527:. Between 1800 and 1821, the conflict between Hudson's Bay and Montreal, at that point represented by the predominantly Scottish North West Company, intensified. The conflict reached its peak in 1801 and witnessed both companies expending more resources on out-competing each other than were expended on the exploration of new fur grounds. Between 1803 and 1804, Hudson's Bay morale had plummeted in the face of fierce Northwest competition and forced the two companies into negotiations but neither side could come to terms. Negotiations broke down again in 1805 and despite employing more aggressive agents and the provision of incentive programs, the Hudson's Bay Company was ready to abandon the fur trade in 1809. The Nor'Westers ability to make region-wide plans based on first-hand knowledge in addition to their ability to react quickly to changing circumstances provided the North West Company with a decisive advantage prior to 1810. After 1810, the combination of new management within the Hudson's Bay Company and the approval of a company-sponsored colony at Red River put the North West Company on the defensive. The establishment of a Hudson's Bay colony in the Red River region denied the Nor'Westers access to vital supplies and restricted the company's ability to expand westwards. Additionally, the establishment of an agricultural colony made the Hudson's Bay company nondependent on the profitable fur trade, a factor that the Nor'Westers simply could not compete with. Moreover, by establishing an agricultural colony, the Hudson's Bay Company gained a decisive advantage over the North West Company by virtue of a viable fallback economy as well as a readily available food source during economic slumps. Much of this new-found confidence hinged on the Selkirk's success at Red River and resulted in the colony becoming the central focus of seven years of inter-company warfare.
670:
791:
least heavily influenced by indigenous or Métis communities. Once the rebellion was put down and
Manitoba was admitted, thousands of largely Protestant, anglophone Ontarians quickly began migrating to the prairies, and their presence swiftly shifted the demographic, national, and linguistic profile of the province, which in turn meant the election of provincial governments decisively oriented towards Ontario and English Canada, rather than French Canada, Métis, First Nations, or balance between these groups. The Manitoba government also sought to encourage immigration and the immediate establishment and expansion of stable agricultural communities, and within a two decades many thousands of international migrants, largely ethnic Ukrainians and Germans, had come to the province as agricultural settlers. The Catholic Church also continued to encouraged migration and settlement from Quebec and francophone Ontario to Manitoba, however these settlers were far outnumbered by English settlers as well international migrants whose communities would be assimilated in Anglo-Canadian society.
627:, an appointed body with representatives of various sections of Red River society (francophone and anglophone, Roman Catholic and Protestant officials, Métis, Scottish, Irish, French-Canadian, etc.), all sharing a common past or present involvement with the Companies. While the end of the fur trade's inspired conflicts on the plains, the Red River settlement was able to grow in both population and economic importance with the expansion of commercially-oriented agriculture (raising of staple crops). The agricultural products, primarily wheat, began to rise in yearly yields. Flour production rose from over 9,100 kilograms (20,000 lb) annually from 1823 to 1829 to over 14,000 kg (30,000 lb) in the early 1830s. The supply of flour reached over 23,000 kg (50,000 lb) by the mid-1830s, rapidly deflating the price the HBC paid the farmers for the product. Numbering over 1,000 by 1827, the farmers began to complain about the deflating rates they received and lack of markets for their goods.
564:. Although the arrival and subsequent settlement of Selkirk's private army finally broke the back of the North West Company, Selkirk spent much of his remaining years, and the majority of his fortune, defending his actions at Fort William. When Selkirk arrived at Red River in 1817, the stability of the colony dramatically improved, especially after the removal of all Indigenous claims to the land. Selkirk achieved this by signing a treaty between the Red River colonists and the local Cree, Assiniboine and Ojibwa. Between 1817 and 1820, Selkirk committed all of his available resources to the betterment of his colonial venture and ironically it was Selkirk's death in the spring of 1820 that ultimately ended Northwest aggression against his beloved colony.
682:, the American annexationists hoped to take advantage of the disruption caused by these political conflicts and present themselves in the forefront as the ideal leaders of the Red River land. The annexation was led by Minnesota senator Alexander Ramsey, and was backed by Zachariah Chandler and Jacob M. Howard- who were both senators of Michigan and represented Detroit merchants. They all shared the same economic vision for the annexation: Ramsey believed that the Red River valley would serve as an important commercial adjunct for his state, while Chandler and Howard believed that annexing the Red River would benefit their Great Lakes Trade. This was done under the belief it would help them in their attempts to colonize the region, as it prevented the
459:
863:
civilization. Although these schools took in all children of the colony, mixed-ancestry children were a large focus due to them being tied to the fur trading post by their
European fathers. John Halkett, a Committee member, wanted Metis families of retired HBC employees to be brought to Red River (from other nearby posts) to be put under the authority of the Roman Catholic Mission or Church Missionary Society. This plan was largely related to keeping retired Metis employees from continuing trade with the Indigenous peoples; however, its effect led to Christianity being a prominent part of culture for the Metis community. The Chaplain of the Hudson's Bay Company,
839:
to the settlement, tensions between the
European and indigenous communities were heightened due to the highly restrictive gender norms these women brought with them from Europe. In part a reflection of their conservative morals, many settlers in the colony also claimed to observe differences between European and indigenous women; Alexander Ross, a Scottish author who lived in the Red River Colony for a number of years, stated in a book written by him on the colony's history that a friend informed him that European women were required to be "graceful" unlike indigenous women, who were exempt from this due to their bashfulness.
734:
in 1869–70 that were carefully structured to be given in severalty, rather than in common. Red River was now developing its own provincial government that had a political voice and political implications upon
Canadian federal government. This rebellion also led to the Métis emerging as a unique, acknowledged group within Canada, and ultimately, the disappearance of the Aboriginal rights paradigm in the public view of Red River. The rebellion was successful in a sense that it allowed the Métis to have a political voice, but it impacted the perception of how other Aboriginals would be viewed in Red River.
855:
Company's journals and a number of witnesses to these events stated that the united caravan was commonly known as a brigade. These brigades did not just focus on buffalo hunting but were used by buffalo hunters to trade and freight during this time. Women were fundamental in both actively participating in the brigade hunts or trade, as well as the bringing together of people prior to the excursion. By studying the social network of the
Trottier Brigade, a community of people from the White Horse Plains in Red River, it is notable that biologically related women brought the majority of the men together.
54:
243:
68:
3234:
438:, the dominant fur trading companies at the time, was essential to the establishment of a colony at Red River. By 1811, the Hudson's Bay Company had reconsidered Selkirk's proposal and granted Selkirk 300,000 km (116,000 sq mi), an area five times the size of Scotland, to establish an agricultural settlement in the region of Red River. Supplies of "produce, such as flour, beef, pork and butter..." would be affordable to manufacture in this colony, and would reduce the costly shipments from Britain.
218:
592:
699:. The Rebellion was an unarmed conflict started by the Métis because Canada was attempting to claim possession of Rupert's Land without any concern for the grievances of the Métis. However, the main American intention behind their decision to support Riel and the Rebellion was an attempt to sway the Métis in favour of the annexation by the US. One of their tools was the New Nation newspaper which elicited rhetoric that advocated annexation by the US because it embodied the popular
859:
livelihoods and practices followed. Metis who chose not to live on prairies and hunt buffalo for the winter remained on lakes such as
Manitoba, Winnipegosis, and Winnipeg to ice fish. Over the course of the first half of the 19th century, up to forty households had developed on the lakeshore of Lake Manitoba. Fishing and trading had become year round practices and the Metis families involved would trade with HBC and ‘Freemen’- traders that did not work at the post.
3221:
257:
831:. Thomas, in her testimony, used the laws in place to challenge Corbett's actions; citing British law against forcing individuals to undergo abortions, which were illegal. She won the case; however, Corbett was freed from jail shortly after by a group of settlers who were opposed to the trial. The courts did not challenge this, fearing a possible insurrection, demonstrating the weakness of the colonial authorities in the nascent colony.
949:
751:
government policy. Riel would subsequently be claimed as a hero and martyr by the French-Canadian, Métis, and various First
Nations for decades. The Canadian government was starting to punish the rebels for their defiance, but the rebellion is still considered a success in the sense that the Metis were still able to acquire the land rights they hoped to achieve, as well as no longer being ignored when it came to federal matters.
