425:
446:
467:
529:
20:
586:
because they can react with water at the surface of the eye producing hydrohalic and organic acids irritating to the eye. Similar problems can result if one inhales acyl halide vapors. In general, acyl halides (even non-volatile compounds such as
932:
570:(HO–CO–OH). Both chlorine atoms in phosgene can undergo reactions analogous to the preceding reactions of acyl halides. Phosgene is used a reactant in the production of
399:
Acyl halides are rather reactive compounds often synthesized to be used as intermediates in the synthesis of other organic compounds. For example, an acyl halide can
334:
fluorides. Aromatic (as well as aliphatic) acyl fluorides are conveniently prepared directly from carboxylic acids, using stable, inexpensive commodity chemicals:
296:
817:
725:
644:
615:
904:
Olah G, Kuhn S (1961). "Preparation of Acyl
Fluorides with Anhydrous Hydrogen Fluoride. The General Use of the Method of Colson and Fredenhagen".
706:
Hosea Cheung, Robin S. Tanke, G. Paul
Torrence "Acetic Acid" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim.
1003:
115:
is the one produced (transiently) on the largest scale. Billions of kilograms are generated annually in the production of
1021:"Diiodosilane. 3. Direct synthesis of acyl iodides from carboxylic acids, esters, lactones, acyl chlorides and anhydrides"
536:
A molecule can have more than one acyl halide functional group. For example, "adipoyl dichloride", usually simply called
414:. This hydrolysis is the most heavily exploited reaction for acyl halides as it occurs in the industrial synthesis of
691:
933:"Direct Access to Acyl Fluorides from Carboxylic Acids Using a Phosphine/Fluoride Deoxyfluorination Reagent System"
931:
Munoz, Socrates B.; Dang, Huong; Ispizua-Rodriguez, Xanath; Mathew, Thomas; Prakash, G. K. Surya (2019-03-15).
834:
742:
986:
Boswell, G. A.; Ripka, W. C.; Scribner, R. M.; Tullock, C. W. (2011). "Fluorination by Sulfur
Tetrafluoride".
544:; see the structure at right. It is the dichloride (i.e., double chloride) of the 6-carbon dicarboxylic acid
1104:
494:
300:
281:
186:
512:
or hydrohalic acid) is also formed. For example, if the acyl halide is an acyl chloride, HCl (
501:
315:
183:
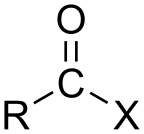
95:) singly bonded to a halogen atom. The general formula for such an acyl halide can be written
1109:
1058:
Allen, C. F. H.; Kibler, C. J.; McLachlin, D. M.; Wilson, C. V. (1946). "Acid
Anhydrides".
361:
8:
433:
308:
968:
1075:
1040:
999:
960:
952:
830:
738:
687:
517:
513:
475:
400:
354:
292:
137:
40:
28:
972:
654:
625:
1067:
1032:
1020:
991:
944:
913:
886:
859:
822:
797:
767:
730:
707:
679:
658:
649:
629:
620:
541:
537:
407:
285:
198:
179:
133:
84:
596:
509:
411:
171:
71:
995:
948:
588:
549:
327:
566:(carbonyl dichloride, Cl–CO–Cl) is a very toxic gas that is the dichloride of
295:
acyl halides are comparable to those for aliphatic acyl halides. For example,
1098:
1071:
1044:
956:
890:
863:
826:
801:
771:
734:
711:
653:, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "
624:, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "
571:
567:
277:
112:
108:
662:
633:
1079:
964:
445:
424:
391:
Acyl bromides and iodides are synthesized accordingly but are less common.
312:
304:
202:
683:
723:
Cheung, Hosea; Tanke, Robin S.; Torrence, G. Paul (2000). "Acetic Acid".
545:
466:
415:
280:, it can be generated from the parent acid and other chlorinating agents
116:
1036:
917:
592:
479:
103:
group, CO is the carbonyl group, and X represents the halide, such as
557:
815:
Maki, Takao; Takeda, Kazuo (2000). "Benzoic Acid and
Derivatives".
