42:
201:
435:
2397:
156:
and more progressive therapies, many individuals can achieve much more than initially thought. It has become clearer that there is a wider range of cognitive abilities in Pitt–Hopkins than reported in much of the scientific literature. No cure is known for Pitt-Hopkins syndrome, but it is possible to
227:
Gastrointestinal difficulties are common in individuals with Pitt-Hopkins and can include constipation, reflux, and burping. Severe constipation often occurs over the entire lifespan. Breathing issues may cause air swallowing and associated pain. Low muscle tone can cause feeding issues at an early
249:
Minor hand and foot anomalies such as slender or small hands and feet, broad fingertips, clinodactyly, tapered fingers, transverse palmar crease, flat feet with hindfoot valgus deformity, overriding toes, and short metatarsals have been reported. Absent flexion creases of the thumbs may occur with
240:
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) reveals that deviations in the brain may occur in individuals with Pitt-Hopkins. These can include a small corpus callosum, wide ventricles, and deviations in the posterior fossa. Many individuals with Pitt
Hopkins can also have typical brain structures.
236:
Epilepsy is not uncommon in Pitt-Hopkins and is reported in 37%-50% of cases. The onset of seizures can occur in infants or throughout adulthood. A variety of seizures can occur. Electroencephalographic (EEG) patterns can be typical or atypical, depending on the individual.
207:
Other features of Pitt-Hopkins syndrome may include constipation and other gastrointestinal problems, an unusually small head (microcephaly), nearsightedness (myopia), eyes that do not look in the same direction (strabismus), short stature, and minor brain abnormalities
327:
Zollino and colleagues defined diagnostic criteria based on characteristic features found in 75% of cases genetically confirmed for PTHS, termed cardinal features. If a person shows 9 cardinal features, they are classified as having PTHS.
551:
Whalen S, Héron D, Gaillon T, Moldovan O, Rossi M, Devillard F, et al. (January 2012). "Novel comprehensive diagnostic strategy in Pitt-Hopkins syndrome: clinical score and further delineation of the TCF4 mutational spectrum".
404:
There is no specific treatment for this condition. It is based on symptomatology. Since there is a lack of treatment, people with PTHS use behavioral and training approaches. Comorbidities may also be treated.
218:
Children with Pitt-Hopkins syndrome typically have a happy, excitable demeanor with frequent smiling, laughter, and hand-flapping movements. However, they can also experience anxiety and behavioral problems.
319:
There is not a certain diagnostic criteria, but there are a few symptoms that support a diagnosis of PTHS. Some examples are: facial dysmorphism, early onset global developmental delay, moderate to severe
1390:
392:
Angelman syndrome most closely resembles PTHS. Both have absent speech and a "happy" disposition. Of the differentials, Rett syndrome is the least close to PTHS. This syndrome is seen as a progressive
1052:"Mutations in TCF4, encoding a class I basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor, are responsible for Pitt-Hopkins syndrome, a severe epileptic encephalopathy associated with autonomic dysfunction"
396:. Both Angelman syndrome and Rett syndrome lack the distinctive facial features of PTHS. Mowat–Wilson syndrome is seen in early infancy and is characterized by distinctive facial abnormalities.
331:
It is possible that a phenotype resembling PTHS can occur without the mutation in the TCF4 gene. Mutations in the TCF4 gene do not always result in stereotypical Pitt-Hopkins syndrome.
369:
When a patient is suspected of having PTHS, genetic tests looking at the TCF4 gene are typically done. Some argue for a genetic test to occur first, followed by a clinical assessment.
1383:
418:
Developmental preschool through public school systems from ages 3 to 5. The child will need an evaluation before getting into the program, to see what kind of therapy is needed.
1376:
2303:
102:(recurrent seizures)often occurs in Pitt-Hopkins. It is part of the clinical spectrum of Rett-like syndromes. Pitt-hopkins syndrome is clinically similar to
751:
141:
gene. Those with PTHS have reported high rates of self-injury and aggressive behaviors usually related to autism and their sensory disorders.
2195:
835:
679:
441:, showing some of the physical traits of Pitt–Hopkins syndrome, including coarse, curly hair, drooping eyelids and large, thick-lipped mouth
415:
Early intervention program from newborn to age 3 will allow access to different therapies (occupational, physical, speech, and feeding).
270:(18q21.2) The mutational spectrum appears to be 40% point mutations, 30% small deletions/insertions and 30% deletions. All appear to be
2417:
121:
As more is learned about Pitt–Hopkins, the developmental spectrum of the disorder is widening, and can also include difficulties with
1368:
702:"Behavioural and psychological characteristics in Pitt-Hopkins syndrome: a comparison with Angelman and Cornelia de Lange syndromes"
1799:
1629:
1558:
1500:
1990:
1490:
661:
1522:
17:
1017:
Sweetser DA, Elsharkawi I, Yonker L, Steeves M, Parkin K, Thibert R (1993), Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA (eds.),
469:
Sweetser DA, Elsharkawi I, Yonker L, Steeves M, Parkin K, Thibert R (1993), Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA (eds.),
408:
Care from a medical team including neurologists, ophthalmologists, pulmonologists, and gastroenterologists may be utilized.