498:, they were forced to hunt bison for food and were completely unprepared for the arrival of 120 additional settlers in October. More settlers were scheduled to arrive in 1813, but due to a fever outbreak on their ship, they did not arrive until June 21, 1814. Dogged by poor harvests and a growing population, Macdonell, now governor of Red River, issued the
871:
French-Canadian traders bringing
Catholic priests and missionaries in their wake, later Scottish traders and the Company brought Protestant missionaries and clergy into Ojibwe-dominated areas. This division into a Cree-French-Catholic oriented group and an Ojibwe-Scottish-Protestant oriented group can be seen in the rise of the two main Métis languages:
721:
Manitoba. The political disputes put the Métis on a platform to voice their disapproval of
Americans ignoring their concerns over these land disputes. They had legitimate claims to the land and they stated that they were the "descendants of the lords of the soil.". Also, under Louis Riel's leadership, the Metis rebels were able to capture
708:
they were eager to create a political union. This ultimately caused the annexation of the North West to fail, despite it being almost within reach. All this ultimately benefited the cause of Riel and the
Rebellion. As a result, the Metis were able to successfully defy Canadian expansion into Rupert's Land.
867:, was also interested in the religious educating of Metis children. According to his book, he wrote to the Governor submitting a plan to gather up a number of children to care for and educate. He stated that he created this plan when he saw these children being raised in a way he deemed ignorant and idle.
854:
The culture and lifestyle of the Metis community living in Red River were not only present at the colony. Metis people had a long-lasting tradition of a semi-annual, commercial, buffalo hunt that took place throughout the prairies starting in the mid-1700s with the western fur trade. The Hudson's Bay
803:
of a secular, English-only public school system which would be the sole recipient of any public funding. The policy was eventually implemented with minor concessions such as the teaching of Catholic doctrine at the end of the day where the number of students warranted, and the role of French in these
543:
and the settlement was abandoned once again. The imminent arrival of Selkirk in 1817, who had been en route to the colony prior to the incident at Seven Oaks, prompted the settlers to return to the colony shortly after. Travelling with a force of approximately 100 soldiers from the recently disbanded
931:
nation, both of whom were later ordained as priests. In 1822, the CMS appointed Revd West to head the mission in the Red River Colony. He was succeeded in 1823 by the Revd David Jones who was joined by the Revd W and Mrs Cockran in 1825. The mission expanded and by 1850, the missionaries were active
786:
was mostly created to prevent another Red River Rebellion. Many of the government officials were inexperienced – especially the three delegates who went to Ottawa to negotiate union terms. None of them had experience with diplomacy or the creation of new governments. Due to the hurried nature of the
733:
The aftermath of the rebellion caused the Métis to no longer be considered as Canadian Aboriginals – they became regarded as their own social group, and were distinct from other Aboriginal groups. In order to pacify the Métis resistance further, the Canadian government gave them generous land grants
729:
as a province, security for their land claims, making English and French the official languages of the colony, as well as financial support for the Red River population. Riel hoped to accomplish a sense of equality for the Métis; he wanted to present them as a civilized people that were deserving of
707:
However, this aggressive propaganda ultimately backfired upon the proposal of annexation. It created even more hostility towards the annexation party and the United States. This great emphasis on materialism never seemed appealing to the Red River people. The Americans became too acquisitive because
473:
The early settlement of the Red River region was marked by a long series of crises and ecological disasters and within the first decade of settling the region it had already suffered renewed warfare, epidemics, prairie fires and a flood. Perhaps the most significant ecological disaster was the rapid
449:
There is continuing debate as to whether Selkirk forced the concession of Assiniboia through a controlling interest of Hudson's Bay stock. The argument against Selkirk claims that he received the concession by controlling the shares in the company. Historians seeking to defend this claim have argued
441:
The grant was also pending the annual provision of 200 men to the company and Selkirk's assurance that the colony would remain out of the fur trade. Selkirk, who once mocked the fur trade for rarely grossing more than £200,000 and only having three ships employed in its service, gladly agreed to the
838:
or Metis spouse. Though only encouraged by the NWC for trade relations, it was a common practice among European employees of both companies due to the various policies by the companies which only allowed males to emigrate to fur trading outposts. When female settlers did eventually start emigrating
769:
in 1870. They believed that this act would accomplish two purposes: this would be able to crush the rebellion, while at the same time, appeasing the French demands of increasing French influence in Canada because the act would create a Western province that was constitutionally supportive of French
677:
American expansionists became heavily interested in the economic potential the territory of the Red River Colony possessed. The ideal soil, climate and socio-economic potential of the area convinced many Americans that they needed to make the territory part of the United States. The result ended up
858:
Throughout the time that Metis people were a part of the Red River community they developed into several different identities, rather than just the common depiction of the bison-hunting French Catholic Metis. Metis identity, at that time as it is today, was diverse and complex due to the different
798:
which legally guaranteed a place for the French language in the province's administration, lawmaking, and judiciary along with a clause ensuring state funding for both Catholic (often de facto French) and Protestant schools, English had become the sole means of communication in the legislature and
790:
Many in French Canada had seen the establishment of Manitoba, officially bilingual and with a large francophone and Catholic population, as a counter-balance to English and Protestant dominance in the Canadian Confederation, while some hoped the province would be a political entity centered or at
750:
in reaction to the execution of a French-speaking, Catholic political leader, and Riel's death was seen on all sides (among those who saw Riel as a traitor who was rightly punished and those outraged at his arrest and execution) as symbolic of the danger that could result from contesting Canadian
690:
The proposal was met with a significant amount of resistance from the inhabitants of the Red River as they were given the chance to address their grievances about the potential loss of land and becoming part of an American colonization project through a proclamation by the Governor-General of the
686:
from establishing sovereignty over the area. A notable example would be James W. Taylor: he was an American special agent and Winnipeg consul who used his political power to shape the destiny of the valley, which called for the removal of all English-Canadian influence. The Canadian government,
538:
who took over as governor the following winter and reinforced the colony's 45 survivors with 84 additional settlers. In 1815, the North West Company once again entered into negotiations with the Hudson's Bay Company under the threat of invasion of Northwest territory. Negotiations were headed by
720:
was created by Red River inhabitants to take the place of the unelected Assiniboia Council. The Canadian government was forced to develop the negotiations that allowed for the Métis demands that were legally entrenched in the Manitoba Act which eventually led to the creation of the province of
870:
The above-mentioned differences in religion, ways of life, and ethnic origins largely followed a pattern based on the initial contact between individuals, groups, and institutions. For example large communities within the Cree nation are thought to have come into contact with French and later
777:
Through the act, the Red River colony was now christened as Manitoba: a new Canadian province that was self-governed, and that had its own rights and responsibilities. It was no longer being viewed as a territory and was now officially part of the Canadian confederation. Provincial status was
704:
protection of the United States government to the Red River Métis and assert themselves as the new leaders and Red River would become American land. They ultimately wanted to create a situation where the Red River could become American territory by allying with the discontented Métis Nation.
703:
ideology. This was meant to help the cause of annexation, the idea being that their support of the Red River Rebellion would encourage local resistance against the Canadian government, and help swing local opinion in favour of independence – then ultimately America would step in to offer the
862:
Christianity played a vital role in shaping the community within the colony, especially for the Metis people. In the early 19th century, considerations were made by the Committee in London to open schools run by the Clergymen to benefit, in their opinion, from instruction in religion and
770:
Canadian language and culture. This was the first steps towards the creation of the present-day province of Manitoba. The act was given royal assent on May 12, 1870, and the commencement of Manitoba with a provincial status came to fruition on July 15, 1870. After the passage of the
782:. Riel wanted to secure Red River for the Canadians against the Americans' colonization projects and sentiments of their Manifest Destiny ideologies. The early Manitoba provincial government initially struggled to be effective. Everything around it felt rushed because the
737:
Once the rebellion ended, Riel and several of his comrades fled to the United States in 1870 upon being informed that several government soldiers and irregulars were looking to kill him to exact revenge for several incidents, in particular, the execution of
725:– a fortified post of the Hudson's Bay Company. This would lead Riel into becoming the leader of the provisional government, and he composed and sent a list of rights to Ottawa. The demands mainly consisted of the Métis wanting Red River to be entered into
415:, decided that emigration was the only viable option to improve the livelihood of the Scottish people. Upon inheriting his father's title in 1799, Selkirk focused the majority of his time and resources on establishing a Scottish colony in North America.
