647:
142:
1156:
392:
36:
516:. Usually these arise as a web ("plexus") of interconnected nerves roots that arrange to form single nerves. These nerves control the functions of the rest of the body. In humans, there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves: 8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, and 1 coccygeal. These nerve roots are named according to the spinal vertebrata which they are adjacent to. In the cervical region, the spinal nerve roots come out
789:. Peripheral neuropathy is associated with a sensory loss in a "glove and stocking" distribution that begins at the peripheral and slowly progresses upwards, and may also be associated with acute and chronic pain. Peripheral neuropathy is not just limited to the somatosensory nerves, but the autonomic nervous system too (
739:. Located only around the digestive tract, this system allows for local control without input from the sympathetic or the parasympathetic branches, though it can still receive and respond to signals from the rest of the body. The enteric system is responsible for various functions related to gastrointestinal system.
709:
are released, which increases heart rate and blood flow in certain areas like muscle, while simultaneously decreasing activities of non-critical functions for survival, like digestion. The systems are independent to each other, which allows activation of certain parts of the body, while others remain
684:
are connected with organs that have smooth muscle, such as the heart, bladder, and other cardiac, exocrine, and endocrine related organs, by ganglionic neurons. The most notable physiological effects from autonomic activity are pupil constriction and dilation, and salivation of saliva. The autonomic
524:
the corresponding vertebrae. This method creates a problem when naming the spinal nerve root between C7 and T1 (so it is called spinal nerve root C8). In the lumbar and sacral region, the spinal nerve roots travel within the dural sac and they travel below the level of L2 as the cauda equina.
726:
allows the body to function in a "rest and digest" state. Consequently, when the parasympathetic system dominates the body, there are increases in salivation and activities in digestion, while heart rate and other sympathetic response decrease. Unlike the sympathetic system, humans have some
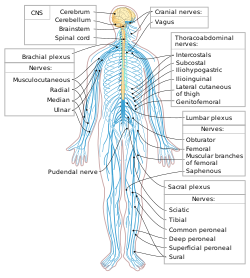
607:, a tangled array of nerves, splitting, combining and recombining, to form the nerves that subserve the upper-limb and upper back. Although the brachial plexus may appear tangled, it is highly organized and predictable, with little variation between people. See
369:
and touch (including fine touch and gross touch) to the spinal cord and brain. The autonomic nervous system is a "self-regulating" system which influences the function of organs outside voluntary control, such as the
776:
include pain and numbness in the thumb, index and middle finger. In peripheral neuropathy, the function one or more nerves are damaged through a variety of means. Toxic damage may occur because of diabetes
685:
nervous system is always activated, but is either in the sympathetic or parasympathetic state. Depending on the situation, one state can overshadow the other, resulting in a release of different kinds of
520:
the corresponding vertebrae (i.e., nerve root between the skull and 1st cervical vertebrae is called spinal nerve C1). From the thoracic region to the coccygeal region, the spinal nerve roots come out
764:. Compression of nerves can occur because of a tumour mass or injury. Alternatively, if a nerve is in an area with a fixed size it may be trapped if the other components increase in size, such as
297:
and the visceral nervous system. Each of these have a sensory and a motor division. The visceral motor division is known as the autonomic nervous system. In the somatic nervous system, the
1266:
313:, which are considered parts of the central nervous system based on developmental origin. The second cranial nerve is not a true peripheral nerve but a tract of the
1127:
206:
807:
1012:. Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven Alexander Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Rebecca B. Orr, Neil A. Campbell (12th ed.). New York, NY. 2021.
1285:
1041:
917:
274:, essentially serving as a relay between the brain and spinal cord and the rest of the body. Unlike the CNS, the PNS is not protected by the
182:
539:
The first 4 cervical spinal nerves, C1 through C4, split and recombine to produce a variety of nerves that serve the neck and back of head.
1220:
100:
1173:
409:
53:
1192:
701:
is activated during a "fight or flight" situation in which mental stress or physical danger is encountered. Neurotransmitters such as
72:
1199:
481:, and mainly control the functions of the anatomic structures of the head with some exceptions. One unique cranial nerve is the
79:
1017:
984:
960:
893:
727:
voluntary controls in the parasympathetic system. The most prominent examples of this control are urination and defecation.