2422:
2281:
1962:
1871:
1593:
1574:
1495:
504:"Haploinsufficiency of TCF4 causes syndromal mental retardation with intermittent hyperventilation (Pitt-Hopkins syndrome)"
2427:
1948:
1316:
1507:
445:
The condition was first described in 1978, by D. Pitt and I. Hopkins (The
Children's Cottages Training Centre, Kew and
1598:
1254:
Pitt D, Hopkins I (September 1978). "A syndrome of mental retardation, wide mouth and intermittent overbreathing".
425:(based on the child's functions and needs). Children are encouraged to stay in school until at least the age of 21.
422:
411:
Recommendations for developmental delay and intellectual disability in the U.S. (may differ depending on country):
363:
1517:
1485:
157:
treat associated symptoms. Researchers have developed cell and rodent models to test therapies for Pitt–Hopkins.
79:
2107:
1532:
2369:
2345:
1976:
334:
Half of the individuals with PTHS are reported to have seizures, starting from childhood to the late teens.
2442:
2076:
2018:
2004:
1757:
1430:
446:
1657:
1578:
1356:
197:
Flat feet, overriding toes, and fetal pads are also common. Short stature and scoliosis occur frequently.
2387:
2133:
1603:
1480:
960:
Zollino M, Zweier C, Van Balkom ID, Sweetser DA, Alaimo J, Bijlsma EK, et al. (18 February 2019).
755:
342:
153:
1398:
606:"Pitt-Hopkins Syndrome: A Review of Current Literature, Clinical Approach, and 23-Patient Case Series"
2432:
2323:
2307:
2295:
2176:
2032:
1904:
1818:
1724:
1588:
386:
111:
2213:
2128:
1583:
1327:
311:
Pitt–Hopkins patients with a TCF4 deletion can lack the syndrome's characteristic facial features.
212:
215:
features, which are important when diagnosing PTHS, become more visible as the person gets older.
1890:
1738:
1512:
1207:"Pitt-Hopkins Syndrome: intellectual disability due to loss of TCF4-regulated gene transcription"
321:
83:
2437:
2299:
2165:
2123:
2071:
1476:
274:
mutations. The risk in siblings is low, but higher than the general population due to parental
337:
Around 50% of those affected show abnormalities on brain imaging. These include a hypoplastic
2171:
1843:
1785:
1771:
1608:
1537:
961:
700:
Watkins A, Bissell S, Moss J, Oliver C, Clayton-Smith J, Haye L, et al. (October 2019).
675:
134:
962:"Diagnosis and management in Pitt-Hopkins syndrome: First international consensus statement"
828:. In Pratt VM, McLeod HL, Rubinstein WS, Scott SA, Dean LC, Kattman BL, et al. (eds.).
2339:
2311:
2190:
2149:
1857:
1743:
1403:
502:
Zweier C, Peippo MM, Hoyer J, Sousa S, Bottani A, Clayton-Smith J, et al. (May 2007).
356:
145:
8:
1804:
281:
A Pitt–Hopkins-like phenotype has been assigned to autosomal recessive mutations of the
1885:
1682:
1613:
1279:
1231:
1206:
1179:
1154:
1125:
1100:
1076:
1051:
878:
728:
701:
638:
605:
577:
528:
503:
438:
275:
259:
1155:"Pitt-Hopkins Syndrome and Differential Diagnosis: A Molecular and Clinical Challenge"
1943:
1663:
1425:
1271:
1236:
1184:
1130:
1081:
1026:
999:
991:
882:
839:
801:
752:"A drug for autism? Potential treatment for Pitt-Hopkins syndrome offers clues; PTHS"
733:
643:
625:
569:
533:
478:
378:
250:
thumb ankylosis. In one individual an absent thumb tendon was found during surgery .
103:
54:
1283:
1050:
Amiel J, Rio M, de
Pontual L, Redon R, Malan V, Boddaert N, et al. (May 2007).
258:
The genetic cause of this disorder was described in 2007. This disorder is due to a
1553:
1399:
1263:
1226:
1218:
1174:
1166:
1120:
1112:
1071:
1063:
981:
973:
932:
908:
870:
723:
713:
633:
617:
581:
561:
523:
515:
91:
87:
63:
308:
Malformations in the CNS can be seen in about 60 to 70% of patients on MRI scans.
