706:
738:
63:
604:
472:
787:
619:
795:
324:
416:
483:
in another 15%, the hydronephrosis persists but is not associated with urinary tract obstruction (so-called non-refluxing, non-obstructive hydronephrosis). For these children, regression of the hydronephrosis occurs spontaneously, usually by age 3. However, in the remaining 35% of cases of prenatal hydronephrosis, a pathological condition can be identified postnatally.
597:(VCUG) is also typically obtained to exclude the possibility of vesicoureteral reflux or anatomical abnormalities such as posterior urethral valves. Finally, if hydronephrosis is significant and obstruction is suspected, such as a ureteropelvic junction (UPJ) or ureterovesical junction (UVJ) obstruction, a nuclear imaging study such as a MAG-3 scan is warranted.
688:
670:
652:
631:
584:(one sided loin pain usually accompanied by a trace of blood in the urine) the initial investigation is usually a spiral or helical CT scan. This has the advantage of showing whether there is any obstruction of flow of urine causing hydronephrosis as well as demonstrating the function of the other kidney. Many stones are not visible on plain
32:
521:, are also important investigations in determining the presence and/ or cause of hydronephrosis. Whilst ultrasound allows for visualisation of the ureters and kidneys (and determine the presence of hydronephrosis and / or hydroureter), an IVU is useful for assessing the anatomical location of the obstruction.
490:
Urinalysis is usually performed to determine the presence of blood (which is typical for kidney stones) or signs of infection (such as a positive leukocyte esterase or nitrite). Impaired concentrating ability or elevated urine pH (distal renal tubular acidosis) are also commonly found due to tubular
486:
Diagnostic workup depends on the age of the patient, as well as whether the hydronephrosis was detected incidentally or prenatally or is associated with other symptoms. Blood tests (such measurement of creatinine) are typically indicated, though they must be interpreted cautiously. Even in cases of
837:
The prognosis of hydronephrosis is extremely variable and depends on the condition leading to hydronephrosis, whether one (unilateral) or both (bilateral) kidneys are affected, the pre-existing kidney function, the duration of hydronephrosis (acute or chronic), and whether hydronephrosis occurred in
130:
Conversely, hydronephrosis that develops gradually over time will generally cause either a dull discomfort or no pain. Nausea and vomiting may also occur. An obstruction that occurs at the urethra or bladder outlet can cause pain and pressure resulting from distension of the bladder. Blocking the
482:
Prenatal diagnosis is possible, and in fact, most cases in pediatric patients are incidentally detected by routine screening ultrasounds obtained during pregnancy. However, approximately half of all prenatally identified hydronephrosis is transient, and resolves by the time the infant is born, and
592:
For incidentally detected prenatal hydronephrosis, the first study to obtain is a postnatal renal ultrasound, since as noted, many cases of prenatal hydronephrosis resolve spontaneously. This is generally done within the first few days after birth, although there is some risk that obtaining an
692:
691:
674:
673:
656:
655:
635:
634:
693:
675:
657:
636:
576:
hydronephrosis receive a renal ultrasound within two days of birth. A renal pelvis greater than 12 mm in a neonate is considered abnormal and suggests significant dilation and possible abnormalities such as obstruction or morphological abnormalities in the urinary tract.
705:
443:
Obstruction that occurs anywhere along the upper urinary tract will lead to increased pressure within the structures of the kidney due to the inability to pass urine from the kidney to the bladder. Common causes of upper tract obstruction include obstructing stones and
690:
672:
654:
633:
593:
imaging study this early may miss some cases of mild hydronephrosis due to the relative oliguria of a newborn. Thus, some experts recommend obtaining a follow-up ultrasound at 4–6 weeks to reduce the false-negative rate of the initial ultrasound. A
548:
O suggests that the urinary collection system is obstructed. When arriving at this pressure measurement, bladder pressure is subtracted from the initial reading of internal pressure. (The test was first described by
Whittaker in 1973 to test the
239:
Compression of one or both ureters can also be caused by other developmental defects not completely occurring during the fetal stage such as an abnormally placed vein, artery, or tumor. Bilateral compression of the ureters can occur during
458:
In pregnancy, dextrorotation (rotation to the right) of the uterus can cause compression on the right ureter, thus making hydronephrosis more common in right kidney than left kidney. Besides, hormones such as oestrogen, progestrerone, and
848:
For example, unilateral hydronephrosis caused by an obstructing stone will likely resolve when the stone passes, and the likelihood of recovery is excellent. Alternately, severe bilateral prenatal hydronephrosis (such as occurs with
761:
for renal pelvic dilation have been defined differently by different sources, with anteroposterior diameters ranging between 10 and 20 mm. About 13% of normal healthy adults have a transverse pelvic diameter of over
744:
The
Society of Fetal Ultrasound (SFU) has developed a grading system for hydronephrosis, initially intended for use in neonatal and infant hydronephrosis, but it is now used for grading hydronephrosis in adults as well:
802:
Treatment of hydronephrosis focuses upon the removal of the obstruction and drainage of the urine that has accumulated behind the obstruction. Therefore, the specific treatment depends upon where the obstruction lies.
