82:
150:
53:. An emerging paradigm in neuroscience is that cognitive tasks are performed not by individual brain regions working in isolation but by networks consisting of several discrete brain regions that are said to be "functionally connected". Functional connectivity networks may be found using algorithms such as
818:
Uddin, LQ; Betzel, Richard F.; Cohen, Jessica R.; Damoiselastx, Jessica S.; De
Brigard, Felipe; Eickhoff, Simon B.; Fornito, Alex; Gratton, Caterina; Gordon, Evan M.; Laird, Angela R.; Larson-Prior, Linda; McIntosh, A. Randal; Nickerson, Lisa D.; Pessoa, Luiz; Pinho, Ana Luísa; Poldrack, Russell A.;
69:
network (RSN). As a physical system with graph-like properties, a large-scale brain network has both nodes and edges and cannot be identified simply by the co-activation of brain areas. In recent decades, the analysis of brain networks was made feasible by advances in imaging techniques as well as
217:
of the right hemisphere. These areas respond when behaviorally relevant stimuli occur unexpectedly. The ventral attention network is inhibited during focused attention in which top-down processing is being used, such as when visually searching for something. This response may prevent goal-driven
164:
Because brain networks can be identified at various different resolutions and with various different neurobiological properties, there is currently no universal atlas of brain networks that fits all circumstances. Uddin, Yeo, and Spreng proposed in 2019 that the following six networks should be
105:
by offering a neural model of how different cognitive functions emerge when different sets of brain regions join together as self-organized coalitions. The number and composition of the coalitions will vary with the algorithm and parameters used to identify them. In one model, there is only the
98:" and the "visual network", while other networks had less agreement. Several issues make the work of creating a common atlas for networks difficult: some of these issues are the variability of spatial and time scales, variability across individuals, and the dynamic nature of some networks.
93:
has created the
Workgroup for HArmonized Taxonomy of NETworks (WHATNET) group to work towards a consensus regarding network nomenclature. WHATNET conducted a survey in 2021 which showed a large degree of agreement about the name and topography of three networks: the "somato network", the
201:
The salience network consists of several structures, including the anterior (bilateral) insula, dorsal anterior cingulate cortex, and three subcortical structures which are the ventral striatum, substantia nigra/ventral tegmental region. It plays the key role of monitoring the
234:
This network is involved in the voluntary, top-down deployment of attention. Within the dorsal attention network, the intraparietal sulcus and frontal eye fields influence the visual areas of the brain. These influencing factors allow for the orientation of
887:
Yeo, B. T. Thomas; Krienen, Fenna M.; Sepulcre, Jorge; Sabuncu, Mert R.; Lashkari, Danial; Hollinshead, Marisa; Roffman, Joshua L.; Smoller, Jordan W.; Zöllei, Lilla; Polimeni, Jonathan R.; Fischl, Bruce; Liu, Hesheng; Buckner, Randy L. (2011-09-01).
1911:
Shulman, Gordon L.; McAvoy, Mark P.; Cowan, Melanie C.; Astafiev, Serguei V.; Tansy, Aaron P.; d'Avossa, Giovanni; Corbetta, Maurizio (2003-11-01). "Quantitative
Analysis of Attention and Detection Signals During Visual Search".
180:
The default mode network is active when an individual is awake and at rest. It preferentially activates when individuals focus on internally-oriented tasks such as daydreaming, envisioning the future, retrieving memories, and
64:
The set of identified brain areas that are linked together in a large-scale network varies with cognitive function. When the cognitive state is not explicit (i.e., the subject is at "rest"), the large-scale brain network is a
114:, but most current analyses show several networks, from a small handful to 17. The most common and stable networks are enumerated below. The regions participating in a functional network may be dynamically reconfigured.
251:
This network initiates and modulates cognitive control and comprises 18 sub-regions of the brain. There is a strong correlation between fluid intelligence and the involvement of the fronto-parietal network with other
1147:
Heine, Lizette; Soddu, Andrea; Gomez, Francisco; Vanhaudenhuyse, Audrey; Tshibanda, Luaba; Thonnard, Marie; Charland-Verville, Vanessa; Kirsch, Murielle; Laureys, Steven; Demertzi, Athena (2012).
2251:
371:
Riedl, Valentin; Utz, Lukas; Castrillón, Gabriel; Grimmer, Timo; Rauschecker, Josef P.; Ploner, Markus; Friston, Karl J.; Drzezga, Alexander; Sorg, Christian (January 12, 2016).
546:
Morris, Peter G.; Smith, Stephen M.; Barnes, Gareth R.; Stephenson, Mary C.; Hale, Joanne R.; Price, Darren; Luckhoo, Henry; Woolrich, Mark; Brookes, Matthew J. (2011-10-04).
1149:"Resting state networks and consciousness. Alterations of multiple resting state network connectivity in physiological, pharmacological and pathological consciousness states"
1749:
Steimke, Rosa; Nomi, Jason S.; Calhoun, Vince D.; Stelzel, Christine; Paschke, Lena M.; Gaschler, Robert; Goschke, Thomas; Walter, Henrik; Uddin, Lucina Q. (2017-12-01).