2401:
2240:
2026:
1937:
1332:
350:
338:
126:
604:
Goodspeed K, Newsom C, Morris MA, Powell C, Evans P, Golla S (10 January 2018).
41:
1696:
1446:
1018:
829:
825:
793:
470:
393:
324:, breathing abnormalities, and a lack of other major congenital abnormalities.
115:
1267:
718:
2411:
2046:
1668:
995:
629:
621:
382:
267:
107:
792:
Sweetser DA, Elsharkawi I, Yonker L, Steeves M, Parkin K, Thibert R (1993).
200:
1240:
1188:
1170:
1134:
1085:
1030:
1003:
843:
805:
737:
647:
573:
537:
482:
302:
290:
149:
49:
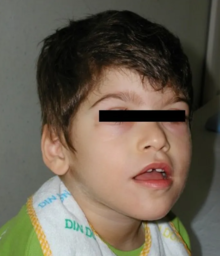
Boy with Pitt–Hopkins syndrome showing the characteristic facial features.
1275:
171:
The earliest signs in infants is the lower face and the high nasal root.
1308:
1222:
1918:
986:
565:
152:
is difficult to measure given motor and speech difficulties. Thanks to
59:
1116:
977:
2364:
862:
434:
282:
133:, and sensory disorders. It is associated with an abnormality within
937:
913:
874:
1351:
1067:
519:
346:
294:
99:
362:
According to the clinical diagnosis. PTHS is in the same group as
286:
122:
1321:
2159:
2154:
1779:
1765:
1710:
1690:
1527:
1016:
959:
791:
468:
662:"Pitt-Hopkins syndrome may point the way to autism treatments"
2275:
2184:
2040:
2012:
1998:
1984:
1970:
1956:
1751:
1718:
298:
95:
2289:
2261:
2065:
1912:
1898:
1879:
1865:
1851:
1837:
1812:
1793:
1732:
1704:
1676:
603:
263:
160:
PTHS is estimated to occur in 1:11,000 to 1:41,000 people.
138:
130:
550:
211:
Adults who have PTHS may have trouble with their speech.
699:
1049:
501:
2385:
1298:
421:
From the ages 5–21 the child's school may create an
174:
The facial features are characteristic and include:
1025:, Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle,
796:. In MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, Wallace SE (eds.).
477:, Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle,
449:, Melbourne, Australia) in two unrelated patients.
144:PTHS has traditionally been associated with severe
2304:Ectrodactyly–ectodermal dysplasia–cleft syndrome 3
2409:
1148:
1146:
1144:
787:
785:
783:
781:
779:
777:
775:
773:
1200:
1198:
1152:
1098:
78:) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by
2196:Yemenite deaf-blind hypopigmentation syndrome
1384:
836:National Center for Biotechnology Information
680:National Center for Biotechnology Information
1141:
819:
817:
815:
770:
137:which causes insufficient expression of the
1253:
1195:
693:
495:
266:) gene which is located on the long arm of
1391:
1377:
1043:
544:
40:
1247:
1230:
1178:
1124:
1075:
985:
936:
912:
812:
727:
717:
637:
527:
372:
1800:Posterior polymorphous corneal dystrophy
1630:Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1
433:
199:
168:PTHS can be seen as early as childhood.
1991:Anterior segment mesenchymal dysgenesis
1153:Marangi G, Zollino M (September 2015).
706:Journal of Neurodevelopmental Disorders
14:
2410:
1204:
1523:X-linked adrenal hypoplasia congenita
1372:
1211:Experimental & Molecular Medicine
955:
953:
951:
949:
947:
857:
855:
853:
800:. University of Washington, Seattle.
163:
1575:Greig cephalopolysyndactyly syndrome
823:
599:
597:
595:
593:
591:
464:
462:
1949:Iridogoniodysgenesis, dominant type
1099:Peippo M, Ignatius J (April 2012).
377:PTHS is symptomatically similar to
359:show an excess of slow components.
353:bulging towards the frontal horns.
222:
178:Broad nasal bridge with bulbous tip
24:
2233:
1056:American Journal of Human Genetics
944:
850:
508:American Journal of Human Genetics
25:
2454:
2418:Transcription factor deficiencies
1294:
664:. Daniel R. Weinberger. May 2019.
