797:
1007:
31:
674:
662:
4085:
1413:
1078:
cyclic bands, or for erosion to have coincidentally removed just the right amount of sediment everywhere before the gypsum was deposited. The proponents claim that the gypsum was deposited directly above the correlated marl layers, and slumped into them, giving the appearance of an unconformable contact. However, their opponents seize upon this apparent inconformity, and claim that the
1150:. The kinematics and dynamics of this plate boundary and of the Gibraltar Arc during the late Miocene are closely related to the causes of the Messinian salinity crisis. Tectonic movements may have closed and re-opened passages, as the region where the connection with the Atlantic Ocean was situated is permeated by
626:, closely followed the contours of the present seafloor, suggesting that it was laid down evenly and consistently at some point in the past. The origin of this layer was largely interpreted as related to salt deposition. However, different interpretations were proposed for the age of salt and its deposition.
3658:
Pierre; Bajo Campos, Ildefonso; Borghi, Enrico; Iliopoulos, George; Antonarakou, Assimina; Kontakiotis, George; Besiou, Evangelia; Zarkogiannis, Stergios D.; Harzhauser, Mathias; Sierro, Francisco Javier; Coll, Marta; Vasiliev, Iuliana; Camerlenghi, Angelo; Garcia-Castellanos, Daniel (30 August 2024).
1326:
experiments showed that for completely desiccated conditions, the
Mediterranean basin would warm by up to 15 °C (27 °F) in summer and 4 °C (7.2 °F) in winter, while for a depressed water surface, temperatures would warm by only about 4 °C (7.2 °F) in summer and 5 °C
1110:
Several possible causes of the series of
Messinian crises have been considered. While there is disagreement on all fronts, the most general consensus seems to agree that climate had a role in forcing the periodic filling and emptying of the basins, and that tectonic factors must have played a part in
1309:
of around 10 °C (18 °F) per kilometer, the maximum possible temperature of an area 4 km (2.5 mi) below sea level would be about 40 °C (72 °F) warmer than it would be at sea level. Under this extreme assumption, maxima would be near 80 °C (176 °F) at the lowest
1035:
Using the concept of deposition in both shallow and deep basins during the
Messinian (i.e. assuming that both Basin types existed during this period), two major groupings are evident: one that favours a synchronous deposition (image c) of the first evaporites in all the basins before the major phase
993:
Research since then has suggested that the desiccation-flooding cycle may have repeated several times during the last 630,000 years of the
Miocene epoch. This could explain the large amount of salt deposited. Recent studies, however, show that the repeated desiccation and flooding is unlikely from a
1268:
Glacioeustatic sea level falls with an amplitude of around 10 metres (33 ft) that began approximately 6.14 Ma were likely responsible for modulating the connection between the
Mediterranean and the Atlantic. One particularly major glacioeustatic fluctuation, a sea level drop of about 30 metres
1077:
The proponents of this hypothesis claim that cyclic variations in bed compositions are astronomically tuned, and the beds' magnitude can be calibrated to show they were contemporaneous—a strong argument. In order to refute it, it is necessary to propose an alternative mechanism for generating these
520:
closed about 5.96 million years ago, sealing the
Mediterranean off from the Atlantic. This resulted in a period of partial desiccation of the Mediterranean Sea, the first of several such periods during the late Miocene. After the strait closed for the last time around 5.6 Ma, the region's generally
3511:
Agiadi, K.; Hohmann, N.; Gliozzi, E.; Thivaiou, D.; Bosellini, F. R.; Taviani, M.; Bianucci, G.; Collareta, A.; Londeix, L.; Faranda, C.; Bulian, F.; Koskeridou, E.; Lozar, F.; Mancini, A. M.; Dominici, S. (2024). "The marine biodiversity impact of the Late
Miocene Mediterranean salinity crisis".
572:
Only the inflow of
Atlantic water maintains the present Mediterranean level. When that was shut off sometime between 6.5 to 6 MYBP, net evaporative loss set in at the rate of around 3,300 cubic kilometers yearly. At that rate, the 3.7 million cubic kilometres of water in the basin would dry up in
3657:
Agiadi, Konstantina; Hohmann, Niklas; Gliozzi, Elsa; Thivaiou, Danae; Bosellini, Francesca R.; Taviani, Marco; Bianucci, Giovanni; Collareta, Alberto; Londeix, Laurent; Faranda, Costanza; Bulian, Francesca; Koskeridou, Efterpi; Lozar, Francesca; Mancini, Alan Maria; Dominici, Stefano; Moissette,
1752:
the remnant Tethys became joined to the
Atlantic, roughly along the line of what was to become the Strait of Gibraltar. About 5.96 million years ago this gap closed, initiating what is known as the Messinian Salinity Crisis, which lasted for more than half a million years before the Atlantic was
1093:
Assuming that this major drawdown corresponds to the major
Messinian drawdown, they concluded that the Mediterranean bathymetry significantly decreased before the precipitation of central basins evaporites. Regarding these works, a deep water formation seems unlikely. The assumption that central
1389:
The Messinian salinity crisis resulted in major extinctions of marine fish and other marine fauna native to the basin. The present day biodiversity gradient of the Mediterranean, where diversity decreases eastward, developed after the crisis. Due to the fusion of the Iberian Peninsula and North
1375:
was a source of water north of the Mediterranean basin until the middle Pleistocene before becoming the Hungarian plain. Debate exists whether the waters of the Wallachian-Pontic basin (and the possibly connected Pannonian Sea) would have had access (thus bringing water) to at least the eastern
1043:
As highlighted in the work of van Dijk (1992) and van Dijk et al. (1998) the history of desiccation and erosion was complexly interacting with tectonic uplift and subsidence events, and erosional episodes. They also questioned again like some previous authors had done, whether the basins now
1416:
1420:
1419:
1415:
1414:
1421:
843:
deposits that have since been brought above sea level by tectonic activity, the salinity crisis started at the same time over all the Mediterranean basin, at 5.96 ± 0.02 million years ago. This episode comprises the second part of what is called the "Messinian" age of the
34:
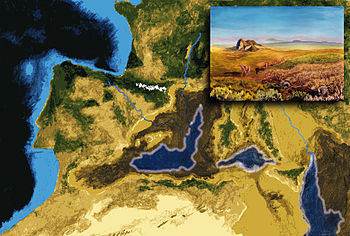
Artistic interpretation of the Mediterranean geography during its evaporative drawdown, after complete disconnection from the Atlantic. The rivers carved deep gorges in the exposed continental margins; The concentration of salt in the remaining water bodies led to rapid
1039:
Another school suggests that desiccation was synchronous, but occurred mainly in shallower basins. This model would suggest that the sea level of the whole Mediterranean basin fell at once, but only shallower basins dried out enough to deposit salt beds. See image b.
910:(but this estimate may be reduced by 50 to 75% when more information becomes available) and more than 1 million cubic kilometres, 50 times the amount of salt normally in the Mediterranean waters. This suggests either a succession of desiccations or a long period of
1277:
The climate of the abyssal plain during the drought is unknown. There is no situation on Earth directly comparable to the dry Mediterranean, and thus it is not possible to know its climate by direct observation of comparable geographic settings. Simulation using a
2654:
van Dijk, J.P. (1992, d); Late Neogene fore-arc basin evolution in the Calabrian Arc (Central Mediterranean). Tectonic sequence stratigraphy and dynamic geohistory. With special reference to the geology of Central Calabria. Geologica Ultrajectina, 92, 288 pp.
1018:
c: Synchronous, basin-wide deposition. Closure or restriction of the Atlantic seaway by tectonic activity (dark grey) causes evaporite deposition simultaneously across the entire basin; the basin may not need to empty completely, as salts are concentrated by
1370:
ocean provided water to the area north of the Mediterranean basin. The Wallachian-Pontic and Hungarian basins were underwater during the Miocene, modifying the climate of what is now the Balkans and other areas north of the Mediterranean basin. The
1418:
1265:, when less solar energy reached the northern hemisphere. This led to less evaporation of the North Atlantic, hence less rainfall over the Mediterranean. This would have starved the basin of water supply from rivers and allowed its desiccation.
1082:
was exposed—therefore eroding—while the Mediterranean sea was depositing evaporites. This would result in the Sorbas Basin being filled with evaporites at 5.5 million years ago (Ma), compared to the main basin at 5.96 Ma.).
1012:
a: Diachronous deposition: Evaporites (pink) were deposited in landward basins first, and closer to the Atlantic as the extent of the Mediterranean Sea (dark blue) diminished towards the gateway. The light blue shows the original sea level.
521:
dry climate at the time dried the Mediterranean basin out nearly completely within a thousand years. This massive desiccation left a deep dry basin, reaching 3 to 5 km (1.9 to 3.1 mi) deep below normal sea level, with a few
1023:
Some major questions remain concerning the beginning of the crisis in the central Mediterranean Basin. The geometric physical link between the evaporitic series identified in marginal basins accessible for field studies, such as the
1247:, and the subsequent upward motion of the overlying crust (which has lost its dense mantle "anchor") may also have caused the observed phenomena although the validity of the "deblobbing" hypothesis has been called into question.
1889:(In these circumstances, I think that I am permitted as the creator of a consistent and logical classification to propose for the stage in question a name that suits it in every way. That name is that of the Messinian stage.)
1887:"Dans ces circonstances, je crois qu'il m'est permis comme créateur d'une classification conséquente et logique de proposer pour l'étage en question un nom qui lui convient en tous points. Ce nom est celui d'Etage messinien."
1036:
of erosion; and the other that favours a diachronous deposition (image a) of the evaporites through more than one phases of desiccation which would first have affected the marginal basins and later the central basins.
1290:
remained at all times. The extent of desiccation is very hard to judge, owing to the reflective seismic nature of the salt beds, and the difficulty in drilling cores, making it difficult to map their thickness.
1015:
b: Synchronous deposition in marginal basins. Sea level drops slightly, but the whole basin is still connected to the Atlantic. Reduced inflow allows the accumulation of evaporites in shallow basins only.
1632:
Krijgsman, W.; Garcés, M.; Langereis, C. G.; Daams, R.; Van Dam, J.; Van Der Meulen, A. J.; Agustí, J.; Cabrera, L. (1996). "A new chronology for the middle to late Miocene continental record in Spain".