61:(ICA), seed based, and others. Synchronized brain regions may also be identified using long-range synchronization of the EEG, MEG, or other dynamic brain signals.
2192:"Brain functional network connectivity based on a visual task: visual information processing-related brain regions are significantly activated in the task state"
945:
Abou
Elseoud, Ahmed; Littow, Harri; Remes, Jukka; Starck, Tuomo; Nikkinen, Juha; Nissilä, Juuso; Timonen, Markku; Tervonen, Osmo; Kiviniemi, Vesa (2011-06-03).
300:
Different methods and data have identified several other brain networks, many of which greatly overlap or are subsets of more well-characterized core networks.
1700:"Large-scale brain networks and intra-axial tumor surgery: a narrative review of functional mapping techniques, critical needs, and scientific opportunities"
1578:
Shafiei, Golia; Zeighami, Yashar; Clark, Crystal A.; Coull, Jennifer T.; Nagano-Saito, Atsuko; Leyton, Marco; Dagher, Alain; Mišić, Bratislav (2018-10-01).
2395:
206:
of external inputs and internal brain events. Specifically, it aids in directing attention by identifying important biological and cognitive events.
218:
attention from being distracted by non-relevant stimuli. It becomes active again when the target or relevant information about the target is found.
1962:"Functional Connectivity of Attention, Visual, and Language Networks During Audio, Illustrated, and Animated Stories in Preschool-Age Children"
2258:
1355:
Smith, SM; Fox, PT; Miller, KL; Glahn, DC; Fox, PM; Mackay, CE; Filippini, N; Watkins, KE; Toro, R; Laird, AR; Beckmann, CF (2009-08-04).
2385:
1036:
Griffiths, Kristi R.; Braund, Taylor A.; Kohn, Michael R.; Clarke, Simon; Williams, Leanne M.; Korgaonkar, Mayuresh S. (2 March 2021).
1199:
255:
Versions of this network have also been called the central executive (or executive control) network and the cognitive control network.
185:. It is negatively correlated with brain systems that focus on external visual signals. It is the most widely researched network.
1534:
Bell, Peter T.; Shine, James M. (2015-11-09). "Estimating Large-Scale
Network Convergence in the Human Functional Connectome".
165:
defined as core networks based on converging evidences from multiple studies to facilitate communication between researchers.
2309:
1832:
35:
90:
1698:
Boerger, Timothy; Pahapill, Peter; Butts, Alissa; Arocho-Quinones, Elsa; Raghavan, Manoj; Krucoff, Max (2023-07-13).
101:
Some large-scale brain networks are identified by their function and provide a coherent framework for understanding
2421:
2416:
1308:"Evaluation of the spatial variability in the major resting-state networks across human brain functional atlases"
677:
2354:
158:
58:
2009:
Fox, Michael D.; Corbetta, Maurizio; Snyder, Abraham Z.; Vincent, Justin L.; Raichle, Marcus E. (2006-06-27).
2359:
2344:
1960:
Hutton, John S.; Dudley, Jonathan; Horowitz-Kraus, Tzipi; DeWitt, Tom; Holland, Scott K. (1 September 2019).
819:
Razi, Adeel; Sadaghiani, Sepideh; Shine, James M.; Yendiki, Anastasia; Yeo, BTT; Spreng, RN (October 2023).
46:
2244:
2135:"The frontoparietal network: function, electrophysiology, and importance of individual precision mapping"
1478:
Yuan, Rui; Di, Xin; Taylor, Paul A.; Gohel, Suril; Tsai, Yuan-Hsiung; Biswal, Bharat B. (30 April 2015).
487:
Buckner, Randy L.; Andrews-Hanna, Jessica R.; Schacter, Daniel L. (2008). "The Brain's
Default Network".
1812:
2349:
2336:
117:
Disruptions in activity in various networks have been implicated in neuropsychiatric disorders such as
2457:
548:"Investigating the electrophysiological basis of resting state networks using magnetoencephalography"
2462:
2278:
343:
228:
210:
126:
75:
31:
2426:
2304:
203:
1634:
Bailey, Stephen K.; Aboud, Katherine S.; Nguyen, Tin Q.; Cutting, Laurie E. (13 December 2018).
2452:
1038:"Structural brain network topology underpinning ADHD and response to methylphenidate treatment"
245:
122:
50:
42:
1414:
Buckner, Randy L. (2012-08-15). "The serendipitous discovery of the brain's default network".
890:"The organization of the human cerebral cortex estimated by intrinsic functional connectivity"
111:
2022:
1368:
901:
743:
559:
496:
384:
265:
174:
107:
95:
373:"Metabolic connectivity mapping reveals effective connectivity in the resting human brain"
8:
2364:
821:"Controversies and progress on standardization of large-scale brain network nomenclature"
2026:
2011:"Spontaneous neuronal activity distinguishes human dorsal and ventral attention systems"
1864:"Dorsal and Ventral Attention Systems: Distinct Neural Circuits but Collaborative Roles"
1726:
1699:
1580:"Dopamine Signaling Modulates the Stability and Integration of Intrinsic Brain Networks"
1372:
905:
845:
820:
747:
563:
500:
388:
2390:
2313:
2218:
2191:
2167:
2134:
2110:
2077:
2053:
2010:
1986:
1961:
1888:
1863:
1824:
1785:
1750:
1662:
1635:
1604:
1579:
1504:
1479:
1447:
1391:
1356:
1332:
1307:
1283:
1258:
1230:
1175:
1148:
1114:
1062:
1037:
973:
946:
922:
889:
800:
705:
642:
617:
590:
547:
528:
464:
431:
407:
372:
154:
66:
2223:
2172:
2154:
2150:
2115:
2097:
2078:"Functions of the human frontoparietal attention network: Evidence from neuroimaging"
2058:
2040:
1991:
1937:
1929:
1893:
1828:
1790:
1772:
1731:
1667:
1609:
1551:
1509:
1439:
1431:
1427:
1396:
1337:
1288:
1222:
1180:
1106:
1067:
978:
927:
850:
804:
792:
697:
647:
595:
577:
520:
512:
469:
451:
447:
432:"Resting oscillations and cross-frequency coupling in the human posteromedial cortex"
412:
118:
1234:
1118:
1086:
2213:
2203:
2190:
Yang, Yan-li; Deng, Hong-xia; Xing, Gui-yang; Xia, Xiao-luan; Li, Hai-fang (2015).
2162:
2146:
2105:
2089:
2048:
2030:
1981:
1973:
1921:
1883:
1875:
1820:
1780:
1762:
1721:
1711:
1657:
1647:
1599:
1591:
1543:
1499:
1491:
1451:
1423:
1386:
1376:
1327:
1319:
1278:
1270:
1214:
1170:
1160:
1098:
1057:
1049:
968:
958:
917:
909:
840:
832:
784:
751:
709:
689:
637:
629:
585:
567:
532:
504:
459:
443:
402:
392:
195:
138:
54:
1357:"Correspondence of the brain's functional architecture during activation and rest"
209:
This network includes the ventral attention network, which primarily includes the
2411:
2093:
1087:"Large-scale brain networks and psychopathology: A unifying triple network model"
633:
338:
272:
2447:
1716:
1361:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
1274:
1102:
1053:
693:
214:
182:
1652:
1495:
1218:
756:
731:
2441:
2369:
2321:
2283:
2208:
2158:
2101:
2076:
Scolari, Miranda; Seidl-Rathkopf, Katharina N; Kastner, Sabine (2015-02-01).
2044:
1933:
1879:
1776:
1435:
1259:"Towards a Universal Taxonomy of Macro-scale Functional Human Brain Networks"
1165:
963:
581:
516:
455:
285:
271:
This network processes somatosensory information and coordinates motion. The
130:
27:
2035:
1977:
1595:
1547:
1381:
947:"Group-ICA Model Order Highlights Patterns of Functional Brain Connectivity"
572:
508:
397:
2326:
2288:
2227:
2176:
2119:
2062:
1995:
1941:
1897:
1794:
1735:
1671:
1613:
1555:
1513:
1443:
1400:
1341:
1292:
1226:
1184:
1110:
1071:
982:
931:
854:
796:
701:
651:
599:
524:
473:
416:
71:
1925:
1767:
1751:"Salience network dynamics underlying successful resistance of temptation"
1636:"Applying a network framework to the neurobiology of reading and dyslexia"
913:
678:"Large scale brain networks in cognition: emerging methods and principles"
836:
788:
38:
2267:
772:
1323:
1006:
2236:
102:
1697:
81:
149:
1480:"Functional topography of the thalamocortical system in human"
153:
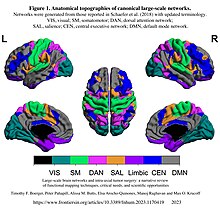
An example that identified 10 large-scale brain networks from
1146:
944:
2075:
817:
486:
259:
545:
134:
1910:
1748:
1577:
1035:
886:
370:
85:
Anatomical topographies of canonical large-scale networks
2008:
1633:
168:
1862:
Vossel, Simone; Geng, Joy J.; Fink, Gereon R. (2014).
222:
1354:
291:
This network handles visual information processing.
239:
1198:Eickhoff, SB; Yeo, BTT; Genon, S (November 2018).
2133:Marek, Scott; Dosenbach, Nico U. F. (June 2018).
1477:
1257:Uddin, LQ; Yeo, BTT; Spreng, RN (November 2019).
2439:
1305:
1200:"Imaging-based parcellations of the human brain"
1197:
1004:
189:
2189:
2015:Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
1005:Bassett, Daniella; Bertolero, Max (July 2019).
676:Bressler, Steven L.; Menon, Vinod (June 2010).
616:Petersen, Steven; Sporns, Olaf (October 2015).
552:Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
430:Foster, Brett L.; Parvizi, Josef (2012-03-01).
144:
2132:
1861:
1306:Doucet, GE; Lee, WH; Frangou, S (2019-10-15).
