1585:
particular, the size of the chamber is large enough to accommodate the sugar groups from lipopolysaccharides (LPS). As has been suggested by several groups, binding of substrate initiates the transport cycle. The "power stroke", that is, ATP binding that induces NBD dimerization and formation of the ATP sandwich, drives the conformational changes in the TMDs. In MsbA, the sugar head groups are sequestered within the chamber during the "power stroke". The cavity is lined with charged and polar residues that are likely solvated creating an energetically unfavorable environment for hydrophobic substrates and energetically favorable for polar moieties in amphiphilic compounds or sugar groups from LPS. Since the lipid cannot be stable for a long time in the chamber environment, lipid A and other hydrophobic molecules may "flip" into an energetically more favorable position within the outer membrane leaflet. The "flipping" may also be driven by the rigid-body shearing of the TMDs while the hydrophobic tails of the LPS are dragged through the lipid bilayer. Repacking of the helices switches the conformation into an outward-facing state. ATP hydrolysis may widen the periplasmic opening and push the substrate towards the outer leaflet of the lipid bilayer. Hydrolysis of the second ATP molecule and release of P
1133:
binding and that subsequent ATP hydrolysis introduces more limited changes. Rotation and tilting of transmembrane α-helices may both contribute to these conformational changes. Other studies have focused on confirming that ATP binding induces NBD closed dimer formation. Biochemical studies of intact transport complexes suggest that the conformational changes in the NBDs are relatively small. In the absence of ATP, the NBDs may be relatively flexible, but they do not involve a major reorientation of the NBDs with respect to the other domains. ATP binding induces a rigid body rotation of the two ABC subdomains with respect to each other, which allows the proper alignment of the nucleotide in the active site and interaction with the designated motifs. There is strong biochemical evidence that binding of two ATP molecules can be cooperative, that is, ATP must bind to the two active site pockets before the NBDs can dimerize and form the closed, catalytically active conformation.
1564:, come together to form a canonical ATP dimer sandwich, that is, the nucleotide is situated in between the P-loop and LSGGQ motif. The conformational transition from MsbA-closed-apo to MsbA-AMP-PNP involves two steps, which are more likely concerted: a ≈10° pivot of TM4/TM5 helices towards TM3/TM6, bringing the NBDs closer but not into alignment followed by tilting of TM4/TM5 helices ≈20° out of plane. The twisting motion results in the separation of TM3/TM6 helices away from TM1/TM2 leading to a change from an inward- to an outward- facing conformation. Thus, changes in both the orientation and spacing of the NBDs dramatically rearrange the packing of transmembrane helices and effectively switch access to the chamber from the inner to the outer leaflet of the membrane. The structures determined for MsbA is basis for the tilting model of transport. The structures described also highlight the dynamic nature of ABC exporters as also suggested by
1802:
transporters, cells expressing MDR1 and/or MRP1 transporters pump the calcein-AM out of the cell before esterases can hydrolyze it. This results in a lower cellular accumulation rate of calcein. The higher the MDR activity is in the cell membrane, the less
Calcein is accumulated in the cytoplasm. In MDR-expressing cells, the addition of an MDR inhibitor or an MDR substrate in excess dramatically increases the rate of Calcein accumulation. Activity of multidrug transporter is reflected by the difference between the amounts of dye accumulated in the presence and the absence of inhibitor. Using selective inhibitors, transport activity of MDR1 and MRP1 can be easily distinguished. This assay can be used to screen drugs for transporter interactions, and also to quantify the MDR activity of cells. The calcein assay is the proprietary assay of SOLVO Biotechnology.
1443:
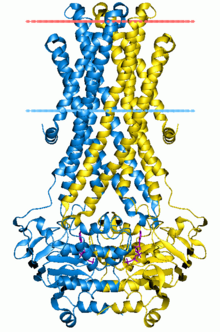
structure to those of other ABC transporters, in which the two ATP binding sites are formed at the dimer interface between the Walker A motif of one NBD and the LSGGQ motif of the other. The ADP-bound structure of Sav1866 shows the NBDs in a closed dimer and the TM helices split into two "wings" oriented towards the periplasm, forming the outward-facing conformation. Each wing consists of helices TM1-2 from one subunit and TM3-6 from the other subunit. It contains long intracellular loops (ICLs or ICD) connecting the TMDs that extend beyond the lipid bilayer into the cytoplasm and interacts with the 8=D. Whereas the importers contain a short coupling helix that contact a single NBD, Sav1866 has two intracellular coupling helices, one (ICL1) contacting the NBDs of both subunits and the other (ICL2) interacting with only the opposite NBD subunit.
1488:-terminal half of human MDR1, suggesting a common mechanism for transport of amphiphatic and hydrophobic substrates. The MsbA gene encodes a half transporter that contains a transmembrane domain (TMD) fused with a nucleotide-binding domain (NBD). It is assembled as a homodimer with a total molecular mass of 129.2 kD. MsbA contains 6 TMDs on the periplasmic side, an NBD located on the cytoplasmic side of the cell membrane, and an intracellular domain (ICD), bridging the TMD and NBD. This conserved helix extending from the TMD segments into or near the active site of the NBD is largely responsible for crosstalk between TMD and NBD. In particular, ICD1 serves as a conserved pivot about which the NBD can rotate, therefore allowing the NBD to disassociate and dimerize during ATP binding and hydrolysis.
1095:
transporters has the NBDs in an open dimer configuration, with low affinity for ATP. This open conformation possesses a chamber accessible to the interior of the transporter. The transport cycle is initiated by binding of substrate to the high-affinity site on the TMDs, which induces conformational changes in the NBDs and enhances the binding of ATP. Two molecules of ATP bind, cooperatively, to form the closed dimer configuration. The closed NBD dimer induces a conformational change in the TMDs such that the TMD opens, forming a chamber with an opening opposite to that of the initial state. The affinity of the substrate to the TMD is reduced, thereby releasing the substrate. Hydrolysis of ATP follows and then sequential release of P
1206:
nucleotide, the two ABC domains are folded and the dimer interface is open. A comparison of the structures with (BtuCDF) and without (BtuCD) binding protein reveals that BtuCD has an opening that faces the periplasm whereas in BtuCDF, the outward-facing conformation is closed to both sides of the membrane. The structures of BtuCD and the BtuCD homolog, HI1470/1, represent two different conformational states of an ABC transporter. The predicted translocation pathway in BtuCD is open to the periplasm and closed at the cytoplasmic side of the membrane while that of HI1470/1 faces the opposite direction and open only to the cytoplasm. The difference in the structures is a 9° twist of one TM subunit relative to the other.
1380:. Without the nucleotide, the TMDs are approximately parallel and form a barrel surrounding a central pore, with the opening facing towards the extracellular side of the membrane and closed at the intracellular face. In the presence of the nonhydrolyzable ATP analog, AMP-PNP, the TMDs have a substantial reorganization with three clearly segregated domains. A central pore, which is enclosed between the TMDs, is slightly open towards the intracellular face with a gap between two domains allowing access of substrate from the lipid phase. Substantial repacking and possible rotation of the TM helices upon nucleotide binding suggests a helix rotation model for the transport mechanism.
1222:-E have only six helices per subunit. The homodimer of ModBC-A is in a conformation in which the TM subunits (ModB) orient in an inverted V-shape with a cavity accessible to the cytoplasm. The ABC subunits (ModC), on the other hand, are arranged in an open, nucleotide-free conformation, in which the P-loop of one subunit faces but is detached from the LSGGQ motif of the other. The binding protein ModA is in a closed conformation with substrate bound in a cleft between its two lobes and attached to the extracellular loops of ModB, wherein the substrate is sitting directly above the closed entrance of the transporter. The MalFGK
885:. In BtuCD, the packing of the helices is complex. The noticeable pattern is that the TM2 helix is positioned through the center of the subunit where it is surrounded in close proximity by the other helices. Meanwhile, the TM5 and TM10 helices are positioned in the TMD interface. The membrane spanning region of ABC exporters is organized into two "wings" that are composed of helices TM1 and TM2 from one subunit and TM3-6 of the other, in a domain-swapped arrangement. A prominent pattern is that helices TM1-3 are related to TM4-6 by an approximate twofold rotation around an axis in the plane of the membrane.
1625:, just like the other ABC transporters, to export a large variety of drugs from the cytosol to the extracellular medium. In multidrug-resistant cells, the MDR1 gene is frequently amplified. This results in a large overproduction of the MDR1 protein. The substrates of mammalian ABCB1 are primarily planar, lipid-soluble molecules with one or more positive charges. All of these substrates compete with one another for transport, suggesting that they bind to the same or overlapping sites on the protein. Many of the drugs that are transported out by ABCB1 are small, nonpolar drugs that diffuse across the
1605:) functions in pumping tumor suppression drugs out of the cell. Pgp also called MDR1, ABCB1, is the prototype of ABC transporters and also the most extensively-studied gene. Pgp is known to transport organic cationic or neutral compounds. A few ABCC family members, also known as MRP, have also been demonstrated to confer MDR to organic anion compounds. The most-studied member in ABCG family is ABCG2, also known as BCRP (breast cancer resistance protein) confer resistance to most Topoisomerase I or II inhibitors such as topotecan, irinotecan, and doxorubicin.
1422:, the essential regulator for plant growth and development. The directional polar transport of auxin mediates plant environmental responses through processes such as phototropism and gravitropism. Two of the best studied auxin transporters, ABCB1 and ABCB19, have been characterized to be primary auxin exporters Other ABCB transporters such as ABCB4 participate in both the export and import of auxin At low intracellular auxin concentrations ABCB4 imports auxin until it reaches a certain threshold which then reverses function to only export auxin.
1104:
different steps in the transport cycle. However, recent structural and biochemical data shows that ATP binding, rather than ATP hydrolysis, provides the "power stroke". It may also be that since ATP binding triggers NBD dimerization, the formation of the dimer may represent the "power stroke." In addition, some transporters have NBDs that do not have similar abilities in binding and hydrolyzing ATP and that the interface of the NBD dimer consists of two ATP binding pockets suggests a concurrent function of the two NBDs in the transport cycle.
1193:, HI1470/1, have also been determined. The structures provided detailed pictures of the interaction of the transmembrane and ABC domains as well as revealed two different conformations with an opening in two opposite directions. Another common feature of importers is that each NBD is bound to one TMD primarily through a short cytoplasmic helix of the TMD, the "coupling helix". This portion of the EAA loop docks in a surface cleft formed between the RecA-like and helical ABC subdomains and lies approximately parallel to the membrane bilayer.
2236:
a 3 TMS precursor, and ABC3 exporters evolved from a 4 TMS precursor which duplicated either extragenicly to give two 4 TMS proteins, both required for transport function, or intragenicly to give 8 or 10 TMS proteins. The 10 TMS proteins appear to have two extra TMSs between the two 4 TMS repeat units. Most uptake systems (all except 3.A.1.21) are of the ABC2 type, divided into type I and type II by the way they handle nucleotides. A special subfamily of ABC2 importers called ECF use a separate subunit for substrate recognition.
1398:). Plant ABC proteins are categorized in 13 subfamilies on the basis of size (full, half or quarter), orientation, and overall amino acid sequence similarity. Multidrug resistant (MDR) homologs, also known as P-glycoproteins, represent the largest subfamily in plants with 22 members and the second largest overall ABC subfamily. The B subfamily of plant ABC transporters (ABCBs) are characterized by their localization to the plasma membrane. Plant ABCB transporters are characterized by heterologously expressing them in
1773:
in an ATP dependent manner. Rapid filtration using glass fiber filters or nitrocellulose membranes are used to separate the vesicles from the incubation solution and the test compound trapped inside the vesicles is retained on the filter. The quantity of the transported unlabelled molecules is determined by HPLC, LC/MS, LC/MS/MS. Alternatively, the compounds are radiolabeled, fluorescent or have a fluorescent tag so that the radioactivity or fluorescence retained on the filter can be quantified.
