3150:
2632:
7170:
4372:
3145:{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}B(\theta )&\approx \Pr \left(T_{n}>1.64~{\big |}~\mu _{D}=\theta \right)\\&=\Pr \left({\frac {{\bar {D}}_{n}-0}{{\hat {\sigma }}_{D}/{\sqrt {n}}}}>1.64~{\Big |}~\mu _{D}=\theta \right)\\&=1-\Pr \left({\frac {{\bar {D}}_{n}-0}{{\hat {\sigma }}_{D}/{\sqrt {n}}}}<1.64~{\Big |}~\mu _{D}=\theta \right)\\&=1-\Pr \left({\frac {{\bar {D}}_{n}-\theta }{{\hat {\sigma }}_{D}/{\sqrt {n}}}}<1.64-{\frac {\theta }{{\hat {\sigma }}_{D}/{\sqrt {n}}}}~{\Big |}~\mu _{D}=\theta \right)\\\end{aligned}}}
925:, hypothesis testing of the type used in classical power analysis is not done. In the Bayesian framework, one updates his or her prior beliefs using the data obtained in a given study. In principle, a study that would be deemed underpowered from the perspective of hypothesis testing could still be used in such an updating process. However, power remains a useful measure of how much a given experiment size can be expected to refine one's beliefs. A study with low power is unlikely to lead to a large change in beliefs.
1185:
7156:
1248:. An effect size can be a direct value of the quantity of interest (for example, a difference in mean of a particular size), or it can be a standardized measure that also accounts for the variability in the population (such as a difference in means expressed as a multiple of the standard deviation). If the researcher is looking for a larger effect, then it should be easier to find with a given experimental or analytic setup, and so power is higher.
1374:), and so would reduce power. Alternatively, there may be different notions of power connected with how the different hypotheses are considered. "Complete power" demands that all true effects are detected across all of the hypotheses, which is a much stronger requirement than the "minimal power" of being able to find at least one true effect, a type of power that might increase with an increasing number of hypotheses.
7194:
7182:
270:
914:. However, excessive demands for power could be connected to wasted resources and ethical problems, for example the use of a large number of animal test subjects when a smaller number would have been sufficient. It could also induce researchers trying to seek funding to overstate their expected effect sizes, or avoid looking for more subtle interaction effects that cannot be easily detected.
1224:
implies that the observation must be at least that unlikely (perhaps by suggesting a sufficiently large estimate of difference) to be considered strong enough evidence against the null. Picking a smaller value to tighten the threshold, so as to reduce the chance of a false positive, would also reduce power, increase the chance of a false negative. Some statistical tests will
902:(in other words, producing an acceptable level of power). For example: "How many times do I need to toss a coin to conclude it is rigged by a certain amount?" If resources and thus sample sizes are fixed, power analyses can also be used to calculate the minimum effect size that is likely to be detected.
1284:
The statistical power of a hypothesis test has an impact on the interpretation of its results. Not finding a result with a more powerful study is stronger evidence against the effect existing than the same finding with a less powerful study. However, this is not completely conclusive. The effect may
869:
of the hypothesis testing procedure to detect a true effect. There is usually a trade-off between demanding more stringent tests (and so, smaller rejection regions) and trying to have a high probability of rejecting the null under the alternative hypothesis. Statistical power may also be extended to
240:
The threshold for significance can be set small to ensure there is little chance of falsely detecting a non-existent effect. However, failing to identify a significant effect does not imply there was none. If we insist on being careful to avoid false positives, we may create false negatives instead.
905:
Funding agencies, ethics boards and research review panels frequently request that a researcher perform a power analysis. An underpowered study is likely be inconclusive, failing to allow one to choose between hypotheses at the desired significance level, while an overpowered study will spend great
1416:
analysis in experimental design is universally accepted, post hoc power analysis is fundamentally flawed. Falling for the temptation to use the statistical analysis of the collected data to estimate the power will result in uninformative and misleading values. In particular, it has been shown that
1415:
analysis of "observed power" is conducted after a study has been completed, and uses the obtained sample size and effect size to determine what the power was in the study, assuming the effect size in the sample is equal to the effect size in the population. Whereas the utility of prospective power
1321:
may be designed to minimise the number of false negatives (type II errors) produced by loosening the threshold of significance, raising the risk of obtaining a false positive (a type I error). The rationale is that it is better to tell a healthy patient "we may have found something—let's
1455:
The following is an example that shows how to compute power for a randomized experiment: Suppose the goal of an experiment is to study the effect of a treatment on some quantity, and so we shall compare research subjects by measuring the quantity before and after the treatment, analyzing the data
1358:
we may include several covariates of potential interest. In situations such as this where several hypotheses are under consideration, it is common that the powers associated with the different hypotheses differ. For instance, in multiple regression analysis, the power for detecting an effect of a
1223:
determines the desired degree of rigor, specifying how unlikely it is for the null hypothesis of no effect to be rejected if it is in fact true. The most commonly used threshold is a probability of rejection of 0.05, though smaller values like 0.01 or 0.001 are sometimes used. This threshold then
1974:
1342:
with this sample would be around . An alternative, albeit related analysis would be required if we wish to be able to measure correlation to an accuracy of +/- 0.1, implying a different (in this case, larger) sample size. Alternatively, multiple under-powered studies can still be useful, if
1255:
underlies the information being used in the test. This will usually involve the sample size, and the sample variability, if that is not implicit in the definition of the effect size. More broadly, the precision with which the data are measured can also be an important factor (such as the
4263:
This can be done with a variety of software packages. Using this methodology with the values before, setting the sample size to 25 leads to an estimated power of around 0.78. The small discrepancy with the previous section is due mainly to inaccuracies with the normal approximation.
1354:. In this setting, the only relevant power pertains to the single quantity that will undergo formal statistical inference. In some settings, particularly if the goals are more "exploratory", there may be a number of quantities of interest in the analysis. For example, in a multiple
1325:
Power analysis focuses on the correct rejection of a null hypothesis. Alternative concerns may however motivate an experiment, and so lead to different needs for sample size. In many contexts, the issue is less about deciding between hypotheses but rather with getting an
3874:
3663:
4281:
setting, parameters are assumed to have a specific value which is unlikely to be true. This issue can be addressed by assuming the parameter has a distribution. The resulting power is sometimes referred to as
Bayesian power which is commonly used in
3423:
1808:
1192:
Statistical power may depend on a number of factors. Some factors may be particular to a specific testing situation, but in normal use, power depends on the following three aspects that can be potentially controlled by the practitioner:
1161:
the to-be-detected difference in the mean values of both samples. This expression can be rearranged, implying for example that 80% power is obtained when looking for a difference in means that exceeds about 4 times the group-wise
4298:
power and
Bayesian power use statistical significance as the success criterion. However, statistical significance is often not enough to define success. To address this issue, the power concept can be extended to the concept of
3232:
1268:. A smaller sampling error could be obtained by larger sample sizes from a less variability population, from more accurate measurements, or from more efficient experimental designs (for example, with the appropriate use of
236:
if there is no difference (the so called null hypothesis). If the actual value calculated on the sample is sufficiently unlikely to arise under the null hypothesis, we say we identified a statistically significant effect.
2453:
1304:
Indeed, although there are no formal standards for power, many researchers and funding bodies assess power using 0.80 (or 80%) as a standard for adequacy. This convention implies a four-to-one trade off between
2132:
1243:
that the researcher has arrived at and wishes to test. Alternatively, in a more practical context it could be determined by the size the effect must be to be useful, for example that which is required to be
3760:
3564:
241:
It may simply be too much to expect that we will be able to find satisfactorily strong evidence of a very subtle difference even if it exists. Statistical power is an attempt to quantify this issue.
2637:
1086:
3337:
4346:
PowerUpR is R package version of PowerUp! and additionally includes functions to determine sample size for various multilevel randomized experiments with or without budgetary constraints.
1797:
1745:
4343:
PowerUp! provides convenient excel-based functions to determine minimum detectable effect size and minimum required sample size for various experimental and quasi-experimental designs.
4586:
Sample Size
Estimation in Clinical Research From Randomized Controlled Trials to Observational Studies, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.03.010, Xiaofeng Wang, PhD; and Xinge Ji, MS
4201:
61:
of interest. High statistical power is related to low variability, large sample sizes, large effects being looked for, and less stringent requirements for statistical significance.
940:, and hence the same false positive rates, but different ability to detect true effects. Consideration of their theoretical power proprieties is a key reason for the common use of
3303:
2312:
2170:
3506:
in this example 0.05. For finite sample sizes and non-zero variability, it is the case here, as is typical, that power cannot be made equal to 1 except in the trivial case where
1159:
1620:
4011:
2515:
4649:
Tsang, R.; Colley, L.; Lynd, L.D. (2009). "Inadequate statistical power to detect clinically significant differences in adverse event rates in randomized controlled trials".
1683:
3753:
2242:
2043:
273:
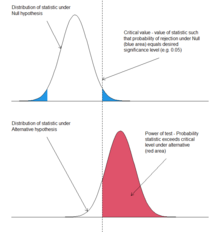
Illustration of the power of a statistical test, for a two sided test, through the probability distribution of the test statistic under the null and alternative hypothesis.
1487:
1370:
will be inflated if appropriate measures are not taken. Such measures typically involve applying a higher threshold of stringency to reject a hypothesis (such as with the
1033:
4258:
4129:
4075:
3718:
3476:
3330:
2598:
2272:
3504:
2544:
2376:
1272:), and such smaller errors would lead to improved power, albeit usually at a cost in resources. How increased sample size translates to higher power is a measure of the
1004:
3691:
3530:
2184:
We can proceed according to our knowledge of statistical theory, though in practice for a standard case like this software will exist to compute more accurate answers.
2003:
1651:
158:
3445:
2332:
178:
4231:
4159:
4102:
4040:
3969:
3939:
3912:
3259:
2625:
2571:
2482:
1544:
1517:
1113:
860:
829:
798:
771:
740:
713:
686:
648:
598:
560:
529:
500:
465:
438:
403:
376:
345:
318:
132:
101:
1285:
exist, but be smaller than what was looked for, meaning the study is in fact underpowered and the sample is thus unable to distinguish it from random chance. Many
2215:
2383:
906:
expense on being able to report significant effects even if they are tiny and so practically meaningless. If a large number of underpowered studies are done and
3557:
1564:
974:
1330:
of the population effect size of sufficient accuracy. For example, a careful power analysis can tell you that 55 pairs of normally distributed samples with a
1317:
is set as 1 - 0.8 = 0.2, while α, the probability of a type I error, is commonly set at 0.05. Some applications require much higher levels of power.
3156:
2054:
1969:{\displaystyle T_{n}={\frac {{\bar {D}}_{n}-\mu _{0}}{{\hat {\sigma }}_{D}/{\sqrt {n}}}}={\frac {{\bar {D}}_{n}-0}{{\hat {\sigma }}_{D}/{\sqrt {n}}}},}
1366:
together. For example, if we consider a false positive to be making an erroneous null rejection on any one of these hypotheses, our likelihood of this
890:
The main application of statistical power is "power analysis", a calculation of power usually done before an experiment is conducted using data from
1359:
given size is related to the variance of the covariate. Since different covariates will have different variances, their powers will differ as well.
6291:
1331:
49:
setup to detect a particular effect if it is truly present. In typical use, it is a function of the test used (including the desired level of
6796:
4699:
1173:
16 is to be replaced with 8. Other values provide an appropriate approximation when the desired power or significance level are different.
804:(the difference between the two distributions being a function of the effect size), the power of the test would be the probability, under
6946:
1038:
6570:
5211:
928:
In addition, the concept of power is used to make comparisons between different statistical testing procedures: for example, between a
3941:. Suppose we have fixed values of the sample size, variability and effect size, and wish to compute power. We can adopt this process:
1431:
power analyses suffer from what is called the "power approach paradox" (PAP), in which a study with a null result is thought to show
1350:
Many statistical analyses involve the estimation of several unknown quantities. In simple cases, all but one of these quantities are
6344:
4686:
The
Essential Guide to Effect Sizes: An Introduction to Statistical Power, Meta-Analysis and the Interpretation of Research Results
1334:
of 0.5 will be sufficient to grant 80% power in rejecting a null that the correlation is no more than 0.2 (using a one-sided test,
248:
Is there a big danger of two very different varieties producing samples that just happen to look indistinguishable by pure chance?
