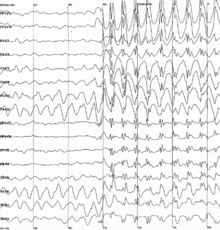
360:(EEG), which records the electrical activity of the brain. This is typically done after a seizure episode in a clinical setting with an attempt to "capture" a seizure while it happens. According to "Harrisons Manual of Medicine," the EEG during the tonic phase will show a "progressive increase in low-voltage fast wave activity, followed by generalized high-amplitude, poly spike discharges." The clonic phase EEG will show "high amplitude activity that is typically interrupted by slow waves to create a spike-and-slow-wave pattern." Additionally, the postictal phase will show suppression of all brain activity, then slowing that gradually recovers as the patient awakens.
335:
especially with a compounding central nervous system condition or a prolonged seizure. Occasionally the patient may vomit or burst into tears from the experienced mental trauma. An additional smaller seizure can also occur several minutes after the main seizure, particularly if the patient's seizure threshold has been brought unusually low by known factors or combinations of such. Examples include: severe hangovers, sleep deprivation, elevated estrogen at ovulation, prolonged physical tiredness, and drug use or abuse (including, but not limited to,
60:
295:
from it, which will cause the patient to fall if standing or sitting. There may also be upward deviation of the eyes with the mouth open. The tonic phase is usually the shortest part of the seizure, normally lasting only 10–20 seconds. The patient may also express brief vocalizations like a loud moan upon entering the tonic stage, due to air being forcefully expelled from the lungs. This vocalization is commonly referred to as an "
313:
rapidly, causing convulsions. These may range from exaggerated twitches of the limbs to violent shaking or vibrating of the stiffened extremities. The patient may roll and stretch as the seizure spreads. Initially, these contractions may be high frequency and low amplitude, which will progress to decreased frequency and high amplitude. An eventual decrease in contraction amplitude just before seizure cessation is also typical.
1462:
413:
Generalized tonic–clonic seizures can have a focal onset (described above) that progresses into a generalized seizure or be a generalized seizure at onset. The term "Grand Mal" is nonspecific, referring to generalized tonic–clonic seizures with either a focal or generalized onset. Due to this lack of
299:
cry." Starting in the tonic phase, there may also be bluing of the skin from respiration impairment as well as pooling of saliva in the back of the throat. Increased blood pressure, pupillary size and heart rate (sympathetic response) may also be noted with clenching of the jaw possibly resulting in
294:
The tonic phase is usually the first phase and consciousness will quickly be lost (though not all generalized tonic–clonic seizures involve a full loss of consciousness), and the skeletal muscles will suddenly tense, often causing the extremities to be pulled towards the body or rigidly pushed away
238:
techniques showing that there is some degree of damage to a large number of neurons. The lesions (i.e., scar tissue) caused by the loss of these neurons can result in groups of neurons forming a seizure "focus" area with episodic abnormal firing that can cause seizures if the focus is not abolished
312:
The clonic phase is an evolution of the tonic phase and is caused by muscle relaxations superimposed on the tonic phase muscle contractions. This phase is longer than the tonic phase with the total ictal period usually lasting no longer than 1 min. Skeletal muscles will start to contract and relax
384:
and/or indication to give rescue medication and call for emergency help, moving close objects out of the way to prevent injury. It is also not recommended to hold a person down that is having a seizure, as that can lead to injury. Nor should anything be put in a person's mouth, as these items can
334:
breathing. Confusion and total amnesia upon regaining consciousness are also usually experienced and slowly wear off as the patient becomes gradually aware that a seizure occurred and remembers their identity and location. Impaired consciousness duration can last several hours after a seizure,
252:
Most generalized tonic–clonic seizures begin without warning and abruptly, but some epileptic patients describe a prodrome. The prodrome of a generalized tonic–clonic seizure is a sort of premonitory feeling hours before a seizure. This type of prodrome is distinct from stereotypic
143:(a vague sense of impending seizure) may also be present before the seizure begins. The seizure itself includes both tonic and clonic contractions, with tonic contractions usually preceding clonic contractions. After these series of contractions, there is an extended
919:
904:
159:. Some generalized seizures start as a smaller seizure that occurs solely on one side of the brain, however, and is referred to as a focal (or partial) seizure. These unilateral seizure types (formerly known as
504:
Herausgeber., Kasper, Dennis L., Herausgeber. Fauci, Anthony S., Herausgeber. Hauser, Stephen L., Herausgeber. Longo, Dan L., 1949– Herausgeber. Jameson, J. Larry, Herausgeber. Loscalzo, Joseph (2016-05-27).