563:
528:
175:
104:
88:
48:
877:
Clarke, H. T.; Taylor, E. R. (1929). "o-Chlorobenzoyl chloride".
64:
44:
930:
556:
or polymerization with certain other organic compounds to form
487:
170:
Common syntheses of acyl chlorides also entail the reaction of
56:
19:
583:
553:
552:
with an organic di-amino compound to form a polyamide called
458:
454:
437:
100:
985:
331:
1057:
758:
Helferich, B.; Schaefer, W. (1929). "n-Butyrl chloride".
788:
Allen, C. F. H.; Barker, W. E. (1932). "Desoxybenzoin".
16:
Oxoacid compound with an –OH group replaced by a halogen
140:
produces a mixture of acetyl chloride and acetic acid:
189:
is used for acyl bromides, which are rarely of value.
111:
are the most commonly encountered acyl halides, but
722:
757:
1096:
850:Adams, Roger (1923). "p-Nitrobenzoyl chloride".
574:polymers, among other industrial applications.
818:Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry
726:Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry
523:
357:converts carboxylic acids to acyl fluorides.
876:
386:
1018:
787:
814:
678:. PATAI'S Chemistry of Functional Groups.
673:
548:. An important use of adipoyl chloride is
192:
783:
781:
127:
903:
527:
132:On an industrial scale, the reaction of
18:
1097:
778:
1019:Keinan, Ehud; Sahai, M. (June 1990).
849:
667:
638:
291:Representative laboratory routes to
13:
650:Compendium of Chemical Terminology
621:Compendium of Chemical Terminology
577:
197:Benzoyl chloride is produced from
99:, where R may be, for example, an
14:
1121:
1090:
321:
1025:The Journal of Organic Chemistry
465:
444:
423:
1051:
1012:
979:
924:
897:
870:
843:
808:
751:
716:
700:
609:
122:
1:
602:
508:In the above reactions, HX (
500:carboxylic acids to form an
394:
360:Carboxylic acids react with
7:
996:10.1002/0471264180.or021.01
949:10.1021/acs.orglett.9b00197
364:to give the acyl fluoride:
78:), the compound contains a
10:
1126:
582:Volatile acyl halides are
524:Multiple functional groups
387:Acyl bromides and iodides
353:in a bench-top protocol.
1072:10.15227/orgsyn.026.0001
891:10.15227/orgsyn.009.0034
864:10.15227/orgsyn.003.0075
827:10.1002/14356007.a03_555
802:10.15227/orgsyn.012.0016
772:10.15227/orgsyn.009.0032
735:10.1002/14356007.a01_045
712:10.1002/14356007.a01_045
674:Saul Patai, ed. (1972).
540:, has two acyl chloride
495:Friedel-Crafts acylation
326:Of commercial interest,
307:as a reagent, or by the
301:Friedel-Crafts acylation
282:phosphorus pentachloride
821:. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH.
729:. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH.
663:10.1351/goldbook.A00124
634:10.1351/goldbook.A00123
502:organic acid anhydrides
193:Aromatic acyl chlorides
187:Phosphorus pentabromide
595:to the eyes, skin and
533:
486:, to form an aromatic
330:react with HF to give
201:using either water or
184:phosphorus trichloride
128:Aliphatic acyl halides
87:, which consists of a
24:
684:10.1002/9780470771273
531:
482:catalyst such as AlCl
299:, a specific type of
22:
362:sulfur tetrafluoride
1037:10.1021/jo00299a042
918:10.1021/jo01060a600
309:direct chlorination
990:. pp. 1–124.
534:
520:) is also formed.
35:(also known as an
25:
1105:Functional groups
1060:Organic Syntheses
1031:(12): 3922–3926.
1005:978-0-471-26418-7
988:Organic Reactions
879:Organic Syntheses
852:Organic Syntheses
790:Organic Syntheses
760:Organic Syntheses
542:functional groups
518:hydrochloric acid
514:hydrogen chloride
476:aromatic compound
355:Cyanuric fluoride
297:chloroformylation
138:hydrogen chloride
70:If the acid is a
41:chemical compound
29:organic chemistry
1117:
1084:
1083:
1055:
1049:
1048:
1016:
1010:
1009:
983:
977:
976:
943:(6): 1659–1663.
