.3 kW/m, cannot be safely accomplished, so operations should take place from a safe
444:
The hazards posed by a hot-zone boilover are significant for several reasons. At industrial scale, hydrocarbon tanks can contain up to hundreds of thousands of barrels of fluid. If a boilover occurs, the amount of blazing liquid erupting from the tank can therefore be huge. Ejected blazing fluids can
100:, which is by a factor of 1500 or more. In practical storage scenarios, the presence of water under the burning fluid is sometimes due to spurious accumulation during plant operation (e.g., rainwater entering a seam in the tank roof, off-specification products from the source, residual water from an
622:
is a phenomenon similar to boilover, although distinct from it. It occurs when water is poured onto the fuel while a pool fire is occurring. If the fire is small enough, the water that instantly boils in contact with the fire or with the lower layers of blazing liquid (which are themselves not on
483:
oil refinery, Poland – A 33-meter (108 ft)-diameter crude oil tank was hit by lightning, which caused a roof collapse and an open-top tank fire. After extended firefighting and a decrease in the fire intensity, boilover occurred, spewing flaming liquids up to 250 meters (820 ft) away. A
184:
Since the upper fuel layers, including the hot zone, are at or near their boiling temperature, it is necessary for the boiling point of the fuel to be high enough, such that the hot zone temperature is higher than the water boiling temperature. Both the effect of the static head of fuel above the
712:. However, it is not clear if these rates are adequate to minimize the potential for a boilover event, especially in cases where foam attack is initiated long after the inception of the tank fire. It has been suggested that foam firefighting should be started within 2–4 hours from ignition.
564:
In a thin-layer boilover, the size of the flames increases upon boilover onset, and a characteristic crackling sound is produced. However, due to the little amount of fuel left, this phenomenon is far less hazardous than a standard boilover. The study of thin-layer boilover is of interest in the
423:
must be sufficiently high to oppose the upwards movement of the steam bubbles. Otherwise, these may flow through the fuel without projecting it out of the blazing tank. Low viscosity may also make it difficult for a stable heavy-components hot zone to form, thanks to more efficient
176:
of steam. When this happens, the abruptness of the expansion further enhances the expulsion of blazing fuel. Typical hot-zone speeds are 0.3–0.5 meters per hour (1.0–1.7 ft/h), although speeds of up to 1.2 meters per hour (4.0 ft/h) have been recorded.
75:
are phenomena similar to boilover but distinct from it. A slopover occurs when pouring water over a liquid pool fire, which may result in sudden expulsion of blazing fluid as well as considerable flame growth if the fire is small, as is the case when dousing water over a
37:
fire) starts boiling, which results in a significant increase in fire intensity accompanied by violent expulsion of burning fluid to the surrounding areas. Boilover can only occur if the liquid fluid is a mixture of different chemical species with sufficiently diverse
1812:
626:
In industrial-scale tank fires, there is no noticeable effect when water is doused on the fire, although water sinking to the bottom of the tank may contribute to a later boilover. However, at smaller scale, slopovers pose significant hazards. Trying to extinguish a
274:
376:
64:
Boilovers at industrial scale are rare but can lead to serious plant damage. Given the sudden and not easily predictable onset of the phenomenon, fatalities can occur, especially among firefighters and bystanders that have not been made to leave the area.
559:
When, regardless of the thickness of the fuel layer, distillation does not occur and a heat wave is not formed. In such a situation, for a boilover to occur, the fuel has to burn down until its warmer top layer reaches the fuel–water
808:, p. 17. " an event in the burning of certain oils in an open-top tank when, after a long period of quiescent burning, there is a sudden increase in fire intensity associated with expulsion of burning oil from the tank."
1045:
108:
condensation) or as a consequence of attempts to extinguish the fire with water. A typical scenario for a tank fire that may eventually result in boilover is an initial confined explosion blowing off the tank roof.
188:
299:
476:, The Netherlands – Water emulsion and hot crude oil mixed and produced frothing, vapor release and boilover. The fire spread thirty acres (120,000 m), destroying several refinery units and 80 tanks.
415:
518:
occurred at a crude storage tank. Filled with more than 46,000 tons of oil, the flaming storage tank experienced multiple boilovers, spreading the fire into the four-acre (16,000 m)
80:. A frothover is a situation occurring when there is a layer of water under a layer of a viscous fuel that, although not on fire, is at higher temperature than the boiling point of water.
701:, intertank distances would have to exceed five tank diameters in order to prevent escalation to adjacent tanks. In most cases, it is not feasible to design for such an arrangement.
1401:
856:
611:
A demonstration of chip pan fire slopover: Oil is heated and ignites, a small amount of water is poured on the fire and a violent plume of flames rises to the room ceiling.
2655:
655:
occurs when a water layer is present under a layer of a viscous oil that is not on fire and whose temperature is higher than the water boiling point. An example is hot
1247:
1001:
440:) pool fires have shown that boilover does not occur. In general, fuel dynamic viscosity has to be higher at least 0.73 cSt, which is the viscosity of kerosene.
691:
Hot-zone boilovers of large tanks are relatively rare events. However, they can be extremely disruptive. Therefore, prevention and control are very important.
556:
When the fuel layer is thin, such as in the case of spillage on a wet surface. In this case the boilover onset time is very short, typically about one minute.
663:
containing some water. Although nothing may happen at first, water may eventually superheat and later start to boil violently, resulting in overflow.
2450:
1596:
381:
1594:
Chan, Eric S.Y.; Chan, Edmund C.K.; Ho, W.S.; King, Walter W.K. (November–December 1997). "Boiling Wax Burn in Mid-autumn
Festival in Hong Kong".