325:
The postictal phase causes are multifactorial to include alteration of cerebral blood flow and effects on multiple neurotransmitters. These changes after a generalized tonic–clonic seizure cause a period of
171:
of the brain and cause a generalized tonic-clonic seizure. This type of seizure has a specific term called "focal to bilateral tonic clonic seizure." Other precipitating factors include chemical and
649:
1000:
538:
818:
Michael, Glen E.; o'Connor, Robert E. (2011-02-01). "The
Diagnosis and Management of Seizures and Status Epilepticus in the Prehospital Setting".
1036:
542:
128:. It is a misconception that they are the sole type of seizure, as they are the main seizure type in approximately 10% of those with epilepsy.
653:
385:
become choking hazards and, depending on what is put in, can potentially break the person's teeth. Long-term therapy may include the use of
414:
specificity in describing the onset of a seizure and being considered an archaic term, it is not typically used by medical professionals.
695:
1404:
1321:
722:
477:
147:
where the person is unresponsive and commonly sleeping with loud snoring. There is usually pronounced confusion upon awakening.
380:
include staying with a person until a seizure is over, paying attention to length of seizure as a possible indication for
1368:
1029:
751:
Fisher, Robert S.; Schachter, Steven C. (2000). "The
Postictal State: A Neglected Entity in the Management of Epilepsy".
1298:
514:
167:
and now referred to as focal aware seizure and focal impaired awareness seizure, respectively) can then spread to both
861:
1383:
1255:
1207:
1005:
582:
17:
1326:
1129:
625:
368:
For a person experiencing a tonic–clonic seizure, first-aid treatment includes rolling the person over into the
1343:
1316:
1022:
1378:
1293:
1348:
1260:
1452:
1265:
28:
1416:
220:
1212:
934:
1177:
1142:
398:
376:
by preventing fluid from entering the lungs. Other general actions to take as recommended by the
164:
1482:
1192:
1172:
1112:
598:
458:
357:
160:
963:
699:
1250:
1197:
438:
1433:
1227:
1217:
1137:
1088:
208:
72:
8:
1421:
1388:
923:
565:
Abou-Khalil, Bassel W.; Gallagher, Martin J.; Macdonald, Robert L. (2012), "Epilepsies",
377:
188:
168:
136:
105:
1308:
1285:
574:
532:
443:
381:
267:
125:
109:
928:
730:
1373:
1202:
1045:
843:
835:
776:
768:
578:
520:
510:
433:
369:
180:
176:
79:
974:
1438:
1427:
1270:
1182:
1083:
827:
794:
760:
570:
390:
172:
674:
1466:
1410:
1275:
1240:
1078:
1073:
995:
939:
453:
428:
327:
278:
144:
1336:
1331:
1245:
1119:
1104:
1068:
394:
340:
254:
219:
and other factors. Tonic–clonic seizures can also be induced deliberately with
216:
68:
913:
831:
179:, both of which have been implicated. The seizure threshold can be altered by
1476:
1161:
1152:
1063:
990:
839:
772:
524:
423:
386:
132:
847:
780:
764:
402:
235:
184:
117:
958:
212:
1014:
896:
331:
156:
969:
336:
204:
84:
124:
and seizures in general and the most common seizure associated with
1049:
373:
344:
227:
200:
192:
140:
121:
1009:
908:
448:
273:
196:
113:
59:
564:
296:
231:
175:
imbalances and a genetically or situationally determined
131:
These seizures typically initiate abruptly with either a
34:
Type of generalized seizure that affects the entire brain
1450:
720:
886:
257:
of focal seizures that become generalized seizures.