1282:
can indicate physically consistent responses to the desiccation. There is no consensus as to whether the Mediterranean Sea dried out completely; it seems likeliest that at least three or four large
863:
The Mediterranean-Atlantic strait closed tight time and time again, and the Mediterranean Sea, for the first time and then repeatedly, partially desiccated. The basin was finally isolated from the
2770:
Braga, J.C.; Martín, J.M.; Riding, R.; Aguirre, J.; Sánchez-almazo, I.M.; Dinarès-turell, J. (2006). "Testing models for the Messinian salinity crisis: The Messinian record in Almería, SE Spain".
871:
applied) lowering of the Mediterranean sea level. During the initial, very dry stages (5.6–5.5 Ma), there was extensive erosion, creating several huge canyon systems (some similar in scale to the
780:
In many places in the Mediterranean, fossilized cracks have been found where muddy sediment had dried and cracked in the sunlight and drought. In the Western Mediterranean series, the presence of
1417:
2725:
Riding, R.; Braga, J.C.; Martín, J.M. (2000). "Late Miocene Mediterranean desiccation: topography and significance of the 'Salinity Crisis' erosion surface on-land in southeast Spain: Reply".
2214:
van Dijk, J.P., Barberis, A., Cantarella, G., and Massa, E. (1998); Central Mediterranean Messinian basin evolution. Tectono-eustasy or eustato-tectonics? Annales Tectonicae, 12, n. 1-2, 7-27.
2238:
Garcia-Castellanos D.; Estrada F.; Jiménez-Munt I.; Gorini C.; Fernàndez M.; Vergés J.; De Vicente R. (2009). "Catastrophic flood of the Mediterranean after the Messinian salinity crisis".
1165:
Shortening and extension occur at the same time in close proximity; sedimentary sequences and their relations to fault activity constrain the rates of uplift and subsidence quite precisely
750:
The massive presence of salt does not require a desiccation of the sea. The main evidence for the evaporative drawdown of the Mediterranean comes from the remains of many (now submerged)
3212:
1820:
Clauzon, Georges; Suc, Jean-Pierre; Gautier, François; Berger, André; Loutre, Marie-France (1996). "Alternate interpretation of the Messinian salinity crisis: Controversy resolved?".
3473:
Murphy L, Kirk-Davidoff D, Mahowald N, Otto-Bliesner B (2009). "A numerical study of the climate response to lowered Mediterranean Sea level during the Messinian Salinity Crisis".
1251:
Of these, only the first model, invoking rollback, seems to explain the rotations observed. However, it is difficult to fit it with the pressure and temperature histories of some
1111:
controlling the height of the sills restricting flow between the Atlantic and Mediterranean. The magnitude and extent of these effects, however, is widely open to interpretation.
918:
points strongly to several cycles of the Mediterranean Sea completely drying and being refilled (Gargani and Rigollet, 2007), with drying periods correlating to periods of cooler
541:). The Messinian salinity crisis ended with the Strait of Gibraltar finally reopening 5.33 Ma, when the Atlantic rapidly filled up the Mediterranean basin in what is known as the
1158:, the geography of the region may have altered enough to open and close seaways. However, the precise tectonic activity behind the motion can be interpreted in a number of ways.
1354:. Climates throughout the central and eastern basin of the Mediterranean and surrounding regions to the north and east would have been drier even above modern sea level. The
1197:
There are three contending geodynamic models that may fit the data, models which have been discussed in an equal way for the other arc shaped features in the Mediterranean:
1047:
Distinguishing between these hypotheses requires the calibration of gypsum deposits. Gypsum is the first salt (calcium sulphate) to be deposited from a desiccating basin.
2325:
651:
1580:
Gautier, F., Clauzon, G., Suc, J.P., Cravatte, J., Violanti, D., 1994. Age and duration of the Messinian salinity crisis. C.R. Acad. Sci., Paris (IIA) 318, 1103–1109.
1541:, but recent studies of the underground structures at the Gibraltar Strait show that the flooding channel descended in a rather gradual way to the dry Mediterranean.
914:
during which incoming water from the Atlantic Ocean was evaporated with the level of the Mediterranean brine being similar to that of the Atlantic. The nature of the
622:
Seismic surveying of the Mediterranean basin in 1961 revealed a geological feature some 100–200 m (330–660 ft) below the seafloor. This feature, dubbed the
1525:
would have poured a vast volume of water through what would have presumably been a relatively narrow channel. This refill has been envisaged as resulting in a large
1331:
response to the introduction of the topographic depression causes patterns of warming and cooling by up to 4 °C (7.2 °F) around the Northern Hemisphere.
3423:
640:
New and high-quality seismic data on the M-reflector were acquired in the Mediterranean Basin in 1970. At the same time, the salt was cored during Leg 13 of the
3261:"Thermal evolution, rate of exhumation, and tectonic significance of metamorphic rocks from the floor of the Alboran extensional basin, western Mediterranean"
3164:
1302:
with altitude. In the empty Mediterranean Basin, the summertime temperatures would probably have been extremely high. As a first approximation, using the dry
2906:
Weijermars, Ruud (May 1988). "Neogene tectonics in the Western Mediterranean may have caused the Messinian salinity crisis and an associated glacial event".
4114:
2584:
1090:"; the termination of the "Mes-1" unconformity bound depositional sequence of van Dijk, 1992) responding to a major drawdown of the Mediterranean seawater.
116:
3893:
Gargani J.; Rigollet C; Scarselli S. (2010). "Isostatic response and geomorphological evolution of the Nile valley during the Messinian salinity crisis".
2052:
Gargani J.; Rigollet C; Scarselli S. (2010). "Isostatic response and geomorphological evolution of the Nile valley during the Messinian salinity crisis".
1055:
is relied upon to compare the dates of sediments. The typical case study compares the gypsum evaporites in the main Mediterranean basin with those of the
926:, or by a river flowing eastwards below sea level into the "Mediterranean Sink" cutting its valley head back west until it let the sea in, similarly to a
3748:
4134:
954:
lake. The fine sediments deposited on a quiet or deep bottom had perfectly even lamination. As the basin was drying up and the water depth decreased,
3712:
1455:
1544:
An enormous deposit of unsorted debris washed in by a massive catastrophic flood-wash has been found in the seabed southeast of the south corner of
1258:
This has led to some interesting combinations of the models which at first hand looked bizarre, in attempts to approach the true state of affairs.
1143:
2599:
Krijgsman W.; Hilgen F. J.; Raffi I.; Sierro F. J.; Wilson D. S. (1999). "Chronology, causes and progression of the Messinian salinity crisis".
1098:
and before the major phase of erosion should imply the observation of a major detritic event above evaporites in the basin. Such a depositional
573:
scarcely more than a thousand years, leaving an extensive layer of salt some tens of meters thick and raising global sea level about 12 meters.
3749:"Terrestrial colonization of the Balearic Islands: New evidence for the Mediterranean sea-level drawdown during the Messinian Salinity Crisis"
1044:
observed as "deep" were actually also deep during the Messinian Episode and gave different names to the end-member scenarios described above.
685:
The first drilling of the Messinian salt at the deeper parts of the Mediterranean Sea came in the summer of 1970, when geologists aboard the
2579:
Garcia-Castellanos, D., A. Villaseñor, 2011. Messinian salinity crisis regulated by competing tectonics and erosion at the Gibraltar Arc.
1114:
In any case, the causes of the closing and isolation of the Mediterranean Sea from the Atlantic Ocean must be found in the area where the
4043:
1483:
Rivers emptying into the basin would have cut their beds much deeper (at least a further 2,400 m (7,900 ft) in the case of the
669:, which formed on the sea floor as a result of evaporation. Evaporation of one metre of seawater precipitates around 1 mm of gypsum.
4089:
4096:
2223:
Blanc, P.-L. (2002) The opening of the Plio-Quaternary Gibraltar Strait: assessing the size of a cataclysm. Geodin. Acta, 15, 303–317.
3260:
1998:
Garcia-Castellanos Villaseñor (2011). "Messinian salinity crisis regulated by competing tectonics and erosion at the Gibraltar Arc".
17:
3875:
1261:
Changes in climate must almost certainly be invoked to explain the periodic nature of the events. They occur during cool periods of
922:; which were therefore drier in the Mediterranean region. Each refilling was presumably caused by a seawater inlet opening, either
490:
109:
1394:
between the two regions occurred. The crisis also allowed the dispersal of terrestrial animals to remote landmasses such as the
1334:
Today the evaporation from the Mediterranean Sea supplies moisture that falls in frontal storms, but without such moisture, the
1154:
and rotating blocks of continental crust. As faulting accommodated the regional compression caused by Africa's convergence with
2945:"Neogene tectonostratigraphy and kinematics of Calabrian Basins. implications for the geodynamics of the Central Mediterranean"
2153:
4139:
4032:
3859:
3832:
2136:
1745:
2340:
1229:
underlying the western Mediterranean. However, this does not account for the periodic emptying and refilling of the basin.
564:), the Mediterranean would mostly evaporate in about a thousand years, after which continued northward movement of Africa
3992:
747:. These layers alternated with layers containing marine fossils, indicating a succession of drying and flooding periods.
102:
658:. These deposits were dated and interpreted for the first time as deep-basin products of the Messinian salinity crisis.
3989:
3165:"Extensional collapse of thickened continental lithosphere: A working hypothesis for the Alboran Sea and Gibraltar arc"
1318:. Further, the altitude 3–5 km (2–3 mi) below sea level would result in 1.45 to 1.71 atm (1102 to 1300 mmHg)
1102:
has not been observed on data. This theory corresponds to one of the end-member scenarios discussed by van Dijk et al.
3547:
Meynard, Christine N.; Mouillot, David; Mouquet, Nicolas; Douzery, Emmanuel J. P. (2012-05-08). Knapp, Michael (ed.).
