112:
95:
became limited. Ferredoxin is iron-dependant as well as oxidant-sensitive. Under these limited iron conditions, ferredoxin was no longer preferred. Flavodoxin on the other hand is the opposite of these traits, as it is oxidant-resistant and has iron-free isofunctional counterparts. Therefore, for
131:
of flavin mononucleotide as well as assist in the formation of folded intermediates. However, it is still not certain what the loops true function is. In addition, the flavin mononucleotide is non-covalently bound to the flavodoxin protein and works to shuttle
278:
Prakash, Divya; Iyer, Prashanti R.; Suharti, Suharti; Walters, Karim A.; Santiago-Martinez, Michel
Geovanni; Golbeck, John H.; Murakami, Katsuhiko S.; Ferry, James G. (2019-12-17).
91:, another redox protein, was the only protein able to be used in this manner. However, when oxygen became present in the environment,
96:
some time flavodoxin was the primary redox protein. Now however, when ferredoxin and flavodoxin are present in the same
252:"RCSB PDB - 6FSG: Crystal structure of oxidised Flavodoxin 1 from Bacillus cereus (1.27 A resolution)"
81:
41:
119:
Flavodoxin proteins may consist of long or short chains. A long chain is determined when 20
8:
339:
279:
312:
227:
180:
155:
Sancho J (April 2006). "Flavodoxins: sequence, folding, binding, function and beyond".
85:
317:
299:
232:
172:
351:
307:
291:
222:
214:
184:
164:
128:
284:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
80:, flavodoxins were discovered over 50 years ago.These proteins evolved from an
17:
168:
303:
73:
57:
49:
295:
321:
236:
176:
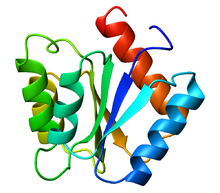
44:. The structure of flavodoxin is characterized by a five-stranded parallel
203:"The long goodbye: the rise and fall of flavodoxin during plant evolution"
280:"Structure and function of an unusual flavodoxin from the domain Archaea"
218:
53:
100:, ferredoxin is still used but under low iron conditions, flavodoxin is
355:
124:
120:
111:
88:
77:
45:
251:
202:
133:
34:
30:
200:
101:
37:
127:. These residues form a loop which may be used to increase the
97:
201:
Pierella
Karlusich JJ, Lodeyro AF, Carrillo N (October 2014).
61:
338:
Houwman, Joseline A.; van Mierlo, Carlo P. M. (2017-04-05).
92:
52:
at either side of the sheet. They have been isolated from
340:"Folding of proteins with a flavodoxin-like architecture"
277:
337:
311:
226:
110:
14:
154:
333:
331:
273:
271:
196:
194:
157:Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences
123:residues are inserted into the last
115:3-D structure of flavodoxin protein
23:
24:
371:
328:
268:
191:
249:
243:
207:Journal of Experimental Botany
148:
13:
1:
142:
67:
106:
7:
10:
376:
250:Bank, RCSB Protein Data.
169:10.1007/s00018-005-5514-4
296:10.1073/pnas.1908578116
116:
60:, and some eukaryotic
29:are electron-transfer
114:
82:anaerobic environment
42:flavin mononucleotide
86:selective pressures.
72:Originally found in
290:(51): 25917–25922.
356:10.1111/febs.14077
219:10.1093/jxb/eru273
117:
350:(19): 3145–3167.
33:.Flavodoxin is a
367:
360:
359:
344:The FEBS Journal
335:
326:
325:
315:
275:
266:
265:
263:
262:
247:
241:
240:
230:
198:
189:
188:
152:
129:binding affinity
48:, surrounded by
375:
374:
370:
369:
368:
366:
365:
364:
363:
336:
329:
276:
269:
260:
258:
248:
244:
213:(18): 5161–78.
199:
192:
163:(7–8): 855–64.
153:
149:
145:
139:
109:
70:
22:
21:
20:
12:
11:
5:
373:
362:
361:
327:
267:
242:
190:
146:
144:
141:
108:
105:
69:
66:
40:that includes
18:User:Noroz6420
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
372:
357:
353:
349:
345:
341:
334:
332:
323:
319:
314:
309:
305:
301:
297:
293:
289:
285:
281:
274:
272:
257:
253:
246:
238:
234:
229:
224:
220:
216:
212:
208:
204:
197:
195:
186:
182:
178:
174:
170:
166:
162:
158:
151:
147:
140:
137:
135:
130:
126:
122:
113:
104:
103:
99:
94:
90:
87:
83:
79:
75:
74:cyanobacteria
65:
63:
59:
58:cyanobacteria
55:
51:
50:alpha helices
47:
43:
39:
36:
32:
28:
19:
347:
343:
287:
283:
259:. Retrieved
256:www.rcsb.org
255:
245:
210:
206:
160:
156:
150:
138:
118:
71:
26:
25:
125:beta-strand
54:prokaryotes
27:Flavodoxins
261:2022-05-05
143:References
121:amino acid
89:Ferredoxin
78:clostridia
68:Background
46:beta sheet
304:0027-8424
134:electrons
107:Structure
84:, due to
35:bacterial
322:31801875
237:25009172
177:16465441
102:induced.
31:proteins
313:6926009
228:4400536
185:6090402
38:protein
320:
310:
302:
235:
225:
183:
175:
98:genome
181:S2CID
62:algae
16:<
318:PMID
300:ISSN
233:PMID
173:PMID
93:iron
76:and
352:doi
348:284
308:PMC
292:doi
288:116
223:PMC
215:doi
165:doi
136:.
346:.
342:.
330:^
316:.
306:.
298:.
286:.
282:.
270:^
254:.
231:.
221:.
211:65
209:.
205:.
193:^
179:.
171:.
161:63
159:.
64:.
56:,
358:.
354::
324:.
294::
264:.
239:.
217::
187:.
167::
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.