817:
265:A tonic–clonic seizure comprises three phases: the
116:muscle contractions. Tonic–clonic seizures are the
1474:
27:"Grand mal" redirects here. For other uses, see
750:
199:-flashes or simple light/dark patterns, raised
696:"Electroconvulsive therapy-Electroshock (ECT)"
155:The vast majority of generalized seizures are
1030:
537:: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (
503:
820:Emergency Medicine Clinics of North America
1037:
1023:
729:. Epilepsy Therapy Project. Archived from
596:
541:) CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (
58:
1044:
626:"2017 Revised Classification of Seizures"
1405:Citizens United for Research in Epilepsy
999:) is being considered for deletion. See
239:or suppressed via anticonvulsant drugs.
53:Grand mal seizure, tonic–clonic seizure
721:Ruben Kuzniecky, M.D. (16 April 2004).
183:, malnutrition, lack of sleep or rest,
14:
1475:
356:Diagnosis can be made definitively by
1018:
652:. Epilepsy Foundation. Archived from
1322:Dentatorubral–pallidoluysian atrophy
620:
618:
560:
558:
556:
554:
552:
499:
497:
495:
493:
491:
489:
487:
485:
108:that produces bilateral, convulsive
1369:Sudden unexpected death in epilepsy
230:, the cause is often determined by
24:
1299:Complex partial status epilepticus
650:"Seizure Mechanisms and Threshold"
575:10.1016/b978-1-4377-0434-1.00092-x
25:
1494:
1384:Psychogenic non-epileptic seizure
1256:Benign familial neonatal seizures
1208:Sleep-related hypermotor epilepsy
1003:to help reach a consensus. ›
882:
615:
549:
482:
1460:
1006:Generalized tonic–clonic seizure
569:, Elsevier, pp. 1583–1633,
94:generalized tonic–clonic seizure
45:Generalized tonic–clonic seizure
854:
811:
787:
744:
1344:Early myoclonic encephalopathy
1317:Progressive myoclonus epilepsy
714:
688:
667:
642:
590:
567:Neurology in Clinical Practice
471:
408:
120:most commonly associated with
13:
1:
988:
464:
363:
1294:Epilepsia partialis continua
507:Harrisons manual of medicine
351:
242:
7:
1349:Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy
1327:Unverricht–Lundborg disease
597:David Y Ko (5 April 2007).
417:
226:In the case of symptomatic
10:
1499:
1266:Myoclonic astatic epilepsy
211:, rapid motion or flight,
29:Grand Mal (disambiguation)
26:
1417:Epilepsy Action Australia
1397:
1361:
1307:
1284:
1226:
1160:
1151:
1128:
1097:
1056:
949:
890:
862:"General First Aid Steps"
832:10.1016/j.emc.2010.08.003
221:electroconvulsive therapy
150:
78:
66:
57:
49:
44:
1379:Landau–Kleffner syndrome
1213:Panayiotopoulos syndrome
1001:templates for discussion
1261:Lennox–Gastaut syndrome
1143:Epilepsy and employment
753:Epilepsy & Behavior
599:"Tonic–Clonic Seizures"
399:vagus nerve stimulation
165:complex partial seizure
1193:Temporal lobe epilepsy
1113:Electroencephalography
795:"Triggers of Seizures"
765:10.1006/ebeh.2000.0023
723:"Looking at the Brain"
675:"Triggers of Seizures"
459:Electroencephalography
358:Electroencephalography
161:simple partial seizure
96:, commonly known as a
67:Generalized 3 Hz
1198:Frontal lobe epilepsy
677:. Epilepsy Foundation
439:Non-epileptic seizure
215:imbalances, anxiety,
1434:Epilepsy Research UK
1218:Vertiginous epilepsy
1138:Epilepsy and driving
1089:Epilepsy in children
372:, which can prevent
209:fluorescent lighting
126:metabolic imbalances
73:electroencephalogram
1422:Epilepsy Foundation
1389:Epilepsy in animals
1069:Aura (warning sign)
866:Epilepsy Foundation
799:Epilepsy Foundation
702:on 24 February 2021
630:Epilepsy Foundation
378:Epilepsy Foundation
106:generalized seizure
1309:Myoclonic epilepsy
1286:Status epilepticus
950:External resources
444:Tonic (physiology)
382:status epilepticus
300:biting the tongue.