2677:"Astrochronology for the Messinian Sorbas basin (SE Spain) and orbital (precessional) forcing for evaporite cyclicity"
2660:
2428:
1866:
1294:
Atmospheric forces can be studied to arrive at a speculation on the climate. As winds blew across the "Mediterranean
39:
of the salt. The inset evokes the transit of mammals (e.g. camels and mice) from Africa to Iberia across the exposed
4104:
4001:
Scientists find new evidences of the megaflood that ended the Messinian Salinity Crisis in the eastern Mediterranean
1879:
Catalogue systématique et descriptif des fossiles des terrains tertiaires qui se trouvent du Musée fédéral de Zürich
3708:"Late Miocene turnover in the Spanish mammal record in relation to palaeoclimate and the Messinian Salinity Crisis"
2289:
Gargani J.; F. Bache; G. Jouannic; C. Gorini (2014). "Slope destabilization during the Messinian Salinity Crisis".
1462:
are now) linked the Mediterranean to the Atlantic. These must have closed, isolating the basin from the open ocean.
1322:, further increasing heat stress. However, these simple estimates are likely far too extreme. Murphy et al.'s 2009
2807:"The Messinian Erosional and Salinity Crises: View from the Provence Basin (Gulf of Lions, Western Mediterranean)"
4110:
3797:
3747:
Mas, Guillem; Maillard, Agnès; Alcover, Josep A.; Fornós, Joan J.; Bover, Pere; Torres-Roig, Enric (2018-06-01).
3449:
3190:
1841:
867:
for a longer period, between 5.59 and 5.33 million years ago, resulting in a large or smaller (depending on the
2806:
1086:
Recent works have highlighted a pre-evaporite phase corresponding to a prominent erosional crisis (also named "
890:
epoch), the barrier at the Strait of Gibraltar broke one last time, re-flooding the Mediterranean basin in the
3320:
800:
A possible palaeogeographical reconstruction of the west end of the Miocene Mediterranean. North to the left.
4119:
1366:
would also be much drier than they are today, even if the westerlies prevailed as they do now. However, the
3969:
2861:
2450:
1944:
Ruggieri, G.; Adams, C.J.; Ager, D.V. (1967). "The Miocene and latter evolution of the Mediterranean Sea".
1063:. The relationship between these two basins is assumed to represent the relationships of the wider region.
3315:
594:, and freshwater sediment layers, and identified them as having been deposited just before the end of the
2944:
681:(Yesares member). The upward-growing cones suggest precipitation on the sea floor (not within sediments).
3964:
3928:
Gargani J. (2004). "Modelling of the erosion in the Rhone valley during the Messinian crisis (France)".
2090:
Gargani J. (2004). "Modelling of the erosion in the Rhone valley during the Messinian crisis (France)".
3358:
Duggen, Svend; Hoernle, Kaj; van den Bogaard, Paul; Rüpke, Lars; Phipps Morgan, Jason (10 April 2003).
1905:
1087:
529:. Then, around 5.5 Ma, wetter climatic conditions resulted in the basin receiving more freshwater from
2496:
2154:"Calcareous nannofossils in extreme environments: The Messinian Salinity Crisis, Polemi Basin, Cyprus"
4154:
4044:"A high-resolution stratigraphic framework for the latest Messinian events in the Mediterranean area"
2676:
1323:
1279:
641:
36:
3099:"Geophysical evidence for lithospheric delamination beneath the Alboran Sea and Rif–Betic mountains"
2992:
3930:
3314:
Jolivet, Laurent; Augier, Romain; Robin, Cécile; Suc, Jean-Pierre; Rouchy, Jean Marie (June 2006).
2949:
2908:
629:
Earlier suggestions from Denizot in 1952 and Ruggieri in 1967 proposed that this layer was of Late
723:, left where the last bitter, mineral-rich waters dried up. One drill core contained a wind-blown
4149:
3707:
3422:
Aharon, Paul; Goldstein, Steven L.; Wheeler, Christopher W.; Jacobson, Gerry (1 September 1993).
2805:
Bache, F.; Olivet, J. L.; Gorini, C.; Rabineau, M.; Baztan, J.; Aslanian, D.; Suc, J. P. (2009).
1465:
The high level of salinity cannot be tolerated by many known organisms, a factor in reducing the
3879:
2326:"Modeling the magnitude and timing of evaporative drawdown during the Messinian salinity crisis"
1713:
3618:"Tethyan changes shaped aquatic diversification: Aquatic diversification in the Tethyan region"
3058:
1233:
986:
4066:
2126:
3849:
3822:
2545:
Govers, R (2009). "Choking the Mediterranean to dehydration: The Messinian salinity crisis".
2420:
1909:
1882:
1735:
1447:
1335:
1138:. In the present day area of the Mediterranean Sea, are three of these arc-shaped belts: the
2825:
1646:
1610:
1001:
978:, or there would be an unusual influx of brackish water from the eastern European lake. The
3939:
3762:
3721:
3562:
3482:
3437:
3373:
3325:
3274:
3226:
3178:
3112:
3063:
3006:
2958:
2917:
2870:
2821:
2779:
2734:
2691:
2608:
2554:
2511:
2459:
2373:
2298:
2247:
2168:
2099:
2007:
1972:
1829:
1781:
1642:
1606:
868:
857:
560:. If the Strait of Gibraltar closes again (which is likely to happen in the near future in
3290:
754:
that were cut into the sides of the dry Mediterranean basin by rivers flowing down to the
8:
3265:
2997:
1557:
1518:
1439:
1244:
1115:
1059:, a smaller basin on the flanks of the Mediterranean Sea that is now exposed in southern
1048:
975:
966:
zone. The intertidal flat was eventually exposed by the final desiccation, at which time
939:
919:
565:
561:
517:
3977:, by Julien Gargani, Isabelle Moretti, Jean Letouzey, First published: 16 January 2008,
3943:
3766:
3725:
3617:
3566:
3486:
3441:
3377:
3329:
3278:
3230:
3182:
3116:
3010:
2962:
2921:
2874:
2783:
2738:
2695:
2612:
2558:
2515:
2463:
2377:
2302:
2251:
2172:
2103:
2011:
1976:
1833:
1785:
1074:
beds, which appear to have given way to gypsum at exactly the same time in both basins.
4144:
3910:
3622:
3593:
3548:
3397:
3138:
3097:
Seber, Dogan; Barazangi, Muawia; Ibenbrahim, Aomar; Demnati, Ahmed (29 February 1996).
3032:
2888:
2837:
2634:
2527:
2497:"Evaporite accumulation during the Messinian Salinity Crisis : The Suez Rift Case"
2477:
2389:
2271:
2237:
2069:
2031:
1799:
1689:
1391:
876:
350:
3659:
2746:
2703:
2587:
504:
Sediment samples from below the deep seafloor of the Mediterranean Sea, which include
4028:
4021:
3914:
3855:
3828:
3778:
3753:
3681:
3664:
3639:
3598:
3580:
3529:
3428:
3389:
3217:
3169:
3036:
2970:
2929:
2892:
2656:
2531:
2481:
2424:
2413:
2408:
2385:
2275:
2263:
2132:
2073:
2035:
2023:
1915:
1862:
1803:
1741:
1654:
1618:
1591:
1473:
1451:
1347:
1303:
1262:
1151:
1067:
1052:
781:
687:
646:
60:
2841:
2393:
2184:
1472:
The basin's low altitude would have made it extremely hot during the summer through
549:
4058:
3947:
3902:
3770:
3729:
3673:
3631:
3588:
3570:
3521:
3490:
3445:
3401:
3381:
3364:
3333:
3282:
3234:
3186:
3142:
3128:
3120:
3103:
3072:
3059:"Magmatism Associated with Orogenic Collapse of the Betic-Alboran Domain, SE Spain"
3022:
3014:
2966:
2925:
2878:
2829:
2787:
2750:
2742:
2707:
2699:
2638:
2624:
2616:
2562:
2519:
2467:
2381:
2310:
2306:
2255:
2176:
2107:
2061:
2015:
1980:
1837:
1789:
1681:
1650:
1614:
1395:
1295:
1252:
979:
950:
The oldest sediment of each cycle was either deposited in a deep sea or in a great
583:
522:
40:
3660:"The marine biodiversity impact of the Late Miocene Mediterranean salinity crisis"
3258:
3076:
2047:
2045:
533:, progressively filling and diluting the hypersaline lakes into larger pockets of
3951:
3733:
3575:
3494:
3424:"Sea-level events in the South Pacific linked with the Messinian salinity crisis"
3337:
2791:
2180:
2111:
1669:
1363:
1328:
1202:
1135:
1025:
788:
suggests that the area was repeatedly flooded and desiccated over 700,000 years.
76:
1631:
989:
would thus be abruptly buried under the fine muds brought in by the next deluge.
4016:
3975:
Evaporite accumulation during the Messinian Salinity Crisis: The Suez Rift case
3906:
3259:
Platt, J.P.; Soto, J.I.; Whitehouse, M.J.; Hurford, A.J.; Kelley, S.P. (1998).
2833:
2065:
2042:
1898:
1522:
1512:
1443:
1123:
943:
891:
864:
836:
692:
655:
614:
layers throughout the Mediterranean region have been dated to the same period.
591:
553:
542:
534:
80:
3359:
1960:
556:, owing to its near isolation by the Strait of Gibraltar and its high rate of
4128:
4003:, February 27, 2018. by Ictja-Csic, Institute of Earth Sciences, Jaume Almera
3782:
3685:
3584:
3549:"A Phylogenetic Perspective on the Evolution of Mediterranean Teleost Fishes"
3533:
1854:
1592:"A new chronology for the middle to late Miocene continental record in Spain"
1538:
1459:
1434:
The notion of a completely waterless Mediterranean Sea has some corollaries.
1372:
1311:
1287:
1269:(98 ft), occurred around 5.26 Ma, around the Miocene-Pliocene boundary.
1214:
1206:
1139:
1131:
1130:. This boundary zone is characterised by an arc-shaped tectonic feature, the
1127:
1119:
982:
927:
911:
755:
732:
724:
3677:
3525:
2804:
2769:
2598:
1495:
There is an opinion that during the Messinian, the Red Sea was connected at
796:
739:, mixed with quartz sand blown in from nearby continents, and ended up in a
4062:
3643:
3602:
3393:
3098:
3027:
2267:
2027:
1984:
1737:
On the Ocean: The Mediterranean and the Atlantic from prehistory to AD 1500
1534:
1500:
1466:
1355:
1319:
1315:
1186:
1147:
1079:
1056:
1029:
959:
872:
770:
728:
678:
377:
3211:
Jackson, J. A.; Austrheim, H.; McKenzie, D.; Priestley, K. (1 July 2004).