493:
with 36 primarily Irish and Scottish settlers. Due to persuasive efforts of the North West Company, only 18 settlers actually arrived at Red River in August 1812. As the planting season had ended before the settlers could complete the construction of
816:'s 1670 Charter; this document gave legislative and judicial powers in Rupert's Land to the company. It is stated within the Charter that the legal status of women is as dependents of a male authority, which included fathers, husbands or brothers.
746:. This caused him to face trial in a Canadian court, and eventually to being executed by the Canadian government in Regina. His death provoked outcry among the French Canadian, First Nations and Métis communities, with particular uproar in
1817:
West, John. The Substance of a Journal During a Residence at the Red River Colony, British North America: and frequent excursions among the North-west American Indians, in the years 1820, 1821, 1822, 1823. London: L.B Seeley, 1824:
646:, British Columbia; then travelled south. Despite such efforts, the British government eventually ceded all claim to land south of the 49th parallel of latitude west of the Rockies to the United States as a resolution to the
523:'s generous grant of Rupert's Land to emigrants who were members of the nobility in 1670. Cause for conflict arose from the inability of either the Montreal traders or the Hudson's Bay Company to gain a monopoly over the
518:
that was initiated by Macdonell's proclamation was only the tail end of a much larger conflict between the Hudson's Bay Company and its fur trade rivals, both English and French, in Montreal. The conflict dates back to
787:
creation of this province, the officials of this new government presented themselves as overwhelmed and unprepared, and this shows that Manitoba was essentially created to re-stabilize political unrest within Canada.
474:
depletion of the bison population. A vital food source, bison numbers had been dwindling since the 1760s due to heavy hunting pressure by Euroamerican traders as well as the aboriginal inhabitants of the prairies.
426:
raised concerns that the proposed colony would interfere with the running of the company. During the first decade of the nineteenth century Selkirk established two unsuccessful agricultural colonies in
730:
the same rights of any British subject. The rebellion became a pivotal moment in acquiring land rights and a political voice for the Métis, who were constantly disregarded for their Aboriginal status.
1727:
Ross, Alexander. The Red River Settlement: Its Rise, Progress, and Present State: With Some Account of Native Races and Its General History, to the Present Day. London: Smith, Elder and Co., 1856: 200
2501:
530:
Red River first came under attack from the North West Company in the summer of 1815. Convinced that Macdonell's proclamation was a deliberate attempt to block Northwest trade, the company destroyed
669:
794:
In the province's first few decades of existence (1870-1900), Manitoba experienced conflicting interests between French and English Canadians. A quarter-century after the implementation of the
765:
The Red River rebellion needed to be finally be put to rest. In order to accomplish this, the Canadian government, which was predominantly led by English-Canadian conservatives, initiated the
774:, the Métis Provisional government was disbanded. There was an assimilation of the Métis people and the European settlers, and the Aboriginal influence was further distanced from Red River.
534:
and burned down all of the surrounding buildings. The fort was later rebuilt but the engagement resulted in the capture of approximately 150 settlers including Macdonell. He was replaced by
2486:
673:
Map showing parts of the Northwest Territories, British Columbia, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba (referred to on the map by its historic name of Red River Settlement), published in 1870.
1006:
847:
The mixed ethnicity of indigenous and European peoples at the Red River Colony, known as Metis, were not always referred to by that name in the beginning years of their existence.
506:
from the colony. In doing so, Macdonell undermined the security of Red River and plunged the colony into a conflict with the North West Company that would not end until 1821.
1179:
The Treaties of Canada with the Indians of Manitoba and the North-West Territories Including the Negotiations on Which They Were Based, and Other Information Relating Thereto
1096:
3253:
350:
West of the Selkirk Concession, it is roughly formed by the current boundary between Saskatchewan and Manitoba. These covered portions consisted of present-day southern
678:
being an annexation proposal of Red River in 1870, in order to convert it into land that American settlers could use for economic purposes. Due to the outbreak of the
446:. At the time of the concession, Red River was the only Hudson Bay Colony that had been established within the company's 610,000-hectare (1.5-million-acre) territory.
271:
1419:
R. Douglas Francis, Richard Jones, and Donald B. Smith. "Origins: Canadian History to Confederation", 4th ed. (Toronto: Harcourt Canada ltd., 2000), at pp. 434–5.
1076:
3297:
3195:
2980:
1026:
851:, an author who lived in the colony, wrote in his book that they were often called "Brules, Metifs, or half-breeds, the bastard sons of Indian concubines".
3200:
3292:
1086:
716:
This political chaos, in a sense, became pivotal for Red River because it allowed for the success of the Métis in their rebellion. In 1870, the elected
1555:
Brown, Jennifer. "Métis, Halfbreeds, and Other Real People: Challenging Cultures and Categories". The History Teacher. 27, 1. November 1993. Pg. 20.
2224:
539:
Selkirk himself and he promptly threw out all of the Nor'Wester proposals. The following year Semple and twenty other settlers were killed in the
2244:
2893:
1693:
FitzGerald, Sharron A.; Muszynski, Alicja (November 2007). "Negotiating Female Morality: place, ideology and agency in the Red River Colony".
450:
that although Selkirk did buy a considerable number of Hudson's Bay shares between 1811 and 1812, Selkirk received his initial grant in 1811.
2870:
1808:
Bradford, Tolly. "Conservative Visions of Christianity and Community in Early Red River, c1800-1821." Manitoba History 71, no. 1 (2013): 36
804:
new public schools was to be highly limited, mainly to use as means of instructing young students who started school not speaking English.
2655:
2187:
3096:
3091:
2664:
1132:
1056:
1434:
2998:
1377:
Gluek, Alvin (1958). "Industrial Experiments in the Wilderness: A sidelight on the Business History of the Hudson's Bay Company".
2291:
692:
3110:
2865:
2730:
2314:
1891:
1829:
1937:
Bruyneel, F. Donald (2010), "Exiled, Executed, Exalted: Louis Riel, "Homo Sacer" and the Production of Canadian Sovereignty",
3081:
2880:
2817:
1987:
1465:
643:
407:, Lord Selkirk was constantly troubled by the plight of his Scottish kin. Selkirk was influenced by humanitarians including
2926:
2913:
2828:
2804:
2309:
38:
17:
3151:
2957:
2705:
2672:
344:
300:
3317:
3034:
2433:
1863:
717:
53:
2428:
2387:
3312:
3141:
2367:
2136:
The Journal of the Bishop of Montreal, during a Visit to the Church Missionary Society's North-West America Mission
1314:
Baker, Robert (1999). "Creating Order in the Wilderness: Transplanting the English Law to Rupert's Land, 1835–51".
620:
596:
834:
In the establishing years of the Hudson's Bay Company and the North West Company, male settlers frequently took a
3190:
2648:
2453:
2382:
2180:
1137:
552:, Selkirk captured Fort William, the North West Company headquarters, and captured several key agents including
2438:
2352:
419:
819:
In an extremely rare example of a woman successfully challenging this status-quo, Maria Thomas, a 16-year-old
3161:
2418:
1066:
1046:
557:
2423:
2357:
631:
1529:. "New Light on Red River Valley History." Minnesota History Bulletin, Vol. 5, No. 8 (Nov., 1924), pg 568.
2810:
2139:
1036:
549:
458:
2039:
695:
tried to depict themselves as favorable figures in the eyes of the Métis by associating themselves with
3224:
3146:
3086:
3003:
2641:
2468:
2173:
1782:
1754:
520:
3302:
2324:
2319:
2295:
1160:
1106:
908:
800:
2760:
2565:
2511:
2413:
2408:
2403:
2372:
2362:
2329:
2254:
739:
524:
3106:
916:
835:
813:
647:
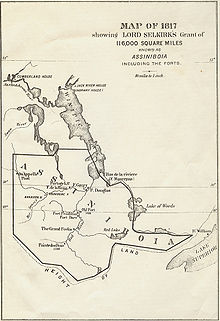
612:
423:
404:
308:
3071:
3029:
2799:
2784:
2750:
2735:
2443:
2377:
2270:
2249:
996:
957:
912:
864:
726:
535:
3322:
2985:
2695:
2585:
1481:
Dawson, Kenneth (1970). "Preliminary Investigation of Fort William in Northwestern Ontario".