1685:
1884:
499:
more than 150 people, including journalists and bystanders not involved in fighting the fire, died when a massive boilover developed from a
2643:
452:
Tank fires that appear to be relatively stable may burst into massive boilovers several hours after the fire starts, as it occurred in the
1805:
683:
2258:
1390:
1239:
445:
travel at speeds up to 32 kilometres per hour (20 mph) and attain distances well in excess of the limits of secondary containment
849:
1948:
1862:
993:
1976:
1539:
Frank, John A. (2008). "Characteristics and
Hazards of Water and Water Additives for Fire Suppression". In Cote, Arthur E. (ed.).
722:
Some approaches are available to assess the probability of and the proximity to boilover in tank fires. An estimation can be made
2622:
1767:
278:
As mentioned above, the composition of the fuel mixture must be sufficiently varied. It has been observed that the gap between
1716:
1552:
1130:
2667:
2661:
1836:
1828:
1742:
1544:
1122:
116:
are not liable to boilover. In order for one to occur, the material must be a mixture of species with sufficiently diverse
1844:
631:
or cooking oil fire with water, for example, causes slopover, which can harm people and spread the fire in the kitchen.
180:
Apart from the presence of a water layer under the fuel, other conditions must be met for a hot-zone boilover to occur:
2163:
1043:
Broeckmann, Bernd; Schecker, Hans-Georg (1995). "Heat
Transfer Mechanisms and Boilover in Burning Oil–Water Systems".
2538:
1870:
1783:
1693:
1252:
1006:
964:
932:
269:{\displaystyle {\bar {T}}_{\text{boil}}={{({T}_{\text{boil,min}}\ {T}_{\text{boil,max}})}^{0.5}}>{\text{120 °C}}}
2823:
735:
applied to the tank walls, or applying a water jet to the walls to assess at what height it starts boiling. Use of
1753:
371:{\displaystyle {{T}_{\text{boil,max}}-\max {({T}_{\text{boil,min}},{{T}_{\text{boil,water}}})}}>{\text{60 °C}}}
2299:
1987:
1920:
623:
fire but may be hotter than the water boiling point) can extend the flames, especially in the upwards direction.
526:
were needed to tackle the blaze. While six firefighters were injured during the two-day fire, no one was killed.
378:
Some sources indicate that the upper range of the boiling temperature has to be above 149 °C (300 °F):
1731:
EI Model Code of Safe
Practice Part 19: Fire Precautions at Petroleum Refineries and Bulk Storage Installations
1568:
2851:
2649:
2606:
2278:
1941:
2767:
2720:
2558:
1307:
1299:
1159:
1151:
835:
827:
296:
and the boiling point of water at the fuel–water interface has to be higher than 60 °C (108 °F):
2591:
2523:
2340:
2173:
515:
731:
being present above the water. Progression of the hot zone can be monitored by using vertical strips of
2158:
2098:
2673:
2508:
2168:
141:
1471:
2811:
2617:
2533:
2513:
2490:
2253:
2018:
1934:
1855:
152:
process takes place in the fuel. Separation of light components from heavier ones occurs thanks to
2856:
2460:
2425:
2273:
2223:
1156:
Interim Study: Prevention and
Suppression of Fires in Large Aboveground Atmospheric Storage Tanks
1391:"Boilover of a Crude Oil Tank – 30 August 1983 – Milford Haven [Wales] – United Kingdom"
773:
Where the fuel layer is thick and distillation does occur, the phenomenon may be referred to as
540:
2846:
2601:
2480:
2455:
2445:
2153:
2113:
523:
132:, are examples of such materials. The fact that these are stored in large atmospheric tanks in
1323:"An Inverse Stefan Problem Relevant to Boilover: Heat Balance Integral Solutions and Analysis"
744:
subject to boilover. However, pumping out product may also reduce the time to boilover onset.
464:
The following are some notable accidents in which a standard, or hot-zone, boilover occurred:
88:
2788:
2762:
2715:
2330:
2218:
2198:
1117:
Slye, Jr., Orville M. (2008). "Flammable and
Combustible Liquids". In Cote, Arthur E. (ed.).
488:
1264:
694:
Boilover can be prevented by regularly checking for and draining water in the tank bottoms.
2485:
2345:
2053:
736:
480:
566:
484:
nearby tank exploded due to ignition of flammable vapors inside. Thirty-three people died.
425:
8:
2528:
2435:
1899:
1018:
956:
636:
492:
473:
101:
2315:
2243:
2208:
2203:
2058:
1613:
1336:
1062:
832:
Fighting Fires in and Around
Flammable and Combustible Liquid Atmospheric Storage Tanks
698:
433:
1609:
2741:
2736:
2731:
2627:
2518:
2500:
2390:
2228:
2138:
2123:
1876:
1866:
1840:
1779:
1738:
1712:
1689:
1676:
Casal, Joaquim; Montiel, Helena; Planas, Eulàlia; Vílchez, Juan A. (September 1999).
1629:
1621:
1548:
1256:
1126:
1070:
1058:
1010:
960:
928:
753:
715:
705:
169:
165:
49:– a far less hazardous phenomenon – can arise from any water-immiscible liquid fuel.