2883:
2857:"Mediterranean Sea level variations during the Messinian Salinity Crisis"
2856:
2523:
2472:
2446:"Mediterranean Sea level variations during the Messinian Salinity Crisis"
2445:
1958:
1794:
1770:"Mediterranean Sea level variations during the Messinian Salinity Crisis"
1769:
1530:
1327:(9.0 °F) in winter. In addition, the model results indicated global
1237:
1172:
1002:
Synchronism versus diachronism—deep water versus shallow water evaporites
773:
in 1967), and 2,500 m (8,200 ft) below sea level just north of
557:
538:
359:
64:
3472:
3385:
3316:"Lithospheric-scale geodynamic context of the Messinian salinity crisis"
2259:
2019:
3978:
3798:"How a salt giant radically reshaped Mediterranean marine biodiversity"
3213:"Metastability, mechanical strength, and the support of mountain belts"
2675:
Krijgsman, W.; Fortuin, A.R.; Hilgen, F.J.; Sierro, F.J. (April 2001).
1693:
1562:
1480:, which is only deposited in water warmer than 35 °C (95 °F).
1367:
1306:
1283:
1210:
1190:
1180:
1095:
1032:, and the evaporitic series of the central basins has never been made.
1006:
995:
963:
955:
942:
broke wide open permanently. Upon closely examining the Hole 124 core,
894:; favouring slope destabilization. The basin has not desiccated since.
736:
696:
413:
305:
3635:
3286:
3018:
2566:
2288:
875:) around the Mediterranean. Later stages (5.50–5.33 Ma) are marked by
27:
Drying-up of the Mediterranean Sea from 5.96 to 5.33 million years ago
3965:
https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1029/2007GL032494
3774:
3238:
3133:
3124:
2755:
2711:
2629:
1959:
Auzende J.M.; Bonnin J.; Olivet J.L.; Pautot G.; Mauffret A. (1971).
1763:
1761:
1533:
at 979 m (3,212 ft), and far more powerful than either the
1526:
1477:
1400:
1299:
1218:
967:
849:
840:
785:
712:
704:
611:
505:
395:
386:
273:
68:
1685:
1051:
offers a broad constraint on timing, but no fine detail. Therefore,
3996:
3553:
2364:
William Ryan (2008). "Decoding the Mediterranean salinity crisis".
1948:. London, England: Systematic Association Publication. p. 283.
1406:
1118:
is now, the location of one of the tectonic boundaries between the
1099:
951:
935:
923:
887:
883:
767:
526:
404:
368:
335:
249:
30:
2620:
1758:
1548:. This is suspected to have been deposited by the Zanclean flood.
731:
ooze that had dried into dust and been blown about on the hot dry
4023:
The Mediterranean Was a Desert: A Voyage of the Glomar Challenger
3357:
3210:
2724:
1359:
1351:
1222:
1176:
1155:
931:
915:
853:
845:
673:
630:
603:
595:
473:
314:
283:
72:
3892:
3851:
Evaporite sequences in petroleum exploration: Geological methods
2051:
1168:
Fault-bounded continental blocks can often be observed to rotate
4084:
3096:
2494:
1545:
1343:
1339:
971:
958:
became more irregular on account of increasing wave agitation.
860:
events, all more or less interrelated (van Dijk et al., 1998).
751:
744:
720:
708:
700:
666:
661:
607:
587:
513:
3421:
3546:
1997:
1943:
1488:
1226:
1060:
774:
763:
762:
cut its bed down to 200 metres (660 feet) below sea level at
740:
716:
610:, Italy. Since then, several other salt-rich and gypsum-rich
530:
3656:
3510:
2674:
962:
was formed then, when the site of deposition fell within an
582:
In the 19th century, the Swiss geologist and paleontologist
3876:"Vast "Grand Canyon" Lurks 8,200 Feet BENEATH Cairo, Egypt"
3450:
10.1130/0091-7613(1993)021<0771:SLEITS>2.3.CO;2
3191:
10.1130/0091-7613(1989)017<0540:ECOTCL>2.3.CO;2
2942:
1842:
10.1130/0091-7613(1996)024<0363:AIOTMS>2.3.CO;2
1496:
1484:
1071:
902:
The amount of Messinian salts has been estimated as around
759:
509:
3706:
van der Made, J.; Morales, J.; Montoya, P. (August 2006).
3705:
1398:, where several animal species, such as the goat-antelope
1161:
Any model must explain a variety of features of the area:
3746:
2085:
2083:
2936:
2443:
1961:"Upper Miocene salt layer in the western Mediterranean"
1819:
848:
epoch. This age was characterised by several stages of
1189:
varies—this constrains the location and extent of any
3878:. Biot Report 403. September 21, 2006. Archived from
3313:
2210:
2208:
2206:
2204:
2080:
1767:
1499:
to the Mediterranean, but was not connected with the
1205:
may have caused periodic regional uplift. Changes in
1881:(Zürich, Switzerland: Librairie Schabelitz, 1867),
617:
3506:
3504:
2650:
2648:
970:was precipitated by saline ground water underlying
879:into a large "lake-sea" basin ("Lago Mare" event).
85:
4020:
2412:
2201:
1010:Hypotheses of evaporite formation during the MSC.
882:About 5.33 million years ago, at the start of the
3824:Evaporites: sediments, resources and hydrocarbons
3713:Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology
3475:Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology
2798:
2161:Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology
2128:Evaporites: sediments, resources and hydrocarbons
1670:"Neogene Expansion of the North American Prairie"
1376:Mediterranean basin at times during the Miocene.
4126:
3848:Majithia, Margaret; Nely, Georges, eds. (1994).
3795:
3501:
2645:
1859:Oasis in space. Earth history from the beginning
1667:
1209:suggest that subduction zones at the rim of the
852:activity and sea level fluctuations, as well as
63:went into a cycle of partial or nearly complete
3163:Platt, J. P.; Vissers, R. L. M. (1 June 1989).
2899:
2854:
1232:The same features can be explained by regional
1094:basin evaporites partly deposited under a high
4095:Arizona University: Geology 212, Lecture 17: "
4015:
3468:
3466:
2151:
1503:, and dried out along with the Mediterranean.
548:Even today, the Mediterranean is considerably
67:(drying-up) throughout the latter part of the
3360:"Deep roots of the Messinian salinity crisis"
2990:
2670:
2668:
2233:
2231:
2229:
1861:, New York: W.W. Norton & Co. Inc., 440.
650:under the supervision of co-chief scientists
586:(1826–1907) studied fossils embedded between
110:
3847:
3162:
2984:
2848:
2495:Gargani J.; Moretti I.; Letouzey J. (2008).
2363:
2323:
1815:
1813:
1661:
1625:
1476:, a conclusion supported by the presence of
577:
489:Subdivision of the Neogene according to the
3463:
3307:
3204:
2991:Lonergan, Lidia; White, Nicky (June 1997).
633:age, and the same Ruggieri coined the term
566:may obliterate the Mediterranean altogether
4111:A brief history of the Messinian on Sicily
3927:
3351:
3050:
2905:
2718:
2665:
2226:
2089:
1753:reunited once more with the Mediterranean.
1272:
117:
103:
59:) was a geological event during which the
4135:Events in the geological history of Earth
3592:
3574:
3252:
3156:
3132:
3090:
3026:
2882:
2763:
2754:
2628:
2471:
2406:
1810:
1793:
1589:
974:. Suddenly seawater would spill over the
1933:. Rev. Geogr. Lyon 27. pp. 327–357.
1733:
1411:
1405:would continue to be isolated until the
1005:
795:
715:minerals that often form from drying of
672:
660:
598:Epoch. In 1867, he named the period the
83:, when the Atlantic reclaimed the basin.
29:
2993:"Origin of the Betic-Rif mountain belt"
1952:
1928:
1740:. Oxford University Press. p. 56.
1429:
1126:and its southern fragments such as the
743:lake interbedded between two layers of
719:or seawater, including in a few places
516:plants, show that the precursor of the
79:(million years ago). It ended with the
14:
4127:
4041:
3820:
3616:Hou, Zhonge; Li, Shuqiang (May 2018).
3056:
2544:
2124:
486:
3615:
1442:was not open, but other seaways (the
1384:
1236:or the loss of a layer of the entire
985:would then again be under water. The
766:(where Ivan S. Chumakov found marine
677:The scale of gypsum formation in the
496:Vertical axis: millions of years ago.
95:
3979:https://doi.org/10.1029/2007GL032494
2943:van Dijk J.P., Okkes F.W.M. (1991).
2145:
1243:Deblobbing, the loss of a "blob" of
1134:, which includes southern Spain and
461:
441:
88:
4107:by Ian West (Internet Archive copy)
2573:
2407:Hsu, K.J. (1983). "A Voyage of the
2400:
1931:Le Pliocène dans la vallée du Rhône
1635:Earth and Planetary Science Letters
1599:Earth and Planetary Science Letters
1425:Messinian salinity crisis animation
1314:, permitting no permanent life but
24:
4009:
1734:Cunliffe, Sir Barry (2017-09-29).
1454:is now, or to the south where the
691:brought up drill cores containing
25:
4166:
4077:
897:
618:Further evidence and confirmation
55:, and in its latest stage as the
4083:
2444:Gargani J., Rigollet C. (2007).
2386:10.1111/j.1365-3091.2008.01031.x
1768:Gargani J.; Rigollet C. (2007).
1506:
930:. The last refilling was at the
4097:When the Mediterranean Dried Up
3983:
3958:
3921:
3886:
3868:
3841:
3814:
3789:
3740:
3699:
3650:
3609:
3540:
3415:
2592:
2538:
2488:
2437:
2357:
2317:
2282:
2217:
2152:Wade, B.S.; Brown P.R. (2006).
2118:
1991:
1946:Aspects of Tethyan Biogeography
1937:
1922:
1903:The Mediterranean Was a Desert,
1892:
1871:
1491:shows) and in the Rhone valley.
1171:The depth and structure of the
4027:. Princeton University Press.