1346:, was originally reported in mammalian cells. In bacteria, Levy and colleagues presented the first evidence that antibiotic resistance was caused by active efflux of a drug. P-glycoprotein is the best-studied efflux pump and as such has offered important insights into the mechanism of bacterial pumps. Although some exporters transport a specific type of substrate, most transporters extrude a diverse class of drugs with varying structure. These transporters are commonly called
786:, embedded in the membrane bilayer. It recognizes a variety of substrates and undergoes conformational changes to transport the substrate across the membrane. The sequence and architecture of TMDs is variable, reflecting the chemical diversity of substrates that can be translocated. The NBD or ATP-binding cassette (ABC) domain, on the other hand, is located in the cytoplasm and has a highly conserved sequence. The NBD is the site for ATP binding. In most exporters, the
1071:. The relative binding affinities of the two conformations for the substrate largely determines the net direction of transport. For importers, since translocation is directed from the periplasm to the cytoplasm, the outward-facing conformation has higher binding affinity for the substrate. In contrast, the substrate binding affinity in exporters is greater in the inward-facing conformation. A model that describes the conformational changes in the
1781:
sensitive to the passive permeability of the compounds and therefore detects all interacting compounds. Yet, it does not provide information on whether the compound tested is an inhibitor of the transporter, or a substrate of the transporter inhibiting its function in a competitive fashion. A typical example of an indirect vesicular transport assay is the detection of the inhibition of taurocholate transport by ABCB11 (
2061:
transduction. Of the nine MRP proteins, four of them, MRP4, 5, 8, 9, (ABCC4, 5, 11, and 12), have a typical ABC structure with four domains, comprising two membrane spanning domains, with each spanning domain followed by a nucleotide binding domain. These are referred to as short MRPs. The remaining 5 MRP's (MRP1, 2, 6, 7) (ABCC1, 2, 3, 6 and 10) are known as long MRPs and feature an additional fifth domain at their
1577:
1244:
696:. Evidence has shown that placental expression of the ABC-transporters P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) are increased in preterm compared to term placentae, with P-gp expression further increased in preterm pregnancies with chorioamnionitis. To a lesser extent, increasing maternal BMI also associated with increased placental ABC-transporter expression, but only at preterm.
2198:
1252:
substrate-loaded binding protein towards the periplasmic side of the transmembrane domains, ATP binds and the NBD dimer closes. This switches the resting state of transporter into an outward-facing conformation, in which the TMDs have reoriented to receive substrate from the binding protein. After hydrolysis of ATP, the NBD dimer opens and substrate is released into the cytoplasm. Release of ADP and P
897:
40:
723:
705:
1492:
241:
229:
1376:. MDR1 consists of a functional monomer with two transmembrane domains (TMD) and two nucleotide-binding domains (NBD). This protein can transport mainly cationic or electrically neutral substrates as well as a broad spectrum of amphiphilic substrates. The structure of the full-size ABCB1 monomer was obtained in the presence and absence of nucleotide using
757:. Also, the structure of the T domains determines the specificity of each ABC protein. In the inward facing conformation, the binding site on the A domain is open directly to the surrounding aqueous solutions. This allows hydrophilic molecules to enter the binding site directly from the inner leaflet of the
6904:
Kevin; Beresini, Maureen H.; Tan, Man-Wah; Sellers, Benjamin D.; Maurer, Till; Koehler, Michael F. T.; Wecksler, Aaron T.; Kiefer, James R.; Verma, Vishal; Xu, Yiming; Nishiyama, Mireille; Payandeh, Jian; Koth, Christopher M. (May 2018). "Structural basis for dual-mode inhibition of the ABC transporter MsbA".
1633:, which block assembly of microtubules, freely cross the membrane into the cytosol, but the export of these drugs by ABCB1 reduces their concentration in the cell. Therefore, it takes a higher concentration of the drugs is required to kill the cells that express ABCB1 than those that do not express the gene.
1601:(MDR). In MDR, patients that are on medication eventually develop resistance not only to the drug they are taking but also to several different types of drugs. This is caused by several factors, one of which is increased expulsion of the drug from the cell by ABC transporters. For example, the ABCB1 protein (
1704:
the absorption of many drugs from the intestine, and pump drugs from the liver cells to the bile as a means of removing foreign substances from the body. A large number of drugs are either transported by ABC transporters themselves or affect the transport of other drugs. The latter scenario can lead to
2235:
Three families of ABC exporters are defined by their evolutionary origins. ABC1 exporters evolved by intragenic triplication of a 2 TMS precursor (TMS = transmembrane segment. A "2 TMS" protein has 2 transmembrane segments) to give 6 TMS proteins. ABC2 exporters evolved by intragenic duplication of
1780:
The vesicular transport assay can be performed in an "indirect" setting, where interacting test drugs modulate the transport rate of a reporter compound. This assay type is particularly suitable for the detection of possible drug-drug interactions and drug-endogenous substrate interactions. It is not
1772:
detects the translocation of molecules by ABC transporters. Membranes prepared under suitable conditions contain inside-out oriented vesicles with the ATP binding site and substrate binding site of the transporter facing the buffer outside. Substrates of the transporter are taken up into the vesicles
1647:
To solve the problems associated with multidrug-resistance by MDR1, different types of drugs can be used or the ABC transporters themselves must be inhibited. For other types of drugs to work, they must bypass the resistance mechanism, which is the ABC transporter. To do this other anticancer drugs
1256:
reverts the transporter into its resting state. The only inconsistency of this mechanism to the ATP-switch model is that the conformation in its resting, nucleotide-free state is different from the expected outward-facing conformation. Although that is the case, the key point is that the NBD does not
1094:
The general mechanism for the transport cycle of ABC transporters has not been fully elucidated, but substantial structural and biochemical data has accumulated to support a model in which ATP binding and hydrolysis is coupled to conformational changes in the transporter. The resting state of all ABC
1017:
residues in the LSGGQ motif. In addition, a residue that suggests the tight coupling of ATP binding and dimerization, is the conserved histidine in the H-loop. This histidine contacts residues across the dimer interface in the Walker A motif and the D loop, a conserved sequence following the Walker B
877:
and the Met transporter MetI. In the MetI transporter, a minimal set of 5 transmembrane helices constitute this fold while an additional helix is present for both ModB and MalG. The common organization of the fold is the "up-down" topology of the TM2-5 helices that lines the translocation pathway and
1793:
Efflux transporter-expressing cells actively pump substrates out of the cell, which results in a lower rate of substrate accumulation, lower intracellular concentration at steady state, or a faster rate of substrate elimination from cells loaded with the substrate. Transported radioactive substrates
1703:
In addition to conferring MDR in tumor cells, ABC transporters are also expressed in the membranes of healthy cells, where they facilitate the transport of various endogenous substances, as well as of substances foreign to the body. For instance, ABC transporters such as Pgp, the MRPs and BCRP limit
1584:
ABC exporters have a transport mechanism that is consistent with both the alternating-access model and ATP-switch model. In the apo states of exporters, the conformation is inward-facing and the TMDs and NBDs are relatively far apart to accommodate amphiphilic or hydrophobic substrates. For MsbA, in
1546:
studies. The relatively large chamber allows it to accommodate large head groups such as that present in lipid A. Significant conformational changes are required to move the large sugar head groups across the membrane. The difference between the two nucleotide-free (apo) structures is the ≈30° pivot
1230:
for ATP hydrolysis. It is in a closed conformation where it contains two ATP molecules, sandwiched between the Walker A and B motifs of one subunit and the LSGGQ motif of the other subunit. The maltose binding protein (MBP or MalE) is docked on the periplasmic side of the TM subunits (MalF and MalG)
1021:
The enzymatic hydrolysis of ATP requires proper binding of the phosphates and positioning of the γ-phosphate to the attacking water. In the nucleotide binding site, the oxygen atoms of the β- and γ-phosphates of ATP are stabilized by residues in the Walker A motif and coordinate with Mg. This Mg ion
753:. When the polypeptides are one domain, they can be referred to as a full domain, and when they are two multi-domains they can be referred to as a half domain. The T domains are each built of typically 10 membrane spanning alpha helices, through which the transported substance can cross through the
352:
Hundreds of ABC transporters have been characterized from both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. ABC genes are essential for many processes in the cell, and mutations in human genes cause or contribute to several human genetic diseases. Forty eight ABC genes have been reported in humans. Among these, many
2147:
Six half transporters with ATP binding sites on the N terminus and trans-membrane domains at the C terminus make up the ABCG subfamily. This orientation is opposite of all other ABC genes. There are only 5 ABCG genes in the human genome, but there are 15 in the
Drosophila genome and 10 in yeast.
1776:
Various types of membranes from different sources (e.g. insect cells, transfected or selected mammalian cell lines) are used in vesicular transport studies. Membranes are commercially available or can be prepared from various cells or even tissues e.g. liver canalicular membranes. This assay type
986:
MalK (TlMalK), and exporters such as TAP, HlyB, MJ0796, Sav1866, and MsbA. In these transporters, ATP is bound to the ABC domain. Two molecules of ATP are positioned at the interface of the dimer, sandwiched between the Walker A motif of one subunit and the LSGGQ motif of the other. This was first
1801:
readily penetrates into intact cells, where the endogenous esterases rapidly hydrolyze it to the fluorescent calcein. In contrast to calcein-AM, calcein has low permeability and therefore gets trapped in the cell and accumulates. As calcein-AM is an excellent substrate of the MDR1 and MRP1 efflux
1777:
has the advantage of measuring the actual disposition of the substrate across the cell membrane. Its disadvantage is that compounds with medium-to-high passive permeability are not retained inside the vesicles making direct transport measurements with this class of compounds difficult to perform.
1205:
importer, BtuCD, contains 10 TM helices and the functional unit consists of two copies each of the nucleotide binding domain (NBD) and transmembrane domain (TMD). The TMD and NBD interact with one another via the cytoplasmic loop between two TM helices and the Q loop in the ABC. In the absence of
1132:
studies have shown that ATP binding to the NBDs induces conformational changes in multidrug resistance-associated protein-1 (MRP1), HisPMQ, LmrA, and Pgp. Two dimensional crystal structures of AMP-PNP-bound Pgp showed that the major conformational change during the transport cycle occurs upon ATP
999:
Nucleotide binding is required to ensure the electrostatic and/or structural integrity of the active site and contribute to the formation of an active NBD dimer. Binding of ATP is stabilized by the following interactions: (1) ring-stacking interaction of a conserved aromatic residue preceding the
977:
Dimer formation of the two ABC domains of transporters requires ATP binding. It is generally observed that the ATP bound state is associated with the most extensive interface between ABC domains, whereas the structures of nucleotide-free transporters exhibit conformations with greater separations
6903:
Ho, Hoangdung; Miu, Anh; Alexander, Mary Kate; Garcia, Natalie K.; Oh, Angela; Zilberleyb, Inna; Reichelt, Mike; Austin, Cary D.; Tam, Christine; Shriver, Stephanie; Hu, Huiyong; Labadie, Sharada S.; Liang, Jun; Wang, Lan; Wang, Jian; Lu, Yan; Purkey, Hans E.; Quinn, John; Franke, Yvonne; Clark,
2060:
Subfamily ABCC contains thirteen members and nine of these transporters are referred to as the
Multidrug Resistance Proteins (MRPs). The MRP proteins are found throughout nature and they mediate many important functions. They are known to be involved in ion transport, toxin secretion, and signal
1694:
strategies have been applied to reverse MDR in different tumor models and this technology is effective in reversing ABC-transporter-mediated MDR in cancer cells and is therefore a promising strategy for overcoming MDR by gene therapeutic applications. RNAi technology could also be considered for
1442:
and others, which suggests similar substrate specificity to P-glycoprotein and therefore a possible common mechanism of substrate translocation. Sav1866 is a homodimer of half transporters, and each subunit contains an N-terminal TMD with six helices and a C-terminal NBD. The NBDs are similar in
740:
All ABC transport proteins share a structural organization consisting of four core domains. These domains consist of two trans-membrane (T) domains and two cytosolic (A) domains. The two T domains alternate between an inward and outward facing orientation, and the alternation is powered by the
1689:
microorganisms as well as neoplastic cells are often found to be resistant to drugs. MDR is frequently associated with overexpression of ABC transporters. Inhibition of ABC transporters by low-molecular weight compounds has been extensively investigated in cancer patients; however, the clinical
1529:
Previously published (and now retracted) X-ray structures of MsbA were inconsistent with the bacterial homolog Sav1866. The structures were reexamined and found to have an error in the assignment of the hand resulting to incorrect models of MsbA. Recently, the errors have been rectified and new
1107:
Some evidence to show that ATP binding is indeed the power stroke of the transport cycle was reported. It has been shown that ATP binding induces changes in the substrate-binding properties of the TMDs. The affinity of ABC transporters for substrates has been difficult to measure directly, and
1672:
of ABC transporters, and would thus not be transported. The other option is to use a combination of ABC inhibitory drugs and anticancer drugs at the same time. This would reverse the resistance to the anticancer drugs so that they could function as intended. The substrates that reverse the
1103:
Several groups studying ABC transporters have differing assumptions on the driving force of transporter function. It is generally assumed that ATP hydrolysis provides the principal energy input or "power stroke" for transport and that the NBDs operate alternately and are possibly involved in
853:
Most transporters have transmembrane domains that consist of a total of 12 α-helices with 6 α-helices per monomer. Since TMDs are structurally diverse, some transporters have varying number of helices (between six and eleven). The TM domains are categorized into three distinct sets of folds:
327:
appear to have evolved independently several times, and thus comprise different protein families. Like the ABC exporters, it is possible that the integral membrane proteins of ABC uptake systems also evolved at least three times independently, based on their high resolution three-dimensional
1251:
The mechanism of transport for importers supports the alternating-access model. The resting state of importers is inward-facing, where the nucleotide binding domain (NBD) dimer interface is held open by the TMDs and facing outward but occluded from the cytoplasm. Upon docking of the closed,
6287:
Kubeš M, Yang H, Richter GL, Cheng Y, Młodzińska E, Wang X, Blakeslee JJ, Carraro N, Petrášek J, Zažímalová E, Hoyerová K, Peer WA, Murphy AS (Feb 2012). "The
Arabidopsis concentration-dependent influx/efflux transporter ABCB4 regulates cellular auxin levels in the root epidermis".