1256:
615:
2252:
675:
429:
1252:
1250:
1248:
1246:
1244:
618:"Brain Networks and Cognitive Architectures"
1755:Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience
2259:
2245:
1693:
1691:
1689:
1687:
1685:
1683:
1681:
1573:
1571:
1569:
1567:
1565:
1000:
998:
996:
994:
992:
671:
669:
667:
665:
663:
661:
611:
609:
489:Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences
2217:
2207:
2166:
2109:
2052:
2034:
1985:
1955:
1953:
1951:
1887:
1857:
1855:
1853:
1851:
1849:
1784:
1766:
1725:
1715:
1661:
1651:
1629:
1627:
1625:
1623:
1603:
1533:
1503:
1390:
1380:
1331:
1282:
1241:
1174:
1164:
1061:
972:
962:
921:
844:
755:
641:
589:
571:
463:
406:
396:
260:Sensorimotor or somatomotor (pericentral)
1142:
1140:
1138:
1136:
1134:
1132:
1130:
1128:
811:
729:
723:
148:
80:
1678:
1640:Journal of Neurodevelopmental Disorders
1562:
1529:
1527:
1525:
1523:
1473:
1471:
1469:
1467:
1465:
1463:
1461:
1413:
989:
658:
606:
366:
364:
362:
360:
358:
2440:
2266:
2082:Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences
1948:
1846:
1620:
882:
880:
878:
876:
874:
872:
870:
868:
866:
864:
2240:
1810:
1806:
1804:
1125:
1084:
770:
279:
2183:
1819:, Academic Press, pp. 597–611,
1520:
1458:
355:
169:Default mode (medial frontoparietal)
91:Organization for Human Brain Mapping
861:
773:"A Brain Network by Any Other Name"
41:or other recording methods such as
13:
2139:Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience
1825:10.1016/B978-0-12-397025-1.00052-X
1801:
14:
2474:
2360:Dorsal frontoparietal (Attention)
951:Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience
777:Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience
295:
223:Attention (dorsal frontoparietal)
2355:Lateral frontoparietal (Control)
1428:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.10.035
448:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.12.019
240:Control (lateral frontoparietal)
26:) are collections of widespread
2422:Psychophysiological Interaction
2417:Dynamic functional connectivity
2345:Medial frontoparietal (Default)
2298:Data acquisition and processing
2126:
2069:
2002:
1904:
1742:
1704:Frontiers in Human Neuroscience
1407:
1348:
1299:
1191:
1078:
1029:
938:
34:by statistical analysis of the
2151:10.31887/DCNS.2018.20.2/smarek
764:
539:
480:
423:
159:independent component analysis
59:independent component analysis
1:
2350:Midcingulo-insular (Salience)
349:
190:Salience (midcingulo-insular)
2196:Neural Regeneration Research
2094:10.1016/j.cobeha.2014.08.003
1815:, in Toga, Arthur W. (ed.),
1484:Brain Structure and Function
1207:Nature Reviews. Neuroscience
1091:Trends in Cognitive Sciences
771:Uddin, Lucina (2022-10-10).
730:Bressler, Steven L. (2008).
682:Trends in Cognitive Sciences
634:10.1016/j.neuron.2015.09.027
145:Commonly identified networks
16:Collections of brain regions
7:
1959:
1085:Menon, Vinod (2011-09-09).
332:
10:
2479:
1914:Journal of Neurophysiology
1717:10.3389/fnhum.2023.1170419
1275:10.1007/s10548-019-00744-6
1103:10.1016/j.tics.2011.08.003
1054:10.1038/s41398-021-01278-x
894:Journal of Neurophysiology
694:10.1016/j.tics.2010.04.004
283:
263:
243:
226:
193:
172:
20:Large-scale brain networks
2404:
2378:
2365:Pericentral (Somatomotor)
2335:
2297:
2274:
1653:10.1186/s11689-018-9251-z
1496:10.1007/s00429-015-1018-7
1219:10.1038/s41583-018-0071-7
1007:"How Matter Becomes Mind"
757:10.4249/scholarpedia.1567
732:"Neurocognitive networks"
328:Visual perception/imagery
2279:Human Connectome Project
2209:10.4103/1673-5374.152386
1880:10.1177/1073858413494269
1811:Menon, V. (2015-01-01),
1166:10.3389/fpsyg.2012.00295
1042:Translational Psychiatry
964:10.3389/fnsys.2011.00037
344:Neural network (biology)
229:Dorsal attention network
211:temporoparietal junction
127:autism spectrum disorder
24:intrinsic brain networks
2427:Dynamic causal modeling
2379:Functional modes/states
2305:Functional neuroimaging
2036:10.1073/pnas.0604187103
1978:10.1089/brain.2019.0679
1548:10.1089/brain.2015.0348
1382:10.1073/pnas.0905267106
1153:Frontiers in Psychology
573:10.1073/pnas.1112685108
509:10.1196/annals.1440.011
398:10.1073/pnas.1513752113
32:functional connectivity
246:Frontoparietal network
161:
86:
2084:. Cognitive control.