994:"C.A. La Electricidad de Caracas, December 19, 1982, Fire (Near) Caracas, Venezuela"
2725:
2063:
1771:
1734:
1726:
1605:
1489:
1346:
1054:
920:
656:
113:
1705:
Evaluation of the
Effects and Consequences of Major Accidents in Industrial Plants
96:
The extreme violence of boilovers is due to the expansion of water from liquid to
2420:
2355:
2294:
2263:
2238:
2188:
2183:
1997:
1957:
1811:(Report). Omega 13 Report no. DRA-15-111777-00792A. Verneuil-en-Halatte, France:
1480:
1327:
709:
1764:
Hydrocarbon Fires: A Study on the
Formation and Evolution of Thin Layer Boilover
522:. However, the fire did not propagate further. In all, 150 firefighters and 120
77:
2586:
2563:
2548:
2410:
2350:
2320:
2289:
2233:
2193:
2128:
2118:
2013:
496:
453:
145:
2840:
2793:
2783:
2581:
2553:
2470:
2088:
2078:
2048:
1992:
1880:
1625:
1617:
1260:
1074:
1066:
1014:
511:
117:
39:
2710:
2596:
2475:
2465:
2400:
2365:
2325:
2284:
2248:
2038:
2033:
2003:
1185:
1183:
1181:
1088:
1086:
1084:
948:
672:
591:
Firefighters demonstrating slopover. Length of the sequence: 2.4 seconds. 1
437:
149:
137:
34:
1633:
924:
879:
877:
2430:
2385:
2375:
2268:
2213:
2178:
2073:
1494:
1475:
1351:
1322:
732:
632:
605:
58:
29:) is an extremely hazardous phenomenon in which a layer of water under a
1502:
1178:
1081:
850:
LASTFIRE Boilover
Research: Position Paper and Practical Lessons Learned
2690:
2543:
2043:
2028:
2008:
1813:
Institut national de l'environnement industriel et des risques (INERIS)
874:
173:
153:
129:
1775:
2612:
2440:
2405:
2395:
2380:
2360:
2335:
2108:
2103:
2068:
2023:
1971:
916:
911:
Biswas, Samarendra Kumar; Mathur, Umesh; Hazra, Swapan Kumar (2021).
740:
469:
420:
121:
50:
30:
1755:
Incendios de hidrocarburos: estudio de la formación y evolución del
2705:
2415:
2370:
2093:
2083:
1789:
1708:
1240:"Case Study: Revisiting the Tacoa Power Plant Boilover 40 Years On"
728:
660:
628:
585:
500:
429:
133:
125:
105:
54:
1926:
1341:
1306:. API Recommended Practice 2021 (4th ed.). Washington, D.C.:
1469:
519:
446:
1915:
1371:
1359:
640:
643:
and pouring water on it for entertainment has become a habit.
2746:
2700:
507:
97:
2695:
2656:
National Council of Examiners for Engineering and Surveying
1470:
Garo, Jean-Pierre; Koseki, Hiroshi; Vantelon, Jean-Pierre;
16:
Expulsion of blazing liquid due to water boiling underneath
1398:
Analyse, Recherche et Information sur les Accidents (ARIA)
410:{\displaystyle {{T}_{\text{boil,max}}}>{\text{149 °C}}}
1675:
1508:
1189:
1092:
883:
834:. API Publication 2021 (3rd ed.). Washington, D.C.:
1543:. FPH2008. Vol. II (20th ed.). Quincy, Mass.:
503:
tank. It is the worst tank fire ever occurred worldwide.
1441:
1439:
1437:
1279:
1277:
1166:
1121:. FPH2008. Vol. I (20th ed.). Quincy, Mass.:
144:, etc. makes boilover a hazard of interest in terms of
1519:
1517:
894:
892:
1640:
1424:
1422:
384:
302:
191:
156:
fluid motion. An intermediate fuel layer, called the
1434:
1274:
1098:
1046:
Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries
1766:] (PhD thesis) (in Spanish). Barcelona, Spain:
1514:
1451:
1206:
1204:
1202:
1200:
1198:
973:
889:
704:Open-top crude oil tank fires can be tackled using
1707:. Amsterdam, The Netherlands and Oxford, England:
1419:
1042:
409:
370:
268:
124:and some commercial hydrocarbon mixtures, such as
2451:Penetrant (mechanical, electrical, or structural)
1853:
1678:Análisis del riesgo en instalaciones industriales
1652:
1377:
1365:
910:
799:
678:
2838:
1216:
1195:
671:Water is generally unsuitable for extinguishing
319:
61:are examples of fuels giving rise to boilover.
1856:Tank Fires: Review of Fire Incidents 1951–2003
1593:
1476:"Combustion of Liquid Fuels Floating on Water"
785:, to avoid confusion with thin-layer boilover.
1942:
1863:SP Sveriges Provnings- och Forskningsinstitut
1861:(Report). SP Rapport 2004:14. Borås, Sweden:
1569:"What to Do in the Event of a Chip Pan Fire"
1304:Management of Atmospheric Storage Tank Fires
1854:Persson, Henry; Lönnermark, Anders (2004).
1806:Standard Boil-over and Thin Layer Boil-over
1545:National Fire Protection Association (NFPA)
1158:. API Publication 2021A. Washington, D.C.:
1123:National Fire Protection Association (NFPA)
2259:Hypoxic air technology for fire prevention
1949:
1935:
1835:. NFPA 30 (2018 ed.). Quincy, Mass.:
1253:Institution of Chemical Engineers (IChemE)
1007:Institution of Chemical Engineers (IChemE)
913:Fundamentals of Process Safety Engineering
168:, in which case part of it goes through a
2644:Fire Equipment Manufacturers' Association
1493:
1350:
1340:
1116:
756:, a similar concept in volcanic eruption.
1977:Boiling liquid expanding vapor explosion
991:
955:(3rd ed.). Washington, D.C., etc.:
682:
539:
87:
2623:Listing and approval use and compliance
1751:
1457:
1320:
1237:
979:
2839:
1833:Flammable and Combustible Liquids Code
1804:
1684:] (in Spanish). Barcelona, Spain:
1682:Risk Analysis in Industrial Facilities
1428:
1233:
1231:
1172:
535:
2668:Society of Fire Protection Engineers
1930:
1702:
1538:
1534:
1532:
1445:
1294:
1292:
1283:
1146:
1144:
1142:
1104:
953:Dispelling Chemical Engineering Myths
898:
2819:
2662:National Fire Protection Association
1837:National Fire Protection Association
1827:
1768:Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya
1523:
862:from the original on 19 October 2021
822:
820:
818:
816:
814:
805:
760:
530:
459:
1956:
1407:from the original on 6 October 2021
1298:
1228:
1150:
855:(Report). LASTFIRE. December 2016.
