31:
274:
In photosystem II, pheophytin plays a very similar role. It again acts as the first electron carrier intermediate in the photosystem. After P680 becomes excited to P680, it transfers an electron to pheophytin, which converts the molecule into a negatively charged radical. Two negatively charged
154:
and plastoquinone (Klimov, Allakhverdiev, Klevanik, Shuvalov). This discovery was met with fierce opposition, since many believed pheophytin to only be a byproduct of chlorophyll degradation. Therefore, more experiments ensued to prove that pheophytin is indeed the primary electron acceptor of
286:
molecule and leaves photosystem II. The reactions outlined above in the section concerning purple bacteria give a general illustration of the actual movement of the electrons through pheophytin and the photosystem. The overall scheme is:
177:
Pheophytin is the first electron carrier intermediate in the photoreaction center (RC P870) of purple bacteria. Its involvement in this system can be broken down into 5 basic steps. The first step is excitation of the
206:
passing an electron to pheophytin, producing a negatively charged radical (the pheophytin) and a positively charged radical (the special pair of chlorophylls), which results in a charge separation.
413:
Xiong, Ling, and
Richard Sayre. "The Identification of Potential Pheophytin Binding Sites in the Photosystem II Reaction Center of Chlamydomondas by Site-Directed Mutagenesis." (2000).
703:
403:
601:
728:
348:
Klimov VV (2003). "Discovery of pheophytin function in the photosynthetic energy conversion as the primary electron acceptor of
Photosystem II".
867:
275:
pheophytin radicals quickly pass their extra electrons to two consecutive plastoquinone molecules. Eventually, the electrons pass through the
556:
85:. In both PS II and RC P870, light drives electrons from the reaction center through pheophytin, which then passes the electrons to a
932:
93:) in RC P870 and RC P680. The overall mechanisms, roles, and purposes of the pheophytin molecules in the two transport chains are
489:
142:
In 1977, scientists
Klevanik, Klimov, Shuvalov performed a series of experiments to demonstrate that it is pheophytin and not
155:
PSII, occurring between P680 and plastoquinone (Klimov, Allakhverdiev, Shuvalov). The data that was obtained is as follows:
165:
Photo-reduction of pheophytin occurs at temperatures as low as 100K, and is observed after the reduction of plastoquinone.
461:. CollinsDictionary.com. Collins English Dictionary - Complete & Unabridged 11th Edition. Retrieved October 19, 2012.
262:
The fifth and final step involves the filling of the “hole” in the special pair by an electron from a heme in cytochrome
969:
150:(EPR), they were able to show that pheophytin was reducible and, therefore, the primary electron acceptor between
147:
266:. This regenerates the substrates and completes the cycle, allowing for subsequent reactions to take place.
482:
17:
159:
Photo-reduction of pheophytin has been observed in various mixtures containing PSII reaction centers.
146:
that serves as the primary electron acceptor in photosystem II. Using several experiments, including
66:
974:
797:
475:
169:
These observations are all characteristic of photo-conversions of reaction center components.
896:
875:
803:
458:
793:
783:
507:
179:
110:
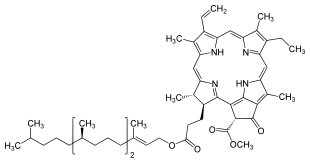
molecule lacking a central Mg ion. It can be produced from chlorophyll by treatment with a
162:
The quantity of pheophytin is in direct proportion to the number of PSII reaction centers.
8:
789:
744:
718:
909:
779:
373:
708:
636:
586:
365:
58:
434:
377:
922:
831:
825:
775:
568:
357:
62:
186:
or the special pair of chlorophylls. This can be seen in the following reaction.
888:
646:
591:
531:
325:
222:
The third step is the rapid electron movement to the tightly bound menaquinone, Q
82:
78:
821:
665:
641:
446:
335:
310:
226:, which immediately donates the electrons to a second, loosely bound quinone (Q
70:
361:
963:
940:
849:
843:
767:
736:
596:
143:
39:
861:
541:
499:
369:
839:
536:
467:
320:
315:
107:
449:
Definition of pheo in The
American Heritage Stedman's Medical Dictionary
713:
619:
578:
526:
276:
656:
628:
521:
115:
111:
917:
546:
813:
86:
30:
695:
689:
683:
677:
393:
74:
673:
437:
Merriam-Webster
Medical Dictionary definition of Pheophytin
330:
151:
114:, producing a dark bluish waxy pigment. The probable
384:
435:http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/pheophytin
961:
389:(4th ed.). Redondo Beach, CA: Plycon Press.