1475:
that disrupt transport results in the accumulation of lipid A in the inner cell membrane resulting to cell death. It is a close bacterial homolog of P-glycoprotein (Pgp) by protein sequence homology and has overlapping substrate specificities with the MDR-ABC transporter LmrA from
1120:) in the presence of nonhydrolyzable ATP analogs, e.g. 5'-adenylyl-β-γ-imidodiphosphate (AMP-PNP), showed that ATP binding, in the absence of hydrolysis, is sufficient to reduce substrate-binding affinity. Also, ATP binding induces substantial conformational changes in the TMDs.
348:
and a range of other inherited human diseases. High level expression of the genes encoding some of these exporters in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms (including human) result in the development of resistance to multiple drugs such as antibiotics and anti-cancer agents.
836:
of a TMD fused to a nucleotide-binding domain (NBD). A full transporter is often required to gain functionality. Some ABC transporters have additional elements that contribute to the regulatory function of this class of proteins. In particular, importers have a high-affinity
1231:
and a large, occluded cavity can be found at the interface of MalF and MalG. The arrangement of the TM helices is in a conformation that is closed toward the cytoplasm but with an opening that faces outward. The structure suggests a possibility that MBP may stimulate the
1099:
and then ADP restores the transporter to its basal configuration. Although a common mechanism has been suggested, the order of substrate binding, nucleotide binding and hydrolysis, and conformational changes, as well as interactions between the domains is still debated.
2031:
maps to a region of chromosome 1p21 that contains the gene for
Stargardt's disease. This gene is found to be highly expressed in rod photoreceptors and is mutated in Stargardt's disease, recessive retinitis pigmentism, and the majority of recessive cone-rod dystrophy.
1608:
It is unclear exactly how these proteins can translocate such a wide variety of drugs, however, one model (the hydrophobic vacuum cleaner model) states that, in P-glycoprotein, the drugs are bound indiscriminately from the lipid phase based on their hydrophobicity.
1058:
and consequently transport molecules. ABC importers and exporters have a common mechanism for transporting substrates. They are similar in their structures. The model that describes the conformational changes associated with the binding of the substrate is the
968:
residue that is also important in the interaction of the ABC domain with ATP. The name ATP-binding cassette is derived from the diagnostic arrangement of the folds or motifs of this class of proteins upon formation of the ATP sandwich and ATP hydrolysis.
685:(GlcCer). Multispecific transport of diverse endogenous lipids through the MDR1 transporter can possibly affect the transbilayer distribution of lipids, in particular of species normally predominant on the inner plasma membrane leaflet such as PS and PE.
1434:. Sav1866 is a homolog of multidrug ABC transporters. It shows significant sequence similarity to human ABC transporters of subfamily B that includes MDR1 and TAP1/TAP2. The ATPase activity of Sav1866 is known to be stimulated by cancer drugs such as
1341:
Bacterial drug resistance has become an increasingly major health problem. One of the mechanisms for drug resistance is associated with an increase in antibiotic efflux from the bacterial cell. Drug resistance associated with drug efflux, mediated by
501:
importers that are also associated with virulence. Transporters are extremely vital in cell survival such that they function as protein systems that counteract any undesirable change occurring in the cell. For instance, a potential lethal increase in
2022:
24. Genes in this second subgroup are distinguished from ABCA1-like genes by having 37-38 exons as opposed to the 50 exons in ABCA1. The ABCA1 subgroup is implicated in the development of genetic diseases. In the recessive
Tangier's disease, the
1612:
The
Discovery of the first eukaryotic ABC transporter protein came from studies on tumor cells and cultured cells that exhibited resistance to several drugs with unrelated chemical structures. These cells were shown to express elevated levels of
1141:
Most ABC transporters that mediate the uptake of nutrients and other molecules in bacteria rely on a high-affinity solute binding protein (BP). BPs are soluble proteins located in the periplasmic space between the inner and outer membranes of
506:
strength is counterbalanced by activation of osmosensing ABC transporters that mediate uptake of solutes. Other than functioning in transport, some bacterial ABC proteins are also involved in the regulation of several physiological processes.
1794:
or labeled fluorescent dyes can be directly measured, or in an indirect set up, the modulation of the accumulation of a probe substrate (e.g. fluorescent dyes like rhodamine 123, or calcein) can be determined in the presence of a test drug.
2114:(ALD) which is a disease characterized by neurodegeneration and adrenal deficiency that typically is initiated in late childhood. The cells of ALD patients feature accumulation of unbranched saturated fatty acids, but the exact role of
1716:
There are a number of assay types that allow the detection of ABC transporter interactions with endogenous and xenobiotic compounds. The complexity of assay range from relatively simple membrane assays. like vesicular transport assay,
1551:
MsbA), the NBDs are aligned and although closer, have not formed an ATP sandwich, and the P loops of opposing monomers are positioned next to one another. In comparison to the open conformation, the dimer interface of the TMDs in the
1538:. The dimer contacts are concentrated between the extracellular loops and while the NBDs are ≈50Å apart, the subunits are facing each other. The distance between the residues in the site of the dimer interface have been verified by
761:. In addition, a gap in the protein is accessible directly from the hydrophobic core of the inner leaflet of the membrane bilayer. This allows hydrophobic molecules to enter the binding site directly from the inner leaflet of the
1337:
where the inner membrane ABC transporter HlyB interacts with an inner membrane fusion protein HlyD and an outer membrane facilitator TolC. TolC allows hemolysin to be transported across the two membranes, bypassing the periplasm.
4337:
Verdon G, Albers SV, Dijkstra BW, Driessen AJ, Thunnissen AM (Jul 2003). "Crystal structures of the ATPase subunit of the glucose ABC transporter from
Sulfolobus solfataricus: nucleotide-free and nucleotide-bound conformations".
2130:
Both of these subgroups are composed of genes that have ATP binding domains that are closely related to other ABC transporters, but these genes do not encode for trans-membrane domains. ABCE consists of only one member, OABP or
1004:
residue in the Walker A motif and the oxygen atoms of the β- and γ-phosphates of ATP and coordination of these phosphates and some residues in the Walker A motif with Mg ion, and (3) γ-phosphate coordination with side chain of
6843:
Zhang, Ge; Baidin, Vadim; Pahil, Karanbir S.; Moison, Eileen; Tomasek, David; Ramadoss, Nitya S.; Chatterjee, Arnab K.; McNamara, Case W.; Young, Travis S.; Schultz, Peter G.; Meredith, Timothy C.; Kahne, Daniel (7 May 2018).
5701:"Secondary and tertiary structure changes of reconstituted LmrA induced by nucleotide binding or hydrolysis. A fourier transform attenuated total reflection infrared spectroscopy and tryptophan fluorescence quenching analysis"
1054:, that is, they use energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to translocate substrates across cell membranes. These proteins harness the energy of ATP binding and/or hydrolysis to drive conformational changes in the
4571:
Schmitt L, Benabdelhak H, Blight MA, Holland IB, Stubbs MT (Jul 2003). "Crystal structure of the nucleotide-binding domain of the ABC-transporter haemolysin B: identification of a variable region within ABC helical domains".
1309:
In gram-negative organisms, ABC transporters mediate secretion of protein substrates across inner and outer membranes simultaneously without passing through the periplasm. This type of secretion is referred to as
1265:
Prokaryotic ABC exporters are abundant and have close homologues in eukaryotes. This class of transporters is studied based on the type of substrate that is transported. One class is involved in the protein (e.g.
1079:. This model presents two principal conformations of the NBDs: formation of a closed dimer upon binding two ATP molecules and dissociation to an open dimer facilitated by ATP hydrolysis and release of inorganic
1916:
These are not actually transporters but merely ATP-binding domains that were derived from the ABC family, but without the transmembrane domains. These proteins mainly regulate protein synthesis or expression.
991:
and E.c.MalK of a maltose transporter. These structures were also consistent with results from biochemical studies revealing that ATP is in close contact with residues in the P-loop and LSGGQ motif during
5663:
Kreimer DI, Chai KP, Ferro-Luzzi Ames G (Nov 2000). "Nonequivalence of the nucleotide-binding subunits of an ABC transporter, the histidine permease, and conformational changes in the membrane complex".
5538:"Combining Mutations That Inhibit Two Distinct Steps of the ATP Hydrolysis Cycle Restores Wild-Type Function in the Lipopolysaccharide Transporter and Shows that ATP Binding Triggers Transport"
745:. ATP binds to the A subunits and it is then hydrolyzed to power the alternation, but the exact process by which this happens is not known. The four domains can be present in four separate
805:
The structural architecture of ABC transporters consists minimally of two TMDs and two NBDs. Four individual polypeptide chains including two TMD and two NBD subunits, may combine to form a
1038:
in the Q-loop, or a histidine in the switch region that forms a hydrogen bond with the γ-phosphate of ATP, is found to catalyze the rate of ATP hydrolysis by promoting the attacking H
381:, and this is how some of them were first identified. When the ABC transport proteins are overexpressed in cancer cells, they can export anticancer drugs and render tumors resistant.
765:. After the ATP powered move to the outward facing conformation, molecules are released from the binding site and allowed to escape into the exoplasmic leaflet or directly into the
956:, lid or γ-phosphate switch, that connects the TMD and ABC. The Q loop is presumed to be involved in the interaction of the NBD and TMD, particularly in the coupling of nucleotide
5000:
Geourjon C, Orelle C, Steinfels E, Blanchet C, Deléage G, Di Pietro A, Jault JM (Sep 2001). "A common mechanism for ATP hydrolysis in ABC transporter and helicase superfamilies".