7220:
6783:
4385:
221:. For example, we may measure the yields of samples of two varieties of a crop, and use a two sample test to assess whether the
4804:
4857:
4571:
5206:
4906:
4315:
Numerous free and/or open source programs are available for performing power and sample size calculations. These include
5810:
4958:
3869:{\displaystyle n>4\left(1.64-\Phi ^{-1}\left(1-0.8\right)\right)^{2}\approx 4\left(1.64+0.84\right)^{2}\approx 24.6.}
4633:
1301:
of an effect also should consider more things than a single test, especially as real world power is rarely close to 1.
6593:
6485:
4838:
4608:
4300:
7198:
6771:
6645:
4465:"Finding the right power balance: Better study design and collaboration can reduce dependence on statistical power"
3658:{\displaystyle {\sqrt {n}}>{\frac {\sigma _{D}}{\theta }}\left(1.64-\Phi ^{-1}\left(1-B(\theta )\right)\right).}
1463:, with a significance level threshold of 0.05. We are interested in being able to detect a positive change of size
181:
1750:
6829:
6490:
6235:
5606:
5196:
4626:
The
Essential Guide to Effect Sizes: Statistical Power, Meta-Analysis, and the Interpretation of Research Results
17:
1691:
6880:
6092:
5899:
5788:
5746:
4760:
5820:
1747:
For our one-sided test, the alternative hypothesis would be that there is a positive effect, corresponding to
7123:
6082:
4985:
4303:(PPOS). The success criterion for PPOS is not restricted to statistical significance and is commonly used in
657:
would then define a corresponding "rejection region" (bounded by certain "critical values"), a set of values
4587:
4164:
6674:
6623:
6608:
6598:
6467:
6339:
6306:
6132:
6087:
5917:
4418:
2343:
1439:-value is smaller, since the apparent power to detect an actual effect would be higher. In fact, a smaller
1225:
3272:
2277:
2139:
228:
Under a frequentist hypothesis testing framework, this is done by calculating a test statistic (such as a
7186:
7018:
6819:
6743:
6044:
5798:
5467:
4931:
2245:
1118:
866:
201:
1688:
Here, it is natural to choose our null hypothesis to be that the expected mean difference is zero, i.e.
1569:
6903:
6875:
6870:
6618:
6377:
6283:
6263:
6171:
5882:
5700:
5183:
5055:
4879:
4826:
4752:
1163:
3974:
3418:{\displaystyle B(\theta )\approx 1-\Phi \left(1.64-{\frac {\theta }{\sigma _{D}/{\sqrt {n}}}}\right).}
2487:
6635:
6403:
6124:
6049:
5978:
5907:
5827:
5815:
5685:
5673:
5666:
5374:
5095:
4724:
2338:
is large, the t-distribution converges to the standard normal distribution (thus no longer involving
1656:
264:
3723:
2220:
2012:
7118:
6885:
6748:
6433:
6398:
6362:
6147:
5589:
5498:
5457:
5369:
5060:
4899:
4403:
1257:
1198:
620:
233:
50:
4514:
Robert Lehr (1992), "SixteenS-squared overD-squared: A relation for crude sample size estimates",
1466:
1012:
7027:
6640:
6580:
6517:
6155:
6139:
5877:
5739:
5729:
5579:
5493:
4397:
4236:
4107:
4048:
3887:
method that works more generally. Once again, we return to the assumption of the distribution of
3696:
3454:
3308:
2576:
2250:
1408:
1293:
of treatments, since such effects may only affect a few patients, even if this difference can be
1273:
1264:
of an experiment or observational study. Ultimately, these factors lead to an expected amount of
244:
In the case of the comparison of the two crop varieties, it enables us to answer questions like:
189:
3485:
2520:
2351:
983:
7065:
6995:
6788:
6725:
6480:
6367:
5364:
5261:
5168:
5047:
4946:
3884:
3670:
3509:
2188:
1457:
1367:
1245:
1212:
1176:
However, a full power analysis should always be performed to confirm and refine this estimate.
918:
218:
104:
1981:
1629:
137:
7090:
7032:
6975:
6801:
6694:
6603:
6329:
6213:
6072:
6064:
5954:
5946:
5761:
5657:
5635:
5594:
5559:
5526:
5472:
5447:
5402:
5341:
5301:
5103:
4926:
3430:
2317:
1298:
1294:
1269:
1261:
941:
929:
214:
210:
4558:. Wiley Series in Probability and Statistics. Hoboken, NJ, USA: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
163:
7013:
6588:
6537:
6513:
6475:
6393:
6372:
6324:
6203:
6181:
6150:
6059:
5936:
5887:
5805:
5778:
5734:
5690:
5452:
5228:
5108:
4769:
4209:
4137:
4080:
4018:
3947:
3917:
3890:
3237:
2603:
2549:
2460:
1522:
1495:
1363:
1091:
838:
807:
776:
749:
718:
691:
664:
626:
576:
538:
507:
478:
443:
416:
381:
354:
323:
296:
110:
79:
1566:, respectively. The possible effect of the treatment should be visible in the differences
910:, published findings are more likely false positives than true results, contributing to a
8:
7160:
7085:
7008:
6689:
6453:
6446:
6408:
6316:
6296:
6268:
6001:
5867:
5862:
5852:
5844:
5662:
5623:
5513:
5503:
5412:
5191:
5147:
5065:
4990:
4892:
3262:
2194:
2187:
Thanks to t-test theory, we know this test statistic under the null hypothesis follows a
1623:
1355:
1339:
922:
874:
are being tested based on a experiment or survey. It is thus also common to refer to the
42:
4773:
4491:
4464:
254:
How different do these varieties need to be before we can expect to notice a difference?
7174:
6985:
6839:
6735:
6684:
6560:
6457:
6441:
6418:
6195:
5929:
5872:
5783:
5678:
5640:
5611:
5571:
5531:
5477:
5394:
5080:
5075:
4377:
3542:
2173:
1549:
1351:
1007:
959:
933:
911:
651:
46:
7169:
7080:
7050:
7042:
6862:
6853:
6778:
6709:
6565:
6550:
6525:
6413:
6354:
6220:
6208:
5834:
5751:
5695:
5618:
5462:
5384:
5163:
5037:
4853:
4834:
4781:
4666:
4629:
4604:
4567:
4535:
4527:
4496:
4371:
2346:
1390:
1371:
1327:
1170:
977:
937:
879:
53:), the assumed distribution of the test (for example, the degree of variability, and
7105:
7060:
6824:
6811:
6704:
6679:
6613:
6545:
6423:
6031:
5924:
5857:
5770:
5717:
5536:
5407:
5201:
5085:
5000:
4967:
4785:
4777:
4733:
4662:
4658:
4559:
4519:
4486:
4476:
907:
871:
206:
4463:
Nakagawa, Shinichi; Lagisz, Malgorzata; Yang, Yefeng; Drobniak, Szymon M. (2024).
3427:
According to this formula, the power increases with the values of the effect size
3227:{\displaystyle {\frac {{\bar {D}}_{n}-\theta }{{\hat {\sigma }}_{D}/{\sqrt {n}}}}}
1407:
power analysis is conducted prior to the research study, and is typically used in
865:
Statistical power is one minus the type II error probability and is also the
746:
takes those values, we would be able to keep the probability of falsely rejecting
7022:
6766:
6628:
6555:
6230:
6104:
6077:
6054:
6023:
5650:
5645:
5599:
5329:
4980:
4481:
4438:
1235:
of interest defines what is being looked for by the test. It can be the expected
73:
65:
6512:
6971:
6966:
5429:
5359:
5005:
4737:
4304:
4283:
1800:
1290:
1286:
1265:
1184:
613:
185:
4873:
7214:
7128:
7095:
6958:
6919:
6730:
6699:
6163:
6117:
5722:
5424:
5251:
5015:
5010:
4531:
1344:
953:
891:
1276:
of the test – for example, the sample size required for a given power.
894:
or a literature review. Power analyses can be used to calculate the minimum
251:
How much effort do we need to put into this comparison to avoid that danger?
7070:
7003:
6980:
6895:
6225:
5521:
5419:
5354:
5296:
5281:
5218:
5173:
4670:
4553:
4523:
4500:
2448:{\displaystyle T_{n}>t_{\alpha }\approx \Phi ^{-1}(0.95)\approx 1.64\,.}
1318:
612:
To make this more concrete, a typical statistical test would be based on a
4563:
4539:
7113:
7075:
6758:
6659:
6521:
6334:
6301:
5793:
5710:
5705:
5349:
5306:
5286:
5266:
5256:
5025:
4409:
4391:
4295:
4278:
2046:
1236:
1208:
899:
895:
229:
222:
58:
54:
31:
2217:
degrees of freedom. If we wish to reject the null at significance level
878:, evaluating a scientific project in terms of its ability to answer the
5959:
5439:
5139:
5070:
5020:
4995:
4915:
4439:"Statistical power and underpowered statistics — Statistics Done Wrong"
1240:
34:
4388: – Statistical measures of whether a finding is likely to be true
293:
Suppose we are conducting a hypothesis test. We define two hypotheses
6112:
5964:
5584:
5379:
5291:
5276:
5271:
5236:
4789:
4700:"Estimating Statistical Power When Using Multiple Testing Procedures"
1289:, for instance, have low statistical power to detect differences in
5628:
5246:
5123:
5118:
5113:
4412: – Statistical considerations on how many observations to make
4310:
3478:. In the trivial case of zero effect size, power is at a minimum (
2127:{\displaystyle {\bar {D}}_{n}={\frac {1}{n}}\sum _{i=1}^{n}D_{i},}
7133:
6834:
4337:
4330:
4319:
3479:
1421:
4806:
Study design with SAS: Estimating power with Monte Carlo methods
1546:
denote the pre-treatment and post-treatment measures on subject
7055:
6036:
6010:
5990:
5241:
5032:
4356:
1460:
351:
is the significance level - being the probability of rejecting
289:, the probability of correctly rejecting under the alternative.
1322:
test further," than to tell a diseased patient "all is well."
1228:, albeit often at the cost of requiring stronger assumptions.
269:
4884:
4323:
4260:
calculated in step 3 and so are rejected. This is the power.
4406: – Theorem about the power of the likelihood ratio test
4394: – Statistical measure of the magnitude of a phenomenon
2517:. Then, writing the power as a function of the effect size,
1435:
evidence that the null hypothesis is actually true when the
773:
within our desired significance level. At the same time, if
347:
the alternative hypothesis. If we design the test such that
4975:
4518:(in German), vol. 11, no. 8, pp. 1099–1102,
898:
required so that one can be reasonably likely to detect an
4462:
1443:-value is properly understood to make the null hypothesis
4688:. United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press. p. 56.
4206:
5. Look at the proportion of these simulated alternative
619:
calculated from the sampled data, which has a particular
4414:
Pages displaying short descriptions of redirect targets
4203:, and compute the corresponding test statistics again.
1492:
We first set up the problem according to our test. Let
72:
is the probability that the test correctly rejects the
4831:
Statistical Power
Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences
1362:
Additional complications arise when we consider these
4239:
4212:
4167:
4140:
4110:
4083:
4051:
4021:
3977:
3950:
3920:
3893:
3763:
3726:
3699:
3673:
3567:
3545:
3512:
3488:
3457:
3433:
3340:
3311:
3275:
3240:
3159:
2635:
2606:
2579:
2552:
2523:
2490:
2463:
2386:
2354:
2320:
2280:
2253:
2223:
2197:
2142:
2057:
2015:
1984:
1811:
1753:
1694:
1659:
1632:
1572:
1552:
1525:
1498:
1469:
1403:
or retrospective power analysis) data are collected.
