1489:
1561:
460:
1463:
1525:
1549:
1501:
1537:
1513:
31:
213:
455:{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\mathbf {n} &=\mathbf {k} \times \mathbf {h} =(-h_{y},h_{x},0)\\\Omega &={\begin{cases}\arccos {{n_{x}} \over {\mathbf {\left|n\right|} }},&n_{y}\geq 0;\\2\pi -\arccos {{n_{x}} \over {\mathbf {\left|n\right|} }},&n_{y}<0.\end{cases}}\end{aligned}}}
218:
521:
equal to zero), ☊ is undefined. For computation it is then, by convention, set equal to zero; that is, the ascending node is placed in the reference direction, which is equivalent to letting
183:
known only from visual observations, it is not possible to tell which node is ascending and which is descending. In this case the orbital parameter which is recorded is simply labeled
558:
175:
onto the plane of the sky) as the origin of longitude. The angle is measured eastwards (or, as seen by the observer, counterclockwise) from north to the node.
663:
146:
as the reference plane, and the FPA as the origin of longitude. The angle is measured counterclockwise (as seen from north of the ecliptic) from the
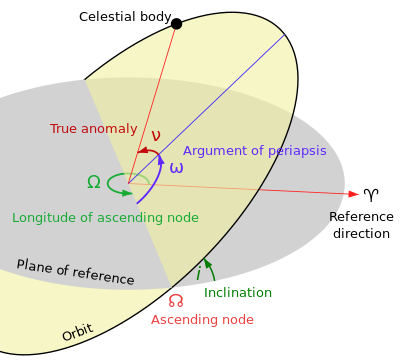
72:. The ascending node is the point where the orbit of the object passes through the plane of reference, as seen in the adjacent image.
600:
1340:
17:
1400:
623:
200:
1395:
1275:
694:
1488:
1360:
608:
131:
at which the spacecraft crosses the equator. Similar definitions exist for satellites around other planets (see
1433:
1072:
1063:
800:
1380:
850:
1325:
132:
1479:
1305:
1132:
1443:
306:
1428:
953:
582:
1438:
746:
168:
1300:
902:
822:
810:
187:, ☊, and represents the longitude of whichever node has a longitude between 0 and 180 degrees.
1423:
1365:
1335:
1123:
1000:
968:
938:
897:
882:
761:
645:, R. G. Aitken, New York: Semi-Centennial Publications of the University of California, 1918.
1448:
1270:
1054:
943:
912:
840:
815:
790:
751:
732:
687:
172:
147:
97:
8:
1553:
1310:
1105:
845:
597:
518:
60:
58:
of an object in space. It is the angle from a specified reference direction, called the
1541:
1529:
983:
872:
770:
514:
139:
1350:
1248:
1178:
933:
887:
805:
657:
1505:
1330:
1262:
1026:
988:
862:
832:
785:
562:
163:
158:
116:
85:
51:
39:
1581:
1370:
963:
867:
857:
756:
680:
627:
604:
128:
102:
100:(FPA) as the origin of longitude. In this case, the longitude is also called the
69:
620:
1586:
1565:
1493:
1466:
1418:
1410:
1405:
1290:
1285:
1216:
1196:
1187:
780:
766:
742:
737:
712:
548:
491:
65:
35:
1575:
1320:
1315:
1234:
877:
795:
196:
1517:
1385:
1295:
1169:
1152:
1010:
907:
775:
553:
543:
154:
1390:
1225:
995:
975:
892:
180:
958:
672:
1560:
1375:
727:
143:
1280:
538:
199:, the longitude of the ascending node can be calculated from the
93:
80:
Commonly used reference planes and origins of longitude include:
506:
is the unit vector (0, 0, 1), which is the normal vector to the
498:-plane, and the origin of longitude is taken to be the positive
1085:
704:
112:
89:
55:
444:
1512:
111:). The angle is measured eastwards (or, as seen from the
30:
1477:
216:
454:
119:) from the FPA to the node. An alternative is the
190:
1573:
167:) as the reference plane, and north (i.e. the
688:
494:. The reference plane is assumed to be the
1462:
695:
681:
171:of the direction from the observer to the
38:(bright green) as a part of a diagram of
702:
638:
636:
29:
27:Defining the orbit of an object in space
653:
651:
598:Orbital Elements and Astronomical Terms
593:
591:
583:Parameters Describing Elliptical Orbits
14:
1574:
1341:Transposition, docking, and extraction
96:plane as the reference plane, and the
676:
633:
607:, Robert A. Egler, Dept. of Physics,
161:at the point of interest (called the
648:
588:
630:, amsat.org, accessed May 17, 2007.