1556:
has extensive contacts. For both apo conformations of MsbA, the chamber opening is facing inward. The structure of MsbA-AMP-PNP (5'-adenylyl-β-γ-imidodiphosphate), obtained from
3712:"Active transport of maltose in Escherichia coli K12. Role of the periplasmic maltose-binding protein and evidence for a substrate recognition site in the cytoplasmic membrane"
3187:"Vibrio cholerae iron transport systems: roles of heme and siderophore iron transport in virulence and identification of a gene associated with multiple iron transport systems"
794:
hemolysin exporter HlyB. Importers have an inverted organization, that is, NBD-TMD-NBD-TMD, where the ABC domain is N-terminal whereas the TMD is C-terminal, such as in the
7205:
Glavinas H, Méhn D, Jani M, Oosterhuis B, Herédi-Szabó K, Krajcsi P (Jun 2008). "Utilization of membrane vesicle preparations to study drug-ABC transporter interactions".
910:). Linear representation of protein sequence above shows the relative positions of the conserved amino acid motifs in the structure (colors match with 3D structure)
2040:
The ABCB subfamily is composed of four full transporters and two half transporters. This is the only human subfamily to have both half and full types of transporters.
311:
Most of the uptake systems also have an extracytoplasmic receptor, a solute binding protein. Some homologous ATPases function in non-transport-related processes such as
3896:
Hvorup RN, Goetz BA, Niederer M, Hollenstein K, Perozo E, Locher KP (Sep 2007). "Asymmetry in the structure of the ABC transporter-binding protein complex BtuCD-BtuF".
841:
that specifically associates with the substrate in the periplasm for delivery to the appropriate ABC transporter. Exporters do not have the binding protein but have an
510:
In bacterial efflux systems, certain substances that need to be extruded from the cell include surface components of the bacterial cell (e.g. capsular polysaccharides,
7611:"The role of the conserved glycines of ATP-binding cassette signature motifs of MRP1 in the communication between the substrate-binding site and the catalytic centers"
7792:
2082:, involved in insulin secretion, neuronal function, and muscle function, are also part of this family of proteins. Mutations in SUR proteins are a potential cause of
1282:, and competence factors) export and the other in drug efflux. ABC transporters have gained extensive attention because they contribute to the resistance of cells to
196:
5587:
Martin C, Higgins CF, Callaghan R (Dec 2001). "The vinblastine binding site adopts high- and low-affinity conformations during a transport cycle of P-glycoprotein".
3491:"The cydD gene product, component of a heterodimeric ABC transporter, is required for assembly of periplasmic cytochrome c and of cytochrome bd in Escherichia coli"
4612:"The crystal structure of the MJ0796 ATP-binding cassette. Implications for the structural consequences of ATP hydrolysis in the active site of an ABC transporter"
2118:
in the process is still undetermined. In addition, the function of other ABCD genes have yet to be determined but have been thought to exert related functions in
7078:
Annaert PP, Turncliff RZ, Booth CL, Thakker DR, Brouwer KL (Oct 2001). "P-glycoprotein-mediated in vitro biliary excretion in sandwich-cultured rat hepatocytes".
308:(ATP) binding and hydrolysis to provide the energy needed for the translocation of substrates across membranes, either for uptake or for export of the substrate.
574:
receptor (SUR), ATP hydrolysis is associated with the regulation of opening and closing of ion channels carried by the ABC protein itself or other proteins.
7108:
Annaert PP, Brouwer KL (Mar 2005). "Assessment of drug interactions in hepatobiliary transport using rhodamine 123 in sandwich-cultured rat hepatocytes".
7949:
2068:
567:
7646:"ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 contains a novel C-terminal VFVNFA motif that is required for its cholesterol efflux and ApoA-I binding activities"
1966:
The ABCA subfamily is composed of 12 full transporters split into two subgroups. The first subgroup consists of seven genes that map to six different
1418:
cells to determine substrate specificity. Plant ABCB transporters have shown to transport the phytohormone indole-3-acetic acid ( IAA), also known as
3615:
Gedeon C, Behravan J, Koren G, Piquette-Miller M (2006). "Transport of glyburide by placental ABC transporters: implications in fetal drug exposure".
1108:
indirect measurements, for instance through stimulation of ATPase activity, often reflects other rate-limiting steps. Recently, direct measurement of
5536:
Simpson, Brent W.; Pahil, Karanbir S.; Owens, Tristan W.; Lundstedt, Emily A.; Davis, Rebecca M.; Kahne, Daniel; Ruiz, Natividad (20 August 2019).
1838:
This family contains some of the largest transporters (over 2,100 amino acids long). Five of them are located in a cluster in the 17q24 chromosome.
637:
is also involved in other biological processes for which lipid transport is the main function. It is found to mediate the secretion of the steroid
485:. These are high-affinity iron-chelating molecules that are secreted by bacteria and reabsorb iron into iron-siderophore complexes. The chvE-gguAB
1091:(ADP). Switching between the open and closed dimer conformations induces conformational changes in the TMD resulting in substrate translocation.
1467:(LPS), a glucosamine-based saccharolipid that makes up the outer monolayer of the outer membranes of most gram-negative bacteria. Lipid A is an
7863:
152:
140:
6506:
Chang G, Roth CB (Sep 2001). "Structure of MsbA from E. coli: a homolog of the multidrug resistance ATP binding cassette (ABC) transporters".
845:
that joins the membrane-spanning helices and the ABC domain. The ICD is believed to be responsible for communication between the TMD and NBD.
1247:
Proposed mechanism of transport for ABC importers. This alternating-access model was based on the crystal structures of ModBC-A and HI1470/1.
7746:
4232:"Cooperative, ATP-dependent association of the nucleotide binding cassettes during the catalytic cycle of ATP-binding cassette transporters"
4062:
Oldham ML, Khare D, Quiocho FA, Davidson AL, Chen J (Nov 2007). "Crystal structure of a catalytic intermediate of the maltose transporter".
790:
transmembrane domain and the C-terminal ABC domains are fused as a single polypeptide chain, arranged as TMD-NBD-TMD-NBD. An example is the
6378:
Velamakanni S, Yao Y, Gutmann DA, van Veen HW (Sep 2008). "Multidrug transport by the ABC transporter Sav1866 from
Staphylococcus aureus".
978:
between the ABC domains. Structures of the ATP-bound state of isolated NBDs have been reported for importers including HisP, GlcV, MJ1267,
550:, drugs and siderophores. They also play important roles in biosynthetic pathways, including extracellular polysaccharide biosynthesis and
319:. ABC transporters are considered to be an ABC superfamily based on the similarities of the sequence and organization of their ATP-binding
6701:
Buchaklian AH, Funk AL, Klug CS (Jul 2004). "Resting state conformation of the MsbA homodimer as studied by site-directed spin labeling".
5792:
Rosenberg MF, Velarde G, Ford RC, Martin C, Berridge G, Kerr ID, Callaghan R, Schmidlin A, Wooding C, Linton KJ, Higgins CF (Oct 2001).
4784:"Structural biology of Rad50 ATPase: ATP-driven conformational control in DNA double-strand break repair and the ABC-ATPase superfamily"
8119:
7768:
4942:"The A-loop, a novel conserved aromatic acid subdomain upstream of the Walker A motif in ABC transporters, is critical for ATP binding"
4281:
Hung LW, Wang IX, Nikaido K, Liu PQ, Ames GF, Kim SH (Dec 1998). "Crystal structure of the ATP-binding subunit of an ABC transporter".
457:. The third subgroup of ABC proteins do not function as transporters, but are rather involved in translation and DNA repair processes.
7924:
7170:
Glavinas H, Krajcsi P, Cserepes J, Sarkadi B (Jan 2004). "The role of ABC transporters in drug resistance, metabolism and toxicity".
4378:"Crystal structures of the MJ1267 ATP binding cassette reveal an induced-fit effect at the ATPase active site of an ABC transporter"
2646:
1815:
There are 49 known ABC transporters present in humans, which are classified into seven families by the Human Genome
Organization.
2003:
344:, and a large variety of primary and secondary metabolites. Some of these exporters in humans are involved in tumor resistance,
930:
that is unique to ABC transporters. The larger domain typically consists of two β-sheets and six α helices, where the catalytic
6163:"Functional expression and characterization of Arabidopsis ABCB, AUX 1 and PIN auxin transporters in Schizosaccharomyces pombe"
4472:"Crystal structure of MalK, the ATPase subunit of the trehalose/maltose ABC transporter of the archaeon Thermococcus litoralis"
2641:
1218:-E, which are in complex with their binding protein, correspond to small (Type I) ABC importers. The TMDs of ModBC-A and MalFGK
778:
5960:"Active efflux of tetracycline encoded by four genetically different tetracycline resistance determinants in Escherichia coli"
4889:
Reyes CL, Ward A, Yu J, Chang G (Feb 2006). "The structures of MsbA: Insight into ABC transporter-mediated multidrug efflux".
2139:
produced in response to certain viral infections. Each member of the ABCF subgroup consist of a pair of ATP binding domains.
1589:
separates the NBDs followed by restoration of the resting state, opening the chamber towards the cytoplasm for another cycle.
881:
The type II ABC importer fold is observed in the twenty TM helix-domain of BtuCD and in Hi1471, a homologous transporter from
7690:
7062:
3169:
2922:
2804:
1392:
is capable of encoding 120 ABC proteins compared to 50-70 ABC proteins that are encoded by the human genome and fruit flies (
108:
7680:
441:, which are present both in prokaryotes and eukaryotes, function as pumps that extrude toxins and drugs out of the cell. In
216:
6601:
Reyes CL, Chang G (May 2005). "Structure of the ABC transporter MsbA in complex with ADP.vanadate and lipopolysaccharide".
1681:
Drug resistance is a common clinical problem that occurs in patients with infectious diseases and in patients with cancer.
562:
Although most eukaryotic ABC transporters are effluxers, some are not directly involved in transporting substrates. In the
5753:"Ligand-mediated tertiary structure changes of reconstituted P-glycoprotein. A tryptophan fluorescence quenching analysis"
5700:
3236:"Sugars induce the Agrobacterium virulence genes through a periplasmic binding protein and a transmembrane signal protein"
6415:"The ATP binding cassette multidrug transporter LmrA and lipid transporter MsbA have overlapping substrate specificities"
3344:"Bacterial osmosensing: roles of membrane structure and electrostatics in lipid-protein and protein-protein interactions"
1162:. Some gram-positive bacteria have BPs fused to the transmembrane domain of the transporter itself. The first successful
8099:
944:(ΦΦΦΦD, of which Φ is a hydrophobic residue) is situated. The helical domain consists of three or four helices and the
2048:
and liver and is thought to be involved in protecting cells from toxins. Cells that overexpress this protein exhibit
1580:
Proposed mechanism of transport for ABC exporters. This model was based on structural and biochemical studies on MsbA.
1364:
P-glycoprotein (3.A.1.201.1) is a well-studied protein associated with multi-drug resistance. It belongs to the human
425:. The membrane-spanning region of the ABC transporter protects hydrophilic substrates from the lipids of the membrane
7266:
4008:
Hollenstein K, Frei DC, Locher KP (Mar 2007). "Structure of an ABC transporter in complex with its binding protein".
3545:
Pohl A, Devaux PF, Herrmann A (Mar 2005). "Function of prokaryotic and eukaryotic ABC proteins in lipid transport".
6741:
Dong J, Yang G, McHaourab HS (May 2005). "Structural basis of energy transduction in the transport cycle of MsbA".
3655:"Preterm Birth Associates With Increased Placental Expression of MDR Transporters Irrespective of Prepregnancy BMI"
2044:
was discovered as a protein overexpressed in certain drug resistant tumor cells. It is expressed primarily in the
1303:
3440:"Function of Escherichia coli MsbA, an essential ABC family transporter, in lipid A and phospholipid biosynthesis"
1201:
The BtuCD and HI1470/1 are classified as large (Type II) ABC importers. The transmembrane subunit of the vitamin B
6103:
Geisler M, Murphy AS (Feb 2006). "The ABC of auxin transport: the role of p-glycoproteins in plant development".
17:
3046:"ABC transporters as multidrug resistance mechanisms and the development of chemosensitizers for their reversal"
2075:, is also considered part of this subfamily. Cystic fibrosis occurs upon mutation and loss of function of CFTR.