1121:
1094:
1041:
1015:
986:
962:
841:
810:
779:
752:
721:
694:
667:
629:
579:
541:
510:
481:
446:
419:
384:
357:
326:
299:
281:, the probability of rejection under null, while the
166:
140:
113:
82:
6797:
Autoregressive conditional heteroskedasticity (ARCH)
4367:
4289:
1622:
which are assumed to be independent and identically
976:(for each group) for the common case of a two-sided
835:falls into our defined rejection region and causes
405:is in fact true, then the power of the test is 1 -
6259:
4875:StatQuest: P-value pitfalls and power calculations
4252:
4225:
4195:
4153:
4123:
4096:
4069:
4034:
4005:
3963:
3933:
3906:
3868:
3747:
3712:
3685:
3657:
3551:
3524:
3498:
3482:) and equal to the significance level of the test
3470:
3439:
3417:
3324:
3297:
3253:
3226:
3144:
2619:
2592:
2565:
2538:
2509:
2476:
2447:
2370:
2326:
2306:
2266:
2236:
2209:
2164:
2126:
2037:
2005:is the mean under the null so we substitute in 0,
1997:
1968:
1791:
1739:
1677:
1645:
1614:
1558:
1538:
1511:
1481:
1427:attained. This has been extended to show that all
1313:-risk, as the probability of a type II error
1188:An example of how sample size affects power levels
1153:
1107:
1081:{\displaystyle n\approx 16{\frac {s^{2}}{d^{2}}},}
1080:
1027:
998:
968:
854:
823:
792:
765:
734:
707:
680:
642:
592:
554:
523:
494:
459:
432:
397:
370:
339:
312:
172:
152:
126:
95:
4850:Applied Power Analysis for the Behavioral Science
4329:WebPower Free online statistical power analysis (
3720:is around 2, say, then we require for a power of
3109:
2938:
2810:
1420:"observed power" is a one-to-one function of the
1377:
232:) for the dataset, which has a known theoretical
7212:
2983:
2855:
2727:
2659:
2378:, we obtain that the null should be rejected if
936:of the same hypothesis. Tests may have the same
6345:Multivariate adaptive regression splines (MARS)
4648:
4400: – Quality measure of a statistical method
4311:Software for power and sample size calculations
4683:
3305:will also converge on to its population value
1115:is an estimate of the population variance and
4900:
4833:(2nd ed.). Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
4722:Hoenig; Heisey (2001). "The Abuse of Power".
4421: – Theoretically optimal hypothesis test
3234:again follows a student-t distribution under
2688:
800:defines its own probability distribution for
192:on there being a true effect or association.
4721:
2457:Now suppose that the alternative hypothesis
1792:{\displaystyle H_{1}:\mu _{D}=\theta >0.}
1179:
4603:. Cambridge University Press. p. 321.
4513:
947:
908:statistically significant results published
4945:
4907:
4893:
4750:
4628:. Cambridge University Press. p. 52.
4592:
4555:Statistical Rules of Thumb, Second Edition
4134:4. Now generate a large number of sets of
3451:, and reduces with increasing variability
1740:{\displaystyle H_{0}:\mu _{D}=\mu _{0}=0.}
1395:Power analysis can either be done before (
5558:
4551:
4490:
4480:
4336:Free and open source online calculators (
4161:according to the alternative hypothesis,
3492:
2441:
2233:
2009:is the sample size (number of subjects),
1626:in distribution, with unknown mean value
1399:or prospective power analysis) or after (
225:of this yield differs between varieties.
4802:
4015:2. Compute the resulting test statistic
1338: = 0.05). But the typical 95%
1183:
413:is the probability of failing to reject
268:
4847:
4598:
4386:Positive and negative predictive values
1215:of the sample used to detect the effect
1204:the magnitude of the effect of interest
64:More formally, in the case of a simple
14:
7213:
6871:Kaplan–Meier estimator (product limit)
4717:
4715:
4713:
4601:The Cambridge Dictionary of Statistics
4196:{\displaystyle N(\theta ,\sigma _{D})}
3944:1. Generate a large number of sets of
3878:
27:Term in statistical hypothesis testing
6944:
6511:
6258:
5557:
5327:
4944:
4888:
4825:
4623:
134:) is true. It is commonly denoted by
7181:
6881:Accelerated failure time (AFT) model
3298:{\displaystyle {\hat {\sigma }}_{D}}
2307:{\displaystyle T_{n}>t_{\alpha }}
2179:
2165:{\displaystyle {\hat {\sigma }}_{D}}
7193:
6476:Analysis of variance (ANOVA, anova)
5328:
4710:
1154:{\displaystyle d=\mu _{1}-\mu _{2}}
24:
6571:Cochran–Mantel–Haenszel statistics
5197:Pearson product-moment correlation
3971:according to the null hypothesis,
3786:
3607:
3362:
3332:Thus power can be approximated as
2414:
2356:
1615:{\displaystyle D_{i}=B_{i}-A_{i},}
1409:estimating sufficient sample sizes
41:is a measure of the ability of an
25:
7232:
4867:
4301:predictive probability of success
4290:Predictive probability of success
4272:
3559:to obtain required sample sizes:
1343:appropriately combined through a
7192:
7180:
7168:
7155:
7154:
6945:
4782:10.1046/j.1523-1739.1997.96102.x
4651:Journal of Clinical Epidemiology
4552:van Belle, Gerald (2008-08-18).
4370:
4006:{\displaystyle N(0,\sigma _{D})}
2510:{\displaystyle \mu _{D}=\theta }
6830:Least-squares spectral analysis
4796:
4744:
4692:
4104:and use that as an estimate of
1678:{\displaystyle \sigma _{D}^{2}}
1239:if it exists, as an scientific
1226:inherently produce better power
885:
180:is the probability of making a
7221:Statistical hypothesis testing
5811:Mean-unbiased minimum-variance
4914:
4753:"Retrospective power analysis"
4677:
4663:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2008.08.005
4642:
4617:
4580:
4545:
4507:
4456:
4431:
4338:https://powerandsamplesize.com
4331:https://webpower.psychstat.org
4190:
4171:
4064:
4052:
4000:
3981:
3748:{\displaystyle B(\theta )=0.8}
3736:
3730:
3639:
3633:
3350:
3344:
3283:
3261:, converging on to a standard
3197:
3170:
3077:
3028:
3001:
2900:
2873:
2772:
2745:
2649:
2643:
2533:
2527:
2432:
2426:
2237:{\displaystyle \alpha =0.05\,}
2150:
2065:
2038:{\displaystyle {\bar {D}}_{n}}
2023:
1936:
1909:
1869:
1835:
1299:probability of actual presence
917:Power analysis is primarily a
258:
13:
1:
7124:Geographic information system
6340:Simultaneous equations models
4425:
4077:th quantile of the simulated
2546:, we find the probability of
2274:such that the probability of
1279:
195:
6307:Coefficient of determination
5918:Uniformly most powerful test
4803:Graebner, Robert W. (1999).
4482:10.1371/journal.pbio.3002423
4419:Uniformly most powerful test
4357:https://www.statsmodels.org/
4355:Python package statsmodels (
4267:
2342:) and so through use of the
1803:in this case is defined as:
1482:{\displaystyle \theta >0}
1028:{\displaystyle \alpha =0.05}
882:they are seeking to answer.
7:
6876:Proportional hazards models
6820:Spectral density estimation
6802:Vector autoregression (VAR)
6236:Maximum posterior estimator
5468:Randomized controlled trial
4443:www.statisticsdonewrong.com
4363:
4253:{\displaystyle t_{\alpha }}
4124:{\displaystyle t_{\alpha }}
4070:{\displaystyle (1-\alpha )}
3883:Alternatively we can use a
3713:{\displaystyle \sigma _{D}}
3471:{\displaystyle \sigma _{D}}
3325:{\displaystyle \sigma _{D}}
2593:{\displaystyle t_{\alpha }}
2314:under the null is equal to
2267:{\displaystyle t_{\alpha }}
1411:to achieve adequate power.
202:Statistical hypothesis test
10:
7237:
6636:Multivariate distributions
5056:Average absolute deviation
4819:
4738:10.1198/000313001300339897
4599:Everitt, Brian S. (2002).
4324:https://www.gpower.hhu.de/
3499:{\displaystyle \alpha \,,}
2539:{\displaystyle B(\theta )}
2371:{\displaystyle \Phi ^{-1}}
1450:
1388:
1164:standard error of the mean
999:{\displaystyle \beta =0.2}
956:says that the sample size
862:to be correctly rejected.
688:was correct. If we reject
504:Probability to not reject
262:
199:
7150:
7104:
7041:
6994:
6957:
6953:
6940:
6912:
6894:
6861:
6852:
6810:
6757:
6718:
6667:
6658:
6624:Structural equation model
6579:
6536:
6532:
6507:
6466:
6432:
6386:
6353:
6315:
6282:
6278:
6254:
6194:
6103:
6022:
5986:
5977:
5960:Score/Lagrange multiplier
5945:
5898:
5843:
5769:
5760:
5570:
5566:
5553:
5512:
5486:
5438:
5393:
5375:Sample size determination
5340:
5336:
5323:
5227:
5182:
5156:
5138:
5094:
5046:
4966:
4957:
4953:
4940:
4922:
4725:The American Statistician
3686:{\displaystyle \theta =1}
3525:{\displaystyle \alpha =1}
1180:Factors influencing power
320:the null hypothesis, and
265:Type I and type II errors
68:with two hypotheses, the
7119:Environmental statistics
6641:Elliptical distributions
6434:Generalized linear model
6363:Simple linear regression
6133:Hodges–Lehmann estimator
5590:Probability distribution
5499:Stochastic approximation
5061:Coefficient of variation
1998:{\displaystyle \mu _{0}}
1646:{\displaystyle \mu _{D}}
1447:less likely to be true.
1297:. Conclusions about the
1199:statistical significance
1197:the test itself and the
948:Rule of thumb for t-test
621:probability distribution
234:probability distribution
153:{\displaystyle 1-\beta }
51:statistical significance
6779:Cross-correlation (XCF)
6387:Non-standard predictors
5821:Lehmann–Scheffé theorem
5494:Adaptive clinical trial
4684:Ellis, Paul D. (2010).
3440:{\displaystyle \theta }
2327:{\displaystyle \alpha }
1258:statistical reliability
1233:magnitude of the effect
661:is unlikely to take if
7175:Mathematics portal
6996:Engineering statistics
6904:Nelson–Aalen estimator
6481:Analysis of covariance
6368:Ordinary least squares
6292:Pearson product-moment
5696:Statistical functional
5607:Empirical distribution
5440:Controlled experiments
5169:Frequency distribution
4947:Descriptive statistics
4848:Aberson, C.L. (2010).
4524:10.1002/sim.4780110811
4516:Statistics in Medicine
4254:
4227:
4197:
4155:
4125:
4098:
4071:
4036:
4007:
3965:
3935:
3914:and the definition of
3908:
3885:Monte Carlo simulation
3870:
3749:
3714:
3687:
3659:
3553:
3526:
3500:
3472:
3441:
3419:
3326:
3299:
3255:
3228:
3146:
2621:
2594:
2567:
2540:
2511:
2478:
2449:
2372:
2328:
2308:
2268:
2238:
2211:
2189:Student t-distribution
2166:
2128:
2110:
2039:
1999:
1970:
1793:
1741:
1679:
1647:
1616:
1560:
1540:
1513:
1483:
1246:clinically significant
1221:significance criterion
1219:For a given test, the
1189:
1155:
1109:
1082:
1029:
1000:
970:
942:likelihood ratio tests
919:frequentist statistics
900:effect of a given size
856:
825:
794:
767:
736:
709:
682:
644:
594:
556:
525:
496:
475:Probability to reject
461:
434:
399:
372:
341:
314:
290:
219:statistical population
174:
173:{\displaystyle \beta }
154:
128:
105:alternative hypothesis
97:
7091:Population statistics
7033:System identification
6767:Autocorrelation (ACF)
6695:Exponential smoothing
6609:Discriminant analysis
6604:Canonical correlation
6468:Partition of variance
6330:Regression validation
6174:(Jonckheere–Terpstra)
6073:Likelihood-ratio test
5762:Frequentist inference
5674:Location–scale family
5595:Sampling distribution
5560:Statistical inference
5527:Cross-sectional study
5514:Observational studies
5473:Randomized experiment
5302:Stem-and-leaf display
5104:Central limit theorem
4564:10.1002/9780470377963
4255:
4228:
4226:{\displaystyle T_{n}}
4198:
4156:
4154:{\displaystyle D_{n}}
4126:
4099:
4097:{\displaystyle T_{n}}
4072:
4037:
4035:{\displaystyle T_{n}}
4008:
3966:
3964:{\displaystyle D_{n}}
3936:
3934:{\displaystyle T_{n}}
3909:
3907:{\displaystyle D_{n}}
3871:
3750:
3715:
3688:
3660:
3554:
3527:
3501:
3473:
3442:
3420:
3327:
3300:
3256:
3254:{\displaystyle H_{1}}
3229:
3147:
2622:
2620:{\displaystyle H_{1}}
2595:
2568:
2566:{\displaystyle T_{n}}
2541:
2512:
2479:
2477:{\displaystyle H_{1}}
2450:
2373:
2329:
2309:
2269:
2239:
2212:
2167:
2129:
2090:
2040:
2000:
1971:
1794:
1742:
1680:
1648:
1617:
1561:
1541:
1539:{\displaystyle B_{i}}
1514:
1512:{\displaystyle A_{i}}
1484:
1389:Further information:
1187:
1156:
1110:
1108:{\displaystyle s^{2}}
1083:
1030:
1001:
971:
857:
855:{\displaystyle H_{0}}
826:
824:{\displaystyle H_{1}}
795:
793:{\displaystyle H_{1}}
768:
766:{\displaystyle H_{0}}
742:only when the sample
737:
735:{\displaystyle H_{1}}
710:
708:{\displaystyle H_{0}}
683:
681:{\displaystyle H_{0}}
645:
643:{\displaystyle H_{0}}
595:
593:{\displaystyle H_{1}}
557:
555:{\displaystyle H_{0}}
526:
524:{\displaystyle H_{0}}
497:
495:{\displaystyle H_{0}}
462:
460:{\displaystyle H_{1}}
440:when the alternative
435:
433:{\displaystyle H_{0}}
400:
398:{\displaystyle H_{0}}
373:
371:{\displaystyle H_{0}}
342:
340:{\displaystyle H_{1}}
315:
313:{\displaystyle H_{0}}
272:
175:
155:
129:
127:{\displaystyle H_{1}}
98:
96:{\displaystyle H_{0}}
7014:Probabilistic design
6599:Principal components
6442:Exponential families
6394:Nonlinear regression
6373:General linear model
6335:Mixed effects models
6325:Errors and residuals
6302:Confounding variable
6204:Bayesian probability
6182:Van der Waerden test
6172:Ordered alternative
5937:Multiple comparisons
5816:Rao–Blackwellization
5779:Estimating equations
5735:Statistical distance
5453:Factorial experiment
4986:Arithmetic-Geometric
4761:Conservation Biology
4624:Ellis, Paul (2010).
