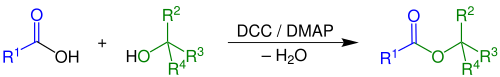107:
183:
150:
124:
can be used. Because the reaction is mild, esters can be obtained that are inaccessible through other methods for instance esters of the sensitive 2,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid. A characteristic is the formal uptake of water generated in the reaction by DCC, forming the
167:. If the esterification is slow, a side-reaction occurs, diminishing the final yield or complicating purification of the product. This side-reaction is a 1,3-rearrangement of the
257:
W. König, R. Geiger (1970). "Eine neue
Methode zur Synthese von Peptiden: Aktivierung der Carboxylgruppe mit Dicyclohexylcarbodiimid unter Zusatz von 1-Hydroxy-benzotriazolen".
178:
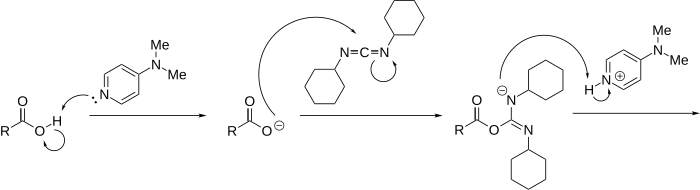
which is unable to further react with the alcohol. DMAP suppresses this side reaction, acting as an acyl transfer-reagent in the following manner:
182:
396:
359:
331:"Esterification of Carboxylic Acids with Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide/4-Dimethylaminopyridine: tert-Butyl ethyl fumarate"
56:
106:
386:
149:
371:
78:
391:
82:
98:
203:
121:
201:
B. Neises, W. Steglich (1978). "Simple Method for the
Esterification of Carboxylic Acids".
8:
295:"A solvent-reagent selection guide for Steglich-type esterification of carboxylic acids"
142:
355:
335:
275:
231:
90:
40:
30:
306:
267:
239:
211:
130:
117:
330:
74:
380:
293:
Jordan, Andrew; Whymark, Kyran D.; Sydenham, Jack; Sneddon, Helen F. (2021).
271:
229:
J. C. Sheehan, G. P. Hess (1955). "A New Method of
Forming Peptide Bonds".
215:
164:
279:
243:
311:
294:
259:
93:
in 1978. It is an adaptation of an older method for the formation of
172:
86:
159:, the reaction proceeds without problems to the corresponding
160:
156:
94:
292:
126:
228:
200:
328:
256:
378:
97:by means of DCC (dicyclohexylcarbodiimide) and
372:Mechanism for the Steglich esterification
354:. 1. Auflage, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2003,
310:
116:This reaction generally takes place at
379:
89:. The reaction was first described by
136:
13:
322:
105:
14:
408:
365:
181:
148:
286:
250:
222:
194:
1:
188:
7:
329:B. Neises and W. Steglich.
10:
413:
81:as a coupling reagent and
345:, vol. 7, p. 93
171:-acyl intermediate to an
145:is described as follows:
63:
52:Organic Chemistry Portal
46:
21:
397:Esterification reactions
272:10.1002/cber.19701030319
163:because amines are more
79:dicyclohexylcarbodiimide
22:Steglich esterification
83:4-dimethylaminopyridine
71:Steglich esterification
57:steglich-esterification
216:10.1002/anie.197805221
122:polar aprotic solvents
111:
99:1-hydroxybenzotriazole
204:Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.
109:
73:is a variation of an
244:10.1021/ja01609a099
387:Coupling reactions
312:10.1039/D1GC02251B
143:reaction mechanism
137:Reaction mechanism
112:
343:Collected Volumes
336:Organic Syntheses
232:J. Am. Chem. Soc.
110:Steglich overview
91:Wolfgang Steglich
67:
66:
41:Coupling reaction
31:Wolfgang Steglich
16:Chemical reaction
404:
346:
339:
317:
316:
314:
290:
284:
283:
254:
248:
247:
238:(4): 1067–1068.
226:
220:
219:
198:
185:
152:
131:dicyclohexylurea
118:room temperature
59:
19:
18:
412:
411:
407:
406:
405:
403:
402:
401:
377:
376:
368:
341:
325:
323:Further reading
320:
291:
287:
255:
251:
227:
223:
199:
195:
191:
139:
120:. A variety of
55:
17:
12:
11:
5:
410:
400:
399:
394:
392:Name reactions
389:
375:
374:
367:
366:External links
364:
363:
362:
352:Esterification
348:
324:
321:
319:
318:
285:
266:(3): 788–798.
249:
221:
210:(7): 522–524.
192:
190:
187:
138:
135:
114:
113:
75:esterification
65:
64:
61:
60:
53:
49:
48:
44:
43:
38:
37:Reaction type
34:
33:
28:
24:
23:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
409:
398:
395:
393:
390:
388:
385:
384:
382:
373:
370:
369:
361:
360:3-527-30490-8
357:
353:
349:
344:
338:
337:
332:
327:
326:
313:
308:
305:: 6405–6413.
304:
300:
296:
289:
281:
277:
273:
269:
265:
262:
261:
253:
245:
241:
237:
234:
233:
225:
217:
213:
209:
206:
205:
197:
193:
186:
184:
179:
177:
175:
170:
166:
162:
158:
153:
151:
146:
144:
134:
132:
128:
123:
119:
108:
104:
103:
102:
100:
96:
92:
88:
84:
80:
76:
72:
62:
58:
54:
51:
50:
45:
42:
39:
36:
35:
32:
29:
26:
25:
20:
351:
342:
334:
302:
298:
288:
263:
258:
252:
235:
230:
224:
207:
202:
196:
180:
173:
168:
165:nucleophilic
154:
147:
140:
115:
70:
68:
47:Identifiers
27:Named after
381:Categories
350:J. Otera:
299:Green Chem
260:Chem. Ber.
189:References
176:-acylurea
129:compound
101:(HOBT).
87:catalyst
280:5436656
133:(DCU).
358:
278:
161:amides
157:amines
95:amides
155:With
85:as a
77:with
356:ISBN
276:PMID
141:The
127:urea
69:The
307:doi
268:doi
264:103
240:doi
212:doi
383::
340:;
333:.
303:23
301:.
297:.
274:.
236:77
208:17
347:.
315:.
309::
282:.
270::
246:.
242::
218:.
214::
174:N
169:O
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.