7761:
7153:"ATP-Binding Cassette Efflux Transporters and Passive Membrane Permeability in Drug Absorption and Disposition"
6246:
1534:
MsbA exhibits an inverted "V" shape with a chamber accessible to the interior of the transporter suggesting an
328:
structures. ABC uptake porters take up a large variety of nutrients, biosynthetic precursors, trace metals and
204:
7776:
7736:
888:
The exporter fold is originally observed in the Sav1866 structure. It contains 12 TM helices, 6 per monomer.
610:
244:
7053:
Lage L (2009). "ABC Transporters as Target for RNA Interference-mediated Reversal of Multidrug Resistance".
2232:
The following classification system for transmembrane solute transporters has been constructed in the TCDB.
1860:
Some are located in the blood–brain barrier, liver, mitochondria, transports peptides and bile, for example.
952:, linker peptide or C motif. The ABC domain also has a glutamine residue residing in a flexible loop called
7682:
The ABC Transporters of Human Physiology and Disease: The Genetics and Biochemistry of ATP Binding Cassette
3580:
Randolph GJ (2001). "Dendritic cell migration to lymph nodes: cytokines, chemokines, and lipid mediators".
1876:
Used in ion transport, cell-surface receptors, toxin secretion. Includes the CFTR protein, which causes
4664:"ATP binding to the motor domain from an ABC transporter drives formation of a nucleotide sandwich dimer"
3653:
Scott, Hailey; Martinelli, Lilian M.; Grynspan, David; Bloise, Enrrico; Connor, Kristin L. (2022-03-24).
3343:
3295:"The Agrobacterium tumefaciens virulence gene chvE is part of a putative ABC-type sugar transport operon"
1621:(P-gp), but it is also referred to as multidrug resistance protein 1 (MDR1) or ABCB1. This protein uses
1430:
The first high-resolution structure reported for an ABC exporter was that of Sav1866 (3.A.1.106.2) from
7785:
6325:"Structure of the multidrug ABC transporter Sav1866 from Staphylococcus aureus in complex with AMP-PNP"
5231:
Hollenstein K, Dawson RJ, Locher KP (Aug 2007). "Structure and mechanism of ABC transporter proteins".
4470:
Diederichs K, Diez J, Greller G, Müller C, Breed J, Schnell C, Vonrhein C, Boos W, Welte W (Nov 2000).
2181:
2083:
646:
602:
581:
in ABC genes and rarely due to complete loss of function of single ABC proteins. Such diseases include
366:
200:
4833:"Vanadate-catalyzed photocleavage of the signature motif of an ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter"
4524:"Structure of the ABC ATPase domain of human TAP1, the transporter associated with antigen processing"
782:. The TMD, also known as membrane-spanning domain (MSD) or integral membrane (IM) domain, consists of
8124:
7754:
5081:"H662 is the linchpin of ATP hydrolysis in the nucleotide-binding domain of the ABC transporter HlyB"
2102:
The ABCD subfamily consists of four genes that encode half transporters expressed exclusively in the
1410:
987:
observed in Rad50 and reported in structures of MJ0796, the NBD subunit of the LolD transporter from
324:
121:
5903:"ABC Transporters in Multidrug Resistance and Pharmacokinetics, and Strategies for Drug Development"
866:
folds. The classification of importer folds is based on detailed characterization of the sequences.
7740:
1669:
1404:
1377:
878:
the TM1 helix wrapped around the outer, membrane-facing surface and contacts the other TM helices.
670:
630:
606:
390:
378:
4376:
Karpowich N, Martsinkevich O, Millen L, Yuan YR, Dai PL, MacVey K, Thomas PJ, Hunt JF (Jul 2001).
1290:
by pumping drugs out of the cells. A common mechanism is the overexpression of ABC exporters like
2184:
have been found to cause the ABCG2 amplification or rearrangement found in resistant cell lines.
2045:
1394:
1320:
642:
469:, and pathogenicity. Iron ABC uptake systems, for example, are important effectors of virulence.
2651:
1143:
742:
578:
442:
353:
have been characterized and shown to be causally related to diseases present in humans such as
305:
6957:"Understanding polyspecificity of multidrug ABC transporters: closing in on the gaps in ABCB1"
6324:
5624:"Intermediate structural states involved in MRP1-mediated drug transport. Role of glutathione"
4178:
873:
transporter. This diagnostic fold can also be found in the MalF and MalG TM subunits of MalFGK
7954:
6471:
6030:
3416:
2905:
Goffeau A, de Hertogh B, Baret PV (2013). "ABC Transporters". In Lane WJ, Lennarz MD (eds.).
2632:
Many structures of water-soluble domains of ABC proteins have been produced in recent years.
2119:
2079:
2049:
2019:
1629:
into the cytosol, where they block various cellular functions. Drugs such as colchicine and
1163:
1088:
772:
The common feature of all ABC transporters is that they consist of two distinct domains, the
294:
267:
are a transport system superfamily that is one of the largest and possibly one of the oldest
5794:"Repacking of the transmembrane domains of P-glycoprotein during the transport ATPase cycle"
7303:
6913:
6857:
6750:
6610:
6515:
6336:
6211:
6112:
5971:
5494:
5441:
5141:
4953:
4898:
4733:
4290:
4126:
4115:"The high-affinity E. coli methionine ABC transporter: structure and allosteric regulation"
4071:
4017:
3961:
3905:
3854:
3839:
3247:
2212:
2111:
1626:
1614:
1598:
1347:
766:
762:
758:
622:
618:
586:
370:
358:
183:
7515:"Topological analysis of integral membrane constituents of prokaryotic ABC efflux systems"
2654:, British structural biologist, first to describe structure of human ABC-transporter ABC10
2533:
3.A.1.24 The Methionine Uptake Transporter (MUT) Family (Similar to 3.A.1.3 and 3.A.1.12)
377:, and persistent and hyperinsulimenic hypoglycemia. ABC transporters are also involved in
8:
7292:"ATP-dependent transport of vinblastine in vesicles from human multidrug-resistant cells"
5485:
Senior AE, al-Shawi MK, Urbatsch IL (Dec 1995). "The catalytic cycle of P-glycoprotein".
3840:"The E. coli BtuCD structure: a framework for ABC transporter architecture and mechanism"
3648:
3646:
3160:
Scott MP, Lodish HF, Berk A, Kaiser, C, Krieger M, Bretscher A, Ploegh H, Amon A (2012).
666:
511:
7405:"Multidrug resistance proteins (MRPs/ABCCs) in cancer chemotherapy and genetic diseases"
7307:
6917:
6861:
6754:
6614:
6519:
6340:
6215:
6116:
5975:
5498:
5445:
5145:
4957:
4902:
4737:
4294:
4130:
4075:
4021:
3965:
3909:
3858:
3251:
2764:
2739:
2211:
Please expand the section to include this information. Further details may exist on the
1726:
Jeffrey P, Summerfield SG (2007). "Challenges for blood-brain barrier (BBB) screening".
1451:
MsbA (3.A.1.106.1) is a multi-drug resistant (MDR) ABC transporter and possibly a lipid
7582:
7555:
7454:"A functional-phylogenetic classification system for transmembrane solute transporters"
7429:
7404:
7377:
7350:
7230:
7152:
7133:
7035:
6981:
6956:
6937:
6880:
6845:
6820:
6793:
6774:
6672:
6664:
6634:
6569:
6561:
6480:
6455:
6360:
6136:
6080:
6053:
5935:
5902:
5861:
5733:
5564:
5537:
5518:
5467:
5398:
5373:
5304:
5105:
5080:
4979:
4922:
4813:
4756:
4721:
4688:
4663:
4314:
4258:
4231:
4209:
4147:
4114:
4095:
4041:
3985:
3952:
Dawson RJ, Locher KP (Sep 2006). "Structure of a bacterial multidrug ABC transporter".
3929:
3878:
3810:
3785:
3692:
3507:
3490:
3374:
3072:
3045:
3016:
2991:
2967:
2942:
2914:
2875:
2850:
2777:
1751:
1464:
674:
531:
389:
ABC transporters utilize the energy of ATP binding and hydrolysis to transport various
7326:
7291:
7258:
5994:
5959:
5878:
5845:
5818:
5793:
5622:
Manciu L, Chang XB, Buyse F, Hou YX, Gustot A, Riordan JR, Ruysschaert JM (Jan 2003).
5454:
5429:
5205:
5188:
5013:
4859:
4832:
4800:
4783:
4679:
4585:
4548:
4523:
4496:
4471:
4394:
4377:
4351:
3728:
3643:
3319:
3294:
3211:
3186:
3130:
3113:
2712:
2679:
2018:. A8-10. All of subgroup 2 is organized into a head to tail cluster of chromosomes on
145:
7686:
7667:
7632:
7587:
7554:
Zheng, WH; Västermark, Å; Shlykov, MA; Reddy, V; Sun, EI; Saier MH, Jr (6 May 2013).
7536:
7483:
7478:
7453:
7434:
7420:
7382:
7331:
7272:
7262:
7222:
7187:
7125:
7087:
7058:
7027:
6986:
6929:
6885:
6825:
6766:
6718:
6653:
6626:
6550:
6531:
6485:
6436:
6395:
6352:
6305:
6301:
6269:
6227:
6184:
6179:
6162:
6128:
6085:
6034:
5999:
5940:
5922:
5918:
5883:
5865:
5823:
5774:
5725:
5681:
5645:
5604:
5569:
5510:
5506:
5459:
5403:
5339:
5296:
5248:
5210:
5169:
5164:
5129:
5110:
5058:
5017:
4971:
4914:
4864:
4805:
4782:
Hopfner KP, Karcher A, Shin DS, Craig L, Arthur LM, Carney JP, Tainer JA (Jun 2000).
4761:
4693:
4633:
4589:
4553:
4501:
4447:
4399:
4355:
4318:
4306:
4263:
4201:
4152:
4087:
4033:
3977:
3921:
3870:
3815:
3733:
3696:
3684:
3676:
3632:
3597:
3562:
3512:
3471:
3420:
3366:
3324:
3275:
3270:
3235:
3216:
3202:
3165:
3135:
3077:
3021:
2972:
2918:
2880:
2800:
2769:
2717:
2699:
2536:
3.A.1.27 The γ-Hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) Family (Similar to 3.A.1.24 and 3.A.1.12)
2420:
3.A.1.146: The actinorhodin (ACT) and undecylprodigiosin (RED) exporter (ARE) family
2302:
3.A.1.202 The Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Exporter (CFTR) Family (ABCC)
1743:
1517:
1507:
1497:
1287:
1000:
Walker A motif and the adenosine ring of ATP, (2) hydrogen-bonds between a conserved
902:
728:
710:
626:
590:
362:
191:
113:
7234:
6941:
6638:
6364:
6140:
5737:
5522:
5471:
5308:
4983:
4926:
4817:
4426:"A tweezers-like motion of the ATP-binding cassette dimer in an ABC transport cycle"
4213:
3989:
3933:
3378:
3310:
2781:
2695:
1755:
77:
7777:
7657:
7622:
7577:
7567:
7526:
7473:
7469:
7465:
7424:
7416:
7372:
7362:
7321:
7311:
7254:
7214:
7179:
7137:
7117:
7039:
7017:
6976:
6968:
6921:
6875:
6865:
6815:
6805:
6778:
6758:
6710:
6687:
6683:
6649:
6645:
6618:
6584:
6580:
6546:
6542:
6523:
6475:
6467:
6426:
6413:
Reuter G, Janvilisri T, Venter H, Shahi S, Balakrishnan L, van Veen HW (Sep 2003).
6387:
6344:
6297:
6261:
6219:
6174:
6120:
6075:
6065:
6026:
5989:
5979:
5930:
5914:
5873:
5857:
5813:
5805:
5764:
5715:
5673:
5635:
5596:
5559:
5549:
5502:
5449:
5393:
5385:
5331:
5288:
5240:
5200:
5159:
5149:
5100:
5092:
5048:
5009:
4961:
4906:
4854:
4844:
4795:
4751:
4741:
4683:
4675:
4662:
Smith PC, Karpowich N, Millen L, Moody JE, Rosen J, Thomas PJ, Hunt JF (Jul 2002).