1206:
86:
1263:
802:
1306:
1188:
68:
1239:
940:
841:
431:
119:
17:
357:. The somatic nervous system is under voluntary control, and transmits signals from the brain to end organs such as
812:
445:
213:
753:
Diseases of the peripheral nervous system can be specific to one or more nerves, or affect the system as a whole.
599:
The last four cervical spinal nerves, C5 through C8, and the first thoracic spinal nerve, T1, combine to form the
1177:
413:
338:
57:
550:. C2 and C3 form many of the nerves of the neck, providing both sensory and motor control. These include the
201:
680:(ANS) controls involuntary responses to regulate physiological functions. The brain and spinal cord of the
781:), alcohol, heavy metals or other toxins; some infections; autoimmune and inflammatory conditions such as
1128:"Introduction to the Nervous System, Part 2: The Autonomic Nervous System and the Central Nervous System"
1213:
1045:
498:
334:
93:
955:
Board Review Series: Neuroanatomy, 4th Ed., Lippincott
Williams & Wilkins, Maryland 2008, p. 177.
1258:
333:. The connection between CNS and organs allows the system to be in two different functional states:
677:
665:
608:
577:
is a nerve essential for our survival which arises from nerve roots C3, C4 and C5. It supplies the
354:
165:
1166:
563:
551:
402:
283:
46:
773:
769:
765:
761:
736:
723:
681:
567:
555:
455:
451:
375:
362:
350:
294:
247:
189:
177:
462:
and consists of sensory nerves and somatic nerves, and many nerves which hold both functions.
1301:
857:
748:
646:
318:
974:
790:
477:
carry somatosensory data. There are twelve cranial nerves, ten of which originate from the
459:
8:
778:
585:. If the spinal cord is transected above C3, then spontaneous breathing is not possible.
1035:
911:
698:
636:
578:
543:
1276:
1076:
Laight, David (September 2013). "Overview of peripheral nervous system pharmacology".
1135:
1093:
1023:
1013:
980:
956:
936:
899:
889:
837:
686:
604:
325:, are part of the PNS. The autonomic nervous system exerts involuntary control over
1085:
640:
502:
275:
1270:
632:
600:
594:
534:
494:
302:
271:
170:
1089:
365:
is part of the somatic nervous system and transmits signals from senses such as
757:
702:
267:
239:
1027:
903:
735:
There is a lesser known division of the autonomic nervous system known as the
1295:
1139:
1097:
719:
660:
655:
628:
624:
574:
474:
326:
298:
194:
643:. For descriptive purposes this plexus is usually divided into three parts:
141:
1007:
883:
509:
314:
786:
782:
706:
513:
482:
306:
263:
416: in this section. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
371:
639:, the first lumbar nerve being frequently joined by a branch from the
219:
582:
478:
243:
1155:
836:(32nd ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Saunders/Elsevier. p. 1862.
512:
are responsible for somatosensory information. These arise from the
391:
35:
1132:
AMWA Journal: American
Medical Writers Association Journal (AMWA J)
620:
322:
546:, which provides motor innervation to muscles at the base of the
490:
255:
486:
358:
310:
27:
Part of the nervous system excluding the brain and spinal cord
547:
366:
330:
287:
279:
266:. The main function of the PNS is to connect the CNS to the
259:
251:
756:
Any peripheral nerve or nerve root can be damaged, called a
470:
466:
935:(10th ed.). New York, NY: McGraw Hill. p. 1076.
559:
146:
The human nervous system. Sky blue is PNS; yellow is CNS.
933:
Anatomy & Physiology: The Unity of Form and
Function
554:, which provides sensation to the back of the head, the
505:, neither of which are located exclusively in the head.
485:, which receives sensory information from organs in the
760:. Such injuries can be because of injury or trauma, or
293:
The peripheral nervous system can be divided into the
650:
3D Medical
Animation still shot of Lumbosacral Plexus
1180:. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
60:. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
808:Connective tissue in the peripheral nervous system
558:, which provides sensation to the area behind the
349:The peripheral nervous system is divided into the
713:
528:
1293:
858:"Slide show: How your brain works - Mayo Clinic"
301:are part of the PNS with the exceptions of the
972:
614:
692:
238:) is one of two components that make up the
1277:Neuropathy: Causes, Symptoms and Treatments
671:
1259:Peripheral nervous system photomicrographs
1040:: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (
916:: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (
881:
588:
140:
1240:Learn how and when to remove this message
979:. McGraw-Hill Professional. pp. 1–.