4404:Neyman–Pearson lemma
4237:
4210:
4165:
4138:
4108:
4081:
4049:
4019:
3975:
3948:
3918:
3891:
3761:
3724:
3697:
3671:
3565:
3543:
3510:
3486:
3455:
3447:and the sample size
3431:
3338:
3309:
3273:
3238:
3157:
2633:
2604:
2577:
2550:
2521:
2488:
2461:
2384:
2352:
2318:
2278:
2251:
2221:
2195:
2140:
2055:
2013:
1982:
1809:
1751:
1692:
1657:
1630:
1570:
1550:
1523:
1496:
1467:
1119:
1092:
1039:
1013:
984:
960:
839:
808:
777:
750:
719:
692:
665:
627:
577:
539:
508:
479:
444:
417:
382:
355:
324:
297:
164:
138:
111:
80:
7086:Official statistics
7009:Methods engineering
6690:Seasonal adjustment
6458:Poisson regressions
6378:Bayesian regression
6317:Regression analysis
6297:Partial correlation
6269:Regression analysis
5868:Prediction interval
5863:Likelihood interval
5853:Confidence interval
5845:Interval estimation
5806:Unbiased estimators
5624:Model specification
5504:Up-and-down designs
5192:Partial correlation
5148:Index of dispersion
5066:Interquartile range
4774:1997ConBi..11..276T
4751:Thomas, L. (1997).
4233:that are above the
3879:Simulation solution
3263:normal distribution
2244:, we must find the
2210:{\displaystyle n-1}
2176:of the difference.
1674:
1368:"family-wise error"
1364:multiple hypotheses
1356:regression analysis
1352:nuisance parameters
1340:confidence interval
923:Bayesian statistics
872:multiple hypotheses
213:to assess, or make
207:Statistical testing
43:experimental design
7106:Spatial statistics
6986:Medical statistics
6886:First hitting time
6840:Whittle likelihood
6491:Degrees of freedom
6486:Multivariate ANOVA
6419:Heteroscedasticity
6231:Bayesian estimator
6196:Bayesian inference
6045:Kolmogorov–Smirnov
5930:Randomization test
5900:Testing hypotheses
5873:Tolerance interval
5784:Maximum likelihood
5679:Exponential family
5612:Density estimation
5572:Statistical theory
5532:Natural experiment
5478:Scientific control
5395:Survey methodology
5081:Standard deviation
4378:Mathematics portal
4352:R package WebPower
4250:
4223:
4193:
4151:
4121:
4094:
4067:
4032:
4003:
3961:
3931:
3904:
3866:
3745:
3710:
3683:
3655:
3549:
3522:
3496:
3468:
3437:
3415:
3322:
3295:
3251:
3224:
3142:
3140:
2617:
2590:
2563:
2536:
2507:
2474:
2445:
2368:
2324:
2304:
2264:
2234:
2207:
2174:standard deviation
2162:
2124:
2049:of the difference
2035:
1995:
1966:
1789:
1737:
1675:
1660:
1643:
1612:
1556:
1536:
1509:
1479:
1456:using a one-sided
1260:), as well as the
1251:The nature of the
1190:
1151:
1105:
1078:
1025:
1008:significance level
996:
966:
934:nonparametric test
912:replication crisis
880:research questions
852:
831:, that the sample
821:
790:
763:
732:
705:
678:
652:significance level
640:
590:
552:
521:
492:
457:
430:
395:
368:
337:
310:
291:
182:type II error
170:
150:
124:
93:
47:hypothesis testing
7208:
7207:
7146:
7145:
7142:
7141:
7081:National accounts
7051:Actuarial science
7043:Social statistics
6936:
6935:
6932:
6931:
6928:
6927:
6863:Survival function
6848:
6847:
6710:Granger causality
6551:Contingency table
6526:Survival analysis
6503:
6502:
6499:
6498:
6355:Linear regression
6250:
6249:
6246:
6245:
6221:Credible interval
6190:
6189:
5973:
5972:
5789:Method of moments
5658:Parametric family
5619:Statistical model
5549:
5548:
5545:
5544:
5463:Random assignment
5385:Statistical power
5319:
5318:
5315:
5314:
5164:Contingency table
5134:
5133:
5001:Generalized/power
4859:978-1-84872-835-6
4573:978-0-470-37796-3
3593:
3573:
3552:{\displaystyle B}
3405:
3402:
3286:
3222:
3219:
3200:
3173:
3116:
3106:
3102:
3099:
3080:
3053:
3050:
3031:
3004:
2945:
2935:
2925:
2922:
2903:
2876:
2817:
2807:
2797:
2794:
2775:
2748:
2695:
2685:
2347:quantile function
2180:Analytic solution
2153:
2088:
2068:
2026:
1961:
1958:
1939:
1912:
1894:
1891:
1872:
1838:
1559:{\displaystyle i}
1391:Post hoc analysis
1372:Bonferroni method
1171:one sample t-test
1073:
978:two-sample t-test
969:{\displaystyle n}
610:
609:
285:shows power, 1 −
70:power of the test
16:(Redirected from
7228:
7196:
7195:
7184:
7183:
7173:
7172:
7158:
7157:
7061:Crime statistics
6955:
6954:
6942:
6941:
6859:
6858:
6825:Fourier analysis
6812:Frequency domain
6792:
6739:
6705:Structural break
6665:
6664:
6614:Cluster analysis
6561:Log-linear model
6534:
6533:
6509:
6508:
6450:
6424:Homoscedasticity
6280:
6279:
6256:
6255:
6175:
6167:
6159:
6158:(Kruskal–Wallis)
6143:
6128:
6083:Cross validation
6068:
6050:Anderson–Darling
5997:
5984:
5983:
5955:Likelihood-ratio
5947:Parametric tests
5925:Permutation test
5908:1- & 2-tails
5799:Minimum distance
5771:Point estimation
5767:
5766:
5718:Optimal decision
5669:
5568:
5567:
5555:
5554:
5537:Quasi-experiment
5487:Adaptive designs
5338:
5337:
5325:
5324:
5202:Rank correlation
4964:
4963:
4955:
4954:
4942:
4941:
4909:
4902:
4895:
4886:
4885:
4876:
4863:
4844:
4814:
4813:
4811:
4800:
4794:
4793:
4757:
4748:
4742:
4741:
4719:
4708:
4707:
4706:. November 2017.
4696:
4690:
4689:
4681:
4675:
4674:
4646:
4640:
4639:
4621:
4615:
4614:
4596:
4590:
4584:
4578:
4577:
4549:
4543:
4542:
4511:
4505:
4504:
4494:
4484:
4460:
4454:
4453:
4451:
4449:
4435:
4415:
4380:
4375:
4374:
4259:
4257:
4256:
4251:
4249:
4248:
4232:
4230:
4229:
4224:
4222:
4221:
4202:
4200:
4199:
4194:
4189:
4188:
4160:
4158:
4157:
4152:
4150:
4149:
4130:
4128:
4127:
4122:
4120:
4119:
4103:
4101:
4100:
4095:
4093:
4092:
4076:
4074:
4073:
4068:
4041:
4039:
4038:
4033:
4031:
4030:
4012:
4010:
4009:
4004:
3999:
3998:
3970:
3968:
3967:
3962:
3960:
3959:
3940:
3938:
3937:
3932:
3930:
3929:
3913:
3911:
3910:
3905:
3903:
3902:
3875:
3873:
3872:
3867:
3859:
3858:
3853:
3849:
3827:
3826:
3821:
3817:
3816:
3812:
3797:
3796:
3755:, a sample size
3754:
3752:
3751:
3746:
3719:
3717:
3716:
3711:
3709:
3708:
3692:
3690:
3689:
3684:
3664:
3662:
3661:
3656:
3651:
3647:
3646:
3642:
3618:
3617:
3594:
3589:
3588:
3579:
3574:
3569:
3558:
3556:
3555:
3550:
3531:
3529:
3528:
3523:
3505:
3503:
3502:
3497:
3477:
3475:
3474:
3469:
3467:
3466:
3450:
3446:
3444:
3443:
3438:
3424:
3422:
3421:
3416:
3411:
3407:
3406:
3404:
3403:
3398:
3396:
3391:
3390:
3377:
3331:
3329:
3328:
3323:
3321:
3320:
3304:
3302:
3301:
3296:
3294:
3293:
3288:
3287:
3279:
3269:. The estimated
3268:
3260:
3258:
3257:
3252:
3250:
3249:
3233:
3231:
3230:
3225:
3223:
3221:
3220:
3215:
3213:
3208:
3207:
3202:
3201:
3193:
3188:
3181:
3180:
3175:
3174:
3166:
3161:
3151:
3149:
3148:
3143:
3141:
3137:
3133:
3126:
3125:
3114:
3113:
3112:
3104:
3103:
3101:
3100:
3095:
3093:
3088:
3087:
3082:
3081:
3073:
3065:
3054:
3052:
3051:
3046:
3044:
3039:
3038:
3033:
3032:
3024:
3019:
3012:
3011:
3006:
3005:
2997:
2992:
2970:
2966:
2962:
2955:
2954:
2943:
2942:
2941:
2933:
2926:
2924:
2923:
2918:
2916:
2911:
2910:
2905:
2904:
2896:
2891:
2884:
2883:
2878:
2877:
2869:
2864:
2842:
2838:
2834:
2827:
2826:
2815:
2814:
2813:
2805:
2798:
2796:
2795:
2790:
2788:
2783:
2782:
2777:
2776:
2768:
2763:
2756:
2755:
2750:
2749:
2741:
2736:
2720:
2716:
2712:
2705:
2704:
2693:
2692:
2691:
2683:
2676:
2675:
2626:
2624:
2623:
2618:
2616:
2615:
2599:
2597:
2596:
2591:
2589:
2588:
2572:
2570:
2569:
2564:
2562:
2561:
2545:
2543:
2542:
2537:
2516:
2514:
2513:
2508:
2500:
2499:
2483:
2481:
2480:
2475:
2473:
2472:
2454:
2452:
2451:
2446:
2425:
2424:
2409:
2408:
2396:
2395:
2377:
2375:
2374:
2369:
2367:
2366:
2341:
2337:
2333:
2331:
2330:
2325:
2313:
2311:
2310:
2305:
2303:
2302:
2290:
2289:
2273:
2271:
2270:
2265:
2263:
2262:
2243:
2241:
2240:
2235:
2216:
2214:
2213:
2208:
2171:
2169:
2168:
2163:
2161:
2160:
2155:
2154:
2146:
2133:
2131:
2130:
2125:
2120:
2119:
2109:
2104:
2089:
2081:
2076:
2075:
2070:
2069:
2061:
2044:
2042:
2041:
2036:
2034:
2033:
2028:
2027:
2019:
2008:
2004:
2002:
2001:
1996:
1994:
1993:
1975:
1973:
1972:
1967:
1962:
1960:
1959:
1954:
1952:
1947:
1946:
1941:
1940:
1932:
1927:
1920:
1919:
1914:
1913:
1905:
1900:
1895:
1893:
1892:
1887:
1885:
1880:
1879:
1874:
1873:
1865:
1860:
1859:
1858:
1846:
1845:
1840:
1839:
1831:
1826:
1821:
1820:
1798:
1796:
1795:
1790:
1776:
1775:
1763:
1762:
1746:
1744:
1743:
1738:
1730:
1729:
1717:
1716:
1704:
1703:
1684:
1682:
1681:
1676:
1673:
1668:
1652:
1650:
1649:
1644:
1642:
1641:
1621:
1619:
1618:
1613:
1608:
1607:
1595:
1594:
1582:
1581:
1565:
1563:
1562:
1557:
1545:
1543:
1542:
1537:
1535:
1534:
1518:
1516:
1515:
1510:
1508:
1507:
1488:
1486:
1485:
1480:
1337:
1316:
1312:
1308:
1160:
1158:
1157:
1152:
1150:
1149:
1137:
1136:
1114:
1112:
1111:
1106:
1104:
1103:
1087:
1085:
1084:
1079:
1074:
1072:
1071:
1062:
1061:
1052:
1034:
1032:
1031:
1026:
1005:
1003:
1002:
997:
980:with power 80% (
975:
973:
972:
967:
876:power of a study
861:
859:
858:
853:
851:
850:
830:
828:
827:
822:
820:
819:
799:
797:
796:
791:
789:
788:
772:
770:
769:
764:
762:
761:
741:
739:
738:
733:
731:
730:
714:
712:
711:
706:
704:
703:
687:
685:
684:
679:
677:
676:
649:
647:
646:
641:
639:
638:
599:
597:
596:
591:
589:
588:
561:
559:
558:
553:
551:
550:
530:
528:
527:
522:
520:
519:
501:
499:
498:
493:
491:
490:
470:
469:
466:
464:
463:
458:
456:
455:
439:
437:
436:
431:
429:
428:
404:
402:
401:
396:
394:
393:
377:
375:
374:
369:
367:
366:
346:
344:
343:
338:
336:
335:
319:
317:
316:
311:
309:
308:
284:
280:
277:is shown as the
179:
177:
176:
171:
159:
157:
156:
151:
133:
131:
130:
125:
123:
122:
102:
100:
99:
94:
92:
91:
21:
7236:
7235:
7231:
7230:
7229:
7227:
7226:
7225:
7211:
7210:
7209:
7204:
7167:
7138:
7100:
7037:
7023:quality control
6990:
6972:Clinical trials
6949:
6924:
6908:
6896:Hazard function
6890:
6844:
6806:
6790:
6753:
6749:Breusch–Godfrey
6737:
6714:
6654:
6629:Factor analysis
6575:
6556:Graphical model
6528:
6495:
6462:
6448:
6428:
6382:
6349:
6311:
6274:
6273:
6242:
6186:
6173:
6165:
6157:
6141:
6126:
6105:Rank statistics
6099:
6078:Model selection
6066:
6024:Goodness of fit
6018:
5995:
5969:
5941:
5894:
5839:
5828:Median unbiased
5756:
5667:
5600:Order statistic
5562:
5541:
5508:
5482:
5434:
5389:
5332:
5330:Data collection
5311:
5223:
5178:
5152:
5130:
5090:
5042:
4959:Continuous data
4949:
4936:
4918:
4913:
4874:
4870:
4860:
4841:
4822:
4817:
4809:
4801:
4797:
4755:
4749:
4745:
4720:
4711:
4698:
4697:
4693:
4682:
4678:
4647:
4643:
4636:
4622:
4618:
4611:
4597:
4593:
4585:
4581:
4574:
4550:
4546:
4512:
4508:
4475:(1): e3002423.
4461:
4457:
4447:
4445:
4437:
4436:
4432:
4428:
4413:
4376:
4369:
4366:
4313:
4292:
4275:
4270:
4244:
4240:
4238:
4235:
4234:
4217:
4213:
4211:
4208:
4207:
4184:
4180:
4166:
4163:
4162:
4145:
4141:
4139:
4136:
4135:
4115:
4111:
4109:
4106:
4105:
4088:
4084:
4082:
4079:
4078:
4050:
4047:
4046:
4045:3. Compute the
4026:
4022:
4020:
4017:
4016:
3994:
3990:
3976:
3973:
3972:
3955:
3951:
3949:
3946:
3945:
3925:
3921:
3919:
3916:
3915:
3898:
3894:
3892:
3889:
3888:
3881:
3854:
3839:
3835:
3834:
3822:
3802:
3798:
3789:
3785:
3778:
3774:
3773:
3762:
3759:
3758:
3725:
3722:
3721:
3704:
3700:
3698:
3695:
3694:
3693:and we believe
3672:
3669:
3668:
3623:
3619:
3610:
3606:
3599:
3595:
3584:
3580:
3578:
3568:
3566:
3563:
3562:
3544:
3541:
3540:
3532:so the null is
3511:
3508:
3507:
3487:
3484:
3483:
3462:
3458:
3456:
3453:
3452:
3448:
3432:
3429:
3428:
3397:
3392:
3386:
3382:
3381:
3376:
3369:
3365:
3339:
3336:
3335:
3316:
3312:
3310:
3307:
3306:
3289:
3278:
3277:
3276:
3274:
3271:
3270:
3266:
3245:
3241:
3239:
3236:
3235:
3214:
3209:
3203:
3192:
3191:
3190:
3189:
3176:
3165:
3164:
3163:
3162:
3160:
3158:
3155:
3154:
3139:
3138:
3121:
3117:
3108:
3107:
3094:
3089:
3083:
3072:
3071:
3070:
3069:
3064:
3045:
3040:
3034:
3023:
3022:
3021:
3020:
3007:
2996:
2995:
2994:
2993:
2991:
2990:
2986:
2968:
2967:
2950:
2946:
2937:
2936:
2917:
2912:
2906:
2895:
2894:
2893:
2892:
2879:
2868:
2867:
2866:
2865:
2863:
2862:
2858:
2840:
2839:
2822:
2818:
2809:
2808:
2789:
2784:
2778:
2767:
2766:
2765:
2764:
2751:
2740:
2739:
2738:
2737:
2735:
2734:
2730:
2718:
2717:
2700:
2696:
2687:
2686:
2671:
2667:
2666:
2662:
2652:
2636:
2634:
2631:
2630:
2611:
2607:
2605:
2602:
2601:
2584:
2580:
2578:
2575:
2574:
2557:
2553:
2551:
2548:
2547:
2522:
2519:
2518:
2495:
2491:
2489:
2486:
2485:
2468:
2464:
2462:
2459:
2458:
2417:
2413:
2404:
2400:
2391:
2387:
2385:
2382:
2381:
2359:
2355:
2353:
2350:
2349:
2339:
2335:
2319:
2316:
2315:
2298:
2294:
2285:
2281:
2279:
2276:
2275:
2258:
2254:
2252:
2249:
2248:
2222:
2219:
2218:
2196:
2193:
2192:
2182:
2156:
2145:
2144:
2143:
2141:
2138:
2137:
2115:
2111:
2105:
2094:
2080:
2071:
2060:
2059:
2058:
2056:
2053:
2052:
2029:
2018:
2017:
2016:
2014:
2011:
2010:
2006:
1989:
1985:
1983:
1980:
1979:
1953:
1948:
1942:
1931:
1930:
1929:
1928:
1915:
1904:
1903:
1902:
1901:
1899:
1886:
1881:
1875:
1864:
1863:
1862:
1861:
1854:
1850:
1841:
1830:
1829:
1828:
1827:
1825:
1816:
1812:
1810:
1807:
1806:
1771:
1767:
1758:
1754:
1752:
1749:
1748:
1725:
1721:
1712:
1708:
1699:
1695:
1693:
1690:
1689:
1669:
1664:
1658:
1655:
1654:
1637:
1633:
1631:
1628:
1627:
1603:
1599:
1590:
1586:
1577:
1573:
1571:
1568:
1567:
1551:
1548:
1547:
1530:
1526:
1524:
1521:
1520:
1503:
1499:
1497:
1494:
1493:
1468:
1465:
1464:
1453:
1393:
1387:
1335:
1314:
1310:
1306:
1291:adverse effects
1287:clinical trials
1282:
1182:
1145:
1141:
1132:
1128:
1120:
1117:
1116:
1099:
1095:
1093:
1090:
1089:
1067:
1063:
1057:
1053:
1051:
1040:
1037:
1036:
1014:
1011:
1010:
985:
982:
981:
961:
958:
957:
952:Lehr's (rough)
950:
930:parametric test
888:
870:the case where
846:
842:
840:
837:
836:
815:
811:
809:
806:
805:
784:
780:
778:
775:
774:
757:
753:
751:
748:
747:
726:
722:
720:
717:
716:
699:
695:
693:
690:
689:
672:
668:
666:
663:
662:
634:
630:
628:
625:
624:
584:
580:
578:
575:
574:
546:
542:
540:
537:
536:
515:
511:
509:
506:
505:
486:
482:
480:
477:
476:
451:
447:
445:
442:
441:
424:
420:
418:
415:
414:
389:
385:
383:
380:
379:
362:
358:
356:
353:
352:
331:
327:
325:
322:
321:
304:
300:
298:
295:
294:
282:
278:
267:
261:
209:uses data from
204:
198:
165:
162:
161:
139:
136:
135:
118:
114:
112:
109:
108:
87:
83:
81:
78:
77:
74:null hypothesis
66:hypothesis test
28:
23:
22:
18:Power of a test
15:
12:
11:
5:
7234:
7224:
7223:
7206:
7205:
7203:
7202:
7190:
7178:
7164:
7151:
7148:
7147:
7144:
7143:
7140:
7139:
7137:
7136:
7131:
7126:
7121:
7116:
7110:
7108:
7102:
7101:
7099:
7098:
7093:
7088:
7083:
7078:
7073:
7068:
7063:
7058:
7053:
7047:
7045:
7039:
7038:
7036:
7035:
7030:
7025:
7016:
7011:
7006:
7000:
6998:
6992:
6991:
6989:
6988:
6983:
6978:
6969:
6967:Bioinformatics
6963:
6961:
6951:
6950:
6938:
6937:
6934:
6933:
6930:
6929:
6926:
6925:
6923:
6922:
6916:
6914:
6910:
6909:
6907:
6906:
6900:
6898:
6892:
6891:
6889:
6888:
6883:
6878:
6873:
6867:
6865:
6856:
6850:
6849:
6846:
6845:
6843:
6842:
6837:
6832:
6827:
6822:
6816:
6814:
6808:
6807:
6805:
6804:
6799:
6794:
6786:
6781:
6776:
6775:
6774:
6772:partial (PACF)
6763:
6761:
6755:
6754:
6752:
6751:
6746:
6741:
6733:
6728:
6722:
6720:
6719:Specific tests
6716:
6715:
6713:
6712:
6707:
6702:
6697:
6692:
6687:
6682:
6677:
6671:
6669:
6662:
6656:
6655:
6653:
6652:
6651:
6650:
6649:
6648:
6633:
6632:
6631:
6621:
6619:Classification
6616:
6611:
6606:
6601:
6596:
6591:
6585:
6583:
6577:
6576:
6574:
6573:
6568:
6566:McNemar's test
6563:
6558:
6553:
6548:
6542:
6540:
6530:
6529:
6505:
6504:
6501:
6500:
6497:
6496:
6494:
6493:
6488:
6483:
6478:
6472:
6470:
6464:
6463:
6461:
6460:
6444:
6438:
6436:
6430:
6429:
6427:
6426:
6421:
6416:
6411:
6406:
6404:Semiparametric
6401:
6396:
6390:
6388:
6384:
6383:
6381:
6380:
6375:
6370:
6365:
6359:
6357:
6351:
6350:
6348:
6347:
6342:
6337:
6332:
6327:
6321:
6319:
6313:
6312:
6310:
6309:
6304:
6299:
6294:
6288:
6286:
6276:
6275:
6272:
6271:
6266:
6260:
6252:
6251:
6248:
6247:
6244:
6243:
6241:
6240:
6239:
6238:
6228:
6223:
6218:
6217:
6216:
6211:
6200:
6198:
6192:
6191:
6188:
6187:
6185:
6184:
6179:
6178:
6177:
6169:
6161:
6145:
6142:(Mann–Whitney)
6137:
6136:
6135:
6122:
6121:
6120:
6109:
6107:
6101:
6100:
6098:
6097:
6096:
6095:
6090:
6085:
6075:
6070:
6067:(Shapiro–Wilk)
6062:
6057:
6052:
6047:
6042:
6034:
6028:
6026:
6020:
6019:
6017:
6016:
6008:
5999:
5987:
5981:
5979:Specific tests
5975:
5974:
5971:
5970:
5968:
5967:
5962:
5957:
5951:
5949:
5943:
5942:
5940:
5939:
5934:
5933:
5932:
5922:
5921:
5920:
5910:
5904:
5902:
5896:
5895:
5893:
5892:
5891:
5890:
5885:
5875:
5870:
5865:
5860:
5855:
5849:
5847:
5841:
5840:
5838:
5837:
5832:
5831:
5830:
5825:
5824:
5823:
5818:
5803:
5802:
5801:
5796:
5791:
5786:
5775:
5773:
5764:
5758:
5757:
5755:
5754:
5749:
5744:
5743:
5742:
5732:
5727:
5726:
5725:
5715:
5714:
5713:
5708:
5703:
5693:
5688:
5683:
5682:
5681:
5676:
5671:
5655:
5654:
5653:
5648:
5643:
5633:
5632:
5631:
5626:
5616:
5615:
5614:
5604:
5603:
5602:
5592:
5587:
5582:
5576:
5574:
5564:
5563:
5551:
5550:
5547:
5546:
5543:
5542:
5540:
5539:
5534:
5529:
5524:
5518:
5516:
5510:
5509:
5507:
5506:
5501:
5496:
5490:
5488:
5484:
5483:
5481:
5480:
5475:
5470:
5465:
5460:
5455:
5450:
5444:
5442:
5436:
5435:
5433:
5432:
5430:Standard error
5427:
5422:
5417:
5416:
5415:
5410:
5399:
5397:
5391:
5390:
5388:
5387:
5382:
5377:
5372:
5367:
5362:
5360:Optimal design
5357:
5352:
5346:
5344:
5334:
5333:
5321:
5320:
5317:
5316:
5313:
5312:
5310:
5309:
5304:
5299:
5294:
5289:
5284:
5279:
5274:
5269:
5264:
5259:
5254:
5249:
5244:
5239:
5233:
5231:
5225:
5224:
5222:
5221:
5216:
5215:
5214:
5209:
5199:
5194:
5188:
5186:
5180:
5179:
5177:
5176:
5171:
5166:
5160:
5158:
5157:Summary tables
5154:
5153:
5151:
5150:
5144:
5142:
5136:
5135:
5132:
5131:
5129:
5128:
5127:
5126:
5121:
5116:
5106:
5100:
5098:
5092:
5091:
5089:
5088:
5083:
5078:
5073:
5068:
5063:
5058:
5052:
5050:
5044:
5043:
5041:
5040:
5035:
5030:
5029:
5028:
5023:
5018:
5013:
5008:
5003:
4998:
4993:
4991:Contraharmonic
4988:
4983:
4972:
4970:
4961:
4951:
4950:
4938:
4937:
4935:
4934:
4929:
4923:
4920:
4919:
4912:
4911:
4904:
4897:
4889:
4883:
4882:
4869:
4868:External links
4866:
4865:
4864:
4858:
4845:
4839:
4821:
4818:
4816:
4815:
4795:
4768:(1): 276–280.
