670:
killed. Some of the soldiers decided to side with Totila and opened the gate for him. Totila's men entered the city and massacred the unsuspecting Roman garrison. The city was then sacked, with only the women spared on the orders of Totila. Expecting the nobles and the remainder of the garrison to flee as soon as the walls were taken, Totila set traps along the roadways to neighboring towns that were not yet under his control. Many Romans were caught by ambush while fleeing Rome; only a few, including
Diogenes, the Roman commander, escaped Totila's takeover of Rome.
146:
32:
666:
take months or years, but was in a far better position than the last siege attempt and decided it was the best course of action. The
Byzantine commander Diogenes had previously made preparations of food stores, had wheat fields sowed, and made ready the city walls in preparation for a long-lasting blockade.
669:
The Roman soldiers, suffering from hunger and mistreatment from
Justinian, were given a choice by Totila: to open the gates of the city, surrender, and be paid a hefty sum, as the garrison had done during the second siege; or continue fighting for Justinian, who had not paid the men in years, and be
665:
Totila first attempted to capture Rome by storming the walls and overpowering and exhausting the small Roman garrison of 3,000, but to no avail. He then decided to blockade the city and starve out the defenders, rather than losing any more of his own soldiers. Totila understood that a blockade could
656:
In 549–550, Totila, the
Ostrogothic leader, besieged Rome for the third and final time. With Belisarius' return to Constantinople the summer before, Totila encountered less difficulty than previously in the campaign. The Ostrogoths had attempted to besiege Rome twice before, but had failed or were
649:. Belisarius, under Justinian, aimed to conquer all of Italy and restore it to its former glory. After Belisarius conquered much of Italy, including the Ostrogoths' capital, Ravenna, the Ostrogoths appointed Totila to power and took back much of Italy as soon as Belisarius returned to
633:, soldiers from the city's garrison opened the gates to the Ostrogothic army. Many of Rome's male inhabitants were killed in the city or while attempting to flee—further reducing Rome's population which had collapsed in recent decades.
545:
560:
252:
758:
704:
459:
575:
550:
641:
At this time Totila, military and political leader of the
Ostrogoths, was attempting to re-conquer the whole of Italy from the Byzantine emperor
823:
245:
96:
49:
68:
803:
75:
765:
238:
828:
355:
82:
798:
793:
64:
592:
350:
808:
115:
727:
365:
751:
555:
429:
53:
454:
20:
540:
474:
89:
375:
404:
307:
686:, the Ostrogoths were resoundingly defeated and Totila was slain. Rome was recaptured later that year.
318:
506:
484:
382:
137:
818:
788:
783:
501:
489:
409:
345:
42:
813:
511:
297:
516:
399:
370:
535:
530:
330:
325:
302:
203:
8:
597:
449:
419:
282:
719:
587:
464:
444:
340:
287:
145:
723:
683:
565:
479:
434:
394:
389:
360:
626:
424:
414:
335:
570:
439:
650:
292:
151:
777:
314:
275:
263:
186:
150:
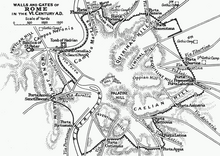
Walls and gates of Rome, 6th century. Totila and his men entered via the
646:
618:
208:
230:
642:
523:
31:
630:
679:
622:
223:
614:
678:
A large
Eastern Roman force was assembled in 550-551 under
610:
175:
761:" Wars of the Ostrogoths (2007): n.pag. Web. 19 Nov 2012.
754:" Reconquest of Italy (2011): n.pag. Web. 19 Nov 2012.
56:. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
653:. These Gothic Wars laid waste to much of Italy.
775:
625:, during a campaign to recapture Italy from the
705:"THE CITY IN DECLINE: ROME IN LATE ANTIQUITY"
246:
768:" Sardinia (2002): n.pag. Web. 19 Nov 2012.
253:
239:
144:
116:Learn how and when to remove this message
260:
776:
824:Sieges involving the Byzantine Empire
702:
234:
54:adding citations to reliable sources
25:
13:
752:History of the Later Roman Empire.
682:, landing in Italy in 552. At the
14:
840:
804:Battles involving the Ostrogoths
30:
41:needs additional citations for
16:Siege of Rome during Gothic War
829:Violence against men in Europe
696:
1:
689:
636:
799:550s in the Byzantine Empire
794:540s in the Byzantine Empire
673:
660:
65:"Siege of Rome" 549–550
7:
566:Onoguris (3rd Archaeopolis)
10:
845:
18:
766:Vandalic and Gothis Wars.
657:defeated by Belisarius.
629:. After Totila imposed a
271:
214:
197:
158:
143:
135:
130:
712:Middle States Geographer
759:Fall of the Ostrogoths.
645:and his great general,
496:Sasanian war of 540–562
166:June 549 – February 550
215:Commanders and leaders
703:Twine, Kevin (1992).
617:in AD 549–550 by the
809:Gothic War (535–554)
356:Babosis and Zerboule
204:Eastern Roman Empire
138:Gothic War (535–554)
50:improve this article
19:For other uses, see
154:, in the southeast.
131:Siege of Rome (549)
757:Morris, Charles. "
588:Conquest of Spania
684:Battle of Taginae
606:
605:
229:
228:
193:
192:
126:
125:
118:
100:
836:
764:Tisi, Claudio. "
743:
742:
740:
738:
732:
726:. Archived from
709:
700:
627:Byzantine Empire
561:2nd Archaeopolis
556:Telephis–Ollaria
546:1st Archaeopolis
266:
255:
248:
241:
232:
231:
160:
159:
148:
128:
127:
121:
114:
110:
107:
101:
99:
58:
34:
26:
844:
843:
839:
838:
837:
835:
834:
833:
774:
773:
747:
746:
736:
734:
730:
707:
701:
697:
692:
676:
663:
639:
607:
602:
593:Anastasian Wall
267:
261:
259:
178:
149:
122:
111:
105:
102:
59:
57:
47:
35:
24:
17:
12:
11:
5:
842:
832:
831:
826:
821:
819:Sieges of Rome
816:
811:
806:
801:
796:
791:
789:550s conflicts
786:
784:540s conflicts
770:
769:
762:
755:
745:
744:
694:
693:
691:
688:
675:
672:
662:
659:
651:Constantinople
638:
635:
604:
603:
601:
600:
595:
590:
584:
583:
579:
578:
573:
568:
563:
558:
553:
548:
543:
538:
533:
520:
519:
514:
509:
504:
498:
497:
493:
492:
487:
485:Mons Lactarius
482:
477:
472:
467:
462:
457:
452:
447:
442:
437:
432:
427:
422:
417:
412:
407:
402:
397:
392:
386:
385:
379:
378:
376:Fields of Cato
373:
368:
363:
358:
353:
348:
343:
338:
333:
328:
322:
321:
311:
310:
305:
300:
295:
290:
285:
279:
278:
272:
269:
268:
258:
257:
250:
243:
235:
227:
226:
221:
217:
216:
212:
211:
206:
200:
199:
195:
194:
191:
190:
184:
180:
179:
174:
172:
168:
167:
164:
156:
155:
152:Porta Asinaria
141:
140:
133:
132:
124:
123:
38:
36:
29:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
841:
830:
827:
825:
822:
820:
817:
815:
814:Sacks of Rome
812:
810:
807:
805:
802:
800:
797:
795:
792:
790:
787:
785:
782:
781:
779:
772:
767:
763:
760:
756:
753:
749:
748:
733:on 2020-02-28
729:
725:
721:
717:
713:
706:
699:
695:
687:
685:
681:
671:
667:
658:
654:
652:
648:
644:
634:
632:
628:
624:
620:
616:
612:
599:
596:
594:
591:
589:
586:
585:
581:
580:
577:
574:
572:
569:
567:
564:
562:
559:
557:
554:
552:
549:
547:
544:
542:
539:
537:
534:
532:
529:
528:
527:
526:
525:
518:
515:
513:
510:
508:
505:
503:
500:
499:
495:
494:
491:
488:
486:
483:
481:
478:
476:
473:
471:
468:
466:
463:
461:
458:
456:
453:
451:
448:
446:
443:
441:
438:
436:
433:
431:
428:
426:
423:
421:
418:
416:
413:
411:
408:
406:
403:
401:
398:
396:
393:
391:
388:
387:
384:
381:
380:
377:
374:
372:
369:
367:
364:
362:
359:
357:
354:
352:
349:
347:
344:
342:
339:
337:
334:
332:
329:
327:
324:
323:
320:
316:
313:
312:
309:
306:
304:
301:
299:
296:
294:
291:
289:
286:
284:
281:
280:
277:
274:
273:
270:
265:
256:
251:
249:
244:
242:
237:
236:
233:
225:
222:
219:
218:
213:
210:
207:
205:
202:
201:
196:
188:
185:
182:
181:
177:
173:
170:
169:
165:
162:
161:
157:
153:
147:
142:
139:
134:
129:
120:
117:
109:
106:February 2013
98:
95:
91:
88:
84:
81:
77:
74:
70:
67: –
66:
62:
61:Find sources:
55:
51:
45:
44:
39:This article
37:
33:
28:
27:
22:
771:
750:Bury, J.B. "
735:. Retrieved
728:the original
715:
711:
698:
677:
668:
664:
655:
640:
609:The city of
608:
522:
521:
475:Sena Gallica
469:
319:Moorish Wars
315:Vandalic War
308:Martyropolis
198:Belligerents
136:Part of the
112:
103:
93:
86:
79:
72:
60:
48:Please help
43:verification
40:
21:Sack of Rome
718:: 134–138.
276:Iberian War
264:Justinian I
187:Ostrogothic
778:Categories
690:References
647:Belisarius
637:Background
619:Ostrogoths
507:Sisauranon
455:2nd Naples
420:Urviventus
400:1st Naples
383:Gothic War
331:Tricamarum
326:Ad Decimum
303:Callinicum
209:Ostrogoths
76:newspapers
737:April 10,
724:130565899
674:Aftermath
661:The siege
643:Justinian
621:, led by
598:Melantias
541:3rd Petra
536:2nd Petra
531:1st Petra
524:Lazic War
490:Volturnus
450:Mucellium
283:Thannuris
631:blockade
615:besieged
470:3rd Rome
465:2nd Rome
445:Faventia
410:Ariminum
405:1st Rome
390:Panormus
366:Sufetula
351:Membresa
346:Carthage
341:Bourgaon
288:Mindouos
262:Wars of
220:Diogenes
171:Location
576:Tzacher
502:Nisibis
480:Taginae
460:Otranto
435:Treviso
430:Ravenna
425:Auximus
415:Urbinus
395:Scardon
361:Cillium
189:victory
90:scholar
722:
680:Narses
623:Totila
571:Phasis
551:Cotais
517:Edessa
512:Anglon
440:Verona
336:Mammes
298:Satala
224:Totila
183:Result
92:
85:
78:
71:
63:
731:(PDF)
720:S2CID
708:(PDF)
582:Other
371:Marta
97:JSTOR
83:books
739:2024
613:was
611:Rome
317:and
293:Dara
176:Rome
163:Date
69:news
52:by
780::
716:25
714:.
710:.
741:.
254:e
247:t
240:v
119:)
113:(
108:)
104:(
94:·
87:·
80:·
73:·
46:.
23:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.