4623:
4581:
4543:
4535:
4491:
4483:
4437:
4389:
4347:
4298:
4253:
4243:
4193:
4142:
4134:
4099:
4079:
4045:
4025:
3969:
3913:
3862:
3805:
3797:
3723:
3666:
3628:
3624:
3589:
3554:
3502:
3461:
3451:
3412:
3358:
3314:
3306:
3265:
3255:
3206:
3198:
3125:
3067:
3057:
3011:
3003:
2962:
2954:
2910:
2870:
2862:
2759:
2751:
2707:
2691:
2148:
The ABCG2 gene was discovered in cell lines selected for high level resistance for
2136:
1735:
1705:
1649:
1543:
1350:(MDR) ABC transporters and sometimes referred to as "hydrophobic vacuum cleaners".
1227:
1051:
869:
The type I ABC importer fold was originally observed in the ModB TM subunit of the
682:
179:
7022:
7005:
6527:
6348:
6124:
4966:
4941:
4910:
3882:
2311:
3.A.1.208 The Drug Conjugate Transporter (DCT) Family (ABCC) (Dębska et al., 2011)
1944:
Transports lipids, diverse drug substrates, bile, cholesterol, and other steroids.
1547:
of TM4/TM5 helices relative to the TM3/TM6 helices. In the closed apo state (from
481:, to scavenge iron that is in complex with high-affinity iron-binding proteins or
157:
7781:
7696:
7531:
7514:
7495:
6810:
5053:
5036:
4442:
4425:
3558:
3362:
2592:
2444:
2401:
2338:
2245:
2072:
1877:
1841:
Responsible for the transportation of cholesterol and lipids, among other things.
754:
594:
563:
354:
345:
312:
133:
89:
7644:
Fitzgerald ML, Okuhira K, Short GF, Manning JJ, Bell SA, Freeman MW (Nov 2004).
4179:"An inward-facing conformation of a putative metal-chelate-type ABC transporter"
692:, indicating they could play a protective role for the developing fetus against
7858:
7296:
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
6972:
6792:
Borbat PP, Surendhran K, Bortolus M, Zou P, Freed JH, Mchaourab HS (Oct 2007).
5964:
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
5809:
5279:
Higgins CF, Linton KJ (Oct 2004). "The ATP switch model for ABC transporters".
5134:
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
4837:
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
4726:
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
4539:
4487:
3240:
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
2417:
3.A.1.145: Peptidase Fused Functionally Uncharacterized ABC2-2 (ABC2-2) Family
1657:
1653:
1622:
1618:
1602:
1568:
and EPR studies. Recent work has resulted in the discovery of MsbA inhibitors.
1359:
1343:
1291:
1117:
634:
446:
7718:
7367:
6925:
6223:
5389:
5335:
5244:
4610:
Yuan YR, Blecker S, Martsinkevich O, Millen L, Thomas PJ, Hunt JF (Aug 2001).
3711:
2958:
2851:"Structure, function, and evolution of bacterial ATP-binding cassette systems"
2755:
2740:"The ABC transporter structure and mechanism: perspectives on recent research"
2209:
about Pfam/InterPro mapping (bit hard to make, need them to improve data too).
1739:
8113:
7218:
7183:
6794:"Conformational motion of the ABC transporter MsbA induced by ATP hydrolysis"
5926:
5869:
5769:
5752:
5720:
5096:
3680:
3671:
3654:
3456:
3439:
3403:
Davidson AL, Chen J (2004). "ATP-binding cassette transporters in bacteria".
2943:"Membrane porters of ATP-binding cassette transport systems are polyphyletic"
2703:
2165:
2087:
1159:
1147:
1042:
O. The precise molecular mechanism of ATP hydrolysis is still controversial.
960:
to the conformational changes of the TMD during substrate translocation. The
932:
783:
678:
654:
515:
426:
394:
320:
293:
ABC transporters often consist of multiple subunits, one or two of which are
7572:
7316:
6870:
6846:"Cell-based screen for discovering lipopolysaccharide biogenesis inhibitors"
6762:
6622:
6070:
5154:
4746:
4197:
4138:
3917:
3866:
3260:
50:
7671:
7662:
7645:
7636:
7627:
7610:
7591:
7540:
7487:
7438:
7386:
7226:
7191:
7129:
7121:
7091:
7031:
6990:
6933:
6889:
6829:
6770:
6722:
6657:
6630:
6554:
6535:
6489:
6440:
6431:
6414:
6399:
6356:
6309:
6273:
6231:
6188:
6132:
6089:
6038:
5984:
5944:
5846:"Genetic analysis of an MDR-like export system: the secretion of colicin V"
5827:
5778:
5729:
5699:
Vigano C, Margolles A, van Veen HW, Konings WN, Ruysschaert JM (Apr 2000).
5685:
5649:
5640:
5623:
5608:
5573:
5463:
5407:
5343:
5300:
5252:
5114:
5062:
5021:
4975:
4918:
4868:
4849:
4809:
4765:
4697:
4637:
4628:
4611:
4593:
4557:
4505:
4451:
4403:
4359:
4267:
4248:
4205:
4156:
4091:
4037:
3981:
3925:
3874:
3819:
3688:
3636:
3601:
3593:
3566:
3424:
3370:
3139:
3081:
3062:
3025:
2976:
2884:
2773:
2457:
3.A.1.211 The Cholesterol/Phospholipid/Retinal (CPR) Flippase Family (ABCA)
2173:
2149:
1747:
1718:
1565:
1279:
1275:
1121:
750:
746:
658:
571:
543:
482:
478:
474:
369:, Byler's disease, progressive familiar intrahepatic cholestasis, X-linked
298:
272:
7609:
Szentpétery Z, Kern A, Liliom K, Sarkadi B, Váradi A, Bakos E (Oct 2004).
7335:
7276:
6661:. If this is an intentional citation to a retracted paper, please replace
6558:. If this is an intentional citation to a retracted paper, please replace
6003:
5887:
5554:
5514:
5214:
5173:
4722:"Flexibility in the ABC transporter MsbA: Alternating access with a twist"
4310:
3737:
3547:
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids
3516:
3475:
3328:
3279:
3220:
3007:
2866:
2721:
2305:
3.A.1.203 The Peroxysomal Fatty Acyl CoA Transporter (P-FAT) Family (ABCD)
1306:(BCRP/ABCG2) in cancer cells that limit the exposure to anticancer drugs.
397:. They are divided into three main functional categories. In prokaryotes,
117:
7556:"Evolutionary relationships of ATP-Binding Cassette (ABC) uptake porters"
6054:"Plant Lessons: Exploring ABCB Functionality Through Structural Modeling"
2177:
1682:
1665:
1630:
1439:
1435:
1283:
1155:
1109:
814:
662:
638:
614:
598:
547:
539:
422:
287:
268:
4083:
4029:
3973:
1597:
ABC transporters are known to play a crucial role in the development of
1495:
Structures of MsbA depicting the three conformational states: open apo (
749:, which occur mostly in bacteria, or present in one or two multi-domain
577:
Human ABC transporters are involved in several diseases that arise from
6265:
5130:"Ras-catalyzed hydrolysis of GTP: a new perspective from model studies"
3466:
2103:
2062:
1967:
1897:
1711:
1686:
1539:
1167:
1129:
957:
787:
693:
633:(MDR) against a variety of structurally unrelated drugs. ABCB1 or MDR1
551:
430:
410:
316:
279:
101:
6714:
6391:
5600:
5079:
Zaitseva J, Jenewein S, Jumpertz T, Holland IB, Schmitt L (Jun 2005).
1521:
1511:
1501:
906:
732:
714:
5751:
Sonveaux N, Vigano C, Shapiro AB, Ling V, Ruysschaert JM (Jun 1999).
5677:
5322:
Locher KP (Aug 2004). "Structure and mechanism of ABC transporters".
2169:
2091:
1695:
overcoming MDR in infectious diseases caused by microbial pathogens.
1661:
1472:
1468:
1330:
1271:
1257:
dimerize unless ATP and binding protein is bound to the transporter.
1151:
1080:
1035:
1031:
1023:
993:
965:
870:
825:
799:
645:
immune cells, possibly related to the outward transport of the lipid
582:
519:
498:
470:
466:
454:
450:
5292:
3801:
688:
More recently, ABC-transporters have been shown to exist within the
8077:
2587:
2451:
3.A.1.204 The Eye Pigment Precursor Transporter (EPP) Family (ABCG)
2439:
2396:
2395:
3.A.1.141 The Ethyl Viologen Exporter (EVE) Family (DUF990 Family;
2333:
2296:
3.A.1.139 The UDP-Glucose Exporter (U-GlcE) Family (UPF0014 Family)
2240:
1636:
Other ABC transporters that contribute to multidrug resistance are
1452:
1174:. Atomic-resolution structures of three other bacterial importers,
1125:
1113:
833:
689:
650:
527:
402:
329:
233:
84:
6955:
Gutmann DA, Ward A, Urbatsch IL, Chang G, van Veen HW (Jan 2010).
4302:
3614:
3438:
Zhou Z, White KA, Polissi A, Georgopoulos C, Raetz CR (May 1998).
649:(PAF). It has also been reported that ABCB1 mediates transport of
2308:
3.A.1.206 The a-Factor Sex Pheromone Exporter (STE) Family (ABCB)
1937:
Consists of 6 "reverse" half-transporters, with the NBF at the NH
1798:
1460:
1182:
1014:
923:
820:. Most exporters, such as in the multidrug exporter Sav1866 from
629:, and others. The human ABCB (MDR/TAP) family is responsible for
503:
494:
414:
301:
96:
6202:
Blakeslee JJ, Peer WA, Murphy AS (Oct 2005). "Auxin transport".
4375:
2320:
3.A.1.212 The Mitochondrial Peptide Exporter (MPE) Family (ABCB)
2197:
900:
Structure of the NBD of ABC transporters with bound nucleotide (
585:
diseases and complex genetic disorders such as cystic fibrosis,
7978:
7973:
7968:
7903:
7842:
7837:
7727:
6245:
Kretzschmar T, Burla B, Lee Y, Martinoia E, Nagy R (Sep 2011).
5078:
4999:
4570:
2559:
3.A.1.26 The Putative Thiamine Uptake Transporter (ThiW) Family
2435:
3.A.1.151: Functionally Uncharacterized ABC2-6 (ABC2-6) Family
2432:
3.A.1.150: Functionally Uncharacterized ABC2-5 (ABC2-5) Family
2429:
3.A.1.149: Functionally Uncharacterized ABC2-4 (ABC2-4) Family
2426:
3.A.1.148: Functionally Uncharacterized ABC2-3 (ABC2-3) Family
2423:
3.A.1.147: Functionally Uncharacterized ABC2-2 (ABC2-2) Family
2414:
3.A.1.144: Functionally Uncharacterized ABC2-1 (ABC2-1) Family
2299:
3.A.1.201 The Multidrug Resistance Exporter (MDR) Family (ABCB)
2015:
1995:
1991:
1844:
1782:
1576:
1456:
1314:, which involves three components that function in concert: an
1267:
1243:
1232:
1063:. In this model, the substrate binding site alternates between
1006:
1001:
535:
374:
337:
275:
211:
7251:
ABC Transporters: Biochemical, Cellular, and Molecular Aspects
7169:
5698:
4609:
3895:
3114:"The human ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter superfamily"
2499:
3.A.1.11 Polyamine/Opine/Phosphonate Uptake Transporter (POPT)
405:
into the cell. The substrates that can be transported include
8085:
8081:
8072:
8067:
8062:
8046:
8041:
8025:
8009:
8004:
7999:
7994:
7962:
7958:
7944:
7939:
7934:
7929:
7919:
7898:
7893:
7888:
7883:
7878:
7832:
7827:
7822:
7817:
7812:
7807:
7731:
7643:
6377:
3652:
2515:
3.A.1.15 Manganese/Zinc/Iron Chelate Uptake Transporter (MZT)
2454:
3.A.1.205 The Pleiotropic Drug Resistance (PDR) Family (ABCG)
2161:
2157:
2153:
2132:
2115:
2107:
2041:
2028:
2024:
2011:
2007:
1999:
1987:
1983:
1979:
1975:
1971:
1950:
1947:
1927:
1923:
1919:
1903:
1883:
1863:
1847:
1641:
1637:
1419:
1299:
1010:
896:
726:
Structure of an ABC exporter: Sav1866 with bound nucleotide (
641:
by the adrenals, and its inhibition blocked the migration of
418:
333:
283:
7608:
7077:
6244:
6052:
Bailly A, Yang H, Martinoia E, Geisler M, Murphy AS (2011).