611:. Web page, accessed May 17, 2007.
490:⟩ is a vector pointing towards the
24:
585:, web page, accessed May 17, 2007.
291:
201:specific relative angular momentum
25:
1598:
1401:Kepler's laws of planetary motion
666:, on line, accessed May 17, 2007.
559:Perturbation of the orbital plane
1559:
1547:
1535:
1523:
1511:
1499:
1487:
1461:
1396:Interplanetary Transport Network
1276:Collision avoidance (spacecraft)
409:
335:
242:
234:
222:
121:local time of the ascending node
68:(☊), as measured in a specified
1361:Astronomical coordinate systems
1115:Longitude of the ascending node
609:North Carolina State University
48:longitude of the ascending node
1434:Retrograde and prograde motion
614:
576:
284:
249:
191:Calculation from state vectors
13:
1:
569:
1381:Equatorial coordinate system
133:planetary coordinate systems
7:
621:Keplerian Elements Tutorial
532:
525:point towards the positive
157:, the plane tangent to the
10:
1603:
1133:Longitude of the periapsis
64:, to the direction of the
1457:
1444:Specific angular momentum
1349:
1261:
1205:
1141:
1094:
1034:
1025:
921:
831:
720:
711:
50:(symbol ☊) is one of the
169:perpendicular projection
75:
1439:Specific orbital energy
153:For orbits outside the
851:Geostationary transfer
565:of the ascending node.
456:
43:
1424:Orbital state vectors
1366:Characteristic energy
1336:Trans-lunar injection
1124:Argument of periapsis
801:Prograde / Retrograde
762:Hyperbolic trajectory
457:
185:longitude of the node
105:of the ascending node
34:The longitude of the
33:
18:Longitude of the node
1271:Bi-elliptic transfer
791:Parabolic trajectory
214:
173:north celestial pole
148:First Point of Aries
98:First Point of Aries
54:used to specify the
1311:Low-energy transfer
659:Celestial Mechanics
515:non-inclined orbits
140:heliocentric orbits
61:origin of longitude
1306:Inclination change
954:Distant retrograde
626:2002-10-14 at the
603:2007-04-03 at the
452:
450:
443:
44:
40:orbital parameters
1475:
1474:
1449:Two-line elements
1257:
1256:
1179:Eccentric anomaly
1021:
1020:
888:Orbit of the Moon
747:Highly elliptical
510:reference plane.