730:
497:which is responsible for innervating the
432:Learn how and when to remove this message
381:
120:Learn how and when to remove this message
966:
834:Dorland's illustrated medical dictionary
645:
493:. The other unique cranial nerve is the
930:
831:
14:
1294:
1075:
1125:
718:Primarily using the neurotransmitter
1178:adding citations to reliable sources
1149:
1121:
1119:
1117:
1115:
1113:
1111:
1109:
1107:
1071:
1069:
1067:
1065:
1063:
1061:
1059:
1057:
1055:
414:adding citations to reliable sources
385:
58:adding citations to reliable sources
29:
885:ADHD : the ultimate teen guide
803:Classification of peripheral nerves
24:
309:(cranial nerve II) along with the
25:
1318:
1252:
1104:
1052:
1154:
973:James S. White (21 March 2008).
813:Preferential motor reinnervation
446:List of nerves of the human body
390:
246:, with the other part being the
214:Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
34:
1165:needs additional citations for
401:needs additional citations for
45:needs additional citations for
1000:
949:
924:
875:
850:
825:
714:Parasympathetic nervous system
542:Spinal nerve C1 is called the
529:Cervical spinal nerves (C1–C4)
13:
1:
818:
286:, which leaves it exposed to
1126:Matic, Agnella Izzo (2014).
344:
7:
1189:"Peripheral nervous system"
1090:10.12968/npre.2013.11.9.448
796:
615:Lumbosacral plexus (L1–Co1)
250:(CNS). The PNS consists of
69:"Peripheral nervous system"
10:
1323:
746:
742:
693:Sympathetic nervous system
592:
532:
508:For the rest of the body,
443:
374:, or the functions of the
1307:Peripheral nervous system
931:Saladin, Kenneth (2024).
882:Aspromonte, John (2019).
722:(ACh) as a mediator, the
232:peripheral nervous system
212:
200:
188:
176:
164:
156:
151:
139:
135:Peripheral nervous system
134:
832:Alberts, Daniel (2012).
678:autonomic nervous system
672:Autonomic nervous system
609:brachial plexus injuries
355:autonomic nervous system
258:, which lie outside the
589:Brachial plexus (C5–T1)
564:greater auricular nerve
552:greater occipital nerve
888:. Lanham. p. 51.
774:carpal tunnel syndrome
770:tarsal tunnel syndrome
766:carpal tunnel syndrome
737:enteric nervous system
731:Enteric nervous system
724:parasympathetic system
682:central nervous system
651:
568:lesser auricular nerve
556:lesser occipital nerve
456:sensory nervous system
452:somatic nervous system
382:Somatic nervous system
363:sensory nervous system
351:somatic nervous system
305:and epithelia and the
295:somatic nervous system
248:central nervous system
1286:Peripheral Neuropathy
1264:Peripheral Neuropathy
1044:) CS1 maint: others (
772:. Common symptoms of
749:Peripheral neuropathy
649:
593:Further information:
533:Further information:
319:Cranial nerve ganglia
1174:improve this article
791:autonomic neuropathy
460:somatosensory system
410:improve this article
54:improve this article
779:diabetic neuropathy
499:sternocleidomastoid
284:blood–brain barrier
1288:at the Mayo Clinic
1281:Medical News Today
1269:2016-12-15 at the
699:sympathetic system
652:
637:lumbosacral plexus
579:thoracic diaphragm
544:suboccipital nerve
1250:
1249:
1242:
1224:
1078:Nurse Prescribing
1019:978-0-13-518874-3
986:978-0-07-149623-0
976:Neurobioscitifity
961:978-0-7817-7245-7
895:978-1-5381-0039-4
687:neurotransmitters
623:divisions of the
605:plexus brachialis
503:trapezius muscles
442:
441:
434:
244:bilateral animals
228:
227:
223:
130:
129:
122:
104:
18:Peripheral nerves
16:(Redirected from
1314:
1245:
1238:
1234:
1231:
1225:
1223:
1182:
1158:
1150:
1144:
1143:
1123:
1102:
1101:
1073:
1050:
1049:
1039:
1031:
1009:Campbell biology
1004:
998:
997:
995:
993:
970:
964:
953:
947:
946:
928:
922:
921:
915:
907:
879:
873:
872:
870:
868:
854:
848:
847:
829:
641:twelfth thoracic
437:
430:
426:
423:
417:
394:
386:
376:digestive system
276:vertebral column
220:edit on Wikidata
217:
144:
132:
131:
125:
118:
114:
111:
105:
103:
62:
38:
30:
21:
1322:
1321:
1317:
1316:
1315:
1313:
1312:
1311:
1292:
1291:
1273:from the US NIH
1271:Wayback Machine
1255:
1246:
1235:
1229:
1226:
1183:
1181:
1171:
1159:
1148:
1147:
1124:
1105:
1074:
1053:
1033:
1032:
1020:
1006:
1005:
1001:
991:
989:
987:
971:
967:
954:
950:
943:
929:
925:
909:
908:
896:
880:
876:
866:
864:
856:
855:
851:
844:
830:
826:
821:
799:
751:
745:
733:
716:
695:
674:
666:pudendal plexus
633:coccygeal nerve
617:
601:brachial plexus
597:
595:Brachial plexus
591:
537:
535:Cervical plexus
531:
495:accessory nerve
448:
438:
427:
421:
418:
407:
395:
384:
347:
339:parasympathetic
303:olfactory nerve
224:
147:
126:
115:
109:
106:
63:
61:
51:
39:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1320:
1310:
1309:
1304:
1290:
1289:
1283:
1274:
1261:
1254:
1253:External links
1251:
1248:
1247:
1162:
1160:
1153:
1146:
1145:
1103:
1084:(9): 448–454.
1051:
1018:
999:
985:
965:
948:
941:
923:
894:
874:
862:mayoclinic.com
849:
842:
823:
822:
820:
817:
816:
815:
810:
805:
798:
795:
758:mononeuropathy
747:Main article:
744:
741:
732:
729:
715:
712:
703:norepinephrine
694:
691:
673:
670:
669:
668:
663:
658:
616:
613:
590:
587:
530:
527:
475:cranial nerves
440:
439:
398:
396:
389:
383:
380:
346:
343:
321:, as with all
299:cranial nerves
240:nervous system
226:
225:
216:
210:
209:
204:
198:
197:
192:
186:
185:
180:
174:
173:
168:
162:
161:
158:
154:
153:
149:
148:
145:
137:
136:
128:
127:
42:
40:
33:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1319:
1308:
1305:
1303:
1300:
1299:
1297:
1287:
1284:
1282:
1278:
1275:
1272:
1268:
1265:
1262:
1260:
1257:
1256:
1244:
1241:
1233:
1230:November 2007
1222:
1219:
1215:
1212:
1208:
1205:
1201:
1198:
1194:
1191: –
1190:
1186:
1185:Find sources:
1179:
1175:
1169:
1168:
1163:This article
1161:
1157:
1152:
1151:
1141:
1137:
1133:
1129:
1122:
1120:
1118:
1116:
1114:
1112:
1110:
1108:
1099:
1095:
1091:
1087:
1083:
1079:
1072:
1070:
1068:
1066:
1064:
1062:
1060:
1058:
1056:
1047:
1043:
1037:
1029:
1025:
1021:
1015:
1011:
1010:
1003:
988:
982:
978:
977:
969:
962:
958:
952:
944:
942:9781266041846
938:
934:
927:
919:
913:
905:
901:
897:
891:
887:
886:
878:
863:
859:
853:
845:
843:9781416062578
839:
835:
828:
824:
814:
811:
809:
806:
804:
801:
800:
794:
792:
788:
784:
780:
775:
771:
767:
763:
759:
754:
750:
740:
738:
728:
725:
721:
720:acetylcholine
711:
708:
704:
700:
690:
688:
683:
679:
667:
664:
662:
661:sacral plexus
659:
657:
656:lumbar plexus
654:
653:
648:
644:
642:
638:
634:
630:
629:sacral nerves
626:
625:lumbar nerves
