161:, but the first one discovered in Sicily resembled the bath at Olympia, where the hip baths were in a rectangular shaped room. The Sicilian Greek baths were innovative in their own ways, specifically because they featured some of the earliest hypocaust systems known to be in Greek bath houses. The North Baths and the baths in Syracuse provide a thorough picture of the height of Greek bath design and technology. The North Baths show a complex system of rooms including reception, waiting,, and changing rooms; relaxation and bathing rooms; and rooms for the furnace, furnace service, and water reservoir. Also first appearing in these locations was the separation of the building into two different zone: one for hygienic bathing and the other for relaxing and socializing (often in an immersion pool).
333:
flooding. The floor also needed to be angled properly so the water would actually run to the drains. It is likely there was some type of waterproof pavement as well. Furthermore, the drains took the waste-water out of the bath house and dumped it outside, likely into a body of water like a canal. Unlike what was common in Roman baths, the Greeks did not often reuse the waste-water. However, there are some instances where the waste-water would be moved to foot or toilet basins. The Greek aqueducts had less output than those of the Romans, so having that water supply Greek baths was not common. Therefore, Greek baths did not have running water like the Romans. More likely is a system of changing out the water daily or regularly refilling the basins.
222:
141:
342:
294:
165:
20:
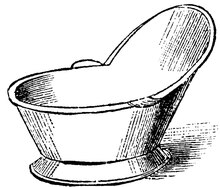
249:. While the bathing space was public, the hip baths were used individually. The construction of the hip baths varied but most were terracotta or stone. The visitor would be seated in their bath while an attendant poured water over them. This style of bathing is reminiscent of showers, where there is a flow of water over their bodies. Due to the design of the hip baths, bathers could not fully submerge their bodies under water.
277:
BCE saw a smaller room added where small built tubs were put along the north and east side and an adjacent swimming pool. The second around the end of the 4th century BCE another room was added on the west side with three of the walls being lined with additional tubs and hot water. The third renovation took place around the 1st century BCE, which saw an addition of a large apsidal room to the south along with a
324:
beforehand so that it would be a suitably warm temperature, rather than boiling hot. The continuous development of heating systems saw the rise of luxury bathing. The heating systems were of course used to heat the water but also for other types of heated bathing, such as sweat rooms, heated pools, and even heated water tanks.
42:. Some of the first baths have been dated back to the 5th century BCE. The public baths had a gradual development into the flourishing, culturally-significant structures of the Hellenistic age. The multiple locations of the baths throughout the Mediterranean offer different, culturally-unique developments.
362:
to fit the growing number of visitors. In many Greek cities, bathing came to include both individual tubs and community immersion pools and sweat baths (also communal). While the sense of community grew in public baths, it was not accepted everywhere. For example, Egypt never adopted the group baths.
45:
Greek baths did not have to follow the same design and construction rules as temples or other civic buildings in Greece and, thus, the baths were very innovative. Greek baths were always the same in their functions, but not the same in their designs. Despite the variability dependent on each location
252:
Aside from the baths themselves, there were braziers to heat the room during the winter and a furnace to heat the water. There was a specific service area for the furnace. In another room, visitors could wait for their turn or change out of their clothes. Greek baths had everything needed to offer a
234:
As a whole, Greek baths were not homogenous, especially as they spread to different regions and societal values and construction methods shifted during the
Hellenistic age. Different cities altered the layouts depending on the needs of the local population. There were, however, certain features that
78:
Public baths were not accepted immediately due to beliefs held by Greek society. The baths were an amenity that provided comfort for its users, contrasting the discipline and masculine virtues expected by Greek men. This slow acceptance resulted in a small number of public baths being built and used
323:
The way water was used in the baths depended on the way it was provisioned as well as the types of baths and heating systems. Public baths required a degree of manual movement of the water. The attendants helped the visitors bathe but they also would have needed to mix the hot water with cold water
276:
as an example, a Greek bathhouse started off as nothing more than a single rectangular structure 20 meters long and four meters wide. A well was situated at one end of the room where the athletes could draw water. The bath was renovated upon several occasions. The first being around the 5th century
314:
brought spring water from the hills and was held in a reservoir that was built next to the bath house. At the
Dipylon Baths in Athens the water was brought from a nearby well. There were also aqueducts in Athens, but, unlike Nemea, no evidence supports that they supplied the bath house with water.