195:, the presence of
1448:
1447:
1362:Related disorders
1357:
1356:
1203:Rolandic epilepsy
984:
983:
434:Epileptic seizure
393:, diet therapy (
370:recovery position
177:seizure threshold
98:grand mal seizure
90:
89:
71:discharges on an
39:Medical condition
18:Grand mal seizure
16:(Redirected from
1490:
1465:
1464:
1463:
1456:
1439:Epilepsy Society
1428:Epilepsy Outlook
1271:Epileptic spasms
1183:Gelastic seizure
1158:
1157:
1084:Neonatal seizure
1039:
1032:
1025:
1016:
1015:
888:
887:
876:
875:
873:
872:
858:
852:
851:
815:
809:
808:
806:
805:
791:
785:
784:
748:
742:
741:
739:
738:
718:
712:
711:
709:
707:
698:. Archived from
692:
686:
685:
683:
682:
671:
665:
664:
662:
661:
646:
640:
639:
637:
636:
622:
613:
612:
610:
609:
594:
588:
587:
562:
547:
546:
536:
528:
501:
480:
475:
391:surgical therapy
173:neurotransmitter
62:
42:
41:
21:
1498:
1497:
1493:
1492:
1491:
1489:
1488:
1487:
1473:
1472:
1471:
1461:
1459:
1451:
1449:
1444:
1411:Epilepsy Action
1393:
1353:
1303:
1280:
1276:Febrile seizure
1241:Absence seizure
1222:
1178:Complex partial
1147:
1130:Personal issues
1124:
1109:Investigations
1105:Anticonvulsants
1093:
1079:Epileptogenesis
1074:Postictal state
1052:
1043:
1004:
985:
980:
979:
945:
944:
899:
885:
880:
879:
870:
868:
860:
859:
855:
816:
812:
803:
801:
793:
792:
788:
749:
745:
736:
734:
719:
715:
705:
703:
694:
693:
689:
680:
678:
673:
672:
668:
659:
657:
648:
647:
643:
634:
632:
624:
623:
616:
607:
605:
595:
591:
585:
563:
550:
530:
529:
517:
502:
483:
476:
472:
467:
454:Postictal state
429:Absence seizure
420:
411:
366:
354:
328:postictal sleep
319:Postictal phase
245:
153:
145:postictal state
104:, is a type of
40:
35:
32:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1496:
1486:
1485:
1470:
1469:
1446:
1445:
1443:
1442:
1436:
1431:
1425:
1419:
1414:
1408:
1401:
1399:
1395:
1394:
1392:
1391:
1386:
1381:
1376:
1374:Todd's paresis
1371:
1365:
1363:
1359:
1358:
1355:
1354:
1352:
1351:
1346:
1341:
1340:
1339:
1337:Lafora disease
1334:
1332:MERRF syndrome
1329:
1324:
1313:
1311:
1305:
1304:
1302:
1301:
1296:
1290:
1288:
1282:
1281:
1279:
1278:
1273:
1268:
1263:
1258:
1253:
1248:
1246:Atonic seizure
1243:
1238:
1232:
1230:
1224:
1223:
1221:
1220:
1215:
1210:
1205:
1200:
1195:
1190:
1186:
1185:
1180:
1175:
1173:Simple partial
1170:
1166:
1164:
1155:
1149:
1148:
1146:
1145:
1140:
1134:
1132:
1126:
1125:
1123:
1122:
1120:Epileptologist
1117:
1116:
1115:
1107:
1101:
1099:
1095:
1094:
1092:
1091:
1086:
1081:
1076:
1071:
1066:
1060:
1058:
1054:
1053:
1042:
1041:
1034:
1027:
1019:
1013:
1012:
982:
981:
978:
977:
966:
954:
953:
951:
947:
946:
943:
942:
931:
916:
900:
895:
894:
892:
891:Classification
884:
883:External links
881:
878:
877:
853:
810:
786:
743:
713:
687:
666:
641:
614:
589:
583:
548:
516:978-0071828529
515:
481:
478:MayoClinic.org
469:
468:
466:
463:
462:
461:
456:
451:
446:
441:
436:
431:
426:
419:
416:
410:
407:
395:ketogenic diet
365:
362:
353:
350:
349:
348:
322:
321:
315:
314:
309:
308:
302:
301:
291:
290:
244:
241:
217:antihistamines
152:
149:
88:
87:
82:
76:
75:
69:spike-and-wave
64:
63:
55:
54:
51:
47:
46:
38:
33:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1495:
1484:
1483:Seizure types
1481:
1480:
1478:
1468:
1458:
1457:
1454:
1440:
1437:
1435:
1432:
1429:
1426:
1423:
1420:
1418:
1415:
1412:
1409:
1406:
1403:
1402:
1400:
1398:Organizations
1396:
1390:
1387:
1385:
1382:
1380:
1377:
1375:
1372:
1370:
1367:
1366:
1364:
1360:
1350:
1347:
1345:
1342:
1338:
1335:
1333:
1330:
1328:
1325:
1323:
1320:
1319:
1318:
1315:
1314:
1312:
1310:
1306:
1300:
1297:
1295:
1292:
1291:
1289:
1287:
1283:
1277:
1274:
1272:
1269:
1267:
1264:
1262:
1259:
1257:
1254:
1252:
1249:
1247:
1244:
1242:
1239:
1237:
1234:
1233:
1231:
1229:
1225:
1219:
1216:
1214:
1211:
1209:
1206:
1204:
1201:
1199:
1196:
1194:
1191:
1188:
1187:
1184:
1181:
1179:
1176:
1174:
1171:
1168:
1167:
1165:
1163:
1159:
1156:
1154:
1153:Seizure types
1150:
1144:
1141:
1139:
1136:
1135:
1133:
1131:
1127:
1121:
1118:
1114:
1111:
1110:
1108:
1106:
1103:
1102:
1100:
1096:
1090:
1087:
1085:
1082:
1080:
1077:
1075:
1072:
1070:
1067:
1065:
1064:Seizure types
1062:
1061:
1059:
1055:
1051:
1047:
1040:
1035:
1033:
1028:
1026:
1021:
1020:
1017:
1011:
1007:
1002:
998:
997:
992:
987:
986:
976:
972:
971:
967:
965:
961:
960:
956:
955:
952:
948:
941:
937:
936:
932:
930:
926:
925:
921:
917:
915:
911:
910:
906:
902:
901:
898:
893:
889:
867:
863:
857:
849:
845:
841:
837:
833:
829:
825:
821:
814:
800:
796:
790:
782:
778:
774:
770:
766:
762:
758:
754:
747:
733:on 2007-10-12
732:
728:
724:
717:
701:
697:
691:
676:
670:
656:on 2017-08-09
655:
651:
645:
631:
627:
621:
619:
604:
600:
593:
586:
584:9781437704341
580:
576:
572:
568:
561:
559:
557:
555:
553:
544:
540:
534:
526:
522:
518:
512:
508:
500:
498:
496:
494:
492:
490:
488:
486:
479:
474:
470:
460:
457:
455:
452:
450:
447:
445:
442:
440:
437:
435:
432:
430:
427:
425:
424:Focal seizure
422:
421:
415:
406:
404:
403:radio surgery
400:
396:
392:
388:
387:antiepileptic
383:
379:
375:
371:
361:
359:
346:
342:
338:
333:
329:
324:
323:
320:
317:
316:
311:
310:
307:
304:
303:
298:
293:
292:
289:
286:
285:
284:
282:
281:
276:
275:
270:
269:
263:
262:
258:
256:
250:
249:
240:
237:
233:
229:
224:
222:
218:
214:
210:
206:
202:
198:
194:
190:
186:
182:
178:
174:
170:
166:
162:
158:
148:
146:
142:
138:
134:
129:
127:
123:
119:
115:
111:
107:
103:
99:
95:
86:
83:
81:
77:
74:
70:
65:
61:
56:
52:
48:
43:
37:
30:
19:
1236:Tonic–clonic
1235:
994:
968:
957:
933:
918:
903:
869:. Retrieved
865:
856:
826:(1): 29–39.