622:
612:
610:
606:
602:
596:
586:
584:
580:
576:
575:phrenic nerve
571:
569:
565:
561:
557:
553:
549:
545:
540:
536:
526:
523:
519:
515:
511:
510:spinal nerves
506:
504:
500:
496:
492:
488:
484:
480:
476:
472:
468:
463:
461:
457:
454:includes the
453:
447:
436:
433:
425:
415:
411:
405:
404:
399:This section
397:
393:
388:
387:
379:
377:
373:
368:
364:
360:
356:
352:
342:
340:
336:
332:
328:
327:smooth muscle
324:
320:
316:
312:
308:
304:
300:
296:
291:
289:
285:
281:
277:
273:
269:
265:
261:
257:
253:
249:
245:
241:
237:
233:
221:
215:
211:
208:
205:
203:
199:
196:
193:
191:
187:
184:
181:
179:
175:
172:
169:
167:
163:
159:
155:
150:
143:
138:
133:
124:
121:
113:
102:
99:
95:
92:
88:
85:
81:
78:
74:
71: –
70:
66:
65:Find sources:
59:
55:
49:
48:
43:This article
41:
37:
32:
31:
19:
1302:Neuroscience
1280:
1236:
1227:
1217:
1210:
1203:
1196:
1184:
1172:Please help
1167:verification
1164:
1131:
1081:
1077:
1008:
1002:
990:. Retrieved
975:
968:
951:
932:
926:
884:
877:
865:. Retrieved
861:
852:
833:
827:
755:
752:
734:
717:
696:
675:
618:
598:
572:
541:
538:
521:
517:
507:
464:
449:
428:
419:
408:Please help
403:verification
400:
348:
315:diencephalon
292:
282:, or by the
235:
231:
229:
183:A14.2.00.001
116:
107:
97:
90:
83:
76:
64:
52:Please help
47:verification
44:
992:17 November
787:sarcoidosis
783:amyloidosis
762:compression
707:epinephrine
581:, enabling
514:spinal cord
483:vagus nerve
335:sympathetic
307:optic nerve
264:spinal cord
152:Identifiers
1296:Categories
1200:newspapers
1028:1119065904
904:1048014796
819:References
444:See also:
372:heart rate
353:, and the
157:Acronym(s)
80:newspapers
1140:1075-6361
1098:1479-9189
1036:cite book
912:cite book
635:form the
583:breathing
479:brainstem
345:Structure
1267:Archived
797:See also
710:rested.
621:anterior
566:and the
458:and the
422:May 2020
262:and the
110:May 2020
1214:scholar
867:17 June
743:Disease
491:abdomen
465:In the
359:muscles
323:ganglia
256:ganglia
171:D017933
94:scholar
1216:
1209:
1202:
1195:
1187:
1138:
1096:
1026:
1016:
983:
959:
939:
902:
892:
840:
705:, and
631:, and
562:, the
487:thorax
361:. The
331:glands
311:retina
288:toxins
272:organs
252:nerves
96:
89:
82:
75:
67:
1279:from
1221:JSTOR
1207:books
603:, or
548:skull
522:below
518:above
367:taste
280:skull
268:limbs
260:brain
218:[
101:JSTOR
87:books
1193:news
1136:ISSN
1094:ISSN
1046:link
1042:link
1024:OCLC
1014:ISBN
994:2010
981:ISBN
957:ISBN
937:ISBN
918:link
900:OCLC
890:ISBN
869:2016
838:ISBN
785:and
768:and
697:The
676:The
619:The
573:The
560:ears
501:and
489:and
471:neck
469:and
467:head
450:The
337:and
329:and
278:and
270:and
254:and
230:The
207:9093
195:6129
178:TA98
166:MeSH
73:news
1176:by
1086:doi
793:).
412:by
242:of
236:PNS
202:FMA
190:TA2
160:PNS
56:by
1298::
1134:.
1130:.
1106:^
1092:.
1082:11
1080:.
1054:^
1038:}}
1034:{{
1022:.
914:}}
910:{{
898:.
860:.
689:.
627:,
611:.
570:.
473:,
378:.
341:.
317:.
290:.
1243:)
1237:(
1232:)
1228:(
1218:·
1211:·
1204:·
1197:·
1170:.
1142:.
1100:.
1088::
1048:)
1030:.
996:.
963:.
945:.
920:)
906:.
871:.
846:.
777:(
435:)
429:(
424:)
420:(
406:.
234:(
222:]
123:)
117:(
112:)
108:(
98:·
91:·
84:·
77:·
50:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.