928:
922:
921:
901:
895:
894:
874:
868:
867:
847:
841:
840:
812:
806:
805:
785:
776:
775:
755:
749:
748:
720:
714:
704:
698:
697:
671:
665:
642:
636:
613:
597:mucous membranes
538:adipoyl chloride
532:Adipoyl chloride
469:
448:
427:
382:
352:
340:
286:thionyl chloride
272:
235:
199:benzotrichloride
180:thionyl chloride
172:carboxylic acids
166:
134:acetic anhydride
94:
85:functional group
82:
77:
62:
54:
43:derived from an
1125:
1124:
1120:
1119:
1118:
1116:
1115:
1114:
1095:
1094:
1093:
1088:
1087:
1056:
1052:
1017:
1013:
1006:
984:
980:
937:Organic Letters
929:
925:
902:
898:
875:
871:
848:
844:
837:
813:
809:
786:
779:
756:
752:
745:
721:
717:
705:
701:
694:
672:
668:
643:
639:
614:
610:
605:
580:
578:General hazards
526:
510:hydrogen halide
485:
412:carboxylic acid
397:
389:
381:+ RC(O)F + HF
380:
376:
372:
368:
350:
346:
342:
339:
335:
324:
270:
266:
262:
258:
254:
250:
246:
242:
238:
233:
229:
225:
221:
217:
213:
209:
195:
164:
160:
156:
152:
148:
144:
130:
125:
92:
80:
75:
72:carboxylic acid
63:, where X is a
60:
52:
47:by replacing a
17:
12:
11:
5:
1123:
1113:
1112:
1107:
1092:
1091:External links
1089:
1086:
1085:
1050:
1011:
1004:
978:
923:
896:
869:
842:
835:
807:
777:
750:
743:
715:
699:
692:
666:
637:
607:
606:
604:
601:
589:tosyl chloride
579:
576:
550:polymerization
525:
522:
506:
505:
498:
483:
471:
470:
462:
461:
450:
449:
441:
440:
429:
428:
420:
419:
396:
393:
388:
385:
384:
383:
378:
374:
370:
348:
344:
337:
328:acyl chlorides
323:
322:Acyl fluorides
320:
278:acyl chlorides
276:As with other
274:
273:
268:
264:
260:
256:
252:
248:
244:
240:
236:
234:COCl + 2 HCl
231:
227:
223:
219:
215:
211:
194:
191:
168:
167:
162:
158:
154:
153:O + HCl → CH
150:
146:
129:
126:
124:
121:
109:Acyl chlorides
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1122:
1111:
1108:
1106:
1103:
1102:
1100:
1081:
1077:
1073:
1069:
1065:
1061:
1054:
1046:
1042:
1038:
1034:
1030:
1026:
1022:
1015:
1007:
1001:
997:
993:
989:
982:
974:
970:
966:
962:
958:
954:
950:
946:
942:
938:
934:
927:
919:
915:
911:
907:
900:
892:
888:
884:
880:
873:
865:
861:
857:
853:
846:
838:
832:
828:
824:
820:
819:
811:
803:
799:
795:
791:
784:
782:
773:
769:
765:
761:
754:
746:
740:
736:
732:
728:
727:
719:
713:
709:
703:
695:
693:9780470771273
689:
685:
681:
677:
670:
664:
660:
656:
652:
651:
646:
641:
635:
631:
627:
623:
622:
617:
612:
608:
600:
598:
594:
590:
585:
575:
573:
572:polycarbonate
569:
568:carbonic acid
565:
561:
559:
555:
551:
547:
543:
539:
530:
521:
519:
515:
511:
503:
499:
496:
493:
489:
481:
477:
473:
472:
468:
464:
463:
460:
456:
452:
451:
447:
443:
442:
439:
435:
431:
430:
426:
422:
421:
417:
413:
409:
406:
405:
404:
402:
392:
367:
366:
365:
363:
358:
356:
333:
329:
319:
317:
314:
310:
306:
302:
298:
294:
289:
287:
283:
279:
237:
208:
207:
206:
204:
200:
190:
188:
185:
181:
177:
173:
143:
142:
141:
139:
135:
120:
118:
114:
113:acetyl iodide
110:
106:
102:
98:
90:
86:
83:
73:
68:
66:
58:
50:
46:
42:
38:
34:
30:
21:
1110:Acyl halides
1063:
1059:
1053:
1028:
1024:
1014:
987:
981:
940:
936:
926:
909:
906:J. Org. Chem
905:
899:
882:
878:
872:
855:
851:
845:
816:
810:
793:
789:
763:
759:
753:
724:
718:
702:
676:Acyl Halides
675:
669:
655:acyl halides
648:
640:
619:
611:
584:lachrymatory
581:
562:
535:
507:
491:
410:, to form a
398:
390:
359:
325:
313:benzaldehyde
305:formaldehyde
290:
275:
271:COCl + HCl
203:benzoic acid
196:
169:
131:
96:
79:
69:
36:
32:
26:
912:: 237–238.