2855:Gargani J, Rigollet C (2007).
2423:: Princeton University Press.
2415:The Mediterranean Was a Desert
2311:10.1016/j.geomorph.2013.12.042
1848:
1727:
1706:
1583:
1574:
1338:that we associate with Italy,
440:
13:
1:
4105:The Messinian Salinity Crisis
2747:10.1016/S0037-0738(00)00039-7
2704:10.1016/S0037-0738(00)00171-8
1568:
1521:was ultimately breached, the
1487:, as the buried canyon under
1409:, over 5 million years later.
1175:is constrained by records of
791:
4140:History of the Mediterranean
4042:Roveri; et al. (2008).
3970:Geophysical Research Letters
3952:10.1016/j.quaint.2004.01.020
3734:10.1016/j.palaeo.2006.03.030
3576:10.1371/journal.pone.0036443
3495:10.1016/j.palaeo.2009.04.016
3338:10.1016/j.sedgeo.2006.02.004
2971:10.1016/0040-1951(91)90288-4
2930:10.1016/0040-1951(88)90129-1
2862:Geophysical Research Letters
2792:10.1016/j.sedgeo.2006.03.002
2504:Geophysical Research Letters
2451:Geophysical Research Letters
2181:10.1016/j.palaeo.2005.10.007
2112:10.1016/j.quaint.2004.01.020
1774:Geophysical Research Letters
1655:10.1016/0012-821X(96)00109-4
1619:10.1016/0012-821X(96)00109-4
1590:Krijgsman, W (August 1996).
1070:to correlate the underlying
7:
3827:. Birkhäuser. p. 147.
3077:10.1093/petrology/40.6.1011
2131:. Birkhäuser. p. 352.
1551:
1298:", they would heat or cool
877:cyclic evaporite deposition
525:pockets similar to today's
487:
244:
10:
4171:
3907:10.2113/gssgfbull.181.1.19
3057:TURNER, S. (1 June 1999).
2834:10.1016/j.epsl.2009.06.021
2339:(3–4): 229. Archived from
2066:10.2113/gssgfbull.181.1.19
1906:Princeton University Press
1510:
1379:
1088:Messinian erosional crisis
1066:Recent work has relied on
695:gravels and red and green
90:Neogene graphical timeline
4090:Messinian salinity crisis
1877:Mayer-Eymar, Karl (1867)
1668:Retallack, G. J. (1997).
1324:general circulation model
1280:general circulation model
1105:
886:age (at the start of the
642:Deep Sea Drilling Program
635:Messinian Salinity Crisis
578:Naming and first evidence
453:Messinian salinity crisis
75:epoch, from 5.96 to 5.33
51:(also referred to as the
49:Messinian salinity crisis
18:Messinian Salinity Crisis
3931:Quaternary International
3821:Warren, John K. (2006).
2092:Quaternary International
1346:would be limited to the
1217:westwards, changing the
127:
3678:10.1126/science.adp3703
3526:10.1126/science.adp3703
2826:2009E&PSL.286..139B
2814:Earth Planet. Sci. Lett
1647:1996E&PSL.142..367K
1611:1996E&PSL.142..367K
1458:or corridors where the
1446:to the north where the
1273:Relationship to climate
806: current coastline
784:interbedded within the
4063:10.29041/strat.05.3.08
3796:University of Vienna.
1985:10.1038/physci230082a0
1426:
1020:
991:
987:chicken-wire anhydrite
832:
682:
670:
575:
200:−10 —
190:−12 —
180:−14 —
170:−16 —
160:−18 —
150:−20 —
140:−22 —
130:−24 —
44:
4099:". (Accessed 7/16/06)
2421:Princeton, New Jersey
2324:William Ryan (2008).
2125:Warren, J.K. (2006).
1910:Princeton, New Jersey
1714:"ICS Timescale Chart"
1469:of much of the basin.
1424:
1336:Mediterranean climate
1179:activity, as well as
1009:
948:
799:
676:
664:
570:
240:−2 —
230:−4 —
220:−6 —
210:−8 —
33:
4092:at Wikimedia Commons
3854:. Editions TECHNIP.
3064:Journal of Petrology
2884:10.1029/2007GL029885
2524:10.1029/2007gl032494
2473:10.1029/2007GL029885
1929:Denizot, G. (1952).
1795:10.1029/2007gl029885
1721:www.stratigraphy.org
1529:higher than today's
1430:Dehydrated geography
727:deposit of deep-sea
711:, and various other
3944:2004QuInt.121...13G
3895:Bull. Soc. Géol. Fr
3767:2018Geo....46..527M
3726:2006PPP...238..228V
3567:2012PLoSO...736443M
3487:2009PPP...279...41M
3442:1993Geo....21..771A
3386:10.1038/nature01553
3378:2003Natur.422..602D
3330:2006SedG..188....9J
3321:Sedimentary Geology
3279:1998Tecto..17..671P
3231:2004Geo....32..625J
3183:1989Geo....17..540P
3117:1996Natur.379..785S
3011:1997Tecto..16..504L
2963:1991Tectp.196...23V
2922:1988Tectp.148..211W
2875:2007GeoRL..3410405G
2784:2006SedG..188..131B
2772:Sedimentary Geology
2739:2000SedG..133..175R
2727:Sedimentary Geology
2696:2001SedG..140...43K
2684:Sedimentary Geology
2613:1999Natur.400..652K
2559:2009Geo....37..167G
2516:2008GeoRL..35.2401G
2464:2007GeoRL..3410405G
2378:2009Sedim..56...95R
2303:2014Geomo.213..128G
2260:10.1038/nature08555
2252:2009Natur.462..778G
2173:2006PPP...233..271W
2104:2004QuInt.121...13G
2054:Bull. Soc. Géol. Fr
2020:10.1038/nature10651
2012:2011Natur.480..359G
1977:1971NPhS..230...82A
1834:1996Geo....24..363C
1786:2007GeoRL..3410405G
1558:Messinian evaporite
1519:Strait of Gibraltar
1440:Strait of Gibraltar
1245:lithospheric mantle
1185:The composition of
1116:Strait of Gibraltar
1049:Magnetostratigraphy
976:Strait of Gibraltar
940:Strait of Gibraltar
938:boundary, when the
920:global temperatures
826:Strait of Gibraltar
811:Sorbas basin, Spain
758:. For example, the
644:conducted from the
537:(much like today's
518:Strait of Gibraltar
3623:Biological Reviews
2869:(L10405): L10405.
2458:(L10405): L10405.
1427:
1392:faunal interchange
1385:Effects on biology
1310:points of the dry
1152:strike-slip faults
1021:
833:
683:
671:
602:after the city of
45:
4088:Media related to
4034:978-0-691-02406-6
3999:, February 2018,
3882:on June 30, 2013.
3861:978-2-7108-0624-0
3834:978-3-540-26011-0
3672:(6712): 986–991.
3636:10.1111/brv.12376
3520:(6712): 986–991.
3372:(6932): 602–606.
3324:. 188–189: 9–33.
3287:10.1029/98TC02204
3111:(6568): 785–790.
3019:10.1029/96TC03937
2607:(6745): 652–655.
2567:10.1130/G25141A.1
2409:Glomar Challenger
2246:(7274): 778–781.
2138:978-3-540-26011-0
2006:(7377): 359–363.
1916:Glomar Challenger
1747:978-0-19-107534-6
1474:adiabatic heating
1452:Baetic Cordillera
1438:At the time, the
1422:
1348:Iberian Peninsula
1263:Milankovic cycles
1253:metamorphic rocks
1068:cyclostratigraphy
1053:cyclostratigraphy
831:Mediterranean sea
688:Glomar Challenger
652:William B.F. Ryan
647:Glomar Challenger
502:
501:
482:
481:
460:
459:
61:Mediterranean Sea
16:(Redirected from
4162:
4155:Regional geology
4120:Messinian online
4087:
4073:
4071:
4065:. Archived from
4057:(3–4): 323–342.
4048:
4038:
4026:
4004:
3987:
3981:
3962:
3956:
3955:
3925:
3919:
3918:
3890:
3884:
3883:
3872:
3866:
3865:
3845:
3839:
3838:
3818:
3812:
3811:
3809:
3808:
3793:
3787:
3786:
3775:10.1130/G40260.1
3744:
3738:
3737:
3720:(1–4): 228–246.
3703:
3697:
3696:
3694:
3692:
3654:
3648:
3647:
3613:
3607:
3606:
3596:
3578:
3544:
3538:
3537:
3508:
3499:
3498:
3470:
3461:
3460:
3458:
3456:
3419:
3413:
3412:
3410:
3408:
3355:
3349:
3348:
3346:
3344:
3311:
3305:
3304:
3302:
3301:
3295:
3289:. Archived from
3256:
3250:
3249:
3247:
3245:
3239:10.1130/G20397.1
3208:
3202:
3201:
3199:
3197:
3160:
3154:
3153:
3151:
3149:
3136:
3125:10.1038/379785a0
3094:
3088:
3087:
3085:
3083:
3071:(6): 1011–1036.
3054:
3048:
3047:
3045:
3043:
3030:
2988:
2982:
2981:
2979:
2977:
2940:
2934:
2933:
2916:(3–4): 211–219.
2903:
2897:
2896:
2886:
2852:
2846:
2845:
2820:(3–4): 139–157.
2811:
2802:
2796:
2795:
2767:
2761:
2760:
2758:
2733:(3–4): 175–184.
2722:
2716:
2715:
2681:
2672:
2663:
2652:
2643:
2642:
2632:
2596:
2590:
2577:
2571:
2570:
2542:
2536:
2535:
2501:
2492:
2486:
2485:
2475:
2441:
2435:
2434:
2418:
2404:
2398:
2397:
2361:
2355:
2354:
2352:
2351:
2345:
2330:
2321:
2315:
2314:
2286:
2280:
2279:
2235:
2224:
2221:
2215:
2212:
2199:
2198:
2196:
2195:
2189:
2183:. Archived from
2167:(3–4): 271–286.
2158:
2149:
2143:
2142:
2122:
2116:
2115:
2087:
2078:
2077:
2049:
2040:
2039:
1995:
1989:
1988:
1956:
1950:
1949:
1941:
1935:
1934:
1926:
1920:
1914:A Voyage of the
1896:
1890:
1875:
1869:
1852:
1846:
1845:
1817:
1808:
1807:
1797:
1765:
1756:
1755:
1731:
1725:
1724:
1718:
1710:
1704:
1703:
1701:
1700:
1665:
1659:
1658:
1641:(3–4): 367–380.
1629:
1623:
1622:
1605:(3–4): 367–380.
1596:
1587:
1581:
1578:
1423:
1396:Balearic Islands
1350:and the western
909:
907:
869:scientific model
805:
584:Karl Mayer-Eymar
477:
467:
462:
455:
447:
442:
416:
407:
398:
389:
380:
371:
362:
353:
344:
329:
299:
267:
241:
236:
231:
226:
221:
216:
211:
206:
201:
196:
191:
186:
181:
176:
171:
166:
161:
156:
151:
146:
141:
136:
131:
119:
112:
105:
99:
86:
41:Gibraltar Strait
21:
4170:
4169:
4165:
4164:
4163:
4161:
4160:
4159:
4125:
4124:
4113:by Rob Butler.
4080:
4069:
4046:
4035:
4012:
4010:Further reading
4007:
3993:see this image)
3988:
3984:
3963:
3959:
3926:
3922:
3891:
3887:
3874:
3873:
3869:
3862:
3846:
3842:
3835:
3819:
3815:
3806:
3804:
3794:
3790:
3745:
3741:
3704:
3700:
3690:
3688:
3655:
3651:
3614:
3610:
3545:
3541:
3509:
3502:
3471:
3464:
3454:
3452:
3420:
3416:
3406:
3404:
3356:
3352:
3342:
3340:
3312:
3308:
3299:
3297:
3293:
3257:
3253:
3243:
3241:
3209:
3205:
3195:
3193:
3161:
3157:
3147:
3145:
3095:
3091:
3081:
3079:
3055:
3051:
3041:
3039:
2989:
2985:
2975:
2973:
2941:
2937:
2904:
2900:
2853:
2849:
2809:
2803:
2799:
2768:
2764:
2723:
2719:
2679:
2673:
2666:
2653:
2646:
2597:
2593:
2578:
2574:
2543:
2539:
2499:
2493:
2489:
2442:
2438:
2431:
2405:
2401:
2362:
2358:
2349:
2347:
2343:
2328:
2322:
2318:
2287:
2283:
2236:
2227:
2222:
2218:
2213:
2202:
2193:
2191:
2187:
2156:
2150:
2146:
2139:
2123:
2119:
2088:
2081:
2050:
2043:
1996:
1992:
1957:
1953:
1942:
1938:
1927:
1923:
1897:
1893:
1885:From page 13:
1876:
1872:
1853:
1849:
1818:
1811:
1766:
1759:
1748:
1732:
1728:
1716:
1712:
1711:
1707:
1698:
1696:
1686:10.2307/3515337
1666:
1662:
1630:
1626:
1594:
1588:
1584:
1579:
1575:
1571:
1554:
1515:
1509:
1456:Rifean corridor
1432:
1412:
1387:
1382:
1364:Hungarian plain
1329:stationary wave
1275:
1203:subduction zone
1136:northern Africa
1108:
1026:Tabernas Desert
1017:
1014:
1011:
1004:
998:point of view.
905:
903:
900:
827:
822:
817:
816:Rifean corridor
812:
807:
803:
801:
794:
620:
580:
562:geological time
498:
497:
495:
478:
472:North American
471:
465:
456:
451:
445:
438:
437:
433:
432:
428:
427:
423:
422:
418:
417:
412:
409:
408:
403:
400:
399:
394:
391:
390:
385:
382:
381:
376:
373:
372:
367:
364:
363:
358:
355:
354:
349:
346:
345:
341:
339:
337:
334:
331:
330:
326:
324:
322:
320:
318:
316:
313:
310:
309:
301:
300:
295:
293:
291:
289:
287:
285:
281:
278:
277:
269:
268:
263:
261:
259:
257:
255:
253:
251:
247:
242:
239:
237:
234:
232:
229:
227:
224:
222:
219:
217:
214:
212:
209:
207:
204:
202:
199:
197:
194:
192:
189:
187:
184:
182:
179:
177:
174:
172:
169:
167:
164:
162:
159:
157:
154:
152:
149:
147:
144:
142:
139:
137:
134:
132:
129:
123:
97:
91:
57:Lago Mare event
53:Messinian event
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
4168:
4158:
4157:
4152:
4150:Paleogeography
4147:
4142:
4137:
4123:
4122:
4117:
4108:
4101:
4100:
4093:
4079:
4078:External links
4076:
4075:
4074:
4072:on 2012-01-21.
4039:
4033:
4017:Kenneth J. Hsu
4011:
4008:
4006:
4005:
3982:
3957:
3920:
3885:
3867:
3860:
3840:
3833:
3813:
3788:
3761:(6): 527–530.
3739:
3698:
3649:
3630:(2): 874–896.
3608:
3539:
3500:
3481:(1–2): 41–59.
3462:
3436:(9): 771–775.
3414:
3350:
3306:
3273:(5): 671–689.
3251:
3203:
3177:(6): 540–543.
3155:
3089:
3049:
3005:(3): 504–522.
2983:
2957:(1–2): 23–60.
2950:Tectonophysics
2935:
2909:Tectonophysics
2898:
2847:
2797:
2762:
2717:
2690:(1–2): 43–60.
2664:
2644:
2591:
2572:
2553:(2): 167–170.
2537:
2487:
2436:
2429:
2399:
2356:
2316:
2281:
2225:
2216:
2200:
2144:
2137:
2117:
2079:
2041:
1990:
1965:Nat. Phys. Sci
1951:
1936:
1921:
1899:Kenneth J. Hsu
1891:
1870:
1847:
1809:
1780:(10): L10405.
1757:
1746:
1726:
1705:
1680:(4): 380–390.
1660:
1624:
1582:
1572:
1570:
1567:
1566:
1565:
1560:
1553:
1550:
1523:Atlantic Ocean
1513:Zanclean flood
1511:Main article:
1508:
1505:
1493:
1492:
1481:
1470:
1463:
1444:Betic corridor
1431:
1428:
1386:
1383:
1381:
1378:
1288:abyssal plains
1274:
1271:
1249:
1248:
1241:
1230:
1207:volcanic rocks
1195:
1194:
1183:
1169:
1166:
1124:European Plate
1107:
1104:
1003:
1000:
944:Kenneth J. Hsu
899:
898:Several cycles
896:
892:Zanclean flood
865:Atlantic Ocean
837:palaeomagnetic
821:Betic corridor
802:
793:
790:
656:Kenneth J. Hsu
619:
616:
579:
576:
554:North Atlantic
543:Zanclean flood
535:brackish water
500:
499:
484:
483:
480:
479:
470:
468:
458:
457:
450:
448:
439:
435:
434:
430:
429:
425:
424:
420:
419:
411:
410:
402:
401:
393:
392:
384:
383:
375:
374:
366:
365:
357:
356:
348:
347:
333:
332:
312:
311:
303:
302:
280:
279:
271:
270:
246:
245:
243:
238:
233:
228:
223:
218:
213:
208:
203:
198:
193:
188:
183:
178:
173:
168:
163:
158:
153:
148:
143:
138:
133:
128:
125:
124:
122:
121:
114:
107:
96:
93:
92:
89:
81:Zanclean flood
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
4167:
4156:
4153:
4151:
4148:
4146:
4143:
4141:
4138:
4136:
4133:
4132:
4130:
4121:
4118:
4116:
4112:
4109:
4106:
4103:
4102:
4098:
4094:
4091:
4086:
4082:
4081:
4068:
4064:
4060:
4056:
4052:
4045:
4040:
4036:
4030:
4025:
4024:
4018:
4014:
4013:
4002:
3998:
3994:
3990:
3986:
3980:
3976:
3972:
3971:
3966:
3961:
3953:
3949:
3945:
3941:
3937:
3933:
3932:
3924:
3916:
3912:
3908:
3904:
3900:
3896:
3889:
3881:
3877:
3871:
3863:
3857:
3853:
3852:
3844:
3836:
3830:
3826:
3825:
3817:
3803:
3799:
3792:
3784:
3780:
3776:
3772:
3768:
3764:
3760:
3756:
3755:
3750:
3743:
3735:
3731:
3727:
3723:
3719:
3715:
3714:
3709:
3702:
3687:
3683:
3679:
3675:
3671:
3667:
3666:
3661:
3653:
3645:
3641:
3637:
3633:
3629:
3625:
3624:
3619:
3612:
3604:
3600:
3595:
3590:
3586:
3582:
3577:
3572:
3568:
3564:
3561:(5): e36443.
3560:
3556:
3555:
3550:
3543:
3535:
3531:
3527:
3523:
3519:
3515:
3507:
3505:
3496:
3492:
3488:
3484:
3480:
3476:
3469:
3467:
3451:
3447:
3443:
3439:
3435:
3431:
3430:
3425:
3418:
3403:
3399:
3395:
3391:
3387:
3383:
3379:
3375:
3371:
3367:
3366:
3361:
3354:
3339:
3335:
3331:
3327:
3323:
3322:
3317:
3310:
3296:on 2008-06-11
3292:
3288:
3284:
3280:
3276:
3272:
3268:
3267:
3262:
3255:
3240:
3236:
3232:
3228:
3224:
3220:
3219:
3214:
3207:
3192:
3188:
3184:
3180:
3176:
3172:
3171:
3166:
3159:
3144:
3140:
3135:
3130:
3126:
3122:
3118:
3114:
3110:
3106:
3105:
3100:
3093:
3078:
3074:
3070:
3066:
3065:
3060:
3053:
3038:
3034:
3029:
3028:10044/1/21686
3024:
3020:
3016:
3012:
3008:
3004:
3000:
2999:
2994:
2987:
2972:
2968:
2964:
2960:
2956:
2952:
2951:
2946:
2939:
2931:
2927:
2923:
2919:
2915:
2911:
2910:
2902:
2894:
2890:
2885:
2880:
2876:
2872:
2868:
2864:
2863:
2858:
2851:
2843:
2839:
2835:
2831:
2827:
2823:
2819:
2815:
2808:
2801:
2793:
2789:
2785:
2781:
2777:
2773:
2766:
2757:
2752:
2748:
2744:
2740:
2736:
2732:
2728:
2721:
2713:
2709:
2705:
2701:
2697:
2693:
2689:
2685:
2678:
2671:
2669:
2662:
2661:90-71577-46-5
2658:
2651:
2649:
2640:
2636:
2631:
2626:
2622:
2621:10.1038/23231
2618:
2614:
2610:
2606:
2602:
2595:
2589:
2586:
2583:, 2011-12-15
2582:
2576:
2568:
2564:
2560:
2556:
2552:
2548:
2541:
2533:
2529:
2525:
2521:
2517:
2513:
2510:(2): L02401.
2509:
2505:
2498:
2491:
2483:
2479:
2474:
2469:
2465:
2461:
2457:
2453:
2452:
2447:
2440:
2432:
2430:9780691082936
2426:
2422:
2417:
2416:
2410:
2403:
2395:
2391:
2387:
2383:
2379:
2375:
2372:(1): 95–136.
2371:
2367:
2366:Sedimentology
2360:
2346:on 2016-03-04
2342:
2338:
2334:
2327:
2320:
2312:
2308:
2304:
2300:
2296:
2292:
2291:Geomorphology
2285:
2277:
2273:
2269:
2265:
2261:
2257:
2253:
2249:
2245:
2241:
2234:
2232:
2230:
2220:
2211:
2209:
2207:
2205:
2190:on 2016-03-03
2186:
2182:
2178:
2174:
2170:
2166:
2162:
2155:
2148:
2140:
2134:
2130:
2129:
2121:
2113:
2109:
2105:
2101:
2097:
2093:
2086:
2084:
2075:
2071:
2067:
2063:
2059:
2055:
2048:
2046:
2037:
2033:
2029:
2025:
2021:
2017:
2013:
2009:
2005:
2001:
1994:
1986:
1982:
1978:
1974:
1971:(12): 82–84.
1970:
1966:
1962:
1955:
1947:
1940:
1932:
1925:
1919:
1917:
1911:
1907:
1904:
1900:
1895:
1888:
1884:
1880:
1874:
1868:
1867:0-393-01952-7
1864:
1860:
1856:
1851:
1843:
1839:
1835:
1831:
1827:
1823:
1816:
1814:
1805:
1801:
1796:
1791:
1787:
1783:
1779:
1775:
1771:
1764:
1762:
1754:
1749:
1743:
1739:
1738:
1730:
1722:
1715:
1709:
1695:
1691:
1687:
1683:
1679:
1675:
1671:
1664:
1656:
1652:
1648:
1644:
1640:
1636:
1628:
1620:
1616:
1612:
1608:
1604:
1600:
1593:
1586:
1577:
1573:
1564:
1561:
1559:
1556:
1555:
1549:
1547:
1542:
1540:
1539:Niagara Falls
1536:
1532:
1528:
1524:
1520:
1514:
1507:Replenishment
1504:
1502:
1498:
1490:
1486:
1482:
1479:
1475:
1471:
1468:
1464:
1461:
1460:Rif Mountains
1457:
1453:
1449:
1448:Sierra Nevada
1445:
1441:
1437:
1436:
1435:
1410:
1408:
1404:
1402:
1397:
1393:
1377:
1374:
1373:Pannonian Sea
1369:
1365:
1361:
1357:
1353:
1349:
1345:
1341:
1337:
1332:
1330:
1325:
1321:
1317:
1316:extremophiles
1313:
1312:abyssal plain
1308:
1305:
1301:
1300:adiabatically
1297:
1292:
1289:
1285:
1281:
1270:
1266:
1264:
1259:
1256:
1254:
1246:
1242:
1239:
1235:
1231:
1228:
1224:
1220:
1216:
1212:
1208:
1204:
1200:
1199:
1198:
1192:
1188:
1187:igneous rocks
1184:
1182:
1178:
1174:
1170:
1167:
1164:
1163:
1162:
1159:
1157:
1153:
1149:
1145:
1144:Calabrian Arc
1141:
1140:Gibraltar Arc
1137:
1133:
1132:Gibraltar Arc
1129:
1128:Iberian Plate
1125:
1121:
1120:African Plate
1117:
1112:
1103:
1101:
1097:
1091:
1089:
1084:
1081:
1075:
1073:
1069:
1064:
1062:
1058:
1054:
1050:
1045:
1041:
1037:
1033:
1031:
1027:
1008:
999:
997:
990:
988:
984:
983:abyssal plain
981:
977:
973:
969:
965:
961:
957:
953:
947:
945:
941:
937:
933:
929:
928:river capture
925:
921:
917:
913:
912:hypersalinity
895:
893:
889:
885:
880:
878:
874:
870:
866:
861:
859:
855:
851:
847:
842:
838:
830:
825:
820:
815:
810:
798:
789:
787:
783:
782:pelagic oozes
778:
776:
772:
769:
765:
761:
757:
756:abyssal plain
753:
748:
746:
742:
738:
734:
733:abyssal plain
730:
729:foraminiferal
726:
722:
718:
714:
710:
706:
702:
698:
694:
690:
689:
680:
675:
668:
663:
659:
657:
653:
649:
648:
643:
638:
636:
632:
627:
625:
615:
613:
609:
605:
601:
597:
593:
589:
585:
574:
569:
567:
563:
559:
555:
551:
546:
544:
540:
536:
532:
528:
524:
519:
515:
511:
507:
494:
493:, as of 2021.
492:
485:
475:
469:
464:
463:
454:
449:
444:
443:
415:
406:
397:
388:
379:
370:
361:
352:
343:
328:
308:
307:
298:
297:
276:
275:
266:
265:
126:
120:
115:
113:
108:
106:
101:
100:
94:
87:
84:
82:
78:
74:
70:
66:
62:
58:
54:
50:
42:
38:
37:precipitation
32:
19:
4067:the original
4054:
4051:Stratigraphy
4050:
4022:
4000:
3985:
3974:
3968:
3960:
3938:(1): 13–22.
3935:
3929:
3923:
3898:
3894:
3888:
3880:the original
3870:
3850:
3843:
3823:
3816:
3805:. Retrieved
3801:
3791:
3758:
3752:
3742:
3717:
3711:
3701:
3691:21 September
3689:. Retrieved
3669:
3663:
3652:
3627:
3621:
3611:
3558:
3552:
3542:
3517:
3513:
3478:
3474:
3453:. Retrieved
3433:
3427:
3417:
3405:. Retrieved
3369:
3363:
3353:
3341:. Retrieved
3319:
3309:
3298:. Retrieved
3291:the original
3270:
3264:
3254:
3242:. Retrieved
3222:
3216:
3206:
3194:. Retrieved
3174:
3168:
3158:
3146:. Retrieved
3108:
3102:
3092:
3080:. Retrieved
3068:
3062:
3052:
3040:. Retrieved
3002:
2996:
2986:
2974:. Retrieved
2954:
2948:
2938:
2913:
2907:
2901:
2866:
2860:
2850:
2817:
2813:
2800:
2775:
2771:
2765:
2730:
2726:
2720:
2687:
2683:
2604:
2600:
2594:
2580:
2575:
2550:
2546:
2540:
2507:
2503:
2490:
2455:
2449:
2439:
2414:
2402:
2369:
2365:
2359:
2348:. Retrieved
2341:the original
2336:
2333:Stratigraphy
2332:
2319:
2294:
2290:
2284:
2243:
2239:
2219:
2192:. Retrieved
2185:the original
2164:
2160:
2147:
2127:
2120:
2098:(1): 13–22.
2095:
2091:
2057:
2053:
2003:
1999:
1993:
1968:
1964:
1954:
1945:
1939:
1930:
1924:
1913:
1902:
1894:
1886:
1878:
1873:
1858:
1850:
1825:
1821:
1777:
1773:
1751:
1736:
1729:
1720:
1708:
1697:. Retrieved
1677:
1673:
1663:
1638:
1634:
1627:
1602:
1598:
1585:
1576:
1543:
1535:Iguazu Falls
1516:
1501:Indian Ocean
1494:
1467:biodiversity
1433:
1399:
1388:
1356:eastern Alps
1333:
1320:air pressure
1293:
1276:
1267:
1260:
1257:
1250:
1234:delamination
1196:
1160:
1113:
1109:
1092:
1085:
1080:Sorbas Basin
1076:
1065:
1057:Sorbas basin
1046:
1042:
1038:
1034:
1030:Sorbas Basin
1022:
1019:evaporation.
992:
960:Stromatolite
949:
946:found that:
924:tectonically
901:
881:
873:Grand Canyon
862:
858:depositional
834:
828:
823:
818:
813:
808:
779:
771:Foraminifera
749:
725:cross-bedded
686:
684:
679:Sorbas basin
645:
639:
634:
628:
623:
621:
599:
581:
571:
547:
503:
488:
452:
378:Serravallian
304:
282:
272:
248:
56:
52:
48:
46:
2778:: 131–154.
2297:: 128–138.
1531:Angel Falls
1284:brine lakes
1238:lithosphere
1215:rolled back
1173:lithosphere
839:datings of
699:silts; and
624:M reflector
558:evaporation
539:Caspian Sea
523:hypersaline
360:Burdigalian
98:This box:
71:age of the
65:desiccation
4129:Categories
3807:2024-09-01
3300:2008-04-04
3294:(abstract)
3225:(7): 625.
2350:2014-11-05
2194:2010-06-09
1828:(4): 363.
1699:2008-02-11
1569:References
1563:Atlantropa
1390:Africa, a
1368:Paratethys
1362:, and the
1342:, and the
1307:lapse rate
1211:Tethys Sea
1191:subduction
1181:tomography
1148:Aegean Arc
1146:, and the
1096:bathymetry
996:geodynamic
964:intertidal
956:lamination
908:10 kg
792:Chronology
786:evaporites
737:sandstorms
697:floodplain
590:-bearing,
508:minerals,
414:Piacenzian
351:Aquitanian
306:Quaternary
4145:Messinian
3915:130839252
3901:: 19–26.
3783:0091-7613
3686:0036-8075
3585:1932-6203
3534:0036-8075
3266:Tectonics
3134:1813/5287
3037:129585666
2998:Tectonics
2893:128771539
2756:1874/1630
2712:1874/1632
2630:1874/1500
2532:129573384
2482:128771539
2276:205218854
2074:130839252
2060:: 19–26.
2036:205227033
1855:Cloud, P.
1804:128771539
1527:waterfall
1517:When the
1478:anhydrite
1401:Myotragus
1304:adiabatic
1219:chemistry
1213:may have
1201:A moving
968:anhydrite
854:erosional
841:Messinian
835:Based on
713:evaporite
709:rock salt
705:anhydrite
665:Cones of
612:evaporite
600:Messinian
552:than the
506:evaporite
396:Messinian
387:Tortonian
274:Paleogene
69:Messinian
4115:Archived
4019:(1987).
3997:Phys.org
3802:phys.org
3644:29024366
3603:22590545
3554:PLOS ONE
3455:20 March
3407:20 March
3394:12686997
3343:20 March
3244:20 March
3196:20 March
3148:20 March
3082:20 March
3042:20 March
2976:20 March
2842:30843908
2585:pdf here
2394:52266741
2268:20010684
2028:22170684
1883:page 13.
1857:(1988).
1552:See also
1407:Holocene
1122:and the
1100:geometry
980:Balearic
952:brackish
936:Pliocene
888:Pliocene
884:Zanclean
850:tectonic
768:Pliocene
592:brackish
527:Dead Sea
405:Zanclean
369:Langhian
3940:Bibcode
3763:Bibcode
3754:Geology
3722:Bibcode
3665:Science
3594:3348158
3563:Bibcode
3514:Science
3483:Bibcode
3438:Bibcode
3429:Geology
3402:4410599
3374:Bibcode
3326:Bibcode
3275:Bibcode
3227:Bibcode
3218:Geology
3179:Bibcode
3170:Geology
3143:4332684
3113:Bibcode
3007:Bibcode
2959:Bibcode
2918:Bibcode
2871:Bibcode
2822:Bibcode
2780:Bibcode
2735:Bibcode
2692:Bibcode
2639:4430026
2609:Bibcode
2555:Bibcode
2547:Geology
2512:Bibcode
2460:Bibcode
2374:Bibcode
2299:Bibcode
2248:Bibcode
2169:Bibcode
2100:Bibcode
2008:Bibcode
1973:Bibcode
1830:Bibcode
1822:Geology
1782:Bibcode
1694:3515337
1674:PALAIOS
1643:Bibcode
1607:Bibcode
1537:or the
1380:Effects
1360:Balkans
1352:Maghreb
1286:on the
1223:density
1177:seismic
1156:Eurasia
972:sabkhas
932:Miocene
846:Miocene
752:canyons
631:Miocene
604:Messina
596:Miocene
550:saltier
476:expands
474:prairie
466:←
446:←
235:–
225:–
215:–
205:–
195:–
185:–
175:–
165:–
155:–
145:–
135:–
73:Miocene
4031:
3913:
3858:
3831:
3781:
3684:
3642:
3601:
3591:
3583:
3532:
3400:
3392:
3365:Nature
3141:
3104:Nature
3035:
2891:
2840:
2659:
2637:
2601:Nature
2581:Nature
2530:
2480:
2427:
2392:
2274:
2266:
2240:Nature
2135:
2072:
2034:
2026:
2000:Nature
1912:1983.
1865:
1802:
1744:
1692:
1546:Sicily
1358:, the
1344:Levant
1340:Greece
1142:, the
1106:Causes
916:strata
804:
745:halite
721:potash
701:gypsum
693:arroyo
667:gypsum
608:Sicily
588:gypsum
531:rivers
514:fossil
512:, and
436:
431:
426:
421:
4070:(PDF)
4047:(PDF)
3991:(and
3911:S2CID
3398:S2CID
3139:S2CID
3033:S2CID
2889:S2CID
2838:S2CID
2810:(PDF)
2680:(PDF)
2635:S2CID
2528:S2CID
2500:(PDF)
2478:S2CID
2390:S2CID
2344:(PDF)
2329:(PDF)
2272:S2CID
2188:(PDF)
2157:(PDF)
2070:S2CID
2032:S2CID
1800:S2CID
1717:(PDF)
1690:JSTOR
1595:(PDF)
1489:Cairo
1227:magma
1061:Spain
775:Cairo
764:Aswan
741:brine
717:brine
510:soils
4029:ISBN
3856:ISBN
3829:ISBN
3779:ISSN
3693:2024
3682:ISSN
3640:PMID
3599:PMID
3581:ISSN
3530:ISSN
3457:2023
3409:2023
3390:PMID
3345:2023
3246:2023
3198:2023
3150:2023
3084:2023
3044:2023
2978:2023
2657:ISBN
2588:Link
2425:ISBN
2264:PMID
2133:ISBN
2024:PMID
1863:ISBN
1742:ISBN
1497:Suez
1485:Nile
1296:Sink
1221:and
1072:marl
1028:and
856:and
760:Nile
654:and
118:edit
111:talk
104:view
47:The
4059:doi
3948:doi
3936:121
3903:doi
3899:181
3771:doi
3730:doi
3718:238
3674:doi
3670:385
3632:doi
3589:PMC
3571:doi
3522:doi
3518:385
3491:doi
3479:279
3446:doi
3382:doi
3370:422
3334:doi
3283:doi
3235:doi
3187:doi
3129:hdl
3121:doi
3109:379
3073:doi
3023:hdl
3015:doi
2967:doi
2955:196
2926:doi
2914:148
2879:doi
2830:doi
2818:286
2788:doi
2776:188
2751:hdl
2743:doi
2731:133
2708:hdl
2700:doi
2688:140
2625:hdl
2617:doi
2605:400
2563:doi
2520:doi
2468:doi
2411:".
2382:doi
2307:doi
2295:213
2256:doi
2244:462
2177:doi
2165:233
2108:doi
2096:121
2062:doi
2058:181
2016:doi
2004:480
1981:doi
1969:230
1838:doi
1790:doi
1682:doi
1651:doi
1639:142
1615:doi
1603:142
1450:or
1225:in
735:by
606:in
491:ICS
4131::
4053:.
4049:.
3995:,
3973:,
3967:,
3946:.
3934:.
3909:.
3897:.
3800:.
3777:.
3769:.
3759:46
3757:.
3751:.
3728:.
3716:.
3710:.
3680:.
3668:.
3662:.
3638:.
3628:93
3626:.
3620:.
3597:.
3587:.
3579:.
3569:.
3557:.
3551:.
3528:.
3516:.
3503:^
3489:.
3477:.
3465:^
3444:.
3434:21
3432:.
3426:.
3396:.
3388:.
3380:.
3368:.
3362:.
3332:.
3318:.
3281:.
3271:17
3269:.
3263:.
3233:.
3223:32
3221:.
3215:.
3185:.
3175:17
3173:.
3167:.
3137:.
3127:.
3119:.
3107:.
3101:.
3069:40
3067:.
3061:.
3031:.
3021:.
3013:.
3003:16
3001:.
2995:.
2965:.
2953:.
2947:.
2924:.
2912:.
2887:.
2877:.
2867:34
2865:.
2859:.
2836:.
2828:.
2816:.
2812:.
2786:.
2774:.
2749:.
2741:.
2729:.
2706:.
2698:.
2686:.
2682:.
2667:^
2647:^
2633:.
2623:.
2615:.
2603:.
2561:.
2551:37
2549:.
2526:.
2518:.
2508:35
2506:.
2502:.
2476:.
2466:.
2456:34
2454:.
2448:.
2419:.
2388:.
2380:.
2370:56
2368:.
2335:.
2331:.
2305:.
2293:.
2270:.
2262:.
2254:.
2242:.
2228:^
2203:^
2175:.
2163:.
2159:.
2106:.
2094:.
2082:^
2068:.
2056:.
2044:^
2030:.
2022:.
2014:.
2002:.
1979:.
1967:.
1963:.
1908:,
1901:,
1836:.
1826:24
1824:.
1812:^
1798:.
1788:.
1778:34
1776:.
1772:.
1760:^
1750:.
1719:.
1688:.
1678:12
1676:.
1672:.
1649:.
1637:.
1613:.
1601:.
1597:.
1255:.
777:.
707:,
703:,
637:.
568:.
545:.
342:o.
77:Ma
4061::
4055:5
4037:.
3954:.
3950::
3942::
3917:.
3905::
3864:.
3837:.
3810:.
3785:.
3773::
3765::
3736:.
3732::
3724::
3695:.
3676::
3646:.
3634::
3605:.
3573::
3565::
3559:7
3536:.
3524::
3497:.
3493::
3485::
3459:.
3448::
3440::
3411:.
3384::
3376::
3347:.
3336::
3328::
3303:.
3285::
3277::
3248:.
3237::
3229::
3200:.
3189::
3181::
3152:.
3131::
3123::
3115::
3086:.
3075::
3046:.
3025::
3017::
3009::
2980:.
2969::
2961::
2932:.
2928::
2920::
2895:.
2881::
2873::
2844:.
2832::
2824::
2794:.
2790::
2782::
2759:.
2753::
2745::
2737::
2714:.
2710::
2702::
2694::
2641:.
2627::
2619::
2611::
2569:.
2565::
2557::
2534:.
2522::
2514::
2484:.
2470::
2462::
2433:.
2396:.
2384::
2376::
2353:.
2337:5
2313:.
2309::
2301::
2278:.
2258::
2250::
2197:.
2179::
2171::
2141:.
2114:.
2110::
2102::
2076:.
2064::
2038:.
2018::
2010::
1987:.
1983::
1975::
1918:.
1844:.
1840::
1832::
1806:.
1792::
1784::
1723:.
1702:.
1684::
1657:.
1653::
1645::
1621:.
1617::
1609::
1403:,
1240:.
1193:.
934:/
906:×
904:4
829:M
824:G
819:B
814:R
809:S
340:i
338:l
336:P
327:e
325:n
323:e
321:c
319:o
317:i
315:M
296:e
294:n
292:e
290:g
288:o
286:e
284:N
264:c
262:i
260:o
258:z
256:o
254:n
252:e
250:C
43:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.