826:
544:Thin-layer boilover onset mechanism
13:
2164:Condensed aerosol fire suppression
1725:
1658:
1646:
1529:
1463:
1289:
1222:
1210:
1139:
666:
487:19 December 1982, Ricardo Zuloaga
14:
2868:
2539:Fire alarm notification appliance
1908:
1733:(3rd ed.). London, England:
947:
811:
552:occurs in one of two situations:
2818:
2807:
2806:
2137:
1914:
604:
584:
2300:Vehicle fire suppression system
1988:Combustibility and flammability
1890:from the original on 6 May 2023
1587:
1561:
1383:
1378:Persson & Lönnermark (2004)
1366:Persson & Lönnermark (2004)
1314:
1110:
1036:
767:
985:
941:
904:
842:
679:Industrial-scale storage sites
355:
323:
247:
217:
199:
1:
2650:Institution of Fire Engineers
2607:Fire Safety Evaluation System
2279:Personal protective equipment
1610:10.1016/S0305-4179(97)00074-0
992:Garrison, William W. (1984).
792:
287:and the higher value between
2721:GHS precautionary statements
2559:Manual fire alarm activation
1308:American Petroleum Institute
1160:American Petroleum Institute
1059:10.1016/0950-4230(95)00016-T
836:American Petroleum Institute
646:
639:celebrations, where boiling
7:
2592:Fire protection engineering
2524:Explosive gas leak detector
2341:Electromagnetic door holder
2174:External water spray system
747:
575:
83:
10:
2873:
2768:Harry C. Bigglestone Award
2159:Automatic fire suppression
2099:K-factor (fire protection)
1668:
915:. Boca Raton, Fla., etc.:
635:have also occurred during
2802:
2776:
2755:
2683:
2674:Underwriters Laboratories
2636:
2572:
2509:Aspirating smoke detector
2499:
2308:
2169:Detonation flame arrester
2146:
2135:
1964:
2618:Kitchen exhaust cleaning
2534:Fire alarm control panel
2514:Carbon monoxide detector
2491:Standpipe (firefighting)
2254:Gaseous fire suppression
2019:Enthalpy of vaporization
1547:. pp. 17-37–17-38.
1541:Fire Protection Handbook
1321:Hristov, Jordan (2006).
1248:Loss Prevention Bulletin
1119:Fire Protection Handbook
1002:Loss Prevention Bulletin
148:. During a pool fire, a
92:Boilover onset mechanism
2461:Pressurisation ductwork
2426:Firewall (construction)
2274:Passive fire protection
2224:Fire suppression system
1752:Ferrero, Fabio (2006).
1703:Casal, Joaquim (2008).
1472:Fernandez-Pello, Carlos
708:at rates of 10–12
595:kg of cooking oil and 1
428:. Thus, experiments on
42:, although a so-called
2637:Industry organizations
2602:Fire-resistance rating
2481:Smoke exhaust ductwork
2456:Penetration (firestop)
2446:Packing (firestopping)
2154:Active fire protection
2114:Spontaneous combustion
1238:Stewart, Ewan (2023).
688:
633:Serious burn incidents
545:
411:
372:
270:
93:
2789:Template:Firefighting
2763:Arthur B. Guise Medal
2716:GHS hazard statements
2219:Fire sprinkler system
2199:Fire-retardant fabric
925:10.1201/9781003107873
737:thermographic cameras
710:L/(min × m)
686:
570:burning of oil spills
543:
516:An open-top tank fire
495:, Venezuela – In the
412:
373:
271:
91:
2852:Petroleum production
2573:Professions, trades,
2486:Smokeproof enclosure
2346:Electromagnetic lock
2054:Flammability diagram
1965:Fundamental concepts
1923:at Wikimedia Commons
1495:10.2298/TSCI0702119G
1352:10.2298/TSCI0702141H
957:Taylor & Francis
481:Czechowice-Dziedzice
382:
300:
189:
2529:Fire alarm call box
2436:Heat and smoke vent
1649:, pp. 176–177.
1575:. 27 September 2022
1509:Casal et al. (1999)
1190:Casal et al. (1999)
1093:Casal et al. (1999)
884:Casal et al. (1999)
687:Tanks in a refinery
637:Mid-autumn Festival
550:thin-layer boilover
536:Thin-layer boilover
489:thermal power plant
33:(e.g., an open-top
2501:Fire alarm systems
2316:Annulus (firestop)
2244:Flashback arrestor
2209:Fire-safe polymers
2204:Fire retardant gel
2059:Flammability limit
1302:(September 2015).
1009:. pp. 26–30.
959:. pp. 96–97.
689:
546:
426:natural convection
407:
368:
266:
94:
2834:
2833:
2742:Safety data sheet
2737:List of S-phrases
2732:List of R-phrases
2628:Sprinkler fitting
2519:Circuit integrity
2391:Fire extinguisher
2229:Firefighting foam
2124:Thermal radiation
1919:Media related to
1815:. 22 January 2015
1729:(November 2012).
1718:978-0-444-53081-3
1554:978-0-87765-758-3
1400:. ARIA no. 6077.
1175:, pp. 16–17.
1132:978-0-87765-758-3
1125:. p. 6-206.