4743:
4709:
4691:
4676:
4657:(6): 609–616.
4641:
4635:978-0521142465
4634:
4616:
4609:
4591:
4579:
4572:
4544:
4506:
4455:
4429:
4427:
4424:
4423:
4422:
4416:
4407:
4401:
4395:
4389:
4382:
4381:
4365:
4362:
4361:
4360:
4353:
4350:
4347:
4344:
4341:
4334:
4327:
4312:
4309:
4305:clinical trial
4291:
4288:
4284:clinical trial
4274:
4273:Bayesian power
4271:
4269:
4266:
4247:
4243:
4220:
4216:
4192:
4187:
4183:
4179:
4176:
4173:
4170:
4148:
4144:
4118:
4114:
4091:
4087:
4066:
4063:
4060:
4057:
4054:
4042:for each set.
4029:
4025:
4002:
3997:
3993:
3989:
3986:
3983:
3980:
3958:
3954:
3928:
3924:
3901:
3897:
3880:
3877:
3865:
3862:
3857:
3852:
3848:
3845:
3842:
3838:
3833:
3830:
3825:
3820:
3815:
3811:
3808:
3805:
3801:
3795:
3792:
3788:
3784:
3781:
3777:
3772:
3769:
3766:
3744:
3741:
3738:
3735:
3732:
3729:
3707:
3703:
3682:
3679:
3676:
3654:
3650:
3645:
3641:
3638:
3635:
3632:
3629:
3626:
3622:
3616:
3613:
3609:
3605:
3602:
3598:
3592:
3587:
3583:
3577:
3572:
3548:
3539:We can invert
3521:
3518:
3515:
3495:
3491:
3465:
3461:
3436:
3414:
3410:
3401:
3395:
3389:
3385:
3380:
3375:
3372:
3368:
3364:
3361:
3358:
3355:
3352:
3349:
3346:
3343:
3319:
3315:
3292:
3285:
3282:
3248:
3244:
3218:
3212:
3206:
3199:
3196:
3187:
3184:
3179:
3172:
3169:
3136:
3132:
3129:
3124:
3120:
3111:
3098:
3092:
3086:
3079:
3076:
3068:
3063:
3060:
3057:
3049:
3043:
3037:
3030:
3027:
3018:
3015:
3010:
3003:
3000:
2989:
2985:
2982:
2979:
2976:
2973:
2971:
2969:
2965:
2961:
2958:
2953:
2949:
2940:
2932:
2929:
2921:
2915:
2909:
2902:
2899:
2890:
2887:
2882:
2875:
2872:
2861:
2857:
2854:
2851:
2848:
2845:
2843:
2841:
2837:
2833:
2830:
2825:
2821:
2812:
2804:
2801:
2793:
2787:
2781:
2774:
2771:
2762:
2759:
2754:
2747:
2744:
2733:
2729:
2726:
2723:
2721:
2719:
2715:
2711:
2708:
2703:
2699:
2690:
2682:
2679:
2674:
2670:
2665:
2661:
2658:
2655:
2653:
2651:
2648:
2645:
2642:
2639:
2638:
2614:
2610:
2587:
2583:
2560:
2556:
2535:
2532:
2529:
2526:
2506:
2503:
2498:
2494:
2471:
2467:
2444:
2440:
2437:
2434:
2431:
2428:
2423:
2420:
2416:
2412:
2407:
2403:
2399:
2394:
2390:
2365:
2362:
2358:
2323:
2301:
2297:
2293:
2288:
2284:
2261:
2257:
2246:critical value
2232:
2229:
2226:
2206:
2203:
2200:
2181:
2178:
2172:is the sample
2159:
2152:
2149:
2123:
2118:
2114:
2108:
2103:
2100:
2097:
2093:
2087:
2084:
2079:
2074:
2067:
2064:
2032:
2025:
2022:
1992:
1988:
1965:
1957:
1951:
1945:
1938:
1935:
1926:
1923:
1918:
1911:
1908:
1898:
1890:
1884:
1878:
1871:
1868:
1857:
1853:
1849:
1844:
1837:
1834:
1824:
1819:
1815:
1801:test statistic
1788:
1785:
1782:
1779:
1774:
1770:
1766:
1761:
1757:
1736:
1733:
1728:
1724:
1720:
1715:
1711:
1707:
1702:
1698:
1672:
1667:
1663:
1640:
1636:
1611:
1606:
1602:
1598:
1593:
1589:
1585:
1580:
1576:
1555:
1533:
1529:
1506:
1502:
1478:
1475:
1472:
1452:
1449:
1386:
1376:
1281:
1278:
1266:sampling error
1217:
1216:
1205:
1202:
1201:criterion used
1181:
1178:
1148:
1144:
1140:
1135:
1131:
1127:
1124:
1102:
1098:
1077:
1070:
1066:
1060:
1056:
1050:
1047:
1044:
1024:
1021:
1018:
995:
992:
989:
965:
949:
946:
887:
884:
849:
845:
818:
814:
787:
783:
760:
756:
729:
725:
702:
698:
675:
671:
637:
633:
614:test statistic
608:
607:
604:
601:
587:
583:
570:
569:
566:
563:
549:
545:
532:
531:
518:
514:
502:
489:
485:
473:
454:
450:
427:
423:
392:
388:
365:
361:
334:
330:
307:
303:
260:
257:
256:
255:
252:
249:
200:Main article:
197:
194:
186:false negative
169:
149:
146:
143:
121:
117:
90:
86:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
7233:
7222:
7219:
7218:
7216:
7201:
7200:
7191:
7189:
7188:
7179:
7177:
7176:
7171:
7165:
7163:
7162:
7153:
7152:
7149:
7135:
7132:
7130:
7129:Geostatistics
7127:
7125:
7122:
7120:
7117:
7115:
7112:
7111:
7109:
7107:
7103:
7097:
7096:Psychometrics
7094:
7092:
7089:
7087:
7084:
7082:
7079:
7077:
7074:
7072:
7069:
7067:
7064:
7062:
7059:
7057:
7054:
7052:
7049:
7048:
7046:
7044:
7040:
7034:
7031:
7029:
7026:
7024:
7020:
7017:
7015:
7012:
7010:
7007:
7005:
7002:
7001:
6999:
6997:
6993:
6987:
6984:
6982:
6979:
6977:
6973:
6970:
6968:
6965:
6964:
6962:
6960:
6959:Biostatistics
6956:
6952:
6948:
6943:
6939:
6921:
6920:Log-rank test
6918:
6917:
6915:
6911:
6905:
6902:
6901:
6899:
6897:
6893:
6887:
6884:
6882:
6879:
6877:
6874:
6872:
6869:
6868:
6866:
6864:
6860:
6857:
6855:
6851:
6841:
6838:
6836:
6833:
6831:
6828:
6826:
6823:
6821:
6818:
6817:
6815:
6813:
6809:
6803:
6800:
6798:
6795:
6793:
6791:(Box–Jenkins)
6787:
6785:
6782:
6780:
6777:
6773:
6770:
6769:
6768:
6765:
6764:
6762:
6760:
6756:
6750:
6747:
6745:
6744:Durbin–Watson
6742:
6740:
6734:
6732:
6729:
6727:
6726:Dickey–Fuller
6724:
6723:
6721:
6717:
6711:
6708:
6706:
6703:
6701:
6700:Cointegration
6698:
6696:
6693:
6691:
6688:
6686:
6683:
6681:
6678:
6676:
6675:Decomposition
6673:
6672:
6670:
6666:
6663:
6661:
6657:
6647:
6644:
6643:
6642:
6639:
6638:
6637:
6634:
6630:
6627:
6626:
6625:
6622:
6620:
6617:
6615:
6612:
6610:
6607:
6605:
6602:
6600:
6597:
6595:
6592:
6590:
6587:
6586:
6584:
6582:
6578:
6572:
6569:
6567:
6564:
6562:
6559:
6557:
6554:
6552:
6549:
6547:
6546:Cohen's kappa
6544:
6543:
6541:
6539:
6535:
6531:
6527:
6523:
6519:
6515:
6510:
6506:
6492:
6489:
6487:
6484:
6482:
6479:
6477:
6474:
6473:
6471:
6469:
6465:
6459:
6455:
6451:
6445:
6443:
6440:
6439:
6437:
6435:
6431:
6425:
6422:
6420:
6417:
6415:
6412:
6410:
6407:
6405:
6402:
6400:
6399:Nonparametric
6397:
6395:
6392:
6391:
6389:
6385:
6379:
6376:
6374:
6371:
6369:
6366:
6364:
6361:
6360:
6358:
6356:
6352:
6346:
6343:
6341:
6338:
6336:
6333:
6331:
6328:
6326:
6323:
6322:
6320:
6318:
6314:
6308:
6305:
6303:
6300:
6298:
6295:
6293:
6290:
6289:
6287:
6285:
6281:
6277:
6270:
6267:
6265:
6262:
6261:
6257:
6253:
6237:
6234:
6233:
6232:
6229:
6227:
6224:
6222:
6219:
6215:
6212:
6210:
6207:
6206:
6205:
6202:
6201:
6199:
6197:
6193:
6183:
6180:
6176:
6170:
6168:
6162:
6160:
6154:
6153:
6152:
6149:
6148:Nonparametric
6146:
6144:
6138:
6134:
6131:
6130:
6129:
6123:
6119:
6118:Sample median
6116:
6115:
6114:
6111:
6110:
6108:
6106:
6102:
6094:
6091:
6089:
6086:
6084:
6081:
6080:
6079:
6076:
6074:
6071:
6069:
6063:
6061:
6058:
6056:
6053:
6051:
6048:
6046:
6043:
6041:
6039:
6035:
6033:
6030:
6029:
6027:
6025:
6021:
6015:
6013:
6009:
6007:
6005:
6000:
5998:
5993:
5989:
5988:
5985:
5982:
5980:
5976:
5966:
5963:
5961:
5958:
5956:
5953:
5952:
5950:
5948:
5944:
5938:
5935:
5931:
5928:
5927:
5926:
5923:
5919:
5916:
5915:
5914:
5911:
5909:
5906:
5905:
5903:
5901:
5897:
5889:
5886:
5884:
5881:
5880:
5879:
5876:
5874:
5871:
5869:
5866:
5864:
5861:
5859:
5856:
5854:
5851:
5850:
5848:
5846:
5842:
5836:
5833:
5829:
5826:
5822:
5819:
5817:
5814:
5813:
5812:
5809:
5808:
5807:
5804:
5800:
5797:
5795:
5792:
5790:
5787:
5785:
5782:
5781:
5780:
5777:
5776:
5774:
5772:
5768:
5765:
5763:
5759:
5753:
5750:
5748:
5745:
5741:
5738:
5737:
5736:
5733:
5731:
5728:
5724:
5723:loss function
5721:
5720:
5719:
5716:
5712:
5709:
5707:
5704:
5702:
5699:
5698:
5697:
5694:
5692:
5689:
5687:
5684:
5680:
5677:
5675:
5672:
5670:
5664:
5661:
5660:
5659:
5656:
5652:
5649:
5647:
5644:
5642:
5639:
5638:
5637:
5634:
5630:
5627:
5625:
5622:
5621:
5620:
5617:
5613:
5610:
5609:
5608:
5605:
5601:
5598:
5597:
5596:
5593:
5591:
5588:
5586:
5583:
5581:
5578:
5577:
5575:
5573:
5569:
5565:
5561:
5556:
5552:
5538:
5535:
5533:
5530:
5528:
5525:
5523:
5520:
5519:
5517:
5515:
5511:
5505:
5502:
5500:
5497:
5495:
5492:
5491:
5489:
5485:
5479:
5476:
5474:
5471:
5469:
5466:
5464:
5461:
5459:
5456:
5454:
5451:
5449:
5446:
5445:
5443:
5441:
5437:
5431:
5428:
5426:
5425:Questionnaire
5423:
5421:
5418:
5414:
5411:
5409:
5406:
5405:
5404:
5401:
5400:
5398:
5396:
5392:
5386:
5383:
5381:
5378:
5376:
5373:
5371:
5368:
5366:
5363:
5361:
5358:
5356:
5353:
5351:
5348:
5347:
5345:
5343:
5339:
5335:
5331:
5326:
5322:
5308:
5305:
5303:
5300:
5298:
5295:
5293:
5290:
5288:
5285:
5283:
5280:
5278:
5275:
5273:
5270:
5268:
5265:
5263:
5260:
5258:
5255:
5253:
5252:Control chart
5250:
5248:
5245:
5243:
5240:
5238:
5235:
5234:
5232:
5230:
5226:
5220:
5217:
5213:
5210:
5208:
5205:
5204:
5203:
5200:
5198:
5195:
5193:
5190:
5189:
5187:
5185:
5181:
5175:
5172:
5170:
5167:
5165:
5162:
5161:
5159:
5155:
5149:
5146:
5145:
5143:
5141:
5137:
5125:
5122:
5120:
5117:
5115:
5112:
5111:
5110:
5107:
5105:
5102:
5101:
5099:
5097:
5093:
5087:
5084:
5082:
5079:
5077:
5074:
5072:
5069:
5067:
5064:
5062:
5059:
5057:
5054:
5053:
5051:
5049:
5045:
5039:
5036:
5034:
5031:
5027:
5024:
5022:
5019:
5017:
5014:
5012:
5009:
5007:
5004:
5002:
4999:
4997:
4994:
4992:
4989:
4987:
4984:
4982:
4979:
4978:
4977:
4974:
4973:
4971:
4969:
4965:
4962:
4960:
4956:
4952:
4948:
4943:
4939:
4933:
4930:
4928:
4925:
4924:
4921:
4917:
4910:
4905:
4903:
4898:
4896:
4891:
4890:
4887:
4881:
4877:
4872:
4871:
4861:
4855:
4852:. Routledge.
4851:
4846:
4842:
4840:0-8058-0283-5
4836:
4832:
4828:
4824:
4823:
4808:
4807:
4799:
4791:
4787:
4783:
4779:
4775:
4771:
4767:
4763:
4762:
4754:
4747:
4739:
4735:
4731:
4727:
4726:
4718:
4716:
4714:
4705:
4701:
4695:
4687:
4680:
4672:
4668:
4664:
4660:
4656:
4652:
4645:
4637:
4631:
4627:
4620:
4612:
4610:0-521-81099-X
4606:
4602:
4595:
4589:
4583:
4575:
4569:
4565:
4561:
4557:
4556:
4548:
4541:
4537:
4533:
4529:
4525:
4521:
4517:
4510:
4502:
4498:
4493:
4488:
4483:
4478:
4474:
4470:
4466:
4459:
4444:
4440:
4434:
4430:
4420:
4417:
4411:
4408:
4405:
4402:
4399:
4396:
4393:
4390:
4387:
4384:
4383:
4379:
4373:
4368:
4358:
4354:
4351:
4349:R package pwr
4348:
4345:
4342:
4339:
4335:
4332:
4328:
4325:
4321:
4318:
4317:
4316:
4308:
4306:
4302:
4297:
4287:
4285:
4280:
4265:
4261:
4245:
4241:
4218:
4214:
4204:
4185:
4181:
4177:
4174:
4168:
4146:
4142:
4132:
4116:
4112:
4089:
4085:
4061:
4058:
4055:
4043:
4027:
4023:
4013:
3995:
3991:
3987:
3984:
3978:
3956:
3952:
3942:
3926:
3922:
3899:
3895:
3886:
3876:
3863:
3860:
3855:
3850:
3846:
3843:
3840:
3836:
3831:
3828:
3823:
3818:
3813:
3809:
3806:
3803:
3799:
3793:
3790:
3782:
3779:
3775:
3770:
3767:
3764:
3756:
3742:
3739:
3733:
3727:
3705:
3701:
3680:
3677:
3674:
3665:
3652:
3648:
3643:
3636:
3630:
3627:
3624:
3620:
3614:
3611:
3603:
3600:
3596:
3590:
3585:
3581:
3575:
3570:
3560:
3546:
3537:
3535:
3519:
3516:
3513:
3493:
3489:
3481:
3463:
3459:
3434:
3425:
3412:
3408:
3399:
3393:
3387:
3383:
3378:
3373:
3370:
3366:
3359:
3356:
3353:
3347:
3341:
3333:
3317:
3313:
3290:
3280:
3264:
3246:
3242:
3216:
3210:
3204:
3194:
3185:
3182:
3177:
3167:
3152:
3134:
3130:
3127:
3122:
3118:
3096:
3090:
3084:
3074:
3066:
3061:
3058:
3055:
3047:
3041:
3035:
3025:
3016:
3013:
3008:
2998:
2987:
2980:
2977:
2974:
2972:
2963:
2959:
2956:
2951:
2947:
2930:
2927:
2919:
2913:
2907:
2897:
2888:
2885:
2880:
2870:
2859:
2852:
2849:
2846:
2844:
2835:
2831:
2828:
2823:
2819:
2802:
2799:
2791:
2785:
2779:
2769:
2760:
2757:
2752:
2742:
2731:
2724:
2722:
2713:
2709:
2706:
2701:
2697:
2680:
2677:
2672:
2668:
2663:
2656:
2654:
2646:
2640:
2628:
2612:
2608:
2585:
2581:
2558:
2554:
2530:
2524:
2504:
2501:
2496:
2492:
2469:
2465:
2455:
2442:
2438:
2435:
2429:
2421:
2418:
2410:
2405:
2401:
2397:
2392:
2388:
2379:
2363:
2360:
2348:
2345:
2344:corresponding
2321:
2299:
2295:
2291:
2286:
2282:
2259:
2255:
2247:
2230:
2227:
2224:
2204:
2201:
2198:
2190:
2185:
2177:
2175:
2157:
2147:
2134:
2121:
2116:
2112:
2106:
2101:
2098:
2095:
2091:
2085:
2082:
2077:
2072:
2062:
2050:
2048:
2030:
2020:
1990:
1986:
1976:
1963:
1955:
1949:
1943:
1933:
1924:
1921:
1916:
1906:
1896:
1888:
1882:
1876:
1866:
1855:
1851:
1847:
1842:
1832:
1822:
1817:
1813:
1804:
1802:
1786:
1783:
1780:
1777:
1772:
1768:
1764:
1759:
1755:
1734:
1731:
1726:
1722:
1718:
1713:
1709:
1705:
1700:
1696:
1686:
1670:
1665:
1661:
1653:and variance
1638:
1634:
1625:
1609:
1604:
1600:
1596:
1591:
1587:
1583:
1578:
1574:
1553:
1531:
1527:
1504:
1500:
1490:
1476:
1473:
1470:
1462:
1459:
1448:
1446:
1442:
1438:
1434:
1430:
1426:
1424:
1419:
1414:
1410:
1406:
1402:
1398:
1392:
1384:
1380:
1375:
1373:
1369:
1365:
1360:
1357:
1353:
1348:
1346:
1345:meta-analysis
1341:
1333:
1329:
1323:
1320:
1319:Medical tests
1302:
1300:
1296:
1292:
1288:
1277:
1275:
1271:
1267:
1263:
1259:
1254:
1249:
1247:
1242:
1238:
1234:
1229:
1227:
1222:
1214:
1210:
1206:
1203:
1200:
1196:
1195:
1194:
1186:
1177:
1174:
1172:
1167:
1165:
1146:
1142:
1138:
1133:
1129:
1125:
1122:
1100:
1096:
1075:
1068:
1064:
1058:
1054:
1048:
1045:
1042:
1022:
1019:
1016:
1009:
993:
990:
987:
979:
963:
955:
954:rule of thumb
945:
943:
939:
935:
931:
926:
924:
920:
915:
913:
909:
903:
901:
897:
893:
892:pilot studies
883:
881:
877:
873:
868:
863:
847:
843:
834:
816:
812:
803:
785:
781:
758:
754:
745:
727:
723:
700:
696:
673:
669:
660:
656:
653:
635:
631:
622:
618:
615:
605:
602:
585:
581:
572:
571:
567:
564:
547:
543:
534:
533:
516:
512:
503:
487:
483:
474:
472:
471:
468:
452:
448:
425:
421:
412:
408:
390:
386:
363:
359:
350:
332:
328:
305:
301:
288:
276:
271:
266:
253:
250:
247:
246:
245:
242:
238:
235:
231:
226:
224:
220:
216:
212:
208:
203:
193:
191:
187:
183:
167:
147:
144:
141:
119:
115:
106:
88:
84:
75:
71:
67:
62:
60:
56:
52:
48:
44:
40:
36:
33:
19:
7197:
7185:
7166:
7159:
7071:Econometrics
7021: /
7004:Chemometrics
6981:Epidemiology
6974: /
6947:Applications
6789:ARIMA model
6736:Q-statistic
6685:Stationarity
6581:Multivariate
6524: /
6520: /
6518:Multivariate
6516: /
6456: /
6452: /
6226:Bayes factor
6125:Signed rank
6037:
6011:
6003:
5991:
5912:
5686:Completeness
5522:Cohort study
5420:Opinion poll
5355:Missing data
5342:Study design
5297:Scatter plot
5219:Scatter plot
5212:Spearman's ρ
5174:Grouped data
4849:
4830:
4805:
4798:
4765:
4759:
4746:
4732:(1): 19–24.