588:
459:
364:Pervasive Developmental Disorders
2395:
1963:Lymphedema–distichiasis syndrome
1559:Tricho–rhino–phalangeal syndrome
1533:Familial partial lipodystrophy 3
2227:(0) Other transcription factors
1518:Estrogen insensitivity syndrome
1486:Androgen insensitivity syndrome
1092:
1010:
920:
896:
262:of the transcription factor 4 (
231:
2108:Hyperimmunoglobulin E syndrome
1513:PHA1AD pseudohypoaldosteronism
744:
668:
654:
13:
1:
2370:Atrichia with papular lesions
1256:Australian Paediatric Journal
1159:Journal of Pediatric Genetics
452:
2077:Popliteal pterygium syndrome
2019:Enlarged vestibular aqueduct
1858:Waardenburg syndrome 1&3
1643:(3) Helix-turn-helix domains
1402:relating to deficiencies of
399:
314:
90:, and possible intermittent
7:
2423:Syndromes affecting the eye
2177:Premature ovarian failure 7
2033:Premature ovarian failure 3
1905:Congenital hypothyroidism 2
931:, Qeios, 10 February 2020,
907:, Qeios, 10 February 2020,
301:) gene on the short arm of
285:associated protein like 2 (
253:
88:distinctive facial features
10:
2459:
2428:Disorders causing seizures
2324:Transcription coregulators
2094:with minor groove contacts
1481:Thyroid hormone resistance
869:. Qeios. 2 February 2020.
831:Medical Genetics Summaries
610:Journal of Child Neurology
429:
345:and posterior part of the
289:) gene on the long arm of
154:augmentative communication
2356:
2346:Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome
2331:
2322:
2253:
2226:
2206:
2172:SRY XY gonadal dysgenesis
2142:
2116:
2100:
2091:
2057:
1977:Bamforth–Lazarus syndrome
1929:
1829:
1649:
1642:
1622:
1589:Duane-radial ray syndrome
1567:
1546:
1538:SF1 XY gonadal dysgenesis
1468:
1459:
1439:
1418:
1411:
1342:
1302:
1268:10.1111/jpc.1978.14.3.182
927:"Pitt-Hopkins syndrome",
903:"Pitt-Hopkins syndrome",
846:. Bookshelf ID: NBK66129.
719:10.1186/s11689-019-9282-0
447:Royal Children's Hospital
53:
48:
39:
34:
2214:Cleidocranial dysostosis
1431:Saethre–Chotzen syndrome
622:10.1177/0883073817750490
2191:Waardenburg syndrome 4c
1891:Coloboma of optic nerve
1739:Tooth and nail syndrome
1579:Pallister–Hall syndrome
1101:"Pitt-Hopkins Syndrome"
1019:"Pitt-Hopkins Syndrome"
863:"Pitt-Hopkins Syndrome"
826:"Pitt-Hopkins Syndrome"
794:"Pitt-Hopkins Syndrome"
471:"Pitt-Hopkins Syndrome"
322:intellectual disability
84:intellectual disability
2134:Ulnar–mammary syndrome
2092:(4) β-Scaffold factors
2072:Van der Woude syndrome
1604:Townes–Brocks syndrome
1477:Intracellular receptor
1205:Sweatt JD (May 2013).
1171:10.1055/s-0035-1564570
1105:Molecular Syndromology
442:
373:Differential diagnosis
204:
2308:Limb–mammary syndrome
2296:Rapp–Hodgkin syndrome
2268:Pitt–Hopkins syndrome
1844:Papillorenal syndrome
1819:Mowat–Wilson syndrome
1725:Nail–patella syndrome
1609:Acrocallosal syndrome
437:
387:Mowat–Wilson syndrome
357:Electroencephalograms
203:
112:Mowat Wilson syndrome
82:, moderate to severe
72:Pitt–Hopkins syndrome
35:Pitt–Hopkins syndrome
18:Pitt-Hopkins syndrome
2150:Campomelic dysplasia
2129:Li–Fraumeni syndrome
1614:Myotonic dystrophy 2
1584:Denys–Drash syndrome
1404:transcription factor
184:Cupid's bow philtrum
146:cognitive impairment
2443:Syndromes with ADHD
1944:Axenfeld syndrome 3
1758:Axenfeld syndrome 1
1697:SPD1 synpolydactyly
1462:DNA-binding domains
1223:10.1038/emm.2013.32
293:(7q33-q36) and the
80:developmental delay
2300:Hay–Wells syndrome
2124:Holt–Oram syndrome
1886:Gillespie syndrome
1805:Fuchs' dystrophy 3
1683:Currarino syndrome
1343:External resources
566:10.1002/humu.21639
443:
439:Peter the Wild Boy
276:germline mosaicism
260:haploinsufficiency
205:
164:Signs and symptoms
2383:
2382:
2379:
2378:
2249:
2248:
2222:
2221:
2087:
2086:
1664:Ohtahara syndrome
1638:
1637:
1508:Kennedy's disease
1455:
1454:
1426:Feingold syndrome
1412:(1) Basic domains
1400:Genetic disorders
1366:
1365:
1117:10.1159/000335287
978:10.1111/cge.13506
966:Clinical Genetics
379:Angelman syndrome
104:Angelman syndrome
69:
68:
29:Medical condition
16:(Redirected from
2450:
2433:Syndromic autism
2400:
2399:
2398:
2391:
2329:
2328:
2231:
2230:
2098:
2097:
1669:Lissencephaly X2
1647:
1646:
1554:Barakat syndrome
1466:
1465:
1416:
1415:
1393:
1386:
1379:
1370:
1369:
1300:
1299:
1288:
1287:
1251:
1245:
1244:
1234:
1202:
1193:
1192:
1182:
1150:
1139:
1138:
1128:
1111:(3–5): 171–180.