4336:
4230:
Moody JE, Millen L, Binns D, Hunt JF, Thomas PJ (Jun 2002).
4113:
Kadaba NS, Kaiser JT, Johnson E, Lee A, Rees DC (Jul 2008).
3437:
2553:
3.A.1.23 The Nickel/Cobalt Uptake Transporter (NiCoT) Family
2347:
3.A.1.101 The Capsular Polysaccharide Exporter (CPSE) Family
1673:
resistance to anticancer drugs are called chemosensitizers.
465:
Bacterial ABC transporters are essential in cell viability,
7872:
7867:
7722:
7553:
6791:
6412:
5662:
4469:
2941:
Wang B, Dukarevich M, Sun EI, Yen MR, Saier MH (Sep 2009).
2438:
3.A.1.152: The lipopolysaccharide export (LptBFG) Family (
2386:
3.A.1.132 The Gliding Motility ABC Transporter (Gld) Family
2371:
3.A.1.124 The 3-component Peptide-5 Exporter (Pep5E) Family
1691:
1415:
1295:
919:
523:
486:
341:
173:
128:
72:
39:
7493:
7204:
6051:
6017:
Rea PA (2007). "Plant ATP-binding cassette transporters".
5791:
5535:
4177:
Pinkett HW, Lee AT, Lum P, Locher KP, Rees DC (Jan 2007).
4061:
2909:(Second ed.). London: Academic Press. pp. 7–11.
2616:
3.A.1.137 The Uncharacterized ABC-3-type (U-ABC3-2) Family
2613:
3.A.1.136 The Uncharacterized ABC-3-type (U-ABC3-1) Family
2518:
3.A.1.16 Nitrate/Nitrite/Cyanate Uptake Transporter (NitT)
722:
708:
Structure of an ABC importer: BtuCD with binding protein (
7247:
This entire volume is dedicated to various methods used:
5750:
4661:
4424:
Chen J, Lu G, Lin J, Davidson AL, Quiocho FA (Sep 2003).
3233:
2317:
3.A.1.210 The Heavy Metal Transporter (HMT) Family (ABCB)
2314:
3.A.1.209 The MHC Peptide Transporter (TAP) Family (ABCB)
2281:
3.A.1.119 The Drug/Siderophore Exporter-3 (DrugE3) Family
1958:
A full list of human ABC transporters can be found from.
1294:(P-gp/ABCB1), multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 (
597:, immune deficiencies, progressive familial intrahepatic
406:
7253:. Methods in Enzymology. Vol. 292. pp. 3–853.
6954:
6456:"Lipid A modification systems in gram-negative bacteria"
6453:
5844:
Gilson, L.; Mahanty, H. K.; Kolter, R. (December 1990).
5127:
2601:
3.A.1.114 The Probable Glycolipid Exporter (DevE) Family
2478:
3.A.1.4 Hydrophobic Amino Acid Uptake Transporter (HAAT)
2350:
3.A.1.102 The Lipooligosaccharide Exporter (LOSE) Family
704:
5230:
4781:
2848:
2408:
3.A.1.142 The Glycolipid Flippase (G.L.Flippase) Family
2380:
3.A.1.130 The Multidrug/Hemolysin Exporter (MHE) Family
2353:
3.A.1.103 The Lipopolysaccharide Exporter (LPSE) Family
1708:, sometimes resulting in altered effects of the drugs.
1571:
1491:
1238:
240:
228:
7348:
6842:
6238:
5586:
5484:
5034:
4112:
2989:
2904:
2556:
3.A.1.25 The Biotin Uptake Transporter (BioMNY) Family
2481:
3.A.1.5 Peptide/Opine/Nickel Uptake Transporter (PepT)
2290:
3.A.1.129 The CydDC Cysteine Exporter (CydDC-E) Family
625:, familial hypoapoproteinemia, Retinitis pigmentosum,
7351:"Human ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter family"
6286:
4720:
Ward A, Reyes CL, Yu J, Roth CB, Chang G (Nov 2007).
4007:
3159:
1026:
residue in the Walker B motif through the attacking H
518:), proteins involved in bacterial pathogenesis (e.g.
7289:
6902:
5374:"Structural insights into ABC transporter mechanism"
4229:
3659:
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism
2940:
2619:
3.A.1.140 The FtsX/FtsE Septation (FtsX/FtsE) Family
2460:
9.B.74 The Phage Infection Protein (PIP) Family
2411:
3.A.1.143 The Exoprotein Secretion System (EcsAB(C))
1712:
Methods to characterize ABC transporter interactions
1676:
1617:(MDR) transport protein which was originally called
1530:
structures have been reported. The resting state of
661:
in ABCB1 transfected cells. MDR1 can also transport
7349:Vasiliou, V; Vasiliou, K; Nebert, DW (April 2009).
7006:"The role of ABC transporters in clinical practice"
6454:Raetz CR, Reynolds CM, Trent MS, Bishop RE (2007).
6201:
6195:
6156:
6154:
6152:
6150:
6096:
5957:
5843:
5621:
5041:
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Bioenergetics
5035:Ye J, Osborne AR, Groll M, Rapoport TA (Nov 2004).
4939:
4176:
3783:
3234:Cangelosi GA, Ankenbauer RG, Nester EW (Sep 1990).
2849:Davidson AL, Dassa E, Orelle C, Chen J (Jun 2008).
2550:
3.A.1.22 The Nickel Uptake Transporter (NiT) Family
2547:
3.A.1.18 The Cobalt Uptake Transporter (CoT) Family
2530:
3.A.1.21 Siderophore-Fe3+ Uptake Transporter (SIUT)
2484:
3.A.1.6 Sulfate/Tungstate Uptake Transporter (SulT)
2377:
3.A.1.128 The SkfA Peptide Exporter (SkfA-E) Family
2362:
3.A.1.107 The Putative Heme Exporter (HemeE) Family
2287:
3.A.1.127 The AmfS Peptide Exporter (AmfS-E) Family
1189:-E), and the putative metal-chelate transporter of
429:thus providing a pathway across the cell membrane.
7496:"3.A.1 The ATP-binding Cassette (ABC) Superfamily"
7207:Expert Opinion on Drug Metabolism & Toxicology
6700:
5371:
5037:"RecA-like motor ATPases--lessons from structures"
4280:
3544:
3351:Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes
3341:
2607:3.A.1.125 The Lipoprotein Translocase (LPT) Family
2502:3.A.1.12 Quaternary Amine Uptake Transporter (QAT)
2475:3.A.1.3 Polar Amino Acid Uptake Transporter (PAAT)
1725:
1721:to more complex cell based assays up to intricate
1690:results have been disappointing. Recently various
1353:
891:
6740:
5186:
5128:Maegley KA, Admiraal SJ, Herschlag D (Aug 1996).
4940:Ambudkar SV, Kim IW, Xia D, Sauna ZE (Feb 2006).
4465:
4463:
4461:
4423:
3292:
2374:3.A.1.126 The β-Exotoxin I Exporter (βETE) Family
2368:3.A.1.116 The Microcin B17 Exporter (McbE) Family
2356:3.A.1.104 The Teichoic Acid Exporter (TAE) Family
2278:3.A.1.118 The Microcin J25 Exporter (McjD) Family
2090:and potassium-channel openers activators such as
2086:. SUR is also the binding site for drugs such as
1075:as a result of ATP binding and hydrolysis is the
8111:
7003:
6596:
6594:
6501:
6499:
6147:
6045:
5423:
5421:
5419:
5417:
4888:
4884:
4882:
4880:
4878:
3111:
2565:3.A.1.29 The Methionine Precursor (Met-P) Family
2472:3.A.1.2 Carbohydrate Uptake Transporter-2 (CUT2)
2469:3.A.1.1 Carbohydrate Uptake Transporter-1 (CUT1)
2392:3.A.1.138 The Unknown ABC-2-type (ABC2-1) Family
2383:3.A.1.131 The Bacitracin Resistance (Bcr) Family
2263:3.A.1.110 The Protein-2 Exporter (Prot2E) Family
2260:3.A.1.109 The Protein-1 Exporter (Prot1E) Family
2257:3.A.1.108 The β-Glucan Exporter (GlucanE) Family
1668:-peptide). These drugs would not function as a
1592:
297:and one or two of which are membrane-associated
265:ATP synthase (ATP)-binding cassette transporters
6850:Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
6371:
5548:(4): e01931–19, /mbio/10/4/mBio.01931–19.atom.
4719:
3398:
3396:
3394:
3392:
3390:
3388:
2610:3.A.1.134 The Peptide-7 Exporter (Pep7E) Family
2574:3.A.1.32 The Cobalamin Precursor (B12-P) Family
2512:3.A.1.14 Iron Chelate Uptake Transporter (FeCT)
2389:3.A.1.133 The Peptide-6 Exporter (Pep6E) Family
2284:3.A.1.123 The Peptide-4 Exporter (Pep4E) Family
2272:3.A.1.113 The Peptide-3 Exporter (Pep3E) Family
2269:3.A.1.112 The Peptide-2 Exporter (Pep2E) Family
2266:3.A.1.111 The Peptide-1 Exporter (Pep1E) Family
7107:
6406:
5226:
5224:
4830:
4657:
4655:
4653:
4651:
4649:
4647:
4458:
3184:
3155:
3153:
3151:
3149:
2990:ter Beek J, Guskov A, Slotboom DJ (Apr 2014).
2604:3.A.1.122 The Macrolide Exporter (MacB) Family
1471:and so loss of MsbA from the cell membrane or
7762:
7730:Archaeal and Bacterial ABC Systems database,
7512:
7103:
7101:
6591:
6496:
6280:
6102:
5414:
5367:
5365:
5363:
5361:
5359:
5357:
5355:
5353:
5278:
4875:
4605:
4603:
4057:
4055:
3837:
3488:
2622:3.A.1.207 The Eukaryotic ABC3 (E-ABC3) Family
2577:3.A.1.33 The Methylthioadenosine (MTA) Family
2568:3.A.1.30 The Thiamin Precursor (Thi-P) Family
2496:3.A.1.10 Ferric Iron Uptake Transporter (FeT)
2493:3.A.1.9 Phosphonate Uptake Transporter (PhnT)
2359:3.A.1.105 The Drug Exporter-1 (DrugE1) Family
2293:3.A.1.135 The Drug Exporter-4 (DrugE4) Family
2275:3.A.1.117 The Drug Exporter-2 (DrugE2) Family
1797:Calcein-AM, A highly permeable derivative of
1562:nucleotide-bound, outward-facing conformation
972:
964:or switch region contains a highly conserved
848:
7445:
7398:
7396:
7290:Horio M, Gottesman MM, Pastan I (May 1988).
6997:
6694:
6447:
6322:
5958:McMurry L, Petrucci RE, Levy SB (Jul 1980).
5785:
5744:
5692:
5656:
5615:
5580:
5189:"How do kinases transfer phosphoryl groups?"
5028:
4824:
4564:
4106:
3951:
3608:
3573:
3402:
3385:
3335:
2254:3.A.1.106 The Lipid Exporter (LipidE) Family
2187:
914:The ABC domain consists of two domains, the
304:. The ATPase subunits utilize the energy of
7248:
6948:
5951:
5372:Oldham ML, Davidson AL, Chen J (Dec 2008).
5221:
5180:
5121:
5074:
5072:
4995:
4993:
4715:
4713:
4711:
4709:
4707:
4644:
4521:
4419:
4417:
4415:
4413:
4274:
3784:Rees DC, Johnson E, Lewinson O (Mar 2009).