269:
27:Chlorophyll molecules lacking a central Mg2+ ion
172:
766:
483:
447:http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/pheo-
497:
490:
476:
394:Nelson, David L.; Cox, Michael M. (2005).
347:
398:(4th ed.). New York: W. H. Freeman.
137:
29:
14:
962:
106:In biochemical terms, pheophytin is a
471:
387:Illustrated Guide to Food Preparation
396:Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
230:). Two electron transfers convert Q
415:America Society of Plant Biologists
408:Library of 3-D Molecular Structures
24:
202:The second step involves the (Chl)
118:comes from this description, with
25:
986:
404:Photosynthetic Molecules Section.
77:, and the type II photosynthetic
421:
148:electron paramagnetic resonance
452:
440:
428:
13:
1:
385:McWilliams, Margaret (1982).
341:
270:Involvement in photosystem II
218:+ ·Pheo (charge separation)
101:
7:
304:
173:Reaction in purple bacteria
10:
991:
300:Regeneration of substrates
931:
908:
887:
812:
757:
727:
664:
655:
627:
618:
577:
564:
555:
517:
506:
67:electron transfer pathway
61:that serves as the first
704:Magnesium protoporphyrin
970:Photosynthetic pigments
362:10.1023/A:1024990408747
297:Plastoquinone reduction
234:to its reduced form (Q
46:
804:Protoporphyrinogen IX
138:History and discovery
33:
897:Bacteriochlorophyll
876:Bacteriochlorophyll
180:bacteriochlorophylls
65:intermediate in the
910:Isobacteriochlorins
745:Protochlorophyllide
719:Zinc protoporphyrin
258:(quinone reduction)
81:(RC P870) found in
45:without the Mg ion.
790:Coproporphyrinogen
194:+ 1 photon → (Chl)
47:
957:
956:
953:
952:
949:
948:
753:
752:
709:Protoporphyrin IX
637:Adenosylcobalamin
614:
613:
610:
609:
587:Phycoerythrobilin
294:Charge separation
59:chemical compound
16:(Redirected from
982:
923:Sirohydrochlorin
889:Bacteriochlorins
776:Uroporphyrinogen
764:
763:
662:
661:
625:
624:
569:Phytochromobilin
562:
561:
515:
514:
492:
485:
478:
469:
468:
462:
456:
450:
444:
438:
432:
399:
390:
381:
63:electron carrier
21:
990:
989:
985:
984:
983:
981:
980:
979:
960:
959:
958:
945:
927:
904:
883:
808:
759:
749:
729:Phytoporphyrins
723:
666:Protoporphyrins
651:
647:Methylcobalamin
606:
602:Phycoviolobilin
592:Phycocyanobilin
573:
551:
532:Stercobilinogen
510:
502:
496:
466:
465:
457:
453:
445:
441:
433:
429:
424:
417:. 22 Apr. 2007.
410:. 22 April 2007
356:(1–3): 247–53.
350:Photosynth. Res
344:
326:Reaction center
307:
283:
272:
257:
253:
249:
246:2·Pheo + 2H + Q
241:
237:
233:
229:
225:
217:
214:+ Pheo → ·(Chl)
213:
205:
197:
193:
185:
175:
140:
104:
92:
83:purple bacteria
79:reaction center
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
988:
978:
977:
972:
955:
954:
951:
950:
947:
946:
944:
943:
937:
935:
929:
928:
926:
925:
920:
914:
912:
906:
905:
903:
902:
893:
891:
885:
884:
882:
881:
873:
855:
837:
822:Chlorophyllide
818:
816:
810:
809:
807:
806:
801:
787:
772:
770:
768:Porphyrinogens
761:
755:
754:
751:
750:
748:
747:
742:
733:
731:
725:
724:
722:
721:
716:
711:
706:
701:
670:
668:
659:
653:
652:
650:
649:
644:
642:Cyanocobalamin
639:
633:
631:
622:
616:
615:
612:
611:
608:
607:
605:
604:
599:
594:
589:
583:
581:
575:
574:
572:
571:
565:
559:
553:
552:
550:
549:
544:
539:
534:
529:
524:
518:
512:
504:
503:
495:
494:
487:
480:
472:
464:
463:
451:
439:
426:
425:
423:
420:
419:
418:
411:
400:
391:
382:
343:
340:
339:
338:
336:Chlorophyllide
333:
328:
323:
318:
313:
311:Photosynthesis
306:
303:
302:
301:
298:
295:
292:
281:
271:
268:
260:
259:
255:
251:
247:
239:
235:
231:
227:
223:
220:
219:
215:
211:
203:
200:
199:
195:
191:
183:
174:
171:
167:
166:
163:
160:
139:
136:
103:
100:
99:
98:
97:to each other.