1096:
1090:
1089:
1079:
1047:
1041:
1040:
1039:
1037:
1014:
1008:
1007:
989:
957:
942:
941:
940:
924:
918:
917:
916:
900:
894:
893:
891:
889:
859:
848:
847:
821:
810:
809:
789:
768:
767:
765:
763:
756:The Conversation
748:
742:
741:
731:
721:
697:
691:
690:
688:
686:
672:
666:
665:
658:
652:
651:
641:
601:
586:
585:
548:
542:
541:
531:
499:
493:
492:
491:
489:
466:
245:Musculoskeletal.
223:Gastrointestinal
92:hyperventilation
64:Medical genetics
44:
32:
31:
21:
2458:
2457:
2453:
2452:
2451:
2449:
2448:
2447:
2408:
2407:
2406:
2396:
2394:
2386:
2384:
2375:
2352:
2318:
2245:
2241:Kabuki syndrome
2218:
2202:
2138:
2112:
2093:
2083:
2053:
1925:
1825:
1634:
1618:
1563:
1542:
1461:
1460:(2) Zinc finger
1451:
1435:
1407:
1406:or coregulators
1397:
1367:
1362:
1361:
1338:
1337:
1311:
1297:
1292:
1291:
1252:
1248:
1203:
1196:
1151:
1142:
1097:
1093:
1048:
1044:
1035:
1033:
1015:
1011:
958:
945:
938:10.32388/l1967e
926:
925:
921:
914:10.32388/l1967e
902:
901:
897:
887:
885:
875:10.32388/nb53oy
861:
860:
851:
824:Dean L (2012).
822:
813:
790:
771:
761:
759:
758:. 26 April 2019
750:
749:
745:
698:
694:
684:
682:
674:
673:
669:
660:
659:
655:
602:
589:
549:
545:
514:(5): 994–1001.
500:
496:
487:
485:
467:
460:
455:
432:
402:
375:
349:, with bulbous
341:with a missing
339:corpus callosum
317:
256:
234:
225:
194:
166:
148:, however true
30:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
2456:
2446:
2445:
2440:
2435:
2430:
2425:
2420:
2405:
2404:
2381:
2380:
2377:
2376:
2374:
2373:
2360:
2358:
2354:
2353:
2351:
2350:
2349:
2348:
2335:
2333:
2326:
2320:
2319:
2317:
2316:
2315:
2314:
2286:
2285:
2284:
2272:
2271:
2270:
2257:
2255:
2251:
2250:
2247:
2246:
2244:
2243:
2237:
2235:
2228:
2224:
2223:
2220:
2219:
2217:
2216:
2210:
2208:
2204:
2203:
2201:
2200:
2199:
2198:
2193:
2181:
2180:
2179:
2174:
2162:
2157:
2152:
2146:
2144:
2140:
2139:
2137:
2136:
2131:
2126:
2120:
2118:
2114:
2113:
2111:
2110:
2104:
2102:
2095:
2089:
2088:
2085:
2084:
2082:
2081:
2080:
2079:
2074:
2061:
2059:
2055:
2054:
2052:
2051:
2050:
2049:
2037:
2036:
2035:
2023:
2022:
2021:
2009:
2008:
2007:
1995:
1994:
1993:
1981:
1980:
1979:
1967:
1966:
1965:
1953:
1952:
1951:
1946:
1933:
1931:
1927:
1926:
1924:
1923:
1922:
1921:
1909:
1908:
1907:
1895:
1894:
1893:
1888:
1876:
1875:
1874:
1862:
1861:
1860:
1848:
1847:
1846:
1833:
1831:
1827:
1826:
1824:
1823:
1822:
1821:
1809:
1808:
1807:
1802:
1790:
1789:
1788:
1776:
1775:
1774:
1762:
1761:
1760:
1748:
1747:
1746:
1741:
1729:
1728:
1727:
1715:
1714:
1713:
1701:
1700:
1699:
1687:
1686:
1685:
1673:
1672:
1671:
1666:
1653:
1651:
1644:
1640:
1639:
1636:
1635:
1633:
1632:
1626:
1624:
1620:
1619:
1617:
1616:
1611:
1606:
1601:
1596:
1591:
1586:
1581:
1571:
1569:
1565:
1564:
1562:
1561:
1556:
1550:
1548:
1544:
1543:
1541:
1540:
1535:
1530:
1525:
1520:
1515:
1510:
1505:
1504:
1503:
1498:
1493:
1483:
1472:
1470:
1463:
1457:
1456:
1453:
1452:
1450:
1449:
1447:Tietz syndrome
1443:
1441:
1437:
1436:
1434:
1433:
1428:
1422:
1420:
1413:
1409:
1408:
1396:
1395:
1388:
1381:
1373:
1364:
1363:
1360:
1359:
1347:
1346:
1344:
1340:
1339:
1336:
1335:
1324:
1312:
1307:
1306:
1304:
1303:Classification
1296:
1295:External links
1293:
1290:
1289:
1246:
1194:
1165:(3): 168–176.
1140:
1091:
1068:10.1086/515582
1062:(5): 988–993.
1042:
1009:
972:(4): 462–478.
943:
919:
895:
849:
811:
769:
743:
692:
676:"Pitt-Hopkins"
667:
653:
616:(3): 233–244.
587:
554:Human Mutation
543:
520:10.1086/515583
494:
457:
456:
454:
451:
431:
428:
427:
426:
419:
416:
401:
398:
394:encephalopathy
374:
371:
351:caudate nuclei
316:
313:
255:
252:
233:
230:
224:
221:
192:
191:
188:
187:Prominent ears
185:
182:
179:
165:
162:
116:ATR-X syndrome
67:
66:
57:
51:
50:
46:
45:
37:
36:
28:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2455:
2444:
2441:
2439:
2438:Rare diseases
2436:
2434:
2431:
2429:
2426:
2424:
2421:
2419:
2416:
2415:
2413:
2403:
2393:
2392:
2389:
2371:
2367:
2366:
2362:
2361:
2359:
2355:
2347:
2344:
2343:
2342:
2341:
2337:
2336:
2334:
2330:
2327:
2325:
2321:
2313:
2309:
2305:
2301:
2297:
2294:
2293:
2292:
2291:
2287:
2283:
2280:
2279:
2278:
2277:
2273:
2269:
2266:
2265:
2264:
2263:
2259:
2258:
2256:
2252:
2242:
2239:
2238:
2236:
2232:
2229:
2225:
2215:
2212:
2211:
2209:
2205:
2197:
2194:
2192:
2189:
2188:
2187:
2186:
2182:
2178:
2175:
2173:
2170:
2169:
2168:
2167:
2163:
2161:
2158:
2156:
2153:
2151:
2148:
2147:
2145:
2141:
2135:
2132:
2130:
2127:
2125:
2122:
2121:
2119:
2115:
2109:
2106:
2105:
2103:
2099:
2096:
2090:
2078:
2075:
2073:
2070:
2069:
2068:
2067:
2063:
2062:
2060:
2056:
2048:
2045:
2044:
2043:
2042:
2038:
2034:
2031:
2030:
2029:
2028:
2024:
2020:
2017:
2016:
2015:
2014:
2010:
2006:
2003:
2002:
2001:
2000:
1996:
1992:
1989:
1988:
1987:
1986:
1982:
1978:
1975:
1974:
1973:
1972:
1968:
1964:
1961:
1960:
1959:
1958:
1954:
1950:
1947:
1945:
1942:
1941:
1940:
1939:
1935:
1934:
1932:
1928:
1920:
1917:
1916:
1915:
1914:
1910:
1906:
1903:
1902:
1901:
1900:
1896:
1892:
1889:
1887:
1884:
1883:
1882:
1881:
1877:
1873:
1870:
1869:
1868:
1867:
1863:
1859:
1856:
1855:
1854:
1853:
1849:
1845:
1842:
1841:
1840:
1839:
1835:
1834:
1832:
1828:
1820:
1817:
1816:
1815:
1814:
1810:
1806:
1803:
1801:
1798:
1797:
1796:
1795:
1791:
1787:
1784:
1783:
1782:
1781:
1777:
1773:
1770:
1769:
1768:
1767:
1763:
1759:
1756:
1755:
1754:
1753:
1749:
1745:
1742:
1740:
1737:
1736:
1735:
1734:
1730:
1726:
1723:
1722:
1721:
1720:
1716:
1712:
1709:
1708:
1707:
1706:
1702:
1698:
1695:
1694:
1693:
1692:
1688:
1684:
1681:
1680:
1679:
1678:
1674:
1670:
1667:
1665:
1662:
1661:
1660:
1659:
1655:
1654:
1652:
1648:
1645:
1641:
1631:
1628:
1627:
1625:
1621:
1615:
1612:
1610:
1607:
1605:
1602:
1600:
1597:
1595:
1592:
1590:
1587:
1585:
1582:
1580:
1576:
1573:
1572:
1570:
1566:
1560:
1557:
1555:
1552:
1551:
1549:
1545:
1539:
1536:
1534:
1531:
1529:
1526:
1524:
1521:
1519:
1516:
1514:
1511:
1509:
1506:
1502:
1499:
1497:
1494:
1492:
1489:
1488:
1487:
1484:
1482:
1478:
1474:
1473:
1471:
1467:
1464:
1458:
1448:
1445:
1444:
1442:
1438:
1432:
1429:
1427:
1424:
1423:
1421:
1417:
1414:
1410:
1405:
1401:
1394:
1389:
1387:
1382:
1380:
1375:
1374:
1371:
1358:
1354:
1353:
1349:
1348:
1345:
1341:
1334:
1330:
1329:
1325:
1323:
1319:
1318:
1314:
1313:
1310:
1305:
1301:
1285:
1281:
1277:
1273:
1269:
1265:
1261:
1257:
1250:
1242:
1238:
1233:
1228:
1224:
1220:
1216:
1212:
1208:
1201:
1199:
1190:
1186:
1181:
1176:
1172:
1168:
1164:
1160:
1156:
1149:
1147:
1145:
1136:
1132:
1127:
1122:
1118:
1114:
1110:
1106:
1102:
1095:
1087:
1083:
1078:
1073:
1069:
1065:
1061:
1057:
1053:
1046:
1032:
1028:
1024:
1020:
1013:
1005:
1001:
997:
993:
988:
983:
979:
975:
971:
967:
963:
956:
954:
952:
950:
948:
939:
934:
930:
923:
915:
910:
906:
899:
884:
880:
876:
872:
868:
864:
858:
856:
854:
845:
841:
837:
833:
832:
827:
820:
818:
816:
807:
803:
799:
795:
788:
786:
784:
782:
780:
778:
776:
774:
757:
753:
747:
739:
735:
730:
725:
720:
715:
711:
707:
703:
696:
681:
677:
671:
663:
657:
649:
645:
640:
635:
631:
627:
623:
619:
615:
611:
607:
600:
598:
596:
594:
592:
583:
579:
575:
571:
567:
563:
559:
555:
547:
539:
535:
530:
525:
521:
517:
513:
509:
505:
498:
484:
480:
476:
472:
465:
463:
458:
450:
448:
440:
436:
424:
420:
417:
414:
413:
412:
409:
406:
397:
395:
390:
388:
384:
383:Rett syndrome
380:
370:
367:
365:
360:
358:
354:
352:
348:
344:
340:
335:
332:
329:
325:
323:
312:
309:
306:
304:
300:
296:
292:
288:
284:
279:
277:
273:
269:
268:chromosome 18
265:
261:
251:
247:
246:
242:
238:
229:
220:
216:
214:
209:
202:
198:
195:
190:Thin eyebrows
189:
186:
183:
180:
177:
176:
175:
172:
169:
161:
158:
155:
151:
147:
142:
140:
136:
135:chromosome 18
132:
128:
124:
119:
117:
113:
109:
108:Rett-syndrome
105:
101:
97:
93:
89:
85:
81:
77:
73:
65:
61:
58:
56:
52:
47:
43:
38:
33:
27:
19:
2363:
2357:Corepressor:
2338:
2332:Coactivator:
2288:
2274:
2267:
2260:
2183:
2164:
2064:
2039:
2025:
2011:
1997:
1983:
1969:
1955:
1936:
1911:
1897:
1878:
1864:
1850:
1836:
1811:
1792:
1778:
1764:
1750:
1731:
1717:
1703:
1689:
1675:
1656:
1350:
1326:
1315:
1262:(3): 182–4.
1259:
1255:
1249:
1214:
1210:
1162:
1158:
1108:
1104:
1094:
1059:
1055:
1045:
1034:, retrieved
1023:GeneReviews®
1022:
1012:
969:
965:
928:
922:
904:
898:
886:. Retrieved
866:
830:
797:
760:. Retrieved
746:
709:
705:
695:
683:. Retrieved
670:
656:
613:
609:
560:(1): 64–72.
557:
553:
546:
511:
507:
497:
486:, retrieved
475:GeneReviews®
474:
444:
410:
407:
403:
391:
376:
368:
361:
355:
336:
333:
330:
326:
318:
310:
307:
303:chromosome 2
291:chromosome 7
280:
271:
257:
248:
244:
243:
239:
235:
232:Neurological
226:
217:
213:Craniofacial
210:
206:
196:
193:
173:
170:
167:
159:
150:intelligence
143:
120:
94:followed by
75:
71:
70:
26:
987:2066/201958
929:Definitions
905:Definitions
867:Definitions
798:GeneReviews
2412:Categories
1217:(5): e21.
888:16 October
685:8 December
453:References
305:(2p16.3).
181:Wide mouth
60:Psychiatry
2254:Ungrouped
996:0009-9163
883:161843893
712:(1): 24.
630:0883-0738
400:Treatment
315:Diagnosis
297:1 alpha (
283:contactin
55:Specialty
2402:Medicine
1352:Orphanet
1284:45629810
1241:23640545
1189:27617128
1135:22670138
1086:17436254
1031:22934316
1004:30677142
844:28520343
838:(NCBI).
806:22934316
738:31586495
648:29318938
574:22045651
538:17436255
483:22934316
347:splenium
295:neurexin
254:Genetics
100:Epilepsy
2005:ACD/MPV
1333:C537403
1232:3674405
1180:4918722
1126:3366706
1077:1852736
1036:26 July
762:10 July
729:6778364
639:5922265
582:9559486
529:1852727
488:17 July
430:History
343:rostrum
287:CNTNAP2
272:de novo
123:anxiety
2388:Portal
2340:CREBBP
2160:MODY 5
2155:MODY 3
1919:STHAG3
1872:MODY 9
1780:POU3F4
1772:DFNA15
1766:POU4F3
1711:MODY 4
1691:HOXD13
1599:MRX 89
1594:MODY 7
1528:MODY 1
1322:610954
1282:
1276:728011
1274:
1239:
1229:
1187:
1177:
1133:
1123:
1084:
1074:
1029:
1002:
994:
881:
842:
804:
736:
726:
646:
636:
628:
580:
572:
536:
526:
481:
127:autism
114:, and
2282:TNDM1
2276:ZFP57
2185:SOX10
2041:FOXP3
2027:FOXL2
2013:FOXI1
1999:FOXF1
1985:FOXE3
1971:FOXE1
1957:FOXC2
1938:FOXC1
1786:DFNX2
1752:PITX2
1719:LMX1B
1280:S2CID
879:S2CID
578:S2CID
299:NRXN1
228:age.
96:apnea
2312:OFC8
2290:TP63
2262:TCF4
2207:4.11
2066:IRF6
2047:IPEX
1913:PAX9
1899:PAX8
1880:PAX6
1866:PAX4
1852:PAX3
1838:PAX2
1813:ZEB2
1794:ZEB1
1744:OFC5
1733:MSX1
1705:PDX1
1677:MNX1
1501:CAIS
1496:MAIS
1491:PAIS
1357:2896
1328:MeSH
1317:OMIM
1272:PMID
1237:PMID
1185:PMID
1131:PMID
1082:PMID
1038:2024
1027:PMID
1000:PMID
992:ISSN
890:2022
840:PMID
802:PMID
764:2019
734:PMID
687:2009
644:PMID
626:ISSN
570:PMID
534:PMID
490:2024
479:PMID
385:and
264:TCF4
139:TCF4
131:ADHD
76:PTHS
2234:0.6
2166:SF1
2143:4.7
2117:4.3
2101:4.2
2058:3.5
1930:3.3
1830:3.2
1658:ARX
1650:3.1
1623:2.5
1568:2.3
1547:2.2
1479:):
1469:2.1
1440:1.3
1419:1.2
1264:doi
1227:PMC
1219:doi
1175:PMC
1167:doi
1121:PMC
1113:doi
1072:PMC
1064:doi
982:hdl
974:doi
933:doi
909:doi
871:doi
724:PMC
714:doi
634:PMC
618:doi
562:doi
524:PMC
516:doi
423:IEP
118:.
2414::
2365:HR
1355::
1331::
1320::
1278:.
1270:.
1260:14
1258:.
1235:.
1225:.
1215:45
1213:.
1209:.
1197:^
1183:.
1173:.
1161:.
1157:.
1143:^
1129:.
1119:.
1107:.
1103:.
1080:.
1070:.
1060:80
1058:.
1054:.
1021:,
998:.
990:.
980:.
970:95
968:.
964:.
946:^
877:.
865:.
852:^
834:.
814:^
772:^
754:.
732:.
722:.
710:11
708:.
704:.
678:.
642:.
632:.
624:.
614:33
612:.
608:.
590:^
576:.
568:.
558:33
556:.
532:.
522:.
512:80
510:.
506:.
473:,
461:^
389:.
381:,
366:.
278:.
129:,
125:,
110:,
106:,
98:.
86:,
62:,
2390::
2372:)
2368:(
2310:/
2306:/
2302:/
2298:/
1577:/
1475:(
1392:e
1385:t
1378:v
1309:D
1286:.
1266::
1243:.
1221::
1191:.
1169::
1163:4
1137:.
1115::
1109:2
1088:.
1066::
1006:.
984::
976::
935::
911::
892:.
873::
808:.
766:.
740:.
716::
689:.
650:.
620::
584:.
564::
540:.
518::
74:(
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.