1926:10.1152/jn.00343.2003
1596:10.1093/cercor/bhy264
914:10.1152/jn.00338.2011
284:Further information:
152:
112:task-positive network
84:
837:10.1162/netn_a_00323
825:Network Neuroscience
789:10.1162/jocn_a_01925
310:Right/left executive
266:Sensorimotor network
175:Default mode network
108:default mode network
2405:Analytic strategies
2337:Functional networks
2027:2006PNAS..10310046F
2021:(26): 10046–10051.
1768:10.1093/scan/nsx123
1373:2009PNAS..10613040S
1312:Human Brain Mapping
1011:Scientific American
906:2011NatSD...2E0031H
748:2008SchpJ...3.1567B
564:2011PNAS..10816783B
558:(40): 16783–16788.
501:2008NYASA1124....1B
389:2016PNAS..113..428R
2391:Resting state fMRI
2370:Occipital (Visual)
2322:Diffusion-weighted
2268:Human connectomics
1966:Brain Connectivity
1868:The Neuroscientist
1813:"Salience Network"
1536:Brain Connectivity
280:Visual (occipital)
162:
155:resting state fMRI
87:
2435:
2434:
2396:Naturalistic fMRI
1834:978-0-12-397316-0
1761:(12): 1928–1939.
1324:10.1002/hbm.24722
1318:(15): 4577–4587.
316:Spatial attention
157:activity through
76:dynamical systems
2470:
2458:Neural circuitry
2261:
2254:
2247:
2238:
2237:
2232:
2231:
2221:
2211:
2187:
2181:
2180:
2170:
2130:
2124:
2123:
2113:
2073:
2067:
2066:
2056:
2038:
2006:
2000:
1999:
1989:
1957:
1946:
1945:
1920:(5): 3384–3397.
1908:
1902:
1901:
1891:
1859:
1844:
1843:
1842:
1841:
1808:
1799:
1798:
1788:
1770:
1746:
1740:
1739:
1729:
1719:
1695:
1676:
1675:
1665:
1655:
1631:
1618:
1617:
1607:
1575:
1560:
1559:
1531:
1518:
1517:
1507:
1490:(4): 1971–1984.
1475:
1456:
1455:
1422:(2): 1137–1145.
1411:
1405:
1404:
1394:
1384:
1352:
1346:
1345:
1335:
1303:
1297:
1296:
1286:
1263:Brain Topography
1254:
1239:
1238:
1204:
1195:
1189:
1188:
1178:
1168:
1144:
1123:
1122:
1082:
1076:
1075:
1065:
1033:
1027:
1026:
1024:
1022:
1002:
987:
986:
976:
966:
942:
936:
935:
925:
900:(3): 1125–1165.
884:
859:
858:
848:
815:
809:
808:
768:
762:
761:
759:
727:
721:
720:
718:
716:
673:
656:
655:
645:
613:
604:
603:
593:
575:
543:
537:
536:
484:
478:
477:
467:
427:
421:
420:
410:
400:
368:
275:may be included.
213:and the ventral
196:Salience network
139:bipolar disorder
55:cluster analysis
2478:
2477:
2473:
2472:
2471:
2469:
2468:
2467:
2463:Neurophysiology
2438:
2437:
2436:
2431:
2412:Network science
2400:
2374:
2331:
2293:
2270:
2265:
2235:
2188:
2184:
2131:
2127:
2074:
2070:
2007:
2003:
1958:
1949:
1909:
1905:
1860:
1847:
1839:
1837:
1835:
1809:
1802:
1747:
1743:
1696:
1679:
1632:
1621:
1584:Cerebral Cortex
1576:
1563:
1532:
1521:
1476:
1459:
1412:
1408:
1367:(31): 13040–5.
1353:
1349:
1304:
1300:
1255:
1242:
1213:(11): 672–686.
1202:
1196:
1192:
1145:
1126:
1097:(10): 483–506.
1083:
1079:
1034:
1030:
1020:
1018:
1003:
990:
943:
939:
885:
862:
816:
812:
783:(10): 363–364.
769:
765:
728:
724:
714:
712:
674:
659:
614:
607:
544:
540:
485:
481:
428:
424:
369:
356:
352:
339:Complex network
335:
298:
288:
282:
273:auditory cortex
268:
262:
248:
242:
231:
225:
198:
192:
177:
171:
147:
96:default network
70:new tools from
22:(also known as
17:
12:
11:
5:
2476:
2466:
2465:
2460:
2455:
2450:
2433:
2432:
2430:
2429:
2424:
2419:
2414:
2408:
2406:
2402:
2401:
2399:
2398:
2393:
2388:
2382:
2380:
2376:
2375:
2373:
2372:
2367:
2362:
2357:
2352:
2347:
2341:
2339:
2333:
2332:
2330:
2329:
2324:
2319:
2307:
2301:
2299:
2295:
2294:
2292:
2291:
2286:
2281:
2275:
2272:
2271:
2264:
2263:
2256:
2249:
2241:
2234:
2233:
2202:(2): 298–307.