90:
71:Photosystem II
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
987:
976:
975:Tetrapyrroles
973:
971:
968:
967:
965:
942:
941:Cofactor F430
939:
938:
936:
934:
930:
924:
921:
919:
916:
915:
913:
911:
907:
901:
900:
895:
894:
892:
890:
886:
880:
879:
874:
871:
870:
865:
864:
859:
856:
853:
852:
847:
846:
841:
838:
835:
834:
829:
828:
823:
820:
819:
817:
815:
811:
805:
802:
799:
795:
791:
788:
785:
781:
777:
774:
773:
771:
769:
765:
762:
756:
746:
743:
741:
740:
735:
734:
732:
730:
726:
720:
717:
715:
712:
710:
707:
705:
702:
699:
698:
693:
692:
687:
686:
681:
680:
675:
672:
671:
669:
667:
663:
660:
658:
654:
648:
645:
643:
640:
638:
635:
634:
632:
630:
626:
623:
621:
617:
603:
600:
598:
597:Phycourobilin
595:
593:
590:
588:
585:
584:
582:
580:
576:
570:
567:
566:
563:
560:
558:
554:
548:
545:
543:
540:
538:
535:
533:
530:
528:
525:
523:
520:
519:
516:
513:
509:
505:
501:
500:tetrapyrroles
493:
488:
486:
481:
479:
474:
473:
470:
460:
455:
448:
443:
436:
431:
427:
416:
412:
409:
405:
401:
397:
392:
388:
383:
379:
375:
371:
367:
363:
359:
355:
351:
346:
345:
337:
334:
332:
329:
327:
324:
322:
319:
317:
314:
312:
309:
308:
299:
296:
293:
290:
289:
288:
285:
278:
267:
265:
245:
244:
243:
209:
208:
207:
189:
188:
187:
181:
170:
164:
161:
158:
157:
156:
153:
149:
145:
144:plastoquinone
135:
133:
129:
125:
121:
117:
113:
109:
96:
88:
84:
80:
76:
72:
68:
64:
60:
56:
52:
49:
48:
44:
43:
37:
32:
19:
898:
877:
868:
862:
857:
850:
844:
832:
826:
738:
737:Chlorophyll
696:
690:
684:
678:
542:Urobilinogen
454:
442:
430:
414:
407:
395:
386:
353:
349:
279:
273:
263:
261:
221:
201:
198:(excitation)
176:
168:
141:
131:
127:
123:
119:
105:
94:
54:
50:
41:
40:chlorophyll
35:
840:Chlorophyll
579:Phycobilins
557:Phytobilins
537:Stercobilin
321:Chlorophyll
316:Photosystem
250:→ 2Pheo + Q
108:chlorophyll
73:(PS II) in
55:phaeophytin
34:Pheophytin
18:Phaeophytin
964:Categories
858:Pheophytin
760:porphyrins
714:Pterobilin
657:Porphyrins
629:Corrinoids
620:Macrocycle
527:Biliverdin
422:References
342:References
291:Excitation
277:cytochrome
132:vegetation
51:Pheophytin
522:Bilirubin
498:Types of
116:etymology
112:weak acid
102:Structure
95:analogous
933:Corphins
918:Siroheme
814:Chlorins
547:Urobilin
511:(Linear)
378:29278470
370:16228584
305:See also
130:meaning
122:meaning
758:Reduced
508:Bilanes
87:quinone
38:, i.e.
376:
368:
75:plants
374:S2CID
210:(Chl)
190:(Chl)
182:(Chl)
124:dusky
57:is a
674:Heme
459:phyt
366:PMID
331:P680
152:P680
128:phyt
126:and
120:pheo
798:III
784:III
358:doi
242:).
69:of
53:or
966::
866:,
848:,
830:,
796:,
782:,
694:,
688:,
682:,
406:"
372:.
364:.
354:76
352:.
134:.
89:(Q
899:a
878:c
872:)
869:b
863:a
860:(
854:)
851:b
845:a
842:(
836:)
833:b
827:a
824:(
800:)
794:I
792:(
786:)
780:I
778:(
739:c
700:)
697:o
691:a
685:c
679:b
676:(
491:e
484:t
477:v
402:"
380:.
360::
284:f
282:6
280:b
264:c
256:2
254:H
252:B
248:B
240:2
238:H
236:B
232:B
228:B
224:A
216:2
212:2
204:2
196:2
192:2
184:2
91:A
42:a
36:a
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.