418:
344:
179:In the case of a
86:geocentric orbits
16:(Redirected from
1594:
1564:
1563:
1552:
1551:
1550:
1540:
1539:
1538:
1528:
1527:
1526:
1516:
1515:
1504:
1503:
1502:
1492:
1491:
1483:
1465:
1464:
1406:Lagrangian point
1301:Hohmann transfer
1246:
1232:
1223:
1214:
1194:
1185:
1176:
1167:
1163:
1159:
1150:
1130:
1121:
1112:
1103:
1083:
1079:
1070:
1061:
1052:
1032:
1031:
1001:Heliosynchronous
950:Lagrange points
903:Transatmospheric
718:
717:
697:
690:
683:
674:
673:
667:
655:
646:
643:The Binary Stars
640:
631:
618:
612:
595:
586:
580:
461:
459:
458:
453:
451:
447:
446:
434:
433:
419:
417:
416:
415:
402:
401:
400:
390:
360:
359:
345:
343:
342:
341:
328:
327:
326:
316:
277:
276:
264:
263:
245:
237:
225:
164:plane of the sky
159:celestial sphere
127:), based on the
117:counterclockwise
52:orbital elements
21:
1602:
1601:
1597:
1596:
1595:
1593:
1592:
1591:
1572:
1571:
1570:
1558:
1548:
1546:
1536:
1534:
1524:
1522:
1510:
1500:
1498:
1486:
1478:
1476:
1471:
1453:
1371:Escape velocity
1352:
1345:
1326:Rocket equation
1253:
1245:
1239:
1230:
1221:
1212:
1201:
1192:
1183:
1174:
1165:
1161:
1157:
1148:
1137:
1128:
1119:
1110:
1101:
1090:
1081:
1077:
1073:Semi-minor axis
1068:
1064:Semi-major axis
1059:
1050:
1044:
1017:
939:Areosynchronous
923:
917:
898:Sun-synchronous
883:Near-equatorial
827:
707:
701:
671:
670:
664:Jeremy B. Tatum
656:
649:
641:
634:
628:Wayback Machine
619:
615:
605:Wayback Machine
596:
589:
581:
577:
572:
535:
489:
482:
475:
449:
448:
442:
441:
429:
425:
423:
405:
404:
403:
396:
392:
391:
389:
371:
370:
355:
351:
349:
331:
330:
329:
322:
318:
317:
315:
302:
301:
294:
288:
287:
272:
268:
259:
255:
241:
233:
226:
221:
217:
215:
212:
211:
193:
129:local mean time
103:right ascension
78:
70:reference plane
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1600:
1590:
1589:
1584:
1569:
1568:
1556:
1544:
1532:
1520:
1508:
1496:
1473:
1472:
1470:
1469:
1467:List of orbits
1458:
1455:
1454:
1452:
1451:
1446:
1441:
1436:
1431:
1426:
1421:
1419:Orbit equation
1416:
1408:
1403:
1398:
1393:
1388:
1383:
1378:
1373:
1368:
1363:
1357:
1355:
1347:
1346:
1344:
1343:
1338:
1333:
1328:
1323:
1318:
1313:
1308:
1303:
1298:
1293:
1291:Gravity assist
1288:
1286:Delta-v budget
1283:
1278:
1273:
1267:
1265:
1259:
1258:
1255:
1254:
1252:
1251:
1243:
1237:
1228:
1219:
1217:Orbital period
1209:
1207:
1203:
1202:
1200:
1199:
1197:True longitude
1190:
1188:Mean longitude
1181:
1172:
1155:
1145:
1143:
1139:
1138:
1136:
1135:
1126:
1117:
1108:
1098:
1096:
1092:
1091:
1089:
1088:
1075:
1066:
1057:
1047:
1045:
1043:
1042:
1039:
1035:
1029:
1023:
1022:
1019:
1018:
1016:
1015:
1014:
1013:
1005:
1004:
1003:
998:
993:
992:
991:
978:
973:
972:
971:
966:
961:
956:
948:
947:
946:
944:Areostationary
941:
936:
927:
925:
919:
918:
916:
915:
913:Very low Earth
910:
905:
900:
895:
890:
885:
880:
875:
870:
865:
860:
855:
854:
853:
848:
841:Geosynchronous
837:
835:
829:
828:
826:
825:
823:Transfer orbit
820:
819:
818:
813:
803:
798:
793:
788:
783:
781:Lagrange point
778:
773:
764:
759:
754:
749:
740:
735:
730:
724:
722:
715:
709:
708:
703:Gravitational
700:
699:
692:
685:
677:
669:
668:
647:
632:
613:
587:
574:
573:
571:
568:
567:
566:
556:
551:
549:List of orbits
546:
541:
534:
531:
492:ascending node
487:
480:
473:
463:
462:
445:
440:
437:
432:
428:
424:
422:
414:
411:
408:
399:
395:
388:
385:
382:
379:
376:
373:
372:
369:
366:
363:
358:
354:
350:
348:
340:
337:
334:
325:
321:
314:
311:
308:
307:
305:
300:
297:
295:
293:
290:
289:
286:
283:
280:
275:
271:
267:
262:
258:
254:
251:
248:
244:
240:
236:
232:
229:
227:
224:
220:
219:
192:
189:
177:
176:
151:
136:
77:
74:
66:ascending node
36:ascending node
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1599:
1588:
1585:
1583:
1580:
1579:
1577:
1567:
1562:
1557:
1555:
1545:
1543:
1533:
1531:
1521:
1519:
1514:
1509:
1507:
1497:
1495:
1490:
1485:
1484:
1481:
1468:
1460:
1459:
1456:
1450:
1447:
1445:
1442:
1440:
1437:
1435:
1432:
1430:
1427:
1425:
1422:
1420:
1417:
1415:
1414:-body problem
1413:
1409:
1407:
1404:
1402:
1399:
1397:
1394:
1392:
1389:
1387:
1384:
1382:
1379:
1377:
1374:
1372:
1369:
1367:
1364:
1362:
1359:
1358:
1356:
1354:
1348:
1342:
1339:
1337:
1334:
1332:
1329:
1327:
1324:
1322:
1319:
1317:
1316:Oberth effect
1314:
1312:
1309:
1307:
1304:
1302:
1299:
1297:
1294:
1292:
1289:
1287:
1284:
1282:
1279:
1277:
1274:
1272:
1269:
1268:
1266:
1264:
1260:
1250:
1242:
1238:
1236:
1235:Orbital speed
1229:
1227:
1220:
1218:
1211:
1210:
1208:
1204:
1198:
1191:
1189:
1182:
1180:
1173:
1171:
1156:
1154:
1147:
1146:
1144:
1140:
1134:
1127:
1125:
1118:
1116:
1109:
1107:
1100:
1099:
1097:
1093:
1087:
1076:
1074:
1067:
1065:
1058:
1056:
1049:
1048:
1046:
1040:
1037:
1036:
1033:
1030:
1028:
1024:
1012:
1009:
1008:
1006:
1002:
999:
997:
994:
990:
989:Earth's orbit
987:
986:
985:
982:
981:
979:
977:
974:
970:
967:
965:
962:
960:
957:
955:
952:
951:
949:
945:
942:
940:
937:
935:
932:
931:
929:
928:
926:
920:
914:
911:
909:
906:
904:
901:
899:
896:
894:
891:
889:
886:
884:
881:
879:
876:
874:
871:
869:
866:
864:
861:
859:
856:
852:
849:
847:
846:Geostationary
844:
843:
842:
839:
838:
836:
834:
830:
824:
821:
817:
814:
812:
809:
808:
807:
804:
802:
799:
797:
794:
792:
789:
787:
784:
782:
779:
777:
774:
772:
768:
765:
763:
760:
758:
755:
753:
750:
748:
744:
741:
739:
736:
734:
731:
729:
726:
725:
723:
719:
716:
714:
710:
706:
698:
693:
691:
686:
684:
679:
678:
675:
665:
661:
660:
654:
652:
644:
639:
637:
629:
625:
622:
617:
610:
606:
602:
599:
594:
592:
584:
579:
575:
564:
560:
557:
555:
552:
550:
547:
545:
544:Kepler orbits
542:
540:
537:
536:
530:
528:
524:
520:
516:
511:
509:
505:
501:
497:
493:
486:
479:
472:
468:
438:
435:
430:
426:
420:
412:
406:
397:
393:
386:
383:
380:
377:
374:
367:
364:
361:
356:
352:
346:
338:
332:
323:
319:
312:
309:
303:
298:
296:
281:
278:
273:
269:
265:
260:
256:
252:
246:
238:
230:
228:
210:
209:
208:
206:
202:
198:
197:astrodynamics
188:
186:
182:
174:
170:
166:
165:
160:
156:
152:
149:
145:
141:
137:
134:
130:
126:
122:
118:
114:
110:
106:
104:
99:
95:
91:
87:
83:
82:
81:
73:
71:
67:
63:
62:
57:
53:
49:
41:
37:
32:
19:
1554:Solar System
1429:Perturbation
1411:
1386:Ground track
1296:Gravity turn
1247:
1240:
1233:
1224:
1215:
1195:
1186:
1177:
1170:True anomaly
1168:
1153:Mean anomaly
1151:
1131:
1122:
1114:
1113:
1104:
1084:
1071:
1062:
1055:Eccentricity
1053:
1011:Lunar cycler
984:Heliocentric
924:other points
873:Medium Earth
771:Non-inclined
658:
642:
616:
578:
554:Orbital node
526:
522:
512:
507:
503:
499:
495:
484:
477:
470:
466:
464:
207:as follows:
204:
194:
184:
178:
162:
155:Solar System
150:to the node.