4729:
4723:
4703:
4694:
4685:
4679:
4654:
4650:
4644:
4625:
4619:
4600:
4594:
4582:
4554:
4547:
4515:
4509:
4472:
4469:PLOS Biology
4468:
4458:
4448:30 September
4446:. Retrieved
4442:
4433:
4314:
4293:
4276:
4262:
4205:
4133:
4044:
4014:
3943:
3882:
3757:
3666:
3561:
3538:
3533:
3426:
3334:
3153:
2629:
2573:being above
2456:
2380:
2186:
2183:
2135:
2051:
1977:
1805:
1687:
1491:
1454:
1444:
1440:
1436:
1432:
1428:
1422:
1417:
1412:
1404:
1400:
1396:
1394:
1382:
1378:
1361:
1349:
1324:
1303:
1283:
1252:
1250:
1232:
1230:
1220:
1218:
1191:
1175:
1168:
951:
927:
916:
904:
889:
886:Applications
875:
864:
832:
801:
743:
715:in favor of
658:
654:
650:. A desired
616:
611:
410:
406:
348:
292:
286:
274:
243:
239:
227:
205:
69:
63:
38:
29:
7199:WikiProject
7114:Cartography
7076:Jurimetrics
7028:Reliability
6759:Time domain
6738:(Ljung–Box)
6660:Time-series
6538:Categorical
6522:Time-series
6514:Categorical
6449:(Bernoulli)
6284:Correlation
6264:Correlation
6060:Jarque–Bera
6032:Chi-squared
5794:M-estimator
5747:Asymptotics
5691:Sufficiency
5458:Interaction
5370:Replication
5350:Effect size
5307:Violin plot
5287:Radar chart
5267:Forest plot
5257:Correlogram
5207:Kendall's τ
4410:Sample size
4392:Effect size
4296:frequentist
4279:frequentist
2484:is true so
2047:sample mean
1332:correlation
1237:effect size
1213:variability
1035:should be:
896:sample size
867:sensitivity
603:1-β (power)
259:Description
230:t-statistic
223:mean values
190:conditional
103:) when the
59:effect size
57:), and the
55:sample size
32:frequentist
7066:Demography
6784:ARMA model
6589:Regression
6166:(Friedman)
6127:(Wilcoxon)
6065:Normality
6055:Lilliefors
6002:Student's
5878:Resampling
5752:Robustness
5740:divergence
5730:Efficiency
5668:(monotone)
5663:Likelihood
5580:Population
5413:Stratified
5365:Population
5184:Dependence
5140:Count data
5071:Percentile
5048:Dispersion
4981:Arithmetic
4916:Statistics
4812:. SUGI 24.
4426:References
4398:Efficiency
3536:rejected.
3265:for large
1445:relatively
1309:-risk and
1280:Discussion
1274:efficiency
1241:hypothesis
263:See also:
215:inferences
196:Background
35:statistics
6447:Logistic
6214:posterior
6140:Rank sum
5888:Jackknife
5883:Bootstrap
5701:Bootstrap
5636:Parameter
5585:Statistic
5380:Statistic
5292:Run chart
5277:Pie chart
5272:Histogram
5262:Fan chart
5237:Bar chart
5119:L-moments
5006:Geometric
4827:Cohen, J.
4790:10023/679
4532:0277-6715
4307:designs.
4268:Extension
4246:α
4182:σ
4175:θ
4117:α
4062:α
4059:−
3992:σ
3861:≈
3829:≈
3807:−
3791:−
3787:Φ
3783:−
3734:θ
3702:σ
3675:θ
3637:θ
3628:−
3612:−
3608:Φ
3604:−
3591:θ
3582:σ
3514:α
3490:α
3460:σ
3435:θ
3384:σ
3379:θ
3374:−
3363:Φ
3360:−
3354:≈
3348:θ
3314:σ
3284:^
3281:σ
3198:^
3195:σ
3186:θ
3183:−
3171:¯
3131:θ
3119:μ
3078:^
3075:σ
3067:θ
3062:−
3029:^
3026:σ
3017:θ
3014:−
3002:¯
2981:−
2960:θ
2948:μ
2901:^
2898:σ
2886:−
2874:¯
2853:−
2832:θ
2820:μ
2773:^
2770:σ
2758:−
2746:¯
2710:θ
2698:μ
2657:≈
2647:θ
2586:α
2531:θ
2505:θ
2493:μ
2436:≈
2419:−
2415:Φ
2411:≈
2406:α
2361:−
2357:Φ
2322:α
2300:α
2260:α
2225:α
2202:−
2151:^
2148:σ
2092:∑
2066:¯
2024:¯
1987:μ
1937:^
1934:σ
1922:−
1910:¯
1870:^
1867:σ
1852:μ
1848:−
1836:¯
1781:θ
1769:μ
1723:μ
1710:μ
1662:σ
1635:μ
1597:−
1471:θ
1295:important
1143:μ
1139:−
1130:μ
1046:≈
1017:α
988:β
921:tool. In
467:is true.
279:blue area
217:about, a
168:β
148:β
145:−
7215:Category
7161:Category
6854:Survival
6731:Johansen
6454:Binomial
6409:Isotonic
5996:(normal)
5641:location
5448:Blocking
5403:Sampling
5282:Q–Q plot
5247:Box plot
5229:Graphics
5124:Skewness
5114:Kurtosis
5086:Variance
5016:Heronian
5011:Harmonic
4829:(1988).
4704:mdrc.org
4671:19013761
4501:38190355
4492:10773938
4364:See also
4286:design.
3667:Suppose
1429:post-hoc
1418:post-hoc
1413:Post-hoc
1405:A priori
1401:post hoc
1397:a priori
1385:analysis
1383:post hoc
1379:A priori
1328:estimate
1270:blocking
283:red area
160:, where
7187:Commons
7134:Kriging
7019:Process
6976:studies
6835:Wavelet
6668:General
5835:Plug-in
5629:L space
5408:Cluster
5109:Moments
4927:Outline
4880:YouTube
4820:Sources
4770:Bibcode
4540:1496197
4320:G*Power
4277:In the
3480:infimum
2045:is the
1451:Example
600:is True
562:is True
211:samples
7056:Census
6646:Normal
6594:Manova
6414:Robust
6164:2-way
6156:1-way
5994:-test
5665:
5242:Biplot
5033:Median
5026:Lehmer
4968:Center
4856:
4837:
4669:
4632:
4607:
4570:
4538:
4530:
4499:
4489:
3534:always
3115:
3105:
2944:
2934:
2816:
2806:
2694:
2684:
2600:under
1978:where
1624:Normal
1461:t-test
1458:paired
1425:-value
1262:design
1253:sample
1169:For a
1088:where
1006:) and
932:and a
623:under
409:where
6680:Trend
6209:prior
6151:anova
6040:-test
6014:-test
6006:-test
5913:Power
5858:Pivot
5651:shape
5646:scale
5096:Shape
5076:Range
5021:Heinz
4996:Cubic
4932:Index
4810:(PDF)
4756:(PDF)
4294:Both
3864:24.6.
2334:. If
2191:with
378:when
39:power
6913:Test
6113:Sign
5965:Wald
5038:Mode
4976:Mean
4854:ISBN
4835:ISBN
4667:PMID
4630:ISBN
4605:ISBN
4568:ISBN
4536:PMID
4528:ISSN
4497:PMID
4450:2019
3847:0.84
3841:1.64
3780:1.64
3768:>
3601:1.64
3576:>
3371:1.64
3059:1.64
3056:<
2931:1.64
2928:<
2803:1.64
2800:>
2681:1.64
2678:>
2439:1.64
2430:0.95
2398:>
2292:>
2231:0.05
2136:and
1799:The
1784:>
1519:and
1474:>
1433:more
1381:vs.
1231:The
1211:and
1209:size
1207:the
1023:0.05
938:size
568:1-α
45:and
6093:BIC
6088:AIC
4878:on
4786:hdl
4778:doi
4734:doi
4659:doi
4588:pdf
4560:doi
4520:doi
4487:PMC
4477:doi
3810:0.8
3743:0.8
994:0.2
573:If
535:If
184:(a
30:In
7217::
4784:.
4776:.
4766:11
4764:.
4758:.
4730:55
4728:.
4712:^
4702:.
4665:.
4655:62
4653:.
4566:.
4534:,
4526:,
4495:.
4485:.
4473:22
4471:.
4467:.
4441:.
4131:.
2984:Pr
2856:Pr
2728:Pr
2660:Pr
2627:.
1787:0.
1735:0.
1685:.
1489:.
1347:.
1166:.
1049:16
944:.
606:β
188:)
37:,
6038:G
6012:F
6004:t
5992:Z
5711:V
5706:U
4908:e
4901:t
4894:v
4862:.
4843:.
4792:.
4788::
4780::
4772::
4740:.
4736::
4673:.
4661::
4638:.
4613:.
4576:.
4562::
4522::
4503:.
4479::
4452:.
4359:)
4340:)
4333:)
4326:)
4322:(
4242:t
4219:n
4215:T
4191:)
4186:D
4178:,
4172:(
4169:N
4147:n
4143:D
4113:t
4090:n
4086:T
4065:)
4056:1
4053:(
4028:n
4024:T
4001:)
3996:D
3988:,
3985:0
3982:(
3979:N
3957:n
3953:D
3927:n
3923:T
3900:n
3896:D
3856:2
3851:)
3844:+
3837:(
3832:4
3824:2
3819:)
3814:)
3804:1
3800:(
3794:1
3776:(
3771:4
3765:n
3740:=
3737:)
3731:(
3728:B
3706:D
3681:1
3678:=
3653:.
3649:)
3644:)
3640:)
3634:(
3631:B
3625:1
3621:(
3615:1
3597:(
3586:D
3571:n
3547:B
3520:1
3517:=
3494:,
3464:D
3449:n
3413:.
3409:)
3400:n
3394:/
3388:D
3367:(
3357:1
3351:)
3345:(
3342:B
3318:D
3291:D
3267:n
3247:1
3243:H
3217:n
3211:/
3205:D
3178:n
3168:D
3135:)
3128:=
3123:D
3110:|
3097:n
3091:/
3085:D
3048:n
3042:/
3036:D
3009:n
2999:D
2988:(
2978:1
2975:=
2964:)
2957:=
2952:D
2939:|
2920:n
2914:/
2908:D
2889:0
2881:n
2871:D
2860:(
2850:1
2847:=
2836:)
2829:=
2824:D
2811:|
2792:n
2786:/
2780:D
2761:0
2753:n
2743:D
2732:(
2725:=
2714:)
2707:=
2702:D
2689:|
2673:n
2669:T
2664:(
2650:)
2644:(
2641:B
2613:1
2609:H
2582:t
2559:n
2555:T
2534:)
2528:(
2525:B
2502:=
2497:D
2470:1
2466:H
2443:.
2433:)
2427:(
2422:1
2402:t
2393:n
2389:T
2364:1
2340:n
2336:n
2296:t
2287:n
2283:T
2256:t
2228:=
2205:1
2199:n
2158:D
2122:,
2117:i
2113:D
2107:n
2102:1
2099:=
2096:i
2086:n
2083:1
2078:=
2073:n
2063:D
2031:n
2021:D
2007:n
1991:0
1964:,
1956:n
1950:/
1944:D
1925:0
1917:n
1907:D
1897:=
1889:n
1883:/
1877:D
1856:0
1843:n
1833:D
1823:=
1818:n
1814:T
1778:=
1773:D
1765::
1760:1
1756:H
1732:=
1727:0
1719:=
1714:D
1706::
1701:0
1697:H
1671:2
1666:D
1639:D
1610:,
1605:i
1601:A
1592:i
1588:B
1584:=
1579:i
1575:D
1554:i
1532:i
1528:B
1505:i
1501:A
1477:0
1441:p
1437:p
1423:p
1336:α
1315:β
1311:α
1307:β
1147:2
1134:1
1126:=
1123:d
1101:2
1097:s
1076:,
1069:2
1065:d
1059:2
1055:s
1043:n
1020:=
991:=
964:n
848:0
844:H
833:t
817:1
813:H
802:t
786:1
782:H
759:0
755:H
744:t
728:1
724:H
701:0
697:H
674:0
670:H
659:t
655:α
636:0
632:H
617:t
586:1
582:H
565:α
548:0
544:H
517:0
513:H
488:0
484:H
453:1
449:H
426:0
422:H
411:β
407:β
391:0
387:H
364:0
360:H
349:α
333:1
329:H
306:0
302:H
287:β
275:α
142:1
120:1
116:H
107:(
89:0
85:H
76:(
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.