2182:
2145:(2): 133–140.
2125:
2068:
2001:
1972:(7): 580–592.
1947:
1903:
1874:(2): 150–159.
1845:
1833:
1800:
1741:
1677:
1619:
1590:(1): 397–409.
1561:
1519:
1457:
1406:
1347:
1298:
1269:(6): 926–942.
1240:
1190:
1124:
1077:
1028:
988:
937:
860:
831:(3): 864–903.
810:
763:
722:
688:(6): 233–290.
657:
628:(1): 207–219.
605:
538:
479:
442:(1): 384–391.
422:
383:(2): 428–433.
353:
351:
348:
347:
346:
341:
334:
331:
330:
329:
326:
323:
322:Lateral visual
320:
317:
314:
311:
308:
305:
297:
296:Other networks
294:
293:
292:
281:
278:
277:
276:
264:Main article:
261:
258:
257:
256:
253:
244:Main article:
241:
238:
237:
236:
227:Main article:
224:
221:
220:
219:
215:frontal cortex
207:
194:Main article:
191:
188:
187:
186:
183:theory of mind
173:Main article:
170:
167:
146:
143:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2475:
2464:
2461:
2459:
2456:
2454:
2453:Neural coding
2451:
2449:
2446:
2445:
2443:
2428:
2425:
2423:
2420:
2418:
2415:
2413:
2410:
2409:
2407:
2403:
2397:
2394:
2392:
2389:
2387:
2384:
2383:
2381:
2377:
2371:
2368:
2366:
2363:
2361:
2358:
2356:
2353:
2351:
2348:
2346:
2343:
2342:
2340:
2338:
2334:
2328:
2325:
2323:
2320:
2317:
2316:
2311:
2310:BOLD-weighted
2308:
2306:
2303:
2302:
2300:
2296:
2290:
2287:
2285:
2284:Brain mapping
2282:
2280:
2277:
2276:
2273:
2269:
2262:
2257:
2255:
2250:
2248:
2243:
2242:
2239:
2229:
2225:
2220:
2215:
2210:
2205:
2201:
2197:
2193:
2186:
2178:
2174:
2169:
2164:
2160:
2156:
2152:
2148:
2144:
2140:
2136:
2129:
2121:
2117:
2112:
2107:
2103:
2099:
2095:
2091:
2087:
2083:
2079:
2072:
2064:
2060:
2055:
2050:
2046:
2042:
2037:
2032:
2028:
2024:
2020:
2016:
2012:
2005:
1997:
1993:
1988:
1983:
1979:
1975:
1971:
1967:
1963:
1956:
1954:
1952:
1943:
1939:
1935:
1931:
1927:
1923:
1919:
1915:
1907:
1899:
1895:
1890:
1885:
1881:
1877:
1873:
1869:
1865:
1858:
1856:
1854:
1852:
1850:
1836:
1830:
1826:
1822:
1818:
1817:Brain Mapping
1814:
1807:
1805:
1796:
1792:
1787:
1782:
1778:
1774:
1769:
1764:
1760:
1756:
1752:
1745:
1737:
1733:
1728:
1723:
1718:
1713:
1709:
1705:
1701:
1694:
1692:
1690:
1688:
1686:
1684:
1682:
1673:
1669:
1664:
1659:
1654:
1649:
1645:
1641:
1637:
1630:
1628:
1626:
1624:
1615:
1611:
1606:
1601:
1597:
1593:
1589:
1585:
1581:
1574:
1572:
1570:
1568:
1566:
1557:
1553:
1549:
1545:
1542:(9): 565–74.