761:Explanatory notes
754:Phreatic eruption
733:intumescent paint
716:Thermal radiation
706:firefighting foam
531:Related phenomena
468:20 January 1968,
460:Notable accidents
434:dynamic viscosity
405:
395:
366:
351:
335:
313:
264:
244:
234:
229:
208:
202:
172:with homogeneous
170:explosive boiling
2864:
2822:
2821:
2810:
2809:
2726:Life Safety Code
2331:Compartmentation
2141:
2064:Flammable liquid
1951:
1944:
1937:
1928:
1927:
1918:
1903:
1897:
1895:
1889:
1860:
1850:
1824:
1822:
1820:
1810:
1801:
1799:
1797:
1788:. Archived from
1748:
1744:978-0-85293-6344
1735:Energy Institute
1722:
1699:
1662:
1656:
1650:
1644:
1638:
1637:
1604:(7–8): 629–630.
1591:
1585:
1584:
1582:
1580:
1565:
1559:
1558:
1536:
1527:
1521:
1512:
1506:
1500:
1499:
1497:
1467:
1461:
1455:
1449:
1443:
1432:
1426:
1417:
1416:
1414:
1412:
1406:
1395:
1387:
1381:
1375:
1369:
1363:
1357:
1356:
1354:
1344:
1318:
1312:
1311:
1296:
1287:
1281:
1272:
1271:
1270:on 22 July 2023.
1269:
1263:. Archived from
1244:
1235:
1226:
1220:
1214:
1208:
1193:
1187:
1176:
1170:
1164:
1163:
1148:
1137:
1136:
1114:
1108:
1102:
1096:
1090:
1079:
1078:
1040:
1034:
1033:
1031:
1029:
1023:
1017:. Archived from
998:
989:
983:
977:
971:
970:
945:
939:
938:
908:
902:
896:
887:
881:
872:
871:
869:
867:
861:
854:
846:
840:
839:
824:
809:
803:
786:
783:classic boilover
771:
608:
598:
594:
588:
520:containment dyke
506:30 August 1983,
416:
414:
413:
408:
406:
403:
398:
397:
396:
393:
391:
377:
375:
374:
369:
367:
364:
359:
358:
354:
353:
352:
349:
347:
337:
336:
333:
331:
315:
314:
311:
309:
295:
286:
275:
273:
272:
267:
265:
262:
257:
256:
255:
250:
246:
245:
242:
240:
232:
231:
230:
227:
225:
210:
209:
206:
204:
203:
195:
114:chemical species
2872:
2871:
2867:
2866:
2865:
2863:
2862:
2861:
2837:
2836:
2835:
2830:
2798:
2772:
2751:
2679:
2632:
2574:
2568:
2495:
2421:Firestop pillow
2356:Emergency light
2309:Building design
2304:
2295:Tank blanketing
2264:Inerting system
2239:Flame retardant
2189:Fire protection
2184:Fire prevention
2142:
2133:
1998:Dangerous goods
1960:
1958:Fire protection
1955:
1911:
1906:
1893:
1891:
1887:
1873:
1858:
1847:
1846:978-145591661-0
1818:
1816:
1808:
1795:
1793:
1792:on 9 March 2017
1786:
1745:
1719:
1696:
1671:
1666:
1665:
1657:
1653:
1645:
1641:
1592:
1588:
1578:
1576:
1567:
1566:
1562:
1555:
1537:
1530:
1522:
1515:
1507:
1503:
1481:Thermal Science
1468:
1464:
1456:
1452:
1444:
1435:
1427:
1420:
1410:
1408:
1404:
1393:
1389:
1388:
1384:
1376:
1372:
1364:
1360:
1328:Thermal Science
1319:
1315:
1297:
1290:
1282:
1275:
1267:
1242:
1236:
1229:
1221:
1217:
1209:
1196:
1188:
1179:
1171:
1167:
1149:
1140:
1133:
1115:
1111:
1103:
1099:
1091:
1082:
1041:
1037:
1027:
1025:
1024:on 22 July 2023
1021:
1005:. No. 57.
996:
990:
986:
978:
974:
967:
946:
942:
935:
909:
905:
897:
890:
882:
875:
865:
863:
859:
852:
848:
847:
843:
825:
812:
804:
800:
795:
790:
789:
772:
768:
763:
750:
681:
669:
667:Fire protection
649:
616:
615:
614:
613:
612:
609:
601:
600:
599:liter of water.
596:
592:
589:
578:
538:
533:
524:fire appliances
462:
402:
392:
387:
386:
385:
383:
380:
379:
363:
348:
343:
342:
341:
332:
327:
326:
322:
310:
305:
304:
303:
301:
298:
297:
294:
288:
285:
279:
261:
251:
241:
236:
235:
226:
221:
220:
216:
215:
214:
205:
194:
193:
192:
190:
187:
186:
86:
17:
12:
11:
5:
2870:
2860:
2859:
2857:Process safety
2854:
2849:
2832:
2831:
2829:
2828:
2816:
2803:
2800:
2799:
2797:
2796:
2791:
2786:
2780:
2778:
2774:
2773:
2771:
2770:
2765:
2759:
2757:
2753:
2752:
2750:
2749:
2744:
2739:
2734:
2729:
2723:
2718:
2713:
2708:
2703:
2698:
2693:
2687:
2685:
2681:
2680:
2678:
2677:
2671:
2665:
2659:
2653:
2647:
2640:
2638:
2634:
2633:
2631:
2630:
2625:
2620:
2615:
2610:
2604:
2599:
2594:
2589:
2587:Fire insurance
2584:
2578:
2576:
2570:
2569:
2567:
2566:
2564:Smoke detector
2561:
2556:
2551:
2549:Flame detector
2546:
2541:
2536:
2531:
2526:
2521:
2516:
2511:
2505:
2503:
2497:
2496:
2494:
2493:
2488:
2483:
2478:
2473:
2468:
2463:
2458:
2453:
2448:
2443:
2438:
2433:
2428:
2423:
2418:
2413:
2411:Fire sprinkler
2408:
2403:
2398:
2393:
2388:
2383:
2378:
2373:
2368:
2363:
2358:
2353:
2351:Emergency exit
2348:
2343:
2338:
2333:
2328:
2323:
2321:Area of refuge
2318:
2312:
2310:
2306:
2305:
2303:
2302:
2297:
2292:
2290:Spark arrestor
2287:
2282:
2276:
2271:
2266:
2261:
2256:
2251:
2246:
2241:
2236:
2234:Flame arrester
2231:
2226:
2221:
2216:
2211:
2206:
2201:
2196:
2194:Fire retardant
2191:
2186:
2181:
2176:
2171:
2166:
2161:
2156:
2150:
2148:
2144:
2143:
2136:
2134:
2132:
2131:
2129:Water pressure
2126:
2121:
2119:Structure fire
2116:
2111:
2106:
2101:
2096:
2091:
2086:
2081:
2076:
2071:
2066:
2061:
2056:
2051:
2046:
2041:
2036:
2031:
2026:
2021:
2016:
2014:Dust explosion
2011:
2006:
2001:
1995:
1990:
1985:
1980:
1974:
1968:
1966:
1962:
1961:
1954:
1953:
1946:
1939:
1931:
1925:
1924:
1921:Chip-pan fires
1910:
1909:External links
1907:
1905:
1904:
1871:
1851:
1845:
1825:
1802:
1784:
1749:
1743:
1723:
1717:
1700:
1694:
1672:
1670:
1667:
1664:
1663:
1661:, p. 179.