588:
or IVU but 99% of stones are visible on CT and therefore CT is becoming a common choice of initial investigation. CT is not used, however, when there is a reason to avoid radiation exposure, e.g. in pregnancy.
536:
In determining the cause of hydronephrosis, the location of obstruction can be determined with a
Whittaker (or pressure perfusion) test, wherein the collecting system of the kidney is accessed
689:
671:
653:
632:
451:
Obstruction occurring in the lower urinary tract can also cause this increased pressure through the reflux of urine into the kidney. Common causes include bladder dysfunction (such as
440:. In acute hydronephrosis full recovery of kidney function is seen. However, with chronic hydronephrosis, permanent loss of kidney function is seen even once obstruction is removed.
198:
that lead to hydronephrosis can occur during fetal development. Some of these congenital defects have been identified as inherited conditions, however, the benefits of linking
178:
within the affected kidney, which impairs acid excretion. Physical examination in a thin patient may detect a palpable abdominal or flank mass caused by the enlarged kidney.
881:
Mergener K, Weinerth JL, Baillie J (December 1997). "Dietl's crisis: a syndrome of episodic abdominal pain of urologic origin that may present to a gastroenterologist".
1022:
Koh JS, Wong MY, Li MK, Foo KT (September 1998). "Idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis with bilateral lower ureteric obstruction--a case report with literature review".
1528:
Emamian SA, Nielsen MB, Pedersen JF, Ytte L (September 1993). "Sonographic evaluation of renal appearance in 665 adult volunteers. Correlation with age and obesity".
1361:
Aksu N, Yavaşcan O, Kangin M, Kara OD, Aydin Y, Erdoğan H, et al. (September 2005). "Postnatal management of infants with antenatally detected hydronephrosis".
765:
Grade 1 (mild) – Mild renal pelvis dilation (anteroposterior diameter less than 10 mm in fetuses) without dilation of the calyces nor parenchymal atrophy
821:
Lower urinary tract obstruction (such as that caused by bladder outflow obstruction secondary to prostatic hypertrophy) is usually treated by insertion of a
911:
455:) and urethral obstruction (such as posterior urethral valves in male infants) or compression (such as from prostatic hypertrophy in older male adults).
487:
severe unilateral hydronephrosis, the overall kidney function may remain normal since the unaffected kidney will compensate for the obstructed kidney.
334:
1008:
186:
Hydronephrosis is the result of any of several abnormal pathophysiological occurrences. Structural abnormalities of the junctions between the
1861:
248:. Changes in hormone levels during this time may also affect the muscle contractions of the bladder, further complicating this condition.
603:
202:
to early diagnosis have not been determined. Other structural abnormalities could be caused by injury, surgery, or radiation therapy.
857:, because obstruction while the kidneys are developing causes permanent kidney damage even if the obstruction is relieved postnatal.
1631:
1049:
Eijk, Anna Maria van; Zulaika, Garazi; Lenchner, Madeline; Mason, Linda; Sivakami, Muthusamy; Nyothach, Elizabeth; Unger, Holger;
984:
463:
can cause ureter dilatation, thus causing hydronephrosis despite the absence of visible obstruction along the urinary tract.
395:
429:
tubules and flattening of the lining of the tubules within the kidneys which in turn causes swelling of the renal calyces.
367:
580:
The choice of imaging depends on the clinical presentation (history, symptoms and examination findings). In the case of
618:
540:, and the liquid is introduced at high pressure and constant rate of 10ml/min while measuring the pressure within the
374:
1512:
1483:
119:, partial or complete, unilateral or bilateral. Hydronephrosis that occurs acutely with sudden onset (as caused by a
353:
1682:
425:
Hydronephrosis is caused by obstruction of urine before the renal pelvis. The obstruction causes dilation of the
381:
1871:
768:
Grade 2 (mild) – Moderate renal pelvis dilation (between 10 and 15 mm in fetuses), including a few calyces
533:
testing helps determine how a given obstruction is effecting urinary functionality in hydronephrotic patients.
1249:
Carmody JB, Carmody RB (December 2011). "Question from the clinician: management of prenatal hydronephrosis".
841:
Permanent kidney damage can occur from prolonged hydronephrosis secondary to compression of kidney tissue and
1687:
1055:"Menstrual cup use, leakage, acceptability, safety, and availability: a systematic review and meta-analysis"
737:
500:
278:. Hydronephrosis can also result from the retrograde flow of urine from the bladder back into the kidneys (
1624:
754:
363:
1658:
790:
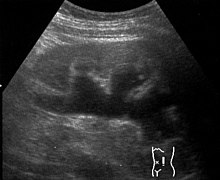
Left sided hydronephrosis in a person with an atrophic right kidney. Stent is also present (image below).
222:
1747:
594:
525:
will show similar findings to an IVU but offer a therapeutic option as well. Real-time ultrasounds and
518:
283:
933:
Toka HR, Toka O, Hariri A, Nguyen HT (July 2010). "Congenital anomalies of kidney and urinary tract".
1782:
1438:
749:
Grade 0 – No renal pelvis dilation. This means an anteroposterior diameter of less than 4 mm in
342:
1932:
1883:
1777:
850:
758:
554:
256:
62:
1787:
1617:
338:
205:
The most common causes of hydronephrosis in children are anatomical abnormalities. These include
163:
132:
1823:
1737:
1729:
1694:
1677:
1563:
Onen A (December 2007). "Treatment and outcome of prenatally detected newborn hydronephrosis".
445:
1471:
1846:
1767:
1500:
1219:
642:
562:
510:
279:
206:
39:
388:
1851:
1717:
291:
302:(which sits immediately behind the prostate), as well as abnormal contractions of bladder
8:
1937:
1818:
826:
530:
506:
100:
1206:
Woodward M, Frank D (January 2002). "Postnatal management of antenatal hydronephrosis".
349:
1909:
1866:
1386:
1231:
1188:
1140:
1113:
1089:
1054:
1002:
526:
452:
448:(UPJ) obstruction caused by intrinsic narrowing of the ureters or an overlying vessel.
307:
251:
Sources of obstruction that can arise from other various causes include kidney stones,
210:
116:
1071:
806:
Acute obstruction of the upper urinary tract is usually treated by the insertion of a
771:
Grade 3 (moderate) – Renal pelvis dilation with all calyces uniformly dilated. Normal
1712:
1580:
1545:
1508:
1479:
1378:
1266:
1223:
1180:
1145:
1094:
1076:
1031:
990:
980:
950:
946:
890:
437:
47:
1390:
1336:
1235:
1759:
1707:
1702:
1572:
1537:
1370:
1258:
1215:
1192:
1172:
1135:
1125:
1084:
1066:
942:
822:
772:
433:
270:
The obstruction may be either partial or complete, and can occur anywhere from the
112:
123:) can cause intense pain in the flank area (between the hips and ribs) known as a
1576:
1176:
303:
295:
271:
233:
199:
1307:
475:
Hydronephrosis due to a kidney stone at the ureteral vesicular junction seen on
111:
The signs and symptoms of hydronephrosis depend upon whether the obstruction is
1772:
1742:
1648:
1640:
1411:
1050:
811:
810:
tube. Chronic upper urinary tract obstruction is treated by the insertion of a
144:
1541:
1374:
1926:
1878:
1813:
1080:
994:
460:
275:
264:
226:
267:
pressing on a ureter. When the cups were removed, the symptoms disappeared.
1904:
1894:
1856:
1584:
1382:
1270:
1262:
1227:
1184:
1149:
1098:
954:
861:
786:
724:
716:
541:
537:
471:
218:
159:
127:. Historically, this type of pain has been described as "Dietl's crisis".
120:
76:
1549:
1035:
894:
1890:
1669:
1476:
Donald School Basic
Textbook of Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology
815:
807:
794:
720:
581:
522:
260:
124:
80:
1130:
777:
Grade 4 (severe) – As grade 3 but with thinning of the renal parenchyma
715:
may look like hydronephrosis on non-contrast CT (left image). However,
712:
550:
514:
352:
if you can. Unsourced or poorly sourced material may be challenged and
167:
155:
56:
561:
usually have ureters that are not obstructed, even though they may be
282:), which can be caused by some of the factors listed above as well as
1808:
1803:
1163:
Estrada CR (July 2008). "Prenatal hydronephrosis: early evaluation".
854:
241:
136:
1443:
842:
558:
252:
229:
214:
1609:
609:
569:
476:
426:
287:
195:
175:
52:
1288:
977:
Pathophysiology: Introductory
Concepts and Clinical Perspectives
1828:
798:
Left sided hydronephrosis, coronal view. Stent is also present.
573:
299:
245:
191:
187:
140:
92:
221:. In older adults, the most common cause of hydronephrosis is
750:
585:
217:. The most common cause of hydronephrosis in young adults is
84:
16:
Dilation of the renal pelvis due to obstruction of urine flow
1292:, 2nd Ed. by Resnick & Novick; 1999, Hanley & Belfus
829:. Surgery is not required in all prenatally detected cases.
135:
which can lead to further development of stones, fever, and
151:
1527:
1469:
259:. A 2019 review found three cases of hydronephrosis with
1439:"Overview of fetal hydronephrosis. Version Version 29.0"
1048:
150:
Blood tests may show impaired kidney function (elevated
31:
880:
171:
1507:(2nd ed.). Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 78.
1360:
553:
that patients whose hydronephrosis persists after the
103:(both the renal pelvicalyceal system and the ureter).
1465:
1463:
1461:
932:
912:"Hydronephrosis: Merck Manuals Home Health Handbook"
612:
of bilateral hydronephrosis due to a bladder cancer
1472:"Chapter 13: Malformations of the Urinary System"
1458:
974:
42:of hydronephrosis caused by a left ureteral stone
1924:
1248:
348:Please review the contents of the section and
1625:
1205:
1053:; Phillips-Howard, Penelope A. (2019-08-01).
624:Massive hydronephrosis as marked by the arrow
1556:
1042:
1021:
1498:
1156:
501:Renal ultrasonography § Hydronephrosis
1632:
1618:
1007:: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (
61:
30:
1406:
1404:
1402:
1400:
1139:
1129:
1088:
1070:
306:resulting from neurological dysfunction (
1597:
1470:D'Addario V, Capuano P, Volpe G (2014).
1302:
1300:
1298:
1220:10.1046/j.1464-4096.2001.woodward.2578.x
883:The American Journal of Gastroenterology
793:
785:
470:
131:flow of urine will commonly be prone to
1331:
1329:
1162:
906:
904:
544:. A rise in pressure above 22 cm H
1925:
1397:
1284:
1282:
1280:
914:. New Jersey: Merck and Co., Inc. 2009
147:(obstructive nephropathy) may follow.
75:describes hydrostatic dilation of the
1613:
1295:
1111:
853:) will likely carry a poor long-term
757:and 7 mm afterwards. In adults,
143:. If complete obstruction occurs, a
106:
99:describes the dilation of the entire
1862:Abderhalden–Kaufmann–Lignac syndrome
1600:Oxford Handbook of Clinical Medicine
1562:
1341:The Lecturio Medical Concept Library
1326:
970:
968:
966:
964:
901:
317:
174:due to the secondary destruction of
158:) or electrolyte imbalances such as
1503:. In Bowra J, McLaughlin R (eds.).
1412:"UOTW #10 - Ultrasound of the Week"
1277:
864:, which is a urological emergency.
523:Antegrade or retrograde pyelography
13:
1639:
1602:. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
1436:
1114:"Urologic issues during pregnancy"
736:
494:
313:
14:
1949:
975:Capriotti T, Frizzell JP (2016).
961:
860:Hydronephrosis can be a cause of
284:compression of the bladder outlet
164:hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis
87:flow downstream. Alternatively,
947:10.1016/j.semnephrol.2010.06.004
704:
686:
668:
650:
629:
617:
602:
414:
322:
1591:
1521:
1492:
1478:. JP Medical Ltd. p. 189.
1430:
1354:
1242:
719:(at right) reveals non-dilated
310:) or other muscular disorders.
1505:Emergency Ultrasound Made Easy
1199:
1105:
1015:
926:
874:
838:developing or mature kidneys.
350:add the appropriate references
91:describes the dilation of the
83:as a result of obstruction to
1:
1072:10.1016/S2468-2667(19)30111-2
867:
432:Hydronephrosis can either be
263:were caused by malpositioned
1577:10.1016/j.jpurol.2007.05.002
1565:Journal of Pediatric Urology
1177:10.1097/MOU.0b013e328302edfe
832:
781:
681:Stone causing hydronephrosis
663:Stone causing hydronephrosis
505:Imaging studies, such as an
466:
7:
1659:Template:Glomerular disease
335:reliable medical references
223:benign prostate hyperplasia
10:
1954:
1748:Balkan endemic nephropathy
1499:Bowra J, McGinn S (2011).
1165:Current Opinion in Urology
732:
529:tests in association with
498:
244:due to enlargement of the
1839:
1796:
1783:Renovascular hypertension
1758:
1728:
1668:
1647:
1542:10.3109/02841859309175388
1455:Last updated Apr 20, 2017
1375:10.1007/s00467-005-1989-3
1118:TheScientificWorldJournal
1024:Singapore Medical Journal
851:posterior urethral valves
555:posterior urethral valves
341:or relies too heavily on
181:
170:may indicate an elevated
46:
38:
29:
24:
1884:Renal papillary necrosis
1778:Hypertensive nephropathy
1501:"Chapter 7: Renal Tract"
1474:. In D'Addario V (ed.).
1059:The Lancet Public Health
595:voiding cystourethrogram
257:retroperitoneal fibrosis
145:postrenal kidney failure
133:urinary tract infections
1788:Renal cortical necrosis
1824:Chronic kidney disease
1738:Interstitial nephritis
1695:Acute tubular necrosis
1678:Renal tubular acidosis
1416:Ultrasound of the Week
1263:10.1542/pir.32-12-e110
1112:Weiss JP (June 2004).
935:Seminars in Nephrology
799:
791:
741:
568:Kay recommends that a
479:
446:ureteropelvic junction
1847:Analgesic nephropathy
1768:Renal artery stenosis
797:
789:
740:
643:Renal ultrasonography
511:renal ultrasonography
499:Further information:
474:
280:vesicoureteral reflux
207:vesicoureteral reflux
40:Renal ultrasonography
1852:Renal osteodystrophy
1363:Pediatric Nephrology
1251:Pediatrics in Review
1124:(Suppl 1): 364–376.
572:born with untreated
292:prostate enlargement
1819:Acute renal failure
1598:Longmore M (2014).
1131:10.1100/tsw.2004.92
827:suprapubic catheter
531:vascular resistance
507:intravenous urogram
491:stress and injury.
101:upper urinary tract
1910:Reflux nephropathy
1867:Diabetes insipidus
1649:Glomerular disease
800:
792:
753:up to 32 weeks of
742:
527:Doppler ultrasound
480:
453:neurogenic bladder
308:neurogenic bladder
211:urethral stricture
107:Signs and symptoms
1920:
1919:
1797:General syndromes
1718:Liddle's syndrome
1713:Gitelman syndrome
1257:(12): e110–e112.
1208:BJU International
986:978-0-8036-1571-7
889:(12): 2289–2291.
694:
676:
658:
645:of hydronephrosis
637:
547:
423:
422:
399:
97:hydronephroureter
70:
69:
19:Medical condition
1945:
1708:Bartter syndrome
1703:Fanconi syndrome
1634:
1627:
1620:
1611:
1610:
1604:
1603:
1595:
1589:
1588:
1560:
1554:
1553:
1530:Acta Radiologica
1525:
1519:
1518:
1496:
1490:
1489:
1467:
1456:
1454:
1452:
1451:
1434:
1428:
1427:
1425:
1423:
1408:
1395:
1394:
1369:(9): 1253–1259.
1358:
1352:
1351:
1349:
1347:
1337:"Hydronephrosis"
1333:
1324:
1323:
1321:
1319:
1308:"Hydronephrosis"
1304:
1293:
1286:
1275:
1274:
1246:
1240:
1239:
1203:
1197:
1196:
1160:
1154:
1153:
1143:
1133:
1109:
1103:
1102:
1092:
1074:
1065:(8): e376–e393.
1046:
1040:
1039:
1019:
1013:
1012:
1006:
998:
979:. Philadelphia.
972:
959:
958:
930:
924:
923:
921:
919:
908:
899:
898:
878:
823:urinary catheter
773:renal parenchyma
708:
696:
695:
678:
677:
660:
659:
639:
638:
621:
606:
545:
418:
417:
409:
406:
400:
398:
364:"Hydronephrosis"
357:
326:
325:
318:
304:detrusor muscles
141:pus in the urine
66:
65:
34:
22:
21:
1953:
1952:
1948:
1947:
1946:
1944:
1943:
1942:
1933:Kidney diseases
1923:
1922:
1921:
1916:
1835:
1792:
1754:
1724:
1664:
1643:
1638:
1608:
1607:
1596:
1592:
1561:
1557:
1526:
1522:
1515:
1497:
1493:
1486:
1468:
1459:
1449:
1447:
1435:
1431:
1421:
1419:
1410:
1409:
1398:
1359:
1355:
1345:
1343:
1335:
1334:
1327:
1317:
1315:
1306:
1305:
1296:
1290:Urology Secrets
1287:
1278:
1247:
1243:
1204:
1200:
1161:
1157:
1110:
1106:
1051:Laserson, Kayla
1047:
1043:
1020:
1016:
1000:
999:
987:
973:
962:
931:
927:
917:
915:
910:
909:
902:
879:
875:
870:
835:
784:
755:gestational age
735:
728:
709:
700:
697:
687:
682:
679:
669:
664:
661:
651:
646:
640:
630:
625:
622:
613:
607:
503:
497:
495:Imaging studies
469:
419:
415:
410:
404:
401:
358:
347:
343:primary sources
327:
323:
316:
314:Pathophysiology
296:fecal impaction
272:urethral meatus
234:prostate cancer
200:genetic testing
184:
109:
60:
20:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1951:
1941:
1940:
1935:
1918:
1917:
1915:
1914:
1913:
1912:
1907:
1902:
1900:Hydronephrosis
1888:
1887:
1886:
1876:
1875:
1874:
1864:
1859:
1854:
1849:
1843:
1841:
1837:
1836:
1834:
1833:
1832:
1831:
1826:
1821:
1811:
1806:
1800:
1798:
1794:
1793:
1791:
1790:
1785:
1780:
1775:
1773:Renal ischemia
1770:
1764:
1762:
1756:
1755:
1753:
1752:
1751:
1750:
1745:
1743:Pyelonephritis
1734:
1732:
1726:
1725:
1723:
1722:
1721:
1720:
1715:
1710:
1705:
1697:
1692:
1691:
1690:
1685:
1674:
1672:
1666:
1665:
1663:
1662:
1653:
1651:
1645:
1644:
1641:Kidney disease
1637:
1636:
1629:
1622:
1614:
1606:
1605:
1590:
1571:(6): 469–476.
1555:
1536:(5): 482–485.
1520:
1513:
1491:
1484:
1457:
1429:
1418:. 22 July 2014
1396:
1353:
1325:
1314:. 3 April 2018
1294:
1276:
1241:
1214:(2): 149–156.
1198:
1171:(4): 401–403.
1155:
1104:
1041:
1030:(9): 416–417.
1014:
985:
960:
941:(4): 374–386.
925:
900:
872:
871:
869:
866:
834:
831:
812:ureteric stent
783:
780:
779:
778:
775:
769:
766:
763:
734:
731:
730:
729:
710:
703:
701:
698:
685:
683:
680:
667:
665:
662:
649:
647:
641:
628:
626:
623:
616:
614:
608:
601:
538:percutaneously
496:
493:
468:
465:
421:
420:
413:
411:
330:
328:
321:
315:
312:
265:menstrual cups
183:
180:
108:
105:
73:Hydronephrosis
68:
67:
50:
44:
43:
36:
35:
27:
26:
25:Hydronephrosis
18:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1950:
1939:
1936:
1934:
1931:
1930:
1928:
1911:
1908:
1906:
1903:
1901:
1898:
1897:
1896:
1892:
1889:
1885:
1882:
1881:
1880:
1879:Renal papilla
1877:
1873:
1870:
1869:
1868:
1865:
1863:
1860:
1858:
1855:
1853:
1850:
1848:
1845:
1844:
1842:
1838:
1830:
1827:
1825:
1822:
1820:
1817:
1816:
1815:
1814:Renal failure
1812:
1810:
1807:
1805:
1802:
1801:
1799:
1795:
1789:
1786:
1784:
1781:
1779:
1776:
1774:
1771:
1769:
1766:
1765:
1763:
1761:
1757:
1749:
1746:
1744:
1741:
1740:
1739:
1736:
1735:
1733:
1731:
1727:
1719:
1716:
1714:
1711:
1709:
1706:
1704:
1701:
1700:
1698:
1696:
1693:
1689:
1686:
1684:
1681:
1680:
1679:
1676:
1675:
1673:
1671:
1667:
1661:
1660:
1655:
1654:
1652:
1650:
1646:
1642:
1635:
1630:
1628:
1623:
1621:
1616:
1615:
1612:
1601:
1594:
1586:
1582:
1578:
1574:
1570:
1566:
1559:
1551:
1547:
1543:
1539:
1535:
1531:
1524:
1516:
1514:9780702048722
1510:
1506:
1502:
1495:
1487:
1485:9789351523376
1481:
1477:
1473:
1466:
1464:
1462:
1446:
1445:
1440:
1433:
1417:
1413:
1407:
1405:
1403:
1401:
1392:
1388:
1384:
1380:
1376:
1372:
1368:
1364:
1357:
1342:
1338:
1332:
1330:
1313:
1309:
1303:
1301:
1299:
1291:
1285:
1283:
1281:
1272:
1268:
1264:
1260:
1256:
1252:
1245:
1237:
1233:
1229:
1225:
1221:
1217:
1213:
1209:
1202:
1194:
1190:
1186:
1182:
1178:
1174:
1170:
1166:
1159:
1151:
1147:
1142:
1137:
1132:
1127:
1123:
1119:
1115:
1108:
1100:
1096:
1091:
1086:
1082:
1078:
1073:
1068:
1064:
1060:
1056:
1052:
1045:
1037:
1033:
1029:
1025:
1018:
1010:
1004:
996:
992:
988:
982:
978:
971:
969:
967:
965:
956:
952:
948:
944:
940:
936:
929:
913:
907:
905:
896:
892:
888:
884:
877:
873:
865:
863:
858:
856:
852:
846:
844:
839:
830:
828:
824:
819:
817:
813:
809:
804:
796:
788:
776:
774:
770:
767:
764:
760:
759:cutoff values
756:
752:
748:
747:
746:
739:
726:
722:
718:
714:
707:
702:
684:
666:
648:
644:
627:
620:
615:
611:
605:
600:
599:
598:
596:
590:
587:
583:
578:
575:
571:
566:
564:
560:
556:
552:
543:
539:
534:
532:
528:
524:
520:
516:
512:
508:
502:
492:
488:
484:
478:
473:
464:
462:
461:prostaglandin
456:
454:
449:
447:
441:
439:
435:
430:
428:
412:
408:
397:
394:
390:
387:
383:
380:
376:
373:
369:
366: –
365:
361:
360:Find sources:
355:
351:
345:
344:
340:
336:
331:This section
329:
320:
319:
311:
309:
305:
301:
297:
293:
289:
285:
281:
277:
276:renal calyces
273:
268:
266:
262:
258:
254:
249:
247:
243:
237:
235:
231:
228:
224:
220:
219:kidney stones
216:
212:
208:
203:
201:
197:
193:
189:
179:
177:
173:
169:
165:
161:
157:
153:
148:
146:
142:
138:
134:
128:
126:
122:
118:
114:
104:
102:
98:
94:
90:
86:
82:
78:
74:
64:
58:
54:
51:
49:
45:
41:
37:
33:
28:
23:
1905:Pyonephrosis
1899:
1857:Nephroptosis
1730:Interstitium
1656:
1599:
1593:
1568:
1564:
1558:
1533:
1529:
1523:
1504:
1494:
1475:
1448:. Retrieved
1442:
1432:
1420:. Retrieved
1415:
1366:
1362:
1356:
1344:. Retrieved
1340:
1316:. Retrieved
1311:
1289:
1254:
1250:
1244:
1211:
1207:
1201:
1168:
1164:
1158:
1121:
1117:
1107:
1062:
1058:
1044:
1027:
1023:
1017:
976:
938:
934:
928:
916:. Retrieved
886:
882:
876:
862:pyonephrosis
859:
847:
840:
836:
820:
805:
801:
743:
717:CT urography
591:
579:
567:
542:renal pelvis
535:
504:
489:
485:
481:
457:
450:
442:
431:
424:
405:January 2020
402:
392:
385:
378:
371:
359:
339:verification
332:
269:
250:
238:
204:
185:
160:hyponatremia
149:
129:
121:kidney stone
110:
96:
88:
77:renal pelvis
72:
71:
1891:Major calyx
1872:Nephrogenic
1437:Baskin LS.
918:November 5,
816:pyeloplasty
808:nephrostomy
762:10 mm.
713:renal cysts
711:Peripelvic
582:renal colic
333:needs more
261:renal colic
253:blood clots
227:intrapelvic
125:renal colic
89:hydroureter
1938:Nephrology
1927:Categories
1450:2017-04-25
868:References
699:Urine jets
557:have been
551:hypothesis
375:newspapers
225:(BPH), or
168:Urinalysis
156:creatinine
57:nephrology
1809:Nephrosis
1804:Nephritis
1081:2468-2667
1003:cite book
995:900626405
855:prognosis
833:Prognosis
782:Treatment
467:Diagnosis
286:into the
242:pregnancy
230:neoplasms
48:Specialty
1760:Vascular
1699:Genetic
1683:proximal
1585:18947797
1444:UpToDate
1391:28080264
1383:16025288
1271:22135428
1236:34661487
1228:11849184
1185:18520762
1150:15349560
1099:31324419
955:20807610
843:ischemia
725:pelvises
574:in utero
232:such as
215:stenosis
176:nephrons
1670:Tubules
1550:8369185
1346:24 July
1318:24 July
1193:6169141
1141:5956501
1090:6669309
1036:9885722
895:9399772
751:fetuses
733:Grading
721:calyces
610:CT scan
570:neonate
563:dilated
559:ablated
509:(IVU),
477:CT scan
438:chronic
427:nephron
389:scholar
354:removed
298:in the
288:urethra
274:to the
196:bladder
117:chronic
81:calyces
53:Urology
1895:pelvis
1829:Uremia
1688:distal
1583:
1548:
1511:
1482:
1422:27 May
1389:
1381:
1269:
1234:
1226:
1191:
1183:
1148:
1138:
1097:
1087:
1079:
1034:
993:
983:
953:
893:
391:
384:
377:
370:
362:
300:rectum
246:uterus
213:, and
192:ureter
188:kidney
182:Causes
95:, and
93:ureter
59:
1840:Other
1387:S2CID
1232:S2CID
1189:S2CID
825:or a
814:or a
586:X-ray
517:, or
434:acute
396:JSTOR
382:books
137:blood
113:acute
85:urine
1657:See
1581:PMID
1546:PMID
1509:ISBN
1480:ISBN
1424:2017
1379:PMID
1348:2021
1320:2021
1267:PMID
1224:PMID
1181:PMID
1146:PMID
1095:PMID
1077:ISSN
1032:PMID
1009:link
991:OCLC
981:ISBN
951:PMID
920:2010
891:PMID
723:and
368:news
337:for
194:and
152:urea
79:and
1573:doi
1538:doi
1371:doi
1312:NHS
1259:doi
1216:doi
1173:doi
1136:PMC
1126:doi
1085:PMC
1067:doi
943:doi
565:.)
519:MRI
436:or
294:or
290:by
255:or
166:.
162:or
154:or
139:or
115:or
1929::
1579:.
1567:.
1544:.
1534:34
1532:.
1460:^
1441:.
1414:.
1399:^
1385:.
1377:.
1367:20
1365:.
1339:.
1328:^
1310:.
1297:^
1279:^
1265:.
1255:32
1253:.
1230:.
1222:.
1212:89
1210:.
1187:.
1179:.
1169:18
1167:.
1144:.
1134:.
1120:.
1116:.
1093:.
1083:.
1075:.
1061:.
1057:.
1028:39
1026:.
1005:}}
1001:{{
989:.
963:^
949:.
939:30
937:.
903:^
887:92
885:.
845:.
818:.
515:CT
513:,
356:.
236:.
209:,
190:,
172:pH
55:,
1893:/
1633:e
1626:t
1619:v
1587:.
1575::
1569:3
1552:.
1540::
1517:.
1488:.
1453:.
1426:.
1393:.
1373::
1350:.
1322:.
1273:.
1261::
1238:.
1218::
1195:.
1175::
1152:.
1128::
1122:4
1101:.
1069::
1063:4
1038:.
1011:)
997:.
957:.
945::
922:.
897:.
727:.
546:2
407:)
403:(
393:·
386:·
379:·
372:·
346:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.