624:
604:
531:
499:
495:
428:
422:'s Voyages in 1801; however, Selkirk was prevented from settling the region in 1802 when the
304:
2903:
2633:
2135:
3205:
3101:
3056:
3019:
3014:
2970:
2491:
2275:
1920:
1900:
1868:
1838:
1656:
743:
683:
540:
8:
2794:
2774:
2740:
2555:
2516:
2234:
2229:
2100:
Warner, Donald F. (1953), "Drang Nach Norden: The United States and the Riel Rebellion",
779:
679:
659:
568:
553:
412:
408:
375:
2602:
1660:
3307:
3066:
3061:
2550:
2117:
2027:
1954:
1710:
1672:
1494:
1402:
1394:
1339:
1331:
711:
616:
600:
545:
435:
312:
264:
72:
1647:
FitzGerald, Sharron A. (June 2007). "Hybrid identities in Canada's Red River Colony".
411:
and, following the forced displacement of Scottish farmers that took place during the
3076:
2755:
2196:
2154:
1983:
1958:
1714:
1676:
1668:
1498:
1461:
1406:
1343:
1116:
848:
635:
340:
328:
324:
2789:
2040:"Prologue to the Red River Resistance: Pre-liminal Politics and the Triumph of Riel"
1980:
Clearing the Plains: Disease, Politics of Starvation and the Loss of Aboriginal Life
3174:
3024:
2617:
2590:
2541:
2496:
2304:
2280:
2109:
2076:
2054:
2019:
1946:
1783:"Variations in Red River: The Traders and Freemen Metis of Saint-Laurent, Manitoba"
1702:
1664:
1486:
1386:
1323:
892:
700:
316:
223:
82:
67:
331:. It then formed a line of 52° 30′ N latitude from Lake Winnipegosis to
3126:
2851:
2778:
2481:
2448:
2239:
2206:
2090:
986:
937:
896:
884:
639:
580:
561:
478:
127:
1302:
Farming the Frontier, The Agricultural Opening of the Oregon Country, 1786–1846.
2947:
2745:
2580:
2476:
1526:
888:
827:
Owen Corbett, to court for repeatedly raping her and subjecting her to illegal
634:
guided 200 settlers from the Red River Colony west in an attempt to retain the
572:
482:
434:
By 1807, Selkirk acknowledged that an alliance with either the Hudson's Bay or
379:
336:
2067:
Gluek, Alvin C. (1955), "The Riel Rebellion and Canadian-American Relations",
1950:
1706:
3286:
3268:
3255:
3238:
3051:
2622:
1016:
953:
880:
876:
812:
The position of many women in the Red River Colony was determined within the
591:
576:
383:
332:
1611:
Flanagan, Thomas. "Louis Riel and the Dispersion of American Metis." Pg. 184
1304:
Vancouver, B.C.: University of British Columbia Press. 1985, pp. 10–13.
3136:
3043:
3039:
2855:
2210:
2159:
1564:
Flanagan, Thomas. "Louis Riel and the Dispersion of American Metis pg. 179"
933:
920:
824:
515:
490:
371:
363:
359:
2081:
899:, and Cree and was mostly spoken by Protestants (Anglican, Presbyterian).
3046:
571:
ceased to be a part of the Red River Colony following the signing of the
378:
ceased to be a part of the Red River Colony following the signing of the
1736:
Chetlain, Augustus L. The Red River Colony. New York: New York, 1878: 50
1176:
3008:
2719:
2560:
2506:
2472:
2463:
2458:
2121:
1490:
1398:
965:
924:
722:
696:
687:
however, did not allow these attempts at U.S. expansionism to succeed.
443:
320:
296:
2031:
1335:
623:, and from then until 1870 the area was under the jurisdiction of the
323:, bounded on the north by the line of 52° N latitude roughly from the
3131:
2841:
2149:
2059:
355:
2165:
2113:
1390:
712:
Legislative Assembly of Assiniboia, Louis Riel, and the Manitoba Act
303:, on 300,000 square kilometres (120,000 sq mi) of land in
2023:
1327:
948:
828:
760:
575:, in which the United Kingdom agreed to cede this territory to the
503:
462:
Protestant Church and Mission School, Red River Colony (Manitoba),
400:
382:, in which the United Kingdom agreed to cede this territory to the
351:
250:
2597:
1688:
1686:
919:, towards the education of some First Nations children, including
820:
742:. Riel, however later returned to Canada in 1885 to help lead the
638:
for British North America. The party crossed the Rockies into the
2685:
1435:"THE WAR OF 1812: European Traces in a British-American Conflict"
961:
486:
442:
terms. Selkirk referred to this new territory as the District of
367:
2010:
Donnelly, M. S. (1957), "Parliamentary Government in Manitoba",
1748:
1746:
1744:
1742:
879:-based mixed-language whose speakers were largely Catholic, and
431:
but continued to pursue the settlement of the Red River region.
418:
Selkirk became interested in the Red River region after reading
2725:
1683:
872:
747:
236:
101:
2005:(1), St. Paul, VA: Minnesota Historical Society Press: 166–177
1945:(3), Ottawa: Canadian Political Science Association: 711–732,
2663:
2142:, an early account of religious life in the Red River Colony.
1739:
1965:
Carter, George (1968), "Lord Selkirk and Red River Colony",
1835:
Missionary Work Around the Winnepegoosis Lake, Rupert's Land
928:
1776:
1774:
1772:
911:(CMS) provided financial assistance in 1820 to Reverend
2053:(1), Ottawa: Canadian Historical Association: 111–123,
2012:
The Canadian Journal of Economics and Political Science
1804:
1802:
1800:
1623:
1621:
1619:
1617:
1595:
1593:
1591:
1589:
1587:
842:
2018:(1), Montreal: Canadian Economics Association: 20–32,
1897:
Voyage from Red River to Fort Simpson, Mackenzie River
1769:
1510:
1508:
1355:
1353:
1277:
1275:
1230:
1228:
1226:
1224:
1222:
1220:
1218:
1216:
1214:
1212:
1210:
1208:
2075:(3), Toronto: University of Toronto Press: 199–221,
1797:
1755:"Rooted in Mobility: Metis Buffalo-Hunting Brigades"
1614:
1584:
1539:
1537:
1535:
1273:
1271:
1269:
1267:
1265:
1263:
1261:
1259:
1257:
1255:
1240:
1206:
1204:
1202:
1200:
1198:
1196:
1194:
1192:
1190:
1188:
691:
dominion. Americans who supported annexation by the
2502:
Riding Mountain Park East Gate Registration Complex
2150:
The Romantic Settlement of Lord Selkirk's Colonists
1997:Davies, K. G. (1966), "From Competition to Union",
1692:
1460:. Canada: University of Toronto Press. p. 80.
1973:(1), Helena, MO: Montana Historical Society: 60–69
1890:
1862:
1828:
1574:
1572:
1570:
1505:
1350:
1752:
1642:
1640:
1638:
1636:
1532:
1252:
1185:
3284:
2108:(4), Oxford: Oxford University Press: 693–712,
1567:
799:the judiciary, while the provincial government
299:, was a colonization project set up in 1811 by
3196:Areas disputed by Canada and the United States
2047:Journal of the Canadian Historical Association
1857:
1855:
1633:
3298:States and territories disestablished in 1870
2649:
2181:
932:throughout the colony and were travelling to
3201:Proposed provinces and territories of Canada
1753:Macdougall, Brenda; St-Onge, Nicole (2013).
902:
664:
509:
1852:
1830:"The Church Missionary Gleaner, March 1857"
108:
3293:States and territories established in 1811
2656:
2642:
2188:
2174:
1892:"The Church Missionary Gleaner, June 1860"
1646:
754:
307:. This land was granted to Douglas by the
66:
2665:Former colonies and territories in Canada
2080:
2058:
1821:
1133:Former colonies and territories in Canada
943:
502:in January 1814 to prevent the export of
27:1811–1870 British colony in modern Canada
2102:The Mississippi Valley Historical Review
2009:
1967:Montana: The Magazine of Western History
1936:
1883:
1627:
1599:
1296:
1294:
1292:
1290:
947:
668:
590:
457:
362:, in addition to small parts of eastern
1977:
1780:
1455:
1359:
883:, a form of speech that developed from
14:
3285:
2315:Montana valley and foothill grasslands
2099:
1996:
1982:. Canada: University of Regina Press.
1964:
1864:"The Church Missionary Atlas (Canada)"
1514:
1480:
1281:
1234:
807:
653:
2637:
2195:
2169:
2066:
1939:Canadian Journal of Political Science
1921:Governors of the Red River Settlement
1543:
1451:
1449:
1447:
1429:
1427:
1425:
1376:
1313:
1287:
823:domestic servant, took her employer,
453:
2310:Canadian aspen forests and parklands
2088:
1372:
1370:
1368:
1246:
843:Métis people of the Red River Colony
619:were forced to merge in 1821 by the
394:
2037:
1578:
956:, driving his family on the frozen
579:. It was later discovered that the
301:Thomas Douglas, 5th Earl of Selkirk
24:
1444:
1422:
25:
3334:
2129:
1365:
718:Legislative Assembly of Assinboia
3232:
3220:
3219:
3191:Territorial evolution after 1867
1669:10.1111/j.1541-0064.2007.00173.x
1458:The Canadian Prairies: A History
586:
269:
255:
241:
216:
52:
2095:, London: Smith, Elder & Co
1929:
1914:
1811:
1730:
1721:
1605:
1558:
1549:
1520:
1474:
1413:
1138:Territorial evolution of Canada
599:along the Red River in 1822 by
1781:St-Onge, Nicole J. M. (1992).
1307:
1170:
1154:
13:
1:
2368:Writing-on-Stone / Áísínai'pi
1923:, Manitoba Historical Society
1143:
463:
3097:British Columbia (1866–1871)
3092:British Columbia (1858–1866)
1148:
489:to the Hudson's Bay post at
7:
2140:George Jehoshaphat Mountain
1379:The Business History Review
1126:
1097:William Bletterman Caldwell
968:in the background (1822–23)
10:
3339:
3004:British Arctic Territories
2069:Canadian Historical Review
1113:September 1859 – July 1870
1103:June 1855 – September 1859
801:attempted the introduction
758:
657:
389:
315:. It included portions of
3318:Scottish-Canadian culture
3214:
3183:
3160:
2979:
2956:
2935:
2912:
2879:
2827:
2704:
2671:
2613:
2573:
2535:
2396:
2373:UNESCO Biosphere Reserves
2346:International recognition
2345:
2339:Parks and protected areas
2338:
2325:Northern short grasslands
2320:Northern mixed grasslands
2289:
2263:
2218:Physiographic sub-regions
2217:
2203:
1951:10.1017/s0008423910000612
1707:10.1080/09612020701447624
1177:Morris, Alexander (1880)
1165:The Canadian Encyclopedia
1107:Francis Godschall Johnson
909:Church Missionary Society
903:Church Missionary Society
665:American annexation plans
510:War between the companies
374:. The lands south of the
195:
191:
187:
183:
173:
163:
159:
151:
147:
143:
133:
121:
117:
107:
95:
88:
78:
65:
49:
44:
37:
32:
2566:District of Saskatchewan
2330:Northern tall grasslands
2255:Rocky Mountain Foothills
2092:The Red River Settlement
2089:Ross, Alexander (1856),
1871:. 1896. pp. 220–226
1456:Friesen, Gerald (2010).
550:De Watteville's Regiment
525:North American fur trade
3107:North-Western Territory
3082:Queen Charlotte Islands
1978:Daschuk, James (2013).
1787:Canadian Ethnic Studies
1649:The Canadian Geographer
1003:August 1816 – June 1822
983:August 1812 – June 1815
952:Governor of Red River,
755:Development of Manitoba
648:Oregon boundary dispute
567:The lands south of the
405:Jacobite rising of 1745
265:Missouri Territory
2561:District of Assiniboia
2444:Cypress Hills Massacre
1695:Women's History Review
1483:Historical Archaeology
1316:Law and History Review
969:
944:Governors of Red River
780:Louis Riel's rebellion
727:Canadian confederation
674:
608:
470:
319:, or the watershed of
175:• Disestablished
3269:49.00000°N 97.23750°W
2586:Blackfoot Confederacy
2082:10.3138/chr-036-03-02
1093:June 1848 – June 1855
1083:June 1847 – June 1848
1077:John Folliott Crofton
1073:June 1846 – June 1847
1063:June 1844 – June 1846
1053:June 1839 – June 1844
1043:June 1833 – June 1839
1033:June 1825 – June 1833
1023:June 1823 – June 1825
1013:June 1822 – June 1823
993:June 1815 – June 1816
951:
672:
594:
583:had also been ceded.
500:Pemmican Proclamation
461:
429:British North America
305:British North America
3313:Hudson's Bay Company
3206:Population of Canada
3057:Prince Edward Island
2581:Plains First Nations
2512:Rocky Mountain House
2353:World Heritage Sites
2038:Ens, Gerard (1994),
1901:Adam Matthew Digital
1869:Adam Matthew Digital
1839:Adam Matthew Digital
1007:Alexander Macdonnell
917:Hudson's Bay Company
814:Hudson's Bay Company
744:North West rebellion
613:Hudson's Bay Company
541:Battle of Seven Oaks
424:Hudson's Bay Company
309:Hudson's Bay Company
73:Selkirk's land grant
18:Red River settlement
3274:49.00000; -97.23750
3265: /
2999:Newfoundland (1583)
2556:District of Alberta
2230:Manitoba Escarpment
1661:2007CGeog..51..186F
1027:Robert Parker Pelly
808:Women in the colony
684:Canadian government
680:Red River Rebellion
660:Red River Rebellion
654:Red River Rebellion
642:, near present-day
569:49th parallel north
554:William McGillivray
420:Alexander MacKenzie
413:Highland Clearances
409:William Wilberforce
403:in the wake of the
376:49th parallel north
370:, and northeastern
165:• Established
3030:Nova Scotia (1710)
2894:Nova Scotia (1621)
2696:L'Anse aux Meadows
2574:Indigenous peoples
2551:Selkirk Concession
2294:) and ecoregions (
2235:Saskatchewan Plain
1491:10.1007/BF03373385
1161:"Red River Colony"
1067:Alexander Christie
1047:Alexander Christie
970:
915:, chaplain to the
675:
644:Radium Hot Springs
621:British government
617:North West Company
609:
601:Peter Rindisbacher
546:Regiment de Meuron
471:
454:Settling Red River
436:North West Company
313:Selkirk Concession
293:Selkirk Settlement
224:Rupert's Land
3248:
3247:
3239:Canada portal
3077:Columbia District
2904:Port Royal Colony
2871:Pacific Northwest
2681:Named territories
2631:
2630:
2525:
2524:
2276:Qu'Appelle Valley
2264:Physical features
2209:, shared with US
2197:Canadian Prairies
2155:Project Gutenberg
1999:Minnesota History
1989:978-0-88977-340-0
1467:978-0-8020-6648-0
1300:Gibson, James R.
1249:, pp. 16–18.
1122:
1121:
1117:William MacTavish
1087:John T. Griffiths
849:Augustus Chetlain
636:Columbia District
625:Assinboia Council
607:in the background
597:narrow river lots
544:Swiss and German
395:Colony conception
341:Lake of the Woods
329:Lake Winnipegosis
325:Assiniboine River
295:), also known as
285:
284:
281:
280:
277:
276:
229:
228:
139:William MacTavish
135:• 1859–1870
123:• 1812–1815
97: • Type
16:(Redirected from
3330:
3303:Red River Colony
3280:
3279:
3277:
3276:
3275:
3270:
3266:
3263:
3262:
3261:
3258:
3237:
3236:
3235:
3223:
3222:
3175:Sverdrup Islands
3171:
3123:
3087:Vancouver Island
2995:
2967:
2944:
2923:
2900:
2890:
2862:
2848:
2838:
2771:
2715:
2692:
2682:
2658:
2651:
2644:
2635:
2634:
2618:Geography portal
2603:Métis in Alberta
2591:Iron Confederacy
2547:Red River Colony
2536:Historic regions
2497:Lower Fort Garry
2454:Fort Livingstone
2343:
2342:
2305:Prairies Ecozone
2281:Red River Valley
2190:
2183:
2176:
2167:
2166:
2157:
2124:
2096:
2085:
2084:
2063:
2062:
2060:10.7202/031075ar
2044:
2034:
2006:
1993:
1974:
1961:
1924:
1918:
1912:
1911:
1909:
1907:
1894:
1887:
1881:
1880:
1878:
1876:
1866:
1859:
1850:
1849:
1847:
1845:
1832:
1825:
1819:
1815:
1809:
1806:
1795:
1794:
1778:
1767:
1766:
1759:Manitoba History
1750:
1737:
1734:
1728:
1725:
1719:
1718:
1690:
1681:
1680:
1644:
1631:
1625:
1612:
1609:
1603:
1597:
1582:
1576:
1565:
1562:
1556:
1553:
1547:
1541:
1530:
1524:
1518:
1512:
1503:
1502:
1478:
1472:
1471:
1453:
1442:
1441:
1439:
1431:
1420:
1417:
1411:
1410:
1374:
1363:
1357:
1348:
1347:
1311:
1305:
1298:
1285:
1279:
1250:
1244:
1238:
1232:
1183:
1174:
1168:
1158:
1057:Duncan Finlayson
972:
971:
701:Manifest Destiny
558:Kenneth McKenzie
468:
467: 1820–1840
465:
289:Red River Colony
273:
272:
259:
258:
245:
244:
233:
232:
220:
219:
213:
212:
197:
196:
98:
83:Upper Fort Garry
70:
56:
33:Red River Colony
30:
29:
21:
3338:
3337:
3333:
3332:
3331:
3329:
3328:
3327:
3283:
3282:
3273:
3271:
3267:
3264:
3259:
3256:
3254:
3252:
3251:
3249:
3244:
3233:
3231:
3210:
3179:
3169:
3156:
3122:Important sites
3121:
2993:
2984:
2975:
2965:
2952:
2942:
2931:
2927:Russian America
2921:
2908:
2898:
2888:
2875:
2860:
2852:Fort San Miguel
2847:Important sites
2846:
2836:
2823:
2779:Annapolis Royal
2770:Important sites
2769:
2713:
2700:
2690:
2680:
2667:
2662:
2632:
2627:
2609:
2569:
2531:
2521:
2482:Frenchman Butte
2449:Fort Battleford
2419:Riding Mountain
2392:
2388:Riding Mountain
2358:Head-Smashed-In
2334:
2285:
2259:
2240:Missouri Coteau
2213:
2207:Interior plains
2199:
2194:
2147:
2132:
2127:
2114:10.2307/1895395
2042:
1990:
1932:
1927:
1919:
1915:
1905:
1903:
1889:
1888:
1884:
1874:
1872:
1861:
1860:
1853:
1843:
1841:
1827:
1826:
1822:
1816:
1812:
1807:
1798:
1779:
1770:
1751:
1740:
1735:
1731:
1726:
1722:
1691:
1684:
1645:
1634:
1626:
1615:
1610:
1606:
1598:
1585:
1577:
1568:
1563:
1559:
1554:
1550:
1542:
1533:
1527:Nute, Grace Lee
1525:
1521:
1513:
1506:
1479:
1475:
1468:
1454:
1445:
1437:
1433:
1432:
1423:
1418:
1414:
1391:10.2307/3111662
1375:
1366:
1358:
1351:
1312:
1308:
1299:
1288:
1280:
1253:
1245:
1241:
1233:
1186:
1175:
1171:
1159:
1155:
1151:
1146:
1129:
1037:Donald McKenzie
987:Miles MacDonell
946:
938:Mackenzie River
905:
875:, a French and
845:
810:
778:accelerated by
763:
757:
714:
693:U.S. government
667:
662:
656:
640:Columbia Valley
589:
581:Northwest Angle
562:John McLoughlin
521:King Charles II
512:
479:Miles Macdonell
466:
456:
397:
392:
366:, northwestern
270:
256:
242:
217:
176:
166:
136:
128:Miles Macdonell
124:
96:
71:
61:
58:
57:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
3336:
3326:
3325:
3320:
3315:
3310:
3305:
3300:
3295:
3246:
3245:
3243:
3242:
3228:
3215:
3212:
3211:
3209:
3208:
3203:
3198:
3193:
3187:
3185:
3181:
3180:
3178:
3177:
3172:
3166:
3164:
3158:
3157:
3155:
3154:
3149:
3144:
3139:
3134:
3129:
3124:
3119:
3114:
3104:
3099:
3094:
3089:
3084:
3079:
3074:
3069:
3064:
3059:
3054:
3049:
3037:
3032:
3027:
3022:
3017:
3012:
3006:
3001:
2996:
2990:
2988:
2977:
2976:
2974:
2973:
2968:
2962:
2960:
2954:
2953:
2951:
2950:
2948:Oregon Country
2945:
2939:
2937:
2933:
2932:
2930:
2929:
2924:
2918:
2916:
2910:
2909:
2907:
2906:
2901:
2896:
2891:
2885:
2883:
2877:
2876:
2874:
2873:
2868:
2863:
2858:
2849:
2844:
2839:
2833:
2831:
2825:
2824:
2822:
2821:
2814:
2807:
2802:
2797:
2792:
2790:Trois-Rivières
2787:
2782:
2772:
2766:
2765:
2764:
2763:
2758:
2756:Pays d'en Haut
2753:
2748:
2746:Domaine du roy
2743:
2738:
2733:
2728:
2716:
2710:
2708:
2702:
2701:
2699:
2698:
2693:
2688:
2683:
2677:
2675:
2669:
2668:
2661:
2660:
2653:
2646:
2638:
2629:
2628:
2626:
2625:
2620:
2614:
2611:
2610:
2608:
2607:
2606:
2605:
2595:
2594:
2593:
2588:
2577:
2575:
2571:
2570:
2568:
2563:
2558:
2553:
2544:
2539:
2537:
2533:
2532:
2530:
2529:
2526:
2523:
2522:
2520:
2519:
2514:
2509:
2504:
2499:
2494:
2489:
2484:
2479:
2477:Fort Gibraltar
2466:
2461:
2456:
2451:
2446:
2441:
2436:
2431:
2429:Historic Sites
2426:
2424:Waterton Lakes
2421:
2416:
2411:
2406:
2400:
2398:
2394:
2393:
2391:
2390:
2385:
2380:
2375:
2370:
2365:
2360:
2355:
2349:
2347:
2340:
2336:
2335:
2333:
2332:
2327:
2322:
2317:
2312:
2307:
2301:
2299:
2287:
2286:
2284:
2283:
2278:
2273:
2267:
2265:
2261:
2260:
2258:
2257:
2252:
2247:
2242:
2237:
2232:
2227:
2225:Manitoba Plain
2221:
2219:
2215:
2214:
2205:Sub-region of
2204:
2201:
2200:
2193:
2192:
2185:
2178:
2170:
2164:
2163:
2144:
2143:
2131:
2130:External links
2128:
2126:
2125:
2097:
2086:
2064:
2035:
2024:10.2307/138726
2007:
1994:
1988:
1975:
1962:
1933:
1931:
1928:
1926:
1925:
1913:
1882:
1851:
1820:
1810:
1796:
1768:
1738:
1729:
1720:
1701:(5): 661–680.
1682:
1655:(2): 186–201.
1632:
1613:
1604:
1583:
1566:
1557:
1548:
1531:
1519:
1504:
1473:
1466:
1443:
1421:
1412:
1385:(4): 423–433.
1364:
1349:
1328:10.2307/744011
1322:(2): 209–246.
1306:
1286:
1251:
1239:
1184:
1169:
1152:
1150:
1147:
1145:
1142:
1141:
1140:
1135:
1128:
1125:
1120:
1119:
1114:
1110:
1109:
1104:
1100:
1099:
1094:
1090:
1089:
1084:
1080:
1079:
1074:
1070:
1069:
1064:
1060:
1059:
1054:
1050:
1049:
1044:
1040:
1039:
1034:
1030:
1029:
1024:
1020:
1019:
1014:
1010:
1009:
1004:
1000:
999:
994:
990:
989:
984:
980:
979:
976:
945:
942:
904:
901:
844:
841:
809:
806:
759:Main article:
756:
753:
713:
710:
666:
663:
658:Main article:
655:
652:
632:James Sinclair
611:The rivalling
588:
585:
573:Treaty of 1818
511:
508:
477:In July 1811,
455:
452:
399:Growing up in
396:
393:
391:
388:
380:Treaty of 1818
358:, and eastern
337:Winnipeg River
283:
282:
279:
278:
275:
274:
267:
261:
260:
253:
247:
246:
239:
230:
227:
226:
221:
209:
208:
203:
193:
192:
189:
188:
185:
184:
181:
180:
177:
174:
171:
170:
167:
164:
161:
160:
157:
156:
153:
149:
148:
145:
144:
141:
140:
137:
134:
131:
130:
125:
122:
119:
118:
115:
114:
111:
105:
104:
99:
93:
92:
90:
86:
85:
80:
76:
75:
63:
62:
59:
51:
50:
47:
46:
42:
41:
39:British colony
35:
34:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
3335:
3324:
3321:
3319:
3316:
3314:
3311:
3309:
3306:
3304:
3301:
3299:
3296:
3294:
3291:
3290:
3288:
3281:
3278:
3241:
3240:
3229:
3227:
3226:
3217:
3216:
3213:
3207:
3204:
3202:
3199:
3197:
3194:
3192:
3189:
3188:
3186:
3182:
3176:
3173:
3168:
3167:
3165:
3163:
3159:
3153:
3150:
3148:
3145:
3143:
3140:
3138:
3135:
3133:
3132:Avalon (1620)
3130:
3128:
3125:
3120:
3118:
3115:
3112:
3108:
3105:
3103:
3100:
3098:
3095:
3093:
3090:
3088:
3085:
3083:
3080:
3078:
3075:
3073:
3072:New Caledonia
3070:
3068:
3067:United Canada
3065:
3063:
3060:
3058:
3055:
3053:
3052:New Brunswick
3050:
3048:
3045:
3041:
3038:
3036:
3033:
3031:
3028:
3026:
3025:Rupert's Land
3023:
3021:
3020:New Yorkshire
3018:
3016:
3013:
3010:
3007:
3005:
3002:
3000:
2997:
2992:
2991:
2989:
2987:
2982:
2978:
2972:
2969:
2964:
2963:
2961:
2959:
2955:
2949:
2946:
2941:
2940:
2938:
2934:
2928:
2925:
2920:
2919:
2917:
2915:
2911:
2905:
2902:
2897:
2895:
2892:
2887:
2886:
2884:
2882:
2878:
2872:
2869:
2867:
2864:
2859:
2857:
2853:
2850:
2845:
2843:
2840:
2835:
2834:
2832:
2830:
2826:
2820:
2819:
2818:List of forts
2815:
2813:
2812:
2811:List of towns
2808:
2806:
2803:
2801:
2798:
2796:
2793:
2791:
2788:
2786:
2783:
2780:
2776:
2773:
2768:
2767:
2762:
2759:
2757:
2754:
2752:
2749:
2747:
2744:
2742:
2739:
2737:
2734:
2732:
2729:
2727:
2724:
2723:
2722:
2721:
2717:
2712:
2711:
2709:
2707:
2703:
2697:
2694:
2689:
2687:
2684:
2679:
2678:
2676:
2674:
2670:
2666:
2659:
2654:
2652:
2647:
2645:
2640:
2639:
2636:
2624:
2623:Canada portal
2621:
2619:
2616:
2615:
2612:
2604:
2601:
2600:
2599:
2596:
2592:
2589:
2587:
2584:
2583:
2582:
2579:
2578:
2576:
2572:
2567:
2564:
2562:
2559:
2557:
2554:
2552:
2548:
2545:
2543:
2542:Rupert's Land
2540:
2538:
2534:
2528:
2527:
2518:
2515:
2513:
2510:
2508:
2505:
2503:
2500:
2498:
2495:
2493:
2492:Linear Mounds
2490:
2488:
2485:
2483:
2480:
2478:
2474:
2470:
2467:
2465:
2462:
2460:
2457:
2455:
2452:
2450:
2447:
2445:
2442:
2440:
2437:
2435:
2432:
2430:
2427:
2425:
2422:
2420:
2417:
2415:
2412:
2410:
2407:
2405:
2402:
2401:
2399:
2395:
2389:
2386:
2384:
2383:Redberry Lake
2381:
2379:
2376:
2374:
2371:
2369:
2366:
2364:
2361:
2359:
2356:
2354:
2351:
2350:
2348:
2344:
2341:
2337:
2331:
2328:
2326:
2323:
2321:
2318:
2316:
2313:
2311:
2308:
2306:
2303:
2302:
2300:
2297:
2293:
2288:
2282:
2279:
2277:
2274:
2272:
2269:
2268:
2266:
2262:
2256:
2253:
2251:
2250:Cypress Hills
2248:
2246:
2245:Alberta Plain
2243:
2241:
2238:
2236:
2233:
2231:
2228:
2226:
2223:
2222:
2220:
2216:
2212:
2208:
2202:
2198:
2191:
2186:
2184:
2179:
2177:
2172:
2171:
2168:
2161:
2156:
2152:
2151:
2146:
2145:
2141:
2137:
2134:
2133:
2123:
2119:
2115:
2111:
2107:
2103:
2098:
2094:
2093:
2087:
2083:
2078:
2074:
2070:
2065:
2061:
2056:
2052:
2048:
2041:
2036:
2033:
2029:
2025:
2021:
2017:
2013:
2008:
2004:
2000:
1995:
1991:
1985:
1981:
1976:
1972:
1968:
1963:
1960:
1956:
1952:
1948:
1944:
1940:
1935:
1934:
1922:
1917:
1902:
1898:
1893:
1886:
1870:
1865:
1858:
1856:
1840:
1836:
1831:
1824:
1814:
1805:
1803:
1801:
1792:
1788:
1784:
1777:
1775:
1773:
1764:
1760:
1756:
1749:
1747:
1745:
1743:
1733:
1724:
1716:
1712:
1708:
1704:
1700:
1696:
1689:
1687:
1678:
1674:
1670:
1666:
1662:
1658:
1654:
1650:
1643:
1641:
1639:
1637:
1629:
1628:Donnelly 1957
1624:
1622:
1620:
1618:
1608:
1601:
1600:Bruyneel 2010
1596:
1594:
1592:
1590:
1588:
1580:
1575:
1573:
1571:
1561:
1552:
1545:
1540:
1538:
1536:
1528:
1523:
1516:
1511:
1509:
1500:
1496:
1492:
1488:
1484:
1477:
1469:
1463:
1459:
1452:
1450:
1448:
1436:
1430:
1428:
1426:
1416:
1408:
1404:
1400:
1396:
1392:
1388:
1384:
1380:
1373:
1371:
1369:
1361:
1356:
1354:
1345:
1341:
1337:
1333:
1329:
1325:
1321:
1317:
1310:
1303:
1297:
1295:
1293:
1291:
1283:
1278:
1276:
1274:
1272:
1270:
1268:
1266:
1264:
1262:
1260:
1258:
1256:
1248:
1243:
1236:
1231:
1229:
1227:
1225:
1223:
1221:
1219:
1217:
1215:
1213:
1211:
1209:
1207:
1205:
1203:
1201:
1199:
1197:
1195:
1193:
1191:
1189:
1182:
1180:
1173:
1166:
1162:
1157:
1153:
1139:
1136:
1134:
1131:
1130:
1124:
1118:
1115:
1112:
1111:
1108:
1105:
1102:
1101:
1098:
1095:
1092:
1091:
1088:
1085:
1082:
1081:
1078:
1075:
1072:
1071:
1068:
1065:
1062:
1061:
1058:
1055:
1052:
1051:
1048:
1045:
1042:
1041:
1038:
1035:
1032:
1031:
1028:
1025:
1022:
1021:
1018:
1017:Andrew Bulger
1015:
1012:
1011:
1008:
1005:
1002:
1001:
998:
997:Robert Semple
995:
992:
991:
988:
985:
982:
981:
977:
974:
973:
967:
963:
959:
955:
954:Andrew Bulger
950:
941:
939:
935:
930:
926:
922:
918:
914:
910:
900:
898:
894:
890:
886:
882:
878:
874:
868:
866:
860:
856:
852:
850:
840:
837:
836:First Nations
832:
830:
826:
822:
817:
815:
805:
802:
797:
792:
788:
785:
781:
775:
773:
768:
762:
752:
749:
745:
741:
735:
731:
728:
724:
719:
709:
705:
702:
698:
694:
688:
685:
681:
671:
661:
651:
649:
645:
641:
637:
633:
628:
626:
622:
618:
614:
606:
602:
598:
593:
587:Rising colony
584:
582:
578:
577:United States
574:
570:
565:
563:
559:
555:
551:
547:
542:
537:
536:Robert Semple
533:
528:
526:
522:
517:
507:
505:
501:
497:
492:
488:
484:
480:
475:
460:
451:
447:
445:
439:
437:
432:
430:
425:
421:
416:
414:
410:
406:
402:
387:
385:
384:United States
381:
377:
373:
369:
365:
361:
357:
353:
348:
346:
342:
338:
335:, and by the
334:
333:Lake Winnipeg
330:
326:
322:
318:
317:Rupert's Land
314:
310:
306:
302:
298:
294:
290:
268:
266:
263:
262:
254:
252:
249:
248:
240:
238:
235:
234:
231:
225:
222:
215:
214:
211:
210:
207:
204:
202:
199:
198:
194:
190:
186:
182:
178:
172:
168:
162:
158:
154:
150:
146:
142:
138:
132:
129:
126:
120:
116:
112:
110:
106:
103:
100:
94:
91:
87:
84:
81:
77:
74:
69:
64:
55:
48:
43:
40:
36:
31:
19:
3323:Pemmican War
3250:
3230:
3218:
3152:Fort Langley
3137:York Factory
3127:Cuper's Cove
3116:
2866:Newfoundland
2856:Nootka Sound
2816:
2809:
2731:Isle St-Jean
2718:
2546:
2378:Beaver Hills
2271:Beaver Hills
2211:Great Plains
2160:George Bryce
2148:
2105:
2101:
2091:
2072:
2068:
2050:
2046:
2015:
2011:
2002:
1998:
1979:
1970:
1966:
1942:
1938:
1930:Bibliography
1916:
1904:. Retrieved
1896:
1885:
1873:. Retrieved
1842:. Retrieved
1834:
1823:
1813:
1790:
1786:
1762:
1758:
1732:
1723:
1698:
1694:
1652:
1648:
1607:
1560:
1551:
1522:
1482:
1476:
1457:
1415:
1382:
1378:
1360:Daschuk 2013
1319:
1315:
1309:
1301:
1242:
1178:
1172:
1164:
1156:
1123:
934:Fort Simpson
921:James Settee
906:
869:
861:
857:
853:
846:
833:
818:
811:
796:Manitoba Act
795:
793:
789:
784:Manitoba Act
783:
776:
772:Manitoba Act
771:
767:Manitoba Act
766:
764:
740:Thomas Scott
736:
732:
715:
706:
689:
676:
629:
610:
605:Fort Douglas
566:
532:Fort Douglas
529:
516:Pemmican War
513:
496:Fort Douglas
491:York Factory
481:sailed from
476:
472:
448:
440:
433:
417:
398:
372:South Dakota
364:Saskatchewan
360:North Dakota
349:
292:
288:
286:
206:Succeeded by
205:
200:
179:15 July 1870
3272: /
3062:Cape Breton
3015:New Britain
2861:Expeditions
2761:Terre Neuve
2469:Forts Rouge
2434:Bar U Ranch
1765:(1): 21–32.
1515:Warner 1953
1282:Davies 1966
1235:Carter 1968
1181:, Chapter I
960:in a horse
354:, northern
345:Rainy River
201:Preceded by
3287:Categories
3260:97°14′15″W
3257:49°00′00″N
3009:New Albion
2971:Nova Dania
2800:Louisbourg
2775:Port Royal
2736:Île Royale
2720:New France
2507:Riel House
2473:Fort Garry
2464:Fort Walsh
2459:Fort Pelly
2414:Grasslands
2409:Elk Island
2290:Ecozones (
1906:24 October
1875:19 October
1844:24 October
1793:(2): 1–21.
1544:Gluek 1955
1144:References
966:Fort Garry
925:Henry Budd
723:Fort Garry
697:Louis Riel
444:Assiniboia
321:Hudson Bay
297:Assiniboia
89:Government
3308:Fur trade
3162:Norwegian
3117:Red River
3111:districts
2842:New Spain
2805:Plaisance
2751:Louisiana
2517:The Forks
2487:Frog Lake
1959:154627246
1715:146586854
1677:145216284
1499:163286840
1407:156364163
1344:145502145
1247:Ross 1856
1149:Footnotes
978:Governor
958:Red River
913:John West
865:John West
829:abortions
630:In 1841,
595:Homes on
356:Minnesota
45:1811–1870
3225:Category
3147:Victoria
3102:Stickeen
2936:American
2881:Scottish
2795:Montreal
2397:National
2363:Dinosaur
1579:Ens 1994
1127:See also
761:Manitoba
504:pemmican
483:Yarmouth
401:Scotland
352:Manitoba
327:east to
251:Manitoba
109:Governor
3184:Related
3142:Halifax
2986:British
2981:English
2914:Russian
2829:Spanish
2686:Vinland
2439:Batoche
2122:1895395
1657:Bibcode
1399:3111662
962:cariole
936:on the
927:of the
893:English
873:Mitchif
487:England
390:History
368:Ontario
311:in the
152:History
79:Capital
3170:Claims
3047:Canada
3035:Quebec
2994:Claims
2966:Claims
2958:Danish
2943:Claims
2922:Claims
2889:Claims
2837:Claims
2785:Quebec
2741:Canada
2726:Acadia
2714:Claims
2706:French
2691:Sites:
2475:, and
2120:
2032:138726
2030:
1986:
1957:
1713:
1675:
1497:
1464:
1405:
1397:
1342:
1336:744011
1334:
897:Gaelic
885:Ojibwe
748:Québec
237:Canada
155:
113:
102:Colony
3044:Upper
3040:Lower
2899:Sites
2673:Norse
2598:Métis
2404:Parks
2158:, by
2138:, by
2118:JSTOR
2043:(PDF)
2028:JSTOR
1955:S2CID
1711:S2CID
1673:S2CID
1495:S2CID
1438:(PDF)
1403:S2CID
1395:JSTOR
1340:S2CID
1332:JSTOR
964:with
889:Scots
881:Bungi
821:Métis
603:with
3042:and
2162:1909
1984:ISBN
1908:2015
1877:2015
1846:2015
1462:ISBN
975:Term
929:Cree
923:and
907:The
877:Cree
825:Rev.
615:and
560:and
548:and
514:The
343:and
291:(or
287:The
169:1811
60:Flag
3011:(?)
2983:and
2296:WWF
2292:CEC
2153:at
2110:doi
2077:doi
2055:doi
2020:doi
1947:doi
1703:doi
1665:doi
1487:doi
1387:doi
1324:doi
3289::
2854:,
2471:,
2116:,
2106:39
2104:,
2073:36
2071:,
2049:,
2045:,
2026:,
2016:23
2014:,
2003:23
2001:,
1971:18
1969:,
1953:,
1943:43
1941:,
1899:.
1895:.
1867:.
1854:^
1837:.
1833:.
1818:12
1799:^
1791:24
1789:.
1785:.
1771:^
1763:71
1761:.
1757:.
1741:^
1709:.
1699:16
1697:.
1685:^
1671:.
1663:.
1653:51
1651:.
1635:^
1616:^
1586:^
1569:^
1534:^
1507:^
1493:.
1485:.
1446:^
1424:^
1401:.
1393:.
1383:32
1381:.
1367:^
1352:^
1338:.
1330:.
1320:17
1318:.
1289:^
1254:^
1187:^
1163:.
940:.
895:,
891:,
887:,
650:.
556:,
485:,
464:c.
386:.
347:.
339:,
3113:)
3109:(
2781:)
2777:(
2657:e
2650:t
2643:v
2549:/
2298:)
2189:e
2182:t
2175:v
2112::
2079::
2057::
2051:5
2022::
1992:.
1949::
1910:.
1879:.
1848:.
1717:.
1705::
1679:.
1667::
1659::
1630:.
1602:.
1581:.
1546:.
1517:.
1501:.
1489::
1470:.
1440:.
1409:.
1389::
1362:.
1346:.
1326::
1284:.
1237:.
1167:.
469:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.