3482:
3431:
3342:Poolman B, Spitzer JJ, Wood JM (Nov 2004).
3286:
3227:
3178:
3146:
3107:
3105:
3103:
3101:
3099:
3097:
3095:
3093:
3091:
3039:
3037:
3035:
2844:
2842:
2840:
2838:
2836:
2794:
2788:
2737:
2733:
2731:
2527:3.A.1.20 Brachyspira Iron Transporter (BIT)
2490:3.A.1.8 Molybdate Uptake Transporter (MolT)
2487:3.A.1.7 Phosphate Uptake Transporter (PhoT)
1857:Consists of 4 full and 7 half transporters.
1166:structure of an intact ABC importer is the
1154:such that their binding protein is often a
7769:
7755:
7500:Transporter Classification Database (TCDB)
7458:Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews
7402:
7098:
6675:|...|intentional=yes}}
6600:
6572:|...|intentional=yes}}
6160:
5350:
5315:
5274:
5272:
5270:
5268:
5266:
5264:
5262:
5187:Matte A, Tari LW, Delbaere LT (Apr 1998).
4777:
4775:
4600:
4052:
3947:
3945:
3943:
3293:Kemner JM, Liang X, Nester EW (Apr 1997).
2992:"Structural diversity of ABC transporters"
2936:
2934:
2855:Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews
2834:
2832:
2830:
2828:
2826:
2824:
2822:
2820:
2818:
2816:
2677:
2524:3.A.1.19 Thiamin Uptake Transporter (ThiT)
2521:3.A.1.17 Taurine Uptake Transporter (TauT)
2071:, the transporter involved in the disease
1788:
1648:can be utilized such as alkylating drugs (
1560:, is similar to Sav1866. The NBDs in this
1235:activity of the transporter upon binding.
936:(GXXGXGKS/T where X is any amino acid) or
38:
7739:at the U.S. National Library of Medicine
7661:
7626:
7581:
7571:
7530:
7477:
7428:
7393:
7376:
7366:
7325:
7315:
7021:
6980:
6879:
6869:
6819:
6809:
6505:
6479:
6430:
6247:"Functions of ABC transporters in plants"
6178:
6079:
6069:
5993:
5983:
5934:
5877:
5817:
5768:
5719:
5639:
5563:
5553:
5453:
5397:
5281:Nature Structural & Molecular Biology
5204:
5163:
5153:
5104:
5052:
4965:
4858:
4848:
4799:
4755:
4745:
4687:
4627:
4547:
4517:
4515:
4495:
4441:
4393:
4371:
4369:
4332:
4330:
4328:
4257:
4247:
4172:
4170:
4168:
4166:
4146:
3809:
3727:
3670:
3506:
3465:
3455:
3318:
3269:
3259:
3210:
3129:
3071:
3061:
3015:
2966:
2900:
2898:
2896:
2894:
2874:
2763:
2711:
2678:Fath, M. J.; Kolter, R. (December 1993).
2571:3.A.1.31 The Unknown-ABC1 (U-ABC1) Family
2562:3.A.1.28 The Queuosine (Queuosine) Family
1660:), and the anthracycline modified drugs (
1045:
813:BtuCD importer involved in the uptake of
6472:10.1146/annurev.biochem.76.010307.145803
6031:10.1146/annurev.arplant.57.032905.105406
6010:
5069:
4990:
4704:
4410:
4225:
4223:
3833:
3831:
3829:
3779:
3777:
3775:
3773:
3771:
3769:
3767:
3579:
3417:10.1146/annurev.biochem.73.011303.073626
3088:
3032:
2728:
2647:Transmembrane domain of ABC transporters
2539:3.A.1.34 The Tryptophan (TrpXYZ) Family
2365:3.A.1.115 The Na+ Exporter (NatE) Family
2110:is responsible for the X-linked form of
1810:
1575:
1490:
1242:
1034:residue adjacent to the Walker B motif,
895:
741:hydrolysis of adenosine triphosphate or
721:
703:
665:, short-chain and long-chain analogs of
534:, S-layer proteins, competence factors,
239:
227:
7150:
6736:
6734:
6732:
5430:"Multidrug resistance ABC transporters"
5259:
4772:
4003:
4001:
3999:
3940:
3838:Locher KP, Lee AT, Rees DC (May 2002).
3786:"ABC transporters: the power to change"
3765:
3763:
3761:
3759:
3757:
3755:
3753:
3751:
3749:
3747:
3540:
3538:
3536:
3534:
3532:
3530:
3528:
3526:
3112:Dean M, Hamon Y, Chimini G (Jul 2001).
2931:
2813:
2680:"ABC transporters: bacterial exporters"
1913:Consists of 1 ABCE and 3 ABCF proteins.
14:
8112:
7678:
7506:
5900:
5478:
5321:
4512:
4366:
4325:
4163:
3709:
2891:
2642:ATP-binding domain of ABC transporters
2135:, which is known to recognize certain
1209:
1196:
445:, exporters transport lipids and some
421:, and other molecules that are mostly
7750:
7513:Khwaja M, Ma Q, Saier MH (Mar 2005).
7502:. University of California San Diego.
7451:
7046:
7004:Leonard GD, Fojo T, Bates SE (2003).
5901:Choi, Young Hee; Yu, Ai-Ming (2014).
5839:
5837:
5427:
5378:Current Opinion in Structural Biology
5324:Current Opinion in Structural Biology
5233:Current Opinion in Structural Biology
4220:
3826:
3790:Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology
3489:Poole RK, Gibson F, Wu G (Apr 1994).
2466:(3.A.1.1 - 3.A.1.34 except 3.A.1.21)
1698:
1383:
1226:-E structure resembles the catalytic
7052:
6729:
3996:
3744:
3523:
3043:
2907:Encyclopedia of Biological Chemistry
2744:Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences
2673:
2671:
2669:
2667:
2191:
1644:(breast cancer resistance protein).
1572:Mechanism of transport for exporters
1239:Mechanism of transport for importers
1214:Structures of the ModBC-A and MalFGK
1030:O. A general base, which may be the
926:and a smaller, structurally diverse
613:of infancy due to focal adenomatous
7650:The Journal of Biological Chemistry
7615:The Journal of Biological Chemistry
6419:The Journal of Biological Chemistry
6016:
5757:The Journal of Biological Chemistry
5708:The Journal of Biological Chemistry
5628:The Journal of Biological Chemistry
4831:Fetsch EE, Davidson AL (Jul 2002).
4616:The Journal of Biological Chemistry
4236:The Journal of Biological Chemistry
3444:The Journal of Biological Chemistry
3185:Henderson DP, Payne SM (Nov 1994).
1022:also coordinates with the terminal
24:
7719:Classification of ABC transporters
7601:
7055:ABC Transporters in Microorganisms
5862:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07606.x
5834:
3508:10.1111/j.1574-6968.1994.tb06768.x
2915:10.1016/B978-0-12-378630-2.00224-3
2797:ABC Transporters in Microorganisms
1763:
1554:closed, inward-facing conformation
1158:bound to the external face of the
25:
8136:
8120:ATP-binding cassette transporters
7737:ATP-Binding+cassette+transporters
7712:
6323:Dawson RJ, Locher KP (Mar 2007).
2996:The Journal of General Physiology
2664:
1998:. The other subgroup consists of
1873:Consists of 12 full transporters.
1677:Reversal of multi drug resistance
1329:. An example is the secretion of
7494:Saier Lab Bioinformatics Group.
7421:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08235.x
6302:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04818.x
6204:Current Opinion in Plant Biology
6180:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.03856.x
5919:10.2174/138161282005140214165212
3203:10.1128/IAI.62.11.5120-5125.1994
3164:. San Francisco: W. H. Freeman.
2861:(2): 317–64, table of contents.
2738:Jones PM, George AM (Mar 2004).
2196:
2125:
1536:open, inward-facing conformation
1515:), and nucleotide-bound (
1304:breast cancer resistance protein
1260:
1136:
7547:
7403:Chen ZS, Tiwari AK (Sep 2011).
7342:
7283:
7241:
7198:
7163:
7144:
7071:
6896:
6836:
6785:
6316:
5894:
5529:
4933:
4522:Gaudet R, Wiley DC (Sep 2001).
3889:
3703:
3311:10.1128/jb.179.7.2452-2458.1997
2947:The Journal of Membrane Biology
2696:10.1128/MMBR.57.4.995-1017.1993
2027:protein is mutated. Also, the
1941:end and the TM at the COO- end.
1893:Consists of 4 half transporters
1354:Human ABCB1/MDR1 P-glycoprotein
1073:nucleotide-binding domain (NBD)
892:Nucleotide-binding domain (NBD)
779:nucleotide-binding domain (NBD)
526:-binding protein, and alkaline
323:(ABC) domains, even though the
7470:10.1128/MMBR.64.2.354-411.2000
6961:Trends in Biochemical Sciences
6688:10.1126/science.314.5807.1875b
6650:10.1126/science.314.5807.1875b
6585:10.1126/science.314.5807.1875b
6547:10.1126/science.314.5807.1875b
6161:Yang H, Murphy AS (Jul 2009).
6019:Annual Review of Plant Biology
5002:Trends in Biochemical Sciences
3629:10.1016/j.placenta.2005.11.012
2983:
2323:3.A.1.21 The Siderophore-Fe3+
1805:
1388:The genome of the model plant
460:
433:do not possess any importers.
13:
1:
7259:10.1016/s0076-6879(00)x0188-7
7023:10.1634/theoncologist.8-5-411
6528:10.1126/science.293.5536.1793
6460:Annual Review of Biochemistry
6349:10.1016/j.febslet.2007.01.073
6125:10.1016/j.febslet.2005.11.054
5907:Current Pharmaceutical Design
5455:10.1016/S0014-5793(03)01085-8
5206:10.1016/S0969-2126(98)00043-4
5014:10.1016/S0968-0004(01)01907-7
4967:10.1016/j.febslet.2005.12.051
4911:10.1016/j.febslet.2005.11.033
4801:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80890-9
4680:10.1016/S1097-2765(02)00576-2
4586:10.1016/S0022-2836(03)00592-8
4395:10.1016/S0969-2126(01)00617-7
4352:10.1016/S0022-2836(03)00575-8
3729:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)83799-7
3405:Annual Review of Biochemistry
3131:10.1016/S0022-2275(20)31588-1
2658:
2168:anticancer drugs, as well as
1593:Role in multi drug resistance
1378:electron cryo crystallography
798:MacB protein responsible for
611:hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia
557:
286:. ABC transporters belong to
168:Available protein structures:
7532:10.1016/j.resmic.2004.07.010
6811:10.1371/journal.pbio.0050271
5507:10.1016/0014-5793(95)01345-8
5054:10.1016/j.bbabio.2004.06.003
4574:Journal of Molecular Biology
4443:10.1016/j.molcel.2003.08.004
4340:Journal of Molecular Biology
3559:10.1016/j.bbalip.2004.12.007
3363:10.1016/j.bbamem.2004.06.013
2080:sulfonylurea receptors (SUR)
1463:, the hydrophobic moiety of
1368:family and is also known as
699:
332:, while exporters transport
7:
7786:membrane transport proteins
2795:Ponte-Sucre A, ed. (2009).
2635:
1327:outer membrane factor (OMF)
1170:transporter (ModBC-A) from
1069:inward-facing conformations
384:
271:. It is represented in all
10:
8141:
7249:Nikaido H, Hall J (1998).
6973:10.1016/j.tibs.2009.07.009
6058:Frontiers in Plant Science
2182:Chromosomal translocations
2084:Neonatal diabetes mellitus
1484:is 36% identical to the NH
1425:
1357:
1056:transmembrane domain (TMD)
973:ATP binding and hydrolysis
849:Transmembrane domain (TMD)
843:intracellular domain (ICD)
774:transmembrane domain (TMD)
647:platelet activating factor
619:sideroblastosis and anemia
325:integral membrane proteins
8100:ABC transporter disