136:
25:
124:
228:
With the completion of the development of the F-25, the main interest in the LFA focused on the F-55. This was a remote-controlled 2-stage supersonic missile (first stage: solid and level flight: liquid). Launching the device was made from an oblique ramp, later also on a modified 88-mm anti-aircraft
211:
The development of the remote control system was at an advanced stage in
February 1943, with research in the wind-tunnel and the construction of a gun rack almost complete. The production of the first F-25 pre-series included 24 specimens made unexpectedly good progress and by July 1943 it was
247:
On 22 November 1944 the
Technical Department of the Air Ministry cut the number of F-55s from 25 to 11 devices. There was a further cut in December 1944 to 20 sample units of the A2 and A3 models. The last documented attempt to fly an F-55A2 took place on 11 December 1944 at Greifswalder Oie.
236:
for the construction of five test samples. The construction of the units was completed in
February 1943. On 9 March there was a delay to the delivery of the batch, now 30 units, due to technical problems, including with the controller and the drive section.
157:, which was developed in 1940 and was shelved because of problems with the controller and the drive section at the end of January 1945 in favour of other projects. The Feuerlilie was built and tested at
244:
three further launches of the F-55A2, which demonstrated their unstable flight behaviour. The launch of the improved F-55A3 was aborted on 21 October 1944 because of technical problems.
255:
in the F-55 A2 and A3. The F-55 would have a larger tail for greater flight stability. As the development was discontinued in late
January 1945 these changes were scrapped.
220:. By mid 1944 at least four F-25s had been fired. However, the test results did not meet expectations and so the development of the F-25 was still set before end of 1944.
205:
430:
192:
was a scaled-down version created in the short term to get an impression of the later flight behaviour of the new weapon. The intention of the
161:
in two versions: the F-25 with a diameter of 25 cm, and the larger F-55 55 cm in diameter. The engines were
Rheinmetall 109-505/515
212:
possible to make further F-25s ready. The work, however, faltered due to lack of motors. The first F-25 in the July 1943 was tested in the
425:
201:
178:
251:
To accelerate the development and to obtain reliable results, on 14 January 1945 it was decided to use the unmodified drive from the
240:
The first launch of an F-55A1 was on 12 May 1944. It flew for 69 seconds and a distance of 7500 m. From 19 October 1944 at
89:
61:
407:
379:
108:
68:
46:
75:
42:
57:
35:
193:
154:
8:
82:
435:
144:
403:
375:
241:
352:
347:
252:
174:
135:
229:
gun launch pad. The first production of the F-55 was completed in April 1942.
419:
374:
Manfred Griehl: Luftwaffe '45 Letzte Flüge und
Projekte, Motorbuch Verlag,
357:
162:
158:
362:
217:
181:- DFL) began to design a remote-controlled rocket under the code name
123:
24:
233:
232:
On 25 January 1943 a contract was sent to the Ardelt company in
213:
208:(RPF). In practice this took place, but only some time later.
185:
to research the construction of anti-aircraft missiles.
153:(English: fire lily) was the code name of a German
49:. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
417:
177:'s German Aviation Research organisation (
338:F-55 - 600 kg with a payload of 100
109:Learn how and when to remove this message
202:Deutsche Forschungsanstalt für Segelflug
179:Deutsche Forschungsanstalt für Luftfahrt
134:
122:
431:World War II guided missiles of Germany
418:
47:adding citations to reliable sources
18:
13:
426:Surface-to-air missiles of Germany
223:
168:
14:
447:
258:
23:
34:needs additional citations for
392:
1:
368:
7:
400:German flak rockets to 1945
341:
200:s, in cooperation with the
10:
452:
385:
312:F-55 - 1260 km / h
206:Reichspost-Forschungsamt
309:F-25 - 840 km / h
216:proving ground on the
147:
132:
296:F-25 to 1500 mm
273:F-55 to 4800 mm
270:F-25 to 1896 mm
196:(RLM) was to test 25
188:The first model, the
155:anti-aircraft missile
138:
131:anti-aircraft missile
126:
299:F-55 - 4500 mm
43:improve this article
286:F-55 - 550 mm
283:F-25 - 250 mm
190:Feuerlilie (4.4 F)
159:Rheinmetall-Borsig
148:
145:RAF Museum Cosford
133:
335:F-25 - not known
322:F-25 - not known
119:
118:
111:
93:
443:
410:
398:Manfred Griehl,
396:
325:F-55 - 10,000 m
242:Greifswalder Oie
114:
107:
103:
100:
94:
92:
51:
27:
19:
451:
450:
446:
445:
444:
442:
441:
440:
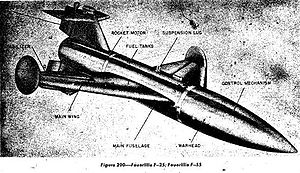
416:
415:
414:
413:
397:
393:
388:
371:
348:Henschel Hs 117
344:
317:Nominal height:
261:
253:Henschel Hs 293
226:
224:Feuerlilie F-55
175:Hermann Goering
171:
169:Feuerlilie F-25
115:
104:
98:
95:
52:
50:
40:
28:
17:
12:
11:
5:
449:
439:
438:
433:
428:
412:
411:
390:
389:
387:
384:
383:
382:
370:
367:
366:
365:
360:
355:
350:
343:
340:
333:
332:
320:
319:
307:
306:
294:
293:
281:
280:
268:
267:
260:
259:Technical data
257:
225:
222:
204:(DFS) and the
170:
167:
117:
116:
31:
29:
22:
16:German missile
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
448:
437:
434:
432:
429:
427:
424:
423:
421:
409:
408:3-7909-0768-5
405:
401:
395:
391:
381:
380:3-613-02474-8
377:
373:
372:
364:
361:
359:
356:
354:
351:
349:
346:
345:
339:
336:
331:
328:
327:
326:
323:
318:
315:
314:
313:
310:
305:
302:
301:
300:
297:
292:
289:
288:
287:
284:
279:
276:
275:
274:
271:
266:
263:
262:
256:
254:
249:
245:
243:
238:
235:
230:
221:
219:
215:
209:
207:
203:
199:
195:
191:
186:
184:
180:
176:
166:
164:
163:solid rockets
160:
156:
152:
146:
142:
137:
130:
125:
121:
113:
110:
102:
91:
88:
84:
81:
77:
74:
70:
67:
63:
60: –
59:
55:
54:Find sources:
48:
44:
38:
37:
32:This article
30:
26:
21:
20:
399:
394:
358:Rheintochter
337:
334:
329:
324:
321:
316:
311:
308:
303:
298:
295:
290:
285:
282:
277:
272:
269:
264:
250:
246:
239:
231:
227:
210:
197:
194:Air Ministry
189:
187:
182:
172:
150:
149:
140:
128:
120:
105:
96:
86:
79:
72:
65:
58:"Feuerlilie"
53:
41:Please help
36:verification
33:
420:Categories
369:Literature
363:Wasserfall
218:Baltic Sea
151:Feuerlilie
141:Feuerlilie
129:feuerlilie
69:newspapers
436:Luftwaffe
278:Diameter:
183:Fire Lily
99:July 2011
342:See also
173:In 1940
386:Sources
330:Weight:
265:Length:
234:Breslau
139:German
127:German
83:scholar
406:
378:
353:Taifun
85:
78:
71:
64:
56:
304:Vmax:
90:JSTOR
76:books
404:ISBN
376:ISBN
291:Span
214:Leba
198:F 25
62:news
143:at
45:by
422::
402:,
165:.
112:)
106:(
101:)
97:(
87:·
80:·
73:·
66:·
39:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.