823:
819:
813:
802:. Retrieved
798:
789:
759:(1): 52–59.
756:
752:
746:
735:. Retrieved
731:the original
727:epilepsy.com
726:
716:
704:. Retrieved
700:the original
690:
679:. Retrieved
669:
658:. Retrieved
654:the original
644:
633:. Retrieved
629:
606:. Retrieved
602:
592:
566:
506:
473:
412:
374:asphyxiation
367:
355:
318:
306:Clonic phase
305:
287:
279:
272:
266:
264:
260:
259:
251:
247:
246:
236:neuroimaging
225:
185:hypertension
154:
130:
118:seizure type
101:
97:
93:
91:
36:
1228:Generalised
989:‹ The
959:MedlinePlus
706:25 November
409:Terminology
288:Tonic phase
213:blood sugar
169:hemispheres
137:generalized
50:Other names
1251:Automatism
1098:Management
871:2018-12-14
804:2018-12-07
737:2008-03-19
681:2017-09-30
660:2015-11-13
635:2018-12-04
608:2008-03-19
465:References
364:Management
337:stimulants
332:stertorous
277:phase and
203:levels at
157:idiopathic
975:neuro/376
970:eMedicine
840:0733-8627
773:1525-5050
603:eMedicine
533:cite book
525:956960804
352:Diagnosis
280:postictal
243:Mechanism
234:or other
205:ovulation
139:onset. A
85:Neurology
80:Specialty
1477:Category
1467:Medicine
1189:Epilepsy
1169:Seizures
1050:epilepsy
1046:Seizures
991:template
848:21109100
781:12609127
418:See also
345:caffeine
248:Prodrome
228:epilepsy
201:estrogen
193:diabetes
141:prodrome
122:epilepsy
993:below (
940:D004830
389:drugs,
341:alcohol
283:phase.
271:phase,
181:fatigue
1453:Portal
1057:Basics
1010:Curlie
996:Curlie
964:000695
846:
838:
779:
771:
581:
523:
513:
449:Clonus
274:clonic
261:Phases
197:strobe
189:stress
151:Causes
114:clonic
1162:Focal
929:345.3
914:G40.3
401:, or
330:with
297:ictal
268:tonic
163:or a
133:focal
110:tonic
1441:(UK)
1430:(UK)
1424:(US)
1413:(UK)
1407:(US)
1048:and
935:MeSH
924:9-CM
844:PMID
836:ISSN
777:PMID
769:ISSN
708:2018
579:ISBN
543:link
539:link
521:OCLC
511:ISBN
343:and
255:aura
112:and
102:GTCS
1008:at
920:ICD
905:ICD
828:doi
761:doi
571:doi
397:),
232:MRI
135:or
100:or
1479::
973::
962::
938::
927::
912::
909:10
864:.
842:.
834:.
824:29
822:.
797:.
775:.
767:.
755:.
725:.
628:.
617:^
601:.
577:,
551:^
535:}}
531:{{
519:.
509:.
484:^
405:.
347:).
339:,
223:.
207:,
191:,
187:,
92:A
1455::
1038:e
1031:t
1024:v
922:-
907:-
897:D
874:.
850:.
830::
807:.
783:.
763::
757:1
740:.
710:.
684:.
663:.
638:.
611:.
573::
545:)
527:.
31:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.