128:
and several other sites. Before the
Hellenistic period, the majority of public baths were outside of the city’s walls. As baths became more accepted, their locations shifted from the outskirts to the inner parts of the city. Specifically, they would be built in very important and accessible areas.
49:
The importance of Greek baths grew overtime and became an important part to the cultures they had involvement with. In many of these cities there was a transition from individual baths to more communal baths and other spaces. Even in places that didn't embrace the communal pools, there was still a
193:
did not have direct access to each other). Or they might have been used simply to have more available bathing space. In Egypt, people bathed separately from each other, rather than in the immersion pools popular in
Western Greece. For a long time, scholars believed the Egyptian Greek baths used
332:
The hip baths and other bath tubs generally did not have run-off devices. As a result, the used water from the tubs would have been bailed out by attendants and dumped onto the floor of the room. A drainage system in the floor was necessary to remove the dumped water and prevent the room from
310:, bringing water from the ground (wells), tapping sources of flowing water nearby such as rivers and springs, and bringing water from more far-off sources. Of these, the Greeks would use the method most suitable to the local area. Take the baths at Nemea and Athens, for example. In Nemea, an
218:, a pool or pond that could be used for bathing and sometimes swimming. Gym baths did not use heated water. Domestic baths, located in private homes, were a single room with only a bath tub and some times a wash basin. Public baths are typically synonymous with Greek baths.
211:
Greek baths can be separated into three types: the gymnasium bath, the domestic bath, and the public bath. The baths at the gym were hardly even baths, rather there were basins of water where the men could stand at and clean themselves. In some cases there would be a
289:
While Greek baths grew in cultural significance, they were generally less complex than their Roman counterparts. The water management of both, however, can be put into four groups: water provisioning, water use, water disposal, and modes of operation.
353:
is the most informed area of Greek bathing culture. However, despite the situational and procedural context of every-day bathing is not often being written down from the past, the evidence from archaeological sites and art can offer information.
91:
The water for the laconia bath was heated one of two different ways. The first being by direct coal burning fires and the other being the hot rock method, which consists of heating up rocks in another room and bringing them inside the bath.
357:
By the 2nd century BCE, public baths were a very important part of Greek culture (and
Egyptian and South Italian culture), as can be seen from the developments in the design of the baths and their locations. The Egyptians added more
363:
The baths at Gortys did not have communal pools, as it did not suit their local customs. Gortys did develop individual immersion baths, which still brought a shift from hygienic bathing to bathing for relaxation purposes.
83:, the baths were at the height of their development. Individual comfort and well-being became more important to Greek society and, as a result, the number of baths increased and held a place of importance to Greek life.
58:
The earliest Greek baths date back to the first half of the 5th century BCE. While it was not the only Greek city with public baths, some of the first archaeological evidence comes from the
Dipylon Baths in Athens.
46:
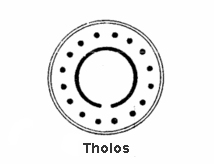
and population, there are certain features that have come to define the Greek bath. Some of the prominent elements include tholoi, hip baths and other types of baths and pools, and heating and water systems.
272:, decorated floors, and other forms of bathing aimed more at relaxation. There are several structures, such as the baths at Olympia, that show these changes and the trend of renovation. Using the
261:
67:
came upon the idea of a hot-air bath. The hot-air bath later came to be known as a laconia bath. The people of
Laconia were from the Sparta area. With this bath came the idea of a
157:
during the 4th century BCE. The baths in this region are clearly Greek, as they were brought over by new Greek inhabitants. Most baths follow the design of the hip baths in the
63:
was a place of great innovation of the public baths. The Greek's original form of bathing consisted of nothing more than a quick plunge into icy water until the people of
257:, although they were typically only deep enough for wading, not swimming. Even more rarely found in public baths are wash basins, which were common in gymnasium baths.
235:
pervaded most bathing structures. The public baths are made up of one or more rooms that are typically circular. This circular floor plan is called a
628:
349:
The culture surrounding Greek baths, and public bathing in general, is not extremely well known or studied. The use of baths for athletes at the
431:
514:
487:
407:
50:
drastic development in the technology of bath houses and the importance of bathing for relaxation as well as cleanliness.
633:
563:
253:
simple place for cleaning and the maintenance of the warm and wet spaces. Occasionally public baths would feature a
221:
273:
30:
were bath complexes suitable for bathing and cleaning in ancient Greece, similar in concept to that of the
587:
435:
350:
140:
306:
The Greeks utilized four different kinds of water provisioning: gathering and keeping rain water in
198:
was uncovered and revealed a developed, distinctly
Egyptian heating system, including heated walls.
311:
38:
countries. These baths have been found in Greece, Egypt, Italy, and there is even one located in
189:
are thought to have been used to separate men and women (further supported by the fact that the
23:
Map of the
Mediterranean. Greek baths have been found in several countries throughout this area.
341:
72:
237:
8:
372:
293:
194:
braziers to heat their water and had no other heating system. However, a new bath called
601:
581:
425:
80:
100:
Greek baths can be found throughout the
Mediterranean. In Greece they can be found in
569:
559:
493:
483:
413:
403:
154:
130:
518:
195:
134:
101:
185:
separated by a central corridor, which is a key element of these baths. The two
79:
during the 5th and 4th centuries BCE. During a time of urban refinement in the
622:
497:
417:
35:
573:
477:
397:
553:
164:
268:
The style of the baths evolved over time including larger or additional
19:
399:
Greek baths and bathing culture : new discoveries and approaches
278:
260:
242:
144:
Syracuse, Italy. Major developments in the Greek bath occurred here.
117:
39:
181:
and were built in strong numbers. Egyptian Greek baths featured two
307:
214:
121:
105:
64:
31:
109:
60:
178:
125:
113:
68:
515:"Mediterranean Baths: Early Greek and Roman Baths"
402:. Sandra K. Lucore, Monika Trümper. Leuven. 2013.
620:
327:
241:. The key feature in early Greek baths was the
129:They can also be found in other countries:
430:: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (
336:
201:
229:
340:
318:
292:
259:
220:
163:
139:
18:
558:. Örjan Wikander. Leiden: Brill. 2000.
297:Example: ruins of a Hellenistic cistern
172:
153:Greek baths reached parts of Italy and
629:Ancient Greek buildings and structures
621:
148:
16:Public bathing place in ancient Greece
475:
471:
469:
467:
465:
301:
225:A hip bath, also known as a sitz bath
555:Handbook of ancient water technology
548:
546:
544:
542:
540:
538:
536:
509:
507:
463:
461:
459:
457:
455:
453:
451:
449:
447:
445:
392:
390:
388:
34:. Greek baths are a feature of some
602:"Description of Olympia Greek Bath"
284:
13:
177:The Greek baths made their way to
14:
645:
533:
504:
479:A Companion to Greek Architecture
442:
385:
206:
86:
594:
274:Greek Baths in ancient Olympia
1:
378:
328:Water disposal and operations
95:
7:
476:Miles, Margaret M. (2016).
366:
10:
650:
53:
634:Culture of ancient Greece
337:Social life and culture
202:Floor plan and features
586:: CS1 maint: others (
346:
298:
265:
230:Key plans and features
226:
169:
145:
24:
434:) CS1 maint: others (
344:
319:Water use and heating
296:
263:
224:
168:Bathing site in Egypt
167:
143:
22:
521:on 23 September 2014
173:Egyptian Greek baths
482:. Somerset: Wiley.
373:Greek baths of Gela
149:Western Greek baths
347:
302:Water provisioning
299:
266:
227:
170:
146:
81:Hellenistic period
25:
489:978-1-118-32760-9
409:978-90-429-2897-8
264:example of tholos
131:Alexandria, Egypt
40:Marseille, France
641:
613:
612:
610:
608:
598:
592:
591:
585:
577:
550:
531:
530:
528:
526:
517:. Archived from
511:
502:
501:
473:
440:
439:
429:
421:
394:
285:Water management
245:centered in the
649:
648:
644:
643:
642:
640:
639:
638:
619:
618:
617:
616:
606:
604:
600:
599:
595:
579:
578:
566:
552:
551:
534:
524:
522:
513:
512:
505:
490:
474:
443:
423:
422:
410:
396:
395:
386:
381:
369:
345:Greek gymnasium
339:
330:
321:
304:
287:
232:
209:
204:
196:Taposiris Magna
175:
151:
135:Syracuse, Italy
98:
89:
56:
17:
12:
11:
5:
647:
637:
636:
631:
615:
614:
593:
564:
532:
503:
488:
441:
408:
383:
382:
380:
377:
376:
375:
368:
365:
338:
335:
329:
326:
320:
317:
303:
300:
286:
283:
231:
228:
208:
207:Types of baths
205:
203:
200:
174:
171:
150:
147:
97:
94:
88:
85:
73:public bathing
55:
52:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
646:
635:
632:
630:
627:
626:
624:
603:
597:
589:
583:
575:
571:
567:
565:90-04-11123-9
561:
557:
556:
549:
547:
545:
543:
541:
539:
537:
520:
516:
510:
508:
499:
495:
491:
485:
481:
480:
472:
470:
468:
466:
464:
462:
460:
458:
456:
454:
452:
450:
448:
446:
437:
433:
427:
419:
415:
411:
405:
401:
400:
393:
391:
389:
384:
374:
371:
370:
364:
361:
355:
352:
343:
334:
325:
316:
313:
309:
295:
291:
282:
280:
275:
271:
262:
258:
256:
250:
248:
244:
240:
239:
223:
219:
217:
216:
199:
197:
192:
188:
184:
180:
166:
162:
160:
156:
142:
138:
137:for example.
136:
132:
127:
123:
119:
115:
111:
107:
103:
93:
84:
82:
76:
74:
70:
66:
62:
51:
47:
43:
41:
37:
33:
29:
21:
605:. Retrieved
596:
554:
523:. Retrieved
519:the original
478:
398:
359:
356:
348:
331:
322:
305:
288:
269:
267:
254:
251:
246:
236:
233:
213:
210:
190:
186:
182:
176:
158:
155:Greek Sicily
152:
99:
90:
87:Laconia bath
77:
57:
48:
44:
27:
26:
71:along with
32:Roman baths
28:Greek baths
623:Categories
607:30 October
525:28 October
379:References
36:Hellenized
582:cite book
498:952247410
426:cite book
418:843861843
351:gymnasium
279:hypocaust
243:hip baths
118:Epidauros
96:Locations
574:43286505
367:See also
312:aqueduct
308:cisterns
281:system.
255:piscina
215:piscina
122:Messene
106:Corinth
102:Olympia
65:Laconia
54:History
572:
562:
496:
486:
416:
406:
360:tholos
270:tholoi
247:tholos
238:tholos
191:tholoi
187:tholoi
183:tholoi
159:tholos
110:Athens
61:Athens
179:Egypt
126:Nemea
114:Delos
609:2014
588:link
570:OCLC
560:ISBN
527:2014
494:OCLC
484:ISBN
436:link
432:link
414:OCLC
404:ISBN
133:and
124:,
69:spa
625::
584:}}
580:{{
568:.
535:^
506:^
492:.
444:^
428:}}
424:{{
412:.
387:^
120:,
116:,
112:,
108:,
104:,
75:.
611:.
590:)
576:.
529:.
500:.
438:)
420:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.