124:
120:
108:
101:
79:
59:
47:
45:
1542:Outer space
1530:Spaceflight
1391:Hill sphere
1226:Mean motion
1106:Inclination
1095:Orientation
996:Mars cycler
934:Areocentric
806:Synchronous
519:inclination
181:binary star
1576:Categories
1331:Rendezvous
1027:Parameters
863:High Earth
833:Geocentric
786:Osculating
743:Elliptical
570:References
563:precession
561:can cause
94:equatorial
1506:Astronomy
1376:Ephemeris
1353:mechanics
1263:Maneuvers
1206:Variation
969:Libration
964:Lissajous
868:Low Earth
858:Graveyard
757:Horseshoe
387:
381:−
378:π
362:≥
313:
292:Ω
253:−
239:×
1142:Position
767:Inclined
738:Circular
624:Archived
601:Archived
533:See also
502:-axis.
144:ecliptic
1566:Science
1494:Physics
1480:Portals
1351:Orbital
1321:Phasing
1281:Delta-v
1086:Apsides
1080:,
878:Molniya
796:Parking
733:Capture
721:General
539:Equinox
529:-axis.
203:vector
1582:Orbits
1007:Other
908:Tundra
776:Kepler
752:Escape
705:orbits
517:(with
465:Here,
384:arccos
310:arccos
142:, the
1587:Angle
1518:Stars
1249:Epoch
1038:Shape
976:Lunar
930:Mars
922:About
893:Polar
713:Types
113:north
90:Earth
76:Types
56:orbit
1041:Size
980:Sun
959:Halo
811:semi
513:For
436:<
138:For
125:LTAN
109:RAAN
84:For
46:The
816:sub
728:Box
469:= ⟨
195:In
92:'s
1578::
1164:,
1160:,
769:/
745:/
662:,
650:^
635:^
590:^
508:xy
496:xy
483:,
476:,
439:0.
135:).
115:,
88:,
1482::
1412:n
1244:0
1241:t
1231:v
1222:n
1213:T
1193:l
1184:L
1175:E
1166:f
1162:θ
1158:ν
1149:M
1129:ϖ
1120:ω
1111:Ω
1102:i
1082:q
1078:Q
1069:b
1060:a
1051:e
696:e
689:t
682:v
527:x
523:n
504:k
500:x
488:z
485:n
481:y
478:n
474:x
471:n
467:n
431:y
427:n
421:,
413:|
410:n
407:|
398:x
394:n
375:2
368:;
365:0
357:y
353:n
347:,
339:|
336:n
333:|
324:x
320:n
304:{
299:=
285:)
282:0
279:,
274:x
270:h
266:,
261:y
257:h
250:(
247:=
243:h
235:k
231:=
223:n
205:h
123:(
107:(
42:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.