626:acyl groups
546:adipic acid
457:to form an
436:to form an
416:acetic acid
316:derivatives
303:which uses
123:Preparation
117:acetic acid
37:acid halide
33:acyl halide
23:Acyl Halide
1099:Categories
836:3527306730
744:3527306730
603:References
558:polyesters
480:Lewis acid
478:, using a
341:, NBS and
1045:0022-3263
957:1523-7060
593:irritants
395:Reactions
263:H → 2 C
157:COCl + CH
55:) with a
1080:20280752
973:73481495
965:30840474
564:Phosgene
377:H → SOF
293:aromatic
226:O → C
176:phosgene
105:chloride
89:carbonyl
76:−C(=O)OH
49:hydroxyl
1066:: 1–3.
434:alcohol
91:group (
81:−C(=O)X
65:halogen
59:group (
51:group (
45:oxoacid
39:) is a
1078:
1043:
1002:
971:
963:
955:
885:: 34.
858:: 75.
833:
796:: 16.
766:: 32.
741:
690:
591:) are
488:ketone
403:with:
182:, and
57:halide
969:S2CID
645:IUPAC
616:IUPAC
554:nylon
459:amide
455:amine
438:ester
408:water
401:react
373:+ RCO
174:with
136:with
101:alkyl
31:, an
1076:PMID
1041:ISSN
1000:ISBN
961:PMID
953:ISSN
831:ISBN
739:ISBN
688:ISBN
332:acyl
251:+ C
222:+ H
97:RCOX
1068:doi
1033:doi
992:doi
945:doi
914:doi
887:doi
860:doi
823:doi
798:doi
768:doi
731:doi
708:doi
680:doi
659:doi
657:".
630:doi
628:".
516:or
492:See
474:an
453:an
432:an
336:PPh
311:of
284:or
247:CCl
218:CCl
149:CO)
145:(CH
93:C=O
67:).
53:−OH
27:In
1101::
1074:.
1064:26
1062:.
1039:.
1029:55
1027:.
1023:.
998:.
967:.
959:.
951:.
941:21
939:.
935:.
910:26
908:.
881:.
854:.
829:.
794:12
792:.
780:^
762:.
737:.
686:.
647:,
618:,
599:.
560:.
490:.
369:SF
351:HF
347:N-
343:Et
318:.
288:.
259:CO
205::
178:,
161:CO
119:.
107:.
61:−X
1082:.
1070::
1047:.
1035::
1008:.
994::
975:.
947::
920:.
916::
893:.
889::
883:9
866:.
862::
856:3
839:.
825::
804:.
800::
774:.
770::
764:9
747:.
733::
710::
696:.
682::
661::
632::
504:.
497:.
484:3
418:.
379:2
375:2
371:4
349:3
345:3
338:3
269:5
267:H
265:6
261:2
257:5
255:H
253:6
249:3
245:5
243:H
241:6
239:C
232:5
230:H
228:6
224:2
220:3
216:5
214:H
212:6
210:C
165:H
163:2
159:3
155:3
151:2
147:3
74:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.