1651:
1639:
1586:
1560:
1553:
1528:
1513:
1511:, p. 145.
1501:
1488:(2): 119–140.
1462:
1458:Ferrero (2006)
1450:
1448:, p. 101.
1433:
1418:
1382:
1370:
1358:
1335:(2): 141–160.
1313:
1288:
1286:, p. 102.
1273:
1227:
1215:
1194:
1192:, p. 139.
1177:
1165:
1138:
1131:
1109:
1107:, p. 103.
1097:
1095:, p. 142.
1080:
1053:(3): 137–147.
1035:
984:
980:Ferrero (2006)
972:
965:
940:
933:
903:
901:, p. 100.
888:
886:, p. 141.
873:
841:
810:
797:
796:
794:
791:
788:
787:
765:
764:
762:
759:
758:
757:
749:
746:
680:
677:
668:
665:
659:loaded into a
648:
645:
610:
603:
602:
590:
583:
582:
581:
580:
579:
577:
574:
562:
561:
557:
537:
534:
532:
529:
528:
527:
510:oil refinery,
504:
497:Tacoa disaster
485:
479:26 June 1971,
477:
461:
458:
454:Tacoa disaster
442:
441:
417:
401:
390:
362:
357:
346:
340:
330:
325:
321:
318:
308:
292:
283:
276:
260:
254:
249:
239:
224:
219:
213:
201:
198:
146:process safety
142:power stations
118:boiling points
85:
82:
40:boiling points
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2869:
2858:
2855:
2853:
2850:
2848:
2847:Types of fire
2845:
2844:
2842:
2827:
2826:
2817:
2815:
2814:
2805:
2804:
2801:
2795:
2794:Template:HVAC
2792:
2790:
2787:
2785:
2784:Template:Fire
2782:
2781:
2779:
2775:
2769:
2766:
2764:
2761:
2760:
2758:
2754:
2748:
2745:
2743:
2740:
2738:
2735:
2733:
2730:
2727:
2724:
2722:
2719:
2717:
2714:
2712:
2709:
2707:
2704:
2702:
2699:
2697:
2694:
2692:
2689:
2688:
2686:
2682:
2675:
2672:
2669:
2666:
2663:
2660:
2657:
2654:
2651:
2648:
2645:
2642:
2641:
2639:
2635:
2629:
2626:
2624:
2621:
2619:
2616:
2614:
2611:
2608:
2605:
2603:
2600:
2598:
2595:
2593:
2590:
2588:
2585:
2583:
2582:Duct cleaning
2580:
2579:
2577:
2571:
2565:
2562:
2560:
2557:
2555:
2554:Heat detector
2552:
2550:
2547:
2545:
2542:
2540:
2537:
2535:
2532:
2530:
2527:
2525:
2522:
2520:
2517:
2515:
2512:
2510:
2507:
2506:
2504:
2502:
2498:
2492:
2489:
2487:
2484:
2482:
2479:
2477:
2474:
2472:
2471:Smoke control
2469:
2467:
2464:
2462:
2459:
2457:
2454:
2452:
2449:
2447:
2444:
2442:
2439:
2437:
2434:
2432:
2429:
2427:
2424:
2422:
2419:
2417:
2414:
2412:
2409:
2407:
2404:
2402:
2399:
2397:
2394:
2392:
2389:
2387:
2384:
2382:
2379:
2377:
2374:
2372:
2369:
2367:
2364:
2362:
2359:
2357:
2354:
2352:
2349:
2347:
2344:
2342:
2339:
2337:
2334:
2332:
2329:
2327:
2324:
2322:
2319:
2317:
2314:
2313:
2311:
2307:
2301:
2298:
2296:
2293:
2291:
2288:
2286:
2283:
2280:
2277:
2275:
2272:
2270:
2267:
2265:
2262:
2260:
2257:
2255:
2252:
2250:
2247:
2245:
2242:
2240:
2237:
2235:
2232:
2230:
2227:
2225:
2222:
2220:
2217:
2215:
2212:
2210:
2207:
2205:
2202:
2200:
2197:
2195:
2192:
2190:
2187:
2185:
2182:
2180:
2177:
2175:
2172:
2170:
2167:
2165:
2162:
2160:
2157:
2155:
2152:
2151:
2149:
2145:
2140:
2130:
2127:
2125:
2122:
2120:
2117:
2115:
2112:
2110:
2107:
2105:
2102:
2100:
2097:
2095:
2092:
2090:
2089:Heat transfer
2087:
2085:
2082:
2080:
2079:Friction loss
2077:
2075:
2072:
2070:
2067:
2065:
2062:
2060:
2057:
2055:
2052:
2050:
2049:Fire triangle
2047:
2045:
2042:
2040:
2037:
2035:
2032:
2030:
2027:
2025:
2022:
2020:
2017:
2015:
2012:
2010:
2007:
2005:
2002:
1999:
1996:
1994:
1993:Conflagration
1991:
1989:
1986:
1984:
1981:
1978:
1975:
1973:
1970:
1969:
1967:
1963:
1959:
1952:
1947:
1945:
1940:
1938:
1933:
1932:
1929:
1922:
1917:
1913:
1912:
1901:
1886:
1882:
1878:
1874:
1872:91-7848-987-3
1868:
1864:
1857:
1852:
1848:
1842:
1838:
1834:
1830:
1826:
1814:
1807:
1803:
1791:
1787:
1785:9788469346976
1781:
1777:
1773:
1769:
1765:
1761:
1760:
1756:
1750:
1746:
1740:
1736:
1732:
1728:
1724:
1720:
1714:
1710:
1706:
1701:
1697:
1695:84-8301-227-8
1691:
1687:
1683:
1679:
1674:
1673:
1660:
1655:
1648:
1643:
1635:
1631:
1627:
1623:
1619:
1615:
1611:
1607:
1603:
1599:
1598:
1590:
1574:
1573:Northantsfire
1570:
1564:
1556:
1550:
1546:
1542:
1535:
1533:
1525:
1520:
1518:
1510:
1505:
1496:
1491:
1487:
1483:
1482:
1477:
1473:
1466:
1459:
1454:
1447:
1442:
1440:
1438:
1430:
1429:INERIS (2015)
1425:
1423:
1403:
1399:
1392:
1386:
1380:, p. A2.
1379:
1374:
1368:, p. B2.
1367:
1362:
1353:
1348:
1343:
1338:
1334:
1330:
1329:
1324:
1317:
1310:. p. 56.
1309:
1305:
1301:
1295:
1293:
1285:
1280:
1278:
1266:
1262:
1258:
1254:
1250:
1249:
1241:
1234:
1232:
1225:, p. 31.
1224:
1219:
1213:, p. 32.
1212:
1207:
1205:
1203:
1201:
1199:
1191:
1186:
1184:
1182:
1174:
1173:INERIS (2015)
1169:
1162:. p. 33.
1161:
1157:
1154:(July 1998).
1153:
1147:
1145:
1143:
1134:
1128:
1124:
1120:
1113:
1106:
1101:
1094:
1089:
1087:
1085:
1076:
1072:
1068:
1064:
1060:
1056:
1052:
1048:
1047:
1039:
1020:
1016:
1012:
1008:
1004:
1003:
995:
988:
981:
976:
968:
966:1-56032-438-4
962:
958:
954:
950:
949:Kletz, Trevor
944:
936:
934:9780367620769
930:
926:
922:
918:
914:
907:
900:
895:
893:
885:
880:
878:
858:
851:
845:
838:. p. 29.
837:
833:
829:
823:
821:
819:
817:
815:
807:
802:
798:
784:
780:
776:
770:
766:
755:
752:
751:
745:
742:
738:
734:
730:
725:
720:
717:
713:
711:
707:
702:
700:
695:
692:
685:
676:
674:
664:
662:
658:
654:
644:
642:
638:
634:
630:
624:
621:
607:
587:
573:
571:
569:
558:
555:
554:
553:
551:
542:
525:
521:
517:
513:
512:Milford Haven
509:
505:
502:
498:
494:
490:
486:
482:
478:
475:
471:
467:
466:
465:
457:
455:
450:
448:
439:
435:
431:
427:
422:
418:
399:
388:
360:
344:
338:
328:
316:
306:
291:
282:
277:
258:
252:
237:
222:
211:
196:
183:
182:
181:
178:
175:
171:
167:
163:
159:
155:
151:
147:
143:
139:
135:
131:
127:
123:
119:
115:
110:
107:
103:
102:oil reservoir
99:
90:
81:
79:
78:chip pan fire
74:
70:
66:
62:
60:
56:
52:
48:
45:
41:
36:
32:
28:
24:
19:
2824:
2812:
2711:Flame spread
2597:Fireproofing
2575:and services
2476:Smoke damper
2466:Safety glass
2401:Fire hydrant
2366:Fire curtain
2326:Booster pump
2285:Relief valve
2249:Fusible link
2039:Fire loading
2034:Fire control
2004:Deflagration
1982:
1898:– via
1892:. Retrieved
1832:
1817:. Retrieved
1794:. Retrieved
1790:the original
1763:
1759:de capa fina
1758:
1754:
1730:
1704:
1686:Edicions UPC
1681:
1677:
1654:
1642:
1601:
1595:
1589:
1577:. Retrieved
1572:
1563:
1540:
1504:
1485:
1479:
1465:
1453:
1446:Casal (2008)
1409:. Retrieved
1397:
1385:
1373:
1361:
1332:
1326:
1316:
1303:
1284:Casal (2008)
1265:the original
1246:
1218:
1168:
1155:
1118:
1112:
1105:Casal (2008)
1100:
1050:
1044:
1038:
1026:. Retrieved
1019:the original
1000:
987:
982:, p. 6.
975:
952:
943:
912:
906:
899:Casal (2008)
864:. Retrieved
844:
831:
801:
782:
778:
774:
769:
723:
721:
714:
703:
699:plant layout
697:In terms of
696:
693:
690:
673:liquid fires
670:
652:
650:
625:
619:
617:
572:over water.
567:
563:
549:
547:
463:
451:
443:
436:≈ 0.37
289:
280:
179:
161:
157:
150:distillation
111:
95:
72:
68:
67:
63:
46:
43:
26:
22:
20:
18:
2431:Grease duct
2386:Fire escape
2376:Fire damper
2269:Intumescent
2214:Fire safety
2179:Fire bucket
2074:Flash point
1894:24 February
1579:27 February
1524:NFPA (2018)
1411:24 February
866:26 February
806:NFPA (2018)
565:context of
514:, Wales –
404:149 °C
263:120 °C
166:superheated
130:diesel oils
59:diesel oils
2841:Categories
2728:(NFPA 101)
2691:CE marking
2544:Fire drill
2147:Technology
2044:Fire point
2029:Fire class
2009:Detonation
1776:10803/6483
793:References
741:pyrometers
719:distance.
560:interface.
491:in Tacoa,
472:refinery,
365:60 °C
350:boil,water
174:nucleation
154:convective
138:tank farms
134:refineries
44:thin-layer
2684:Standards
2613:Fire test
2441:Occupancy
2406:Fire pump
2396:Fire hose
2381:Fire door
2361:Exit sign
2336:Crash bar
2109:Pyrolysis
2104:Pool fire
2069:Flashover
2024:Explosive
1972:Backdraft
1881:0284-5172
1659:EI (2012)
1647:EI (2012)
1626:0305-4179
1618:1879-1409
1342:1012.2534
1261:0260-9576
1223:EI (2012)
1211:EI (2012)
1075:0950-4230
1067:1873-3352
1015:0260-9576
917:CRC Press
653:frothover
647:Frothover
641:candlewax
421:viscosity
419:The fuel
317:−
200:¯
162:heat wave
128:and some
122:Crude oil
73:frothover
57:and some
51:Crude oil
31:pool fire
27:boil-over
2813:Category
2777:See also
2706:EN 16034
2416:Firestop
2371:Fire cut
2094:Jet fire
2084:Gas leak
2000:(HAZMAT)
1983:Boilover
1885:Archived
1831:(2018).
1796:5 August
1757:boilover
1709:Elsevier
1474:(2007).
1402:Archived
857:Archived
830:(1991).
779:hot-zone
775:standard
748:See also
729:emulsion
724:a priori
661:tank car
629:chip pan
620:slopover
576:Slopover
501:fuel oil
430:gasoline
394:boil,max
334:boil,min
312:boil,max
293:boil,min
284:boil,max
243:boil,max
228:boil,min
158:hot zone
126:kerosene
106:humidity
84:Features
69:Slopover
55:kerosene
47:boilover
23:boilover
2825:Commons
2658:(NCEES)
1979:(BLEVE)
1819:20 July
1669:Sources
1634:9568338
1255:: 2–6.
1251:(290).
1028:22 July
657:asphalt
568:in-situ
447:bunding
2756:Awards
2670:(SFPE)
2664:(NFPA)
2646:(FEMA)
2609:(FSES)
1879:
1869:
1843:
1782:
1741:
1715:
1692:
1632:
1624:
1616:
1551:
1259:
1129:
1073:
1065:
1013:
963:
931:
597:
593:
493:Vargas
474:Pernis
233:
2747:UL 94
2701:EN 54
2652:(IFE)
2281:(PPE)
1888:(PDF)
1859:(PDF)
1809:(PDF)
1762:[
1680:[
1614:eISSN
1597:Burns
1405:(PDF)
1394:(PDF)
1337:arXiv
1268:(PDF)
1243:(PDF)
1063:eISSN
1022:(PDF)
997:(PDF)
860:(PDF)
853:(PDF)
508:Amoco
470:Shell
112:Pure
104:, or
98:steam
2696:EN 3
2676:(UL)
1900:DiVA
1896:2024
1877:ISSN
1867:ISBN
1841:ISBN
1829:NFPA
1821:2023
1798:2023
1780:ISBN
1739:ISBN
1713:ISBN
1690:ISBN
1630:PMID
1622:ISSN
1581:2024
1549:ISBN
1413:2024
1257:ISSN
1127:ISBN
1071:ISSN
1030:2023
1011:ISSN
961:ISBN
929:ISBN
868:2024
400:>
361:>
259:>
207:boil
71:and
35:tank
25:(or
1772:hdl
1606:doi
1490:doi
1347:doi
1300:API
1152:API
1055:doi
921:doi
828:API
781:or
739:or
438:cSt
320:max
253:0.5
160:or
2843::
1883:.
1875:.
1865:.
1839:.
1778:.
1770:.
1737:.
1727:EI
1711:.
1688:.
1628:.
1620:.
1612:.
1602:23
1600:.
1571:.
1531:^
1516:^
1486:11
1484:.
1478:.
1436:^
1421:^
1396:.
1345:.
1333:11
1331:.
1325:.
1291:^
1276:^
1245:.
1230:^
1197:^
1180:^
1141:^
1083:^
1069:.
1061:.
1049:.
999:.
951:.
927:.
919:.
891:^
876:^
813:^
777:,
651:A
618:A
548:A
140:,
136:,
120:.
53:,
21:A
1950:e
1943:t
1936:v
1902:.
1849:.
1823:.
1800:.
1774::
1747:.
1721:.
1698:.
1636:.
1608::
1583:.
1557:.
1498:.
1492::
1460:.
1431:.
1415:.
1355:.
1349::
1339::
1135:.
1077:.
1057::
1051:8
1032:.
969:.
937:.
923::
870:.
432:(
389:T
356:)
345:T
339:,
329:T
324:(
307:T
290:T
281:T
248:)
238:T
223:T
218:(
212:=
197:T
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.