1541:
1537:
1530:
1528:
1526:
1524:
1515:
1511:
1506:
1501:
1497:
1493:
1489:
1485:
1481:
1474:
1472:
1470:
1468:
1466:
1464:
1462:
1453:
1449:
1445:
1441:
1437:
1433:
1429:
1425:
1421:
1417:
1410:
1402:
1398:
1393:
1388:
1383:
1378:
1374:
1370:
1366:
1362:
1358:
1351:
1343:
1339:
1334:
1329:
1325:
1321:
1317:
1313:
1309:
1302:
1294:
1290:
1285:
1280:
1276:
1272:
1268:
1264:
1260:
1253:
1251:
1249:
1247:
1245:
1236:
1232:
1228:
1224:
1220:
1216:
1212:
1208:
1201:
1194:
1186:
1182:
1177:
1172:
1167:
1162:
1158:
1154:
1150:
1143:
1141:
1139:
1137:
1135:
1133:
1131:
1129:
1120:
1116:
1112:
1108:
1104:
1100:
1096:
1092:
1088:
1081:
1073:
1069:
1064:
1059:
1055:
1051:
1047:
1043:
1039:
1032:
1016:
1012:
1008:
1001:
999:
997:
995:
993:
984:
980:
975:
970:
965:
960:
956:
952:
948:
941:
933:
929:
924:
919:
915:
911:
907:
903:
899:
895:
891:
883:
881:
879:
877:
875:
873:
871:
869:
867:
865:
856:
852:
847:
842:
838:
834:
830:
826:
822:
814:
806:
802:
798:
794:
790:
786:
782:
778:
774:
767:
758:
753:
749:
745:
741:
737:
733:
726:
711:
707:
703:
699:
695:
691:
687:
683:
679:
672:
670:
668:
666:
664:
662:
653:
649:
644:
639:
635:
631:
627:
623:
619:
612:
610:
601:
597:
592:
587:
583:
579:
574:
569:
565:
561:
557:
553:
549:
542:
534:
530:
526:
522:
518:
514:
510:
506:
502:
498:
494:
490:
483:
475:
471:
466:
461:
457:
453:
449:
445:
441:
437:
433:
426:
418:
414:
409:
404:
399:
394:
390:
386:
382:
378:
374:
367:
365:
363:
361:
359:
354:
345:
342:
340:
337:
336:
327:
324:
321:
318:
315:
312:
309:
306:
303:
302:
301:
290:
289:
287:
286:Visual cortex
274:
270:
269:
267:
254:
250:
249:
247:
233:
232:
230:
216:
212:
208:
205:
200:
199:
197:
184:
179:
178:
176:
166:
160:
156:
151:
142:
140:
136:
132:
131:schizophrenia
128:
124:
120:
115:
113:
109:
104:
99:
97:
92:
83:
79:
77:
73:
68:
67:resting state
62:
60:
56:
52:
48:
44:
40:
37:
33:
29:
28:brain regions
25:
21:
2327:Tractography
2314:
2289:Neuroimaging
2199:
2195:
2185:
2142:
2138:
2128:
2085:
2081:
2071:
2018:
2014:
2004:
1969:
1965:
1917:
1913:
1906:
1871:
1867:
1838:, retrieved
1816:
1758:
1754:
1744:
1707:
1703:
1643:
1639:
1587:
1583:
1539:
1535:
1487:
1483:
1419:
1415:
1409:
1364:
1360:
1350:
1315:
1311:
1301:
1266:
1262:
1210:
1206:
1193:
1156:
1152:
1094:
1090:
1080:
1045:
1041:
1031:
1019:. Retrieved
1014:
1010:
954:
950:
940:
897:
893:
828:
824:
813:
780:
776:
766:
739:
736:Scholarpedia
735:
725:
713:. Retrieved
685:
681:
625:
621:
555:
551:
541:
492:
488:
482:
439:
435:
425:
380:
376:
299:
163:
116:
100:
88:
72:graph theory
63:
23:
19:
18:
742:(2): 1567.
495:(1): 1–38.
123:Alzheimer's
39:BOLD signal
2442:Categories
1840:2019-12-08
1416:NeuroImage
1048:(1): 150.
715:24 January
436:NeuroImage
350:References
313:Cerebellar
235:attention.
119:depression
57:, spatial
2386:Task fMRI
2315:task-free
2159:1294-8322
2102:2352-1546
2088:: 32–39.
2045:0027-8424
1934:0022-3077
1777:1749-5016
1646:(1): 37.
1436:1053-8119
805:252844955
582:0027-8424
517:1749-6632
456:1053-8119
252:networks.
103:cognition
2228:25883631
2177:30250390
2120:27398396
2063:16788060
1996:31144523
1942:12917383
1898:23835449
1795:29048582
1736:37520929
1727:10372448
1672:30541433
1614:30357316
1556:26005099
1514:25924563
1444:22037421
1401:19620724
1342:31322303
1293:31707621
1235:52954265
1227:30305712
1185:22969735
1119:26653572
1111:21908230
1072:33654073
983:21687724
932:21653723
855:37781138
846:10473266
797:36223250
702:20493761
652:26447582
600:21930901
525:18400922
474:22227048
417:26712010
333:See also
325:Temporal
319:Language
307:Auditory
204:salience
110:and the
30:showing
2219:4392680
2168:6136121
2111:4936532
2054:1480402
2023:Bibcode
1987:6775495
1889:4107817
1786:5716209
1663:6291929
1605:6294404
1505:6363530
1452:9880586
1392:2722273
1369:Bibcode
1333:6771873
1284:7325607
1176:3427917
1159:: 295.
1063:7925571
1021:23 June
1017:(1): 32
974:3109774
923:3174820
902:Bibcode
744:Bibcode
710:5967761
643:4598639
591:3189080
560:Bibcode
533:3167595
497:Bibcode
465:3596417
408:4720331
385:Bibcode
2226:
2216:
2175:
2165:
2157:
2118:
2108:
2100:
2061:
2051:
2043:
1994:
1984:
1940:
1932:
1896:
1886:
1831:
1793:
1783:
1775:
1734:
1724:
1670:
1660:
1612:
1602:
1554:
1512:
1502:
1450:
1442:
1434:
1399:
1389:
1340:
1330:
1291:
1281:
1233:
1225:
1183:
1173:
1117:
1109:
1070:
1060:
981:
971:
957:: 37.
930:
920:
853:
843:
803:
795:
708:
700:
650:
640:
622:Neuron
598:
588:
580:
531:
523:
515:
472:
462:
454:
415:
405:
304:Limbic
2448:Brain
1448:S2CID
1231:S2CID
1203:(PDF)
1115:S2CID
801:S2CID
706:S2CID
529:S2CID
2224:PMID
2173:PMID
2155:ISSN
2116:PMID
2098:ISSN
2059:PMID
2041:ISSN
1992:PMID
1938:PMID
1930:ISSN
1894:PMID
1829:ISBN
1791:PMID
1773:ISSN
1732:PMID
1668:PMID
1610:PMID
1552:PMID
1510:PMID
1440:PMID
1432:ISSN
1397:PMID
1338:PMID
1289:PMID
1223:PMID
1181:PMID
1107:PMID
1068:PMID
1023:2019
979:PMID
928:PMID
851:PMID
793:PMID
781:2022
717:2016
698:PMID
648:PMID
596:PMID
578:ISSN
521:PMID
513:ISSN
493:1124
470:PMID
452:ISSN
413:PMID
377:PNAS
137:and
135:ADHD
89:The
74:and
49:and
36:fMRI
2214:PMC
2204:doi
2163:PMC
2147:doi
2106:PMC
2090:doi
2049:PMC
2031:doi
2019:103
1982:PMC
1974:doi
1922:doi
1884:PMC
1876:doi
1821:doi
1781:PMC
1763:doi
1722:PMC
1712:doi
1658:PMC
1648:doi
1600:PMC
1592:doi
1544:doi
1500:PMC
1492:doi
1488:221
1424:doi
1387:PMC
1377:doi
1365:106
1328:PMC
1320:doi
1279:PMC
1271:doi
1215:doi
1171:PMC
1161:doi
1099:doi
1058:PMC
1050:doi
1015:321
969:PMC
959:doi
918:PMC
910:doi
898:106
841:PMC
833:doi
785:doi
752:doi
690:doi
638:PMC
630:doi
586:PMC
568:doi
556:108
505:doi
460:PMC
444:doi
403:PMC
393:doi
381:113
51:MEG
47:PET
43:EEG
2444::
2222:.
2212:.
2200:10
2198:.
2194:.
2171:.
2161:.
2153:.
2143:20
2141:.
2137:.
2114:.
2104:.
2096:.
2080:.
2057:.
2047:.
2039:.
2029:.
2017:.
2013:.
1990:.
1980:.
1968:.
1964:.
1950:^
1936:.
1928:.
1918:90
1916:.
1892:.
1882:.
1872:20
1870:.
1866:.
1848:^
1827:,
1803:^
1789:.
1779:.
1771:.
1759:12
1757:.
1753:.
1730:.
1720:.
1710:.
1708:17
1706:.
1702:.
1680:^
1666:.
1656:.
1644:10
1642:.
1638:.
1622:^
1608:.
1598:.
1588:29
1586:.
1582:.
1564:^
1550:.
1538:.
1522:^
1508:.
1498:.
1486:.
1482:.
1460:^
1446:.
1438:.
1430:.
1420:62
1418:.
1395:.
1385:.
1375:.
1363:.
1359:.
1336:.
1326:.
1316:40
1314:.
1310:.
1287:.
1277:.
1267:32
1265:.
1261:.
1243:^
1229:.
1221:.
1211:19
1209:.
1205:.
1179:.
1169:.
1155:.
1151:.
1127:^
1113:.
1105:.
1095:15
1093:.
1089:.
1066:.
1056:.
1046:11
1044:.
1040:.
1013:.
1009:.
991:^
977:.
967:.
953:.
949:.
926:.
916:.
908:.
896:.
892:.
863:^
849:.
839:.
827:.
823:.
799:.
791:.
779:.
775:.
750:.
738:.
734:.
704:.
696:.
686:14
684:.
680:.
660:^
646:.
636:.
626:88
624:.
620:.
608:^
594:.
584:.
576:.
566:.
554:.
550:.
527:.
519:.
511:.
503:.
491:.
468:.
458:.
450:.
440:60
438:.
434:.
411:.
401:.
391:.
379:.
375:.
357:^
141:.
133:,
129:,
125:,
121:,
78:.
45:,
2318:)
2312:(
2260:e
2253:t
2246:v
2230:.
2206::
2179:.
2149::
2122:.
2092::
2086:1
2065:.
2033::
2025::
1998:.
1976::
1970:9
1944:.
1924::
1900:.
1878::
1823::
1797:.
1765::
1738:.
1714::
1674:.
1650::
1616:.
1594::
1558:.
1546::
1540:5
1516:.
1494::
1454:.
1426::
1403:.
1379::
1371::
1344:.
1322::
1295:.
1273::
1237:.
1217::
1187:.
1163::
1157:3
1121:.
1101::
1074:.
1052::
1025:.
985:.
961::
955:5
934:.
912::
904::
857:.
835::
829:7
807:.
787::
760:.
754::
746::
740:3
719:.
692::
654:.
632::
602:.
570::
562::
535:.
507::
499::
476:.
446::
419:.
395::
387::
94:"
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.