287:
61:
156:
Microbodies were first discovered and named in 1954 by Rhodin. Two years later in 1956, Rouiller and
Bernhard presented the first worldwide accepted images of microbodies in liver cells. Then in 1965, Christian de Duve and coworkers isolated microbodies from the liver of a rat. De Duve also believed
144:, which help to convert stored lipids into carbohydrates so they can be used for plant growth. In glyoxysomes the fatty acids are hydrolyzed to acetyl-CoA by peroxisomal β-oxidation enzymes. Besides peroxisomal functions, glyoxysomes also possess the key enzymes of the
96:
within the cell. This facilitates the breakdown of fats, alcohols and amino acids. Generally microbodies are involved in detoxification of peroxides and in photo respiration in plants. Different types of microbodies have different functions:
115:, react hydrogen peroxide as a byproduct of its enzymatic reactions. Within the peroxisome, hydrogen peroxide can then be converted to water by enzymes like
161:
because of its relationship with hydrogen peroxide. In 1967, Breidenbach and
Beevers were the first to isolate microbodies from plants, which they named
111:
is a type of microbody that functions to help the body break down large molecules and detoxify hazardous substances. It contains enzymes like
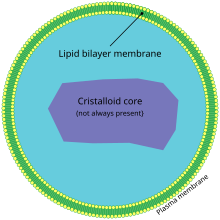
80:. They are surrounded by a single phospholipid bilayer membrane and they contain a matrix of intracellular material including
52:. Many membrane bound vesicles called microbodies that contain various enzymes, are present in both plant and animal cells
188:"Microbodies." Molecular Biology of Plant Cells. Ed. H. Smith. N.p.: University of California, 1978. 136-54. Print.
68:
Microbodies are different type of bodies present in the cytosol, also known as cytosomes. A microbody is usually a
69:
84:
and other proteins, but they do not seem to contain any genetic material to allow them to self-replicate.
28:
that is found in the cells of plants, protozoa, and animals. Organelles in the microbody family include
72:
with a spherical shape, ranging from 0.2-1.5 micrometers in diameter. Microbodies are found in the
308:
202:
92:
Microbodies contain enzymes that participate in the preparatory or intermediate stages of
8:
313:
77:
268:
260:
225:
124:
272:
252:
217:
166:
145:
221:
292:
302:
141:
41:
256:
93:
264:
229:
162:
158:
136:
120:
107:
33:
29:
73:
37:
25:
286:
116:
243:
de Duve C (1969). "The peroxisome: a new cytoplasmic organelle".
112:
81:
49:
157:
that the name
Microbody was too general and chose the name of
44:. In vertebrates, microbodies are especially prevalent in the
60:
45:
200:
76:
of a cell, but they are only visible with the use of an
282:
196:
194:
165:because they were found to contain enzymes of the
203:"Peroxisomes (Microbodies and Related Particles)"
300:
191:
140:are specialized peroxisomes found in plants and
184:
182:
236:
242:
179:
59:
301:
13:
64:Microbody Structure - A Peroxisome
14:
325:
201:de Duve C and Baudhuin P (1966).
285:
245:Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci
130:
100:
1:
222:10.1152/physrev.1966.46.2.323
172:
55:
7:
87:
10:
330:
151:
123:. Discovered and named by
257:10.1098/rspb.1969.0039
65:
210:Physiological Reviews
94:biochemical reactions
63:
78:electron microscope
66:
125:Christian de Duve
321:
295:
290:
289:
277:
276:
240:
234:
233:
207:
198:
189:
186:
167:Glyoxylate cycle
146:Glyoxylate cycle
329:
328:
324:
323:
322:
320:
319:
318:
299:
298:
291:
284:
281:
280:
241:
237:
205:
199:
192:
187:
180:
175:
154:
133:
103:
90:
58:
24:) is a type of
12:
11:
5:
327:
317:
316:
311:
297:
296:
293:Biology portal
279:
278:
235:
216:(2): 323–357.
190:
177:
176:
174:
171:
153:
150:
132:
129:
102:
99:
89:
86:
57:
54:
42:hydrogenosomes
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
326:
315:
312:
310:
307:
306:
304:
294:
288:
283:
274:
270:
266:
262:
258:
254:
251:(30): 71–83.
250:
246:
239:
231:
227:
223:
219:
215:
211:
204:
197:
195:
185:
183:
178:
170:
168:
164:
160:
149:
147:
143:
139:
138:
128:
126:
122:
118:
114:
110:
109:
98:
95:
85:
83:
79:
75:
71:
62:
53:
51:
47:
43:
39:
35:
31:
27:
23:
19:
309:Cell biology
248:
244:
238:
213:
209:
155:
135:
134:
106:
104:
91:
67:
21:
17:
15:
163:Glyoxysomes
137:Glyoxysomes
131:Glyoxysomes
101:Peroxisomes
34:glyoxysomes
30:peroxisomes
314:Organelles
303:Categories
173:References
159:Peroxisome
121:peroxidase
108:peroxisome
38:glycosomes
74:cytoplasm
56:Structure
26:organelle
18:microbody
273:86579094
117:catalase
88:Function
22:cytosome
265:4389648
230:5325972
152:History
113:oxidase
82:enzymes
70:vesicle
271:
263:
228:
50:kidney
269:S2CID
206:(PDF)
46:liver
261:PMID
226:PMID
142:mold
119:and
48:and
40:and
20:(or
253:doi
249:173
218:doi
127:.
305::
267:.
259:.
247:.
224:.
214:46
212:.
208:.
193:^
181:^
169:.
148:.
105:A
36:,
32:,
16:A
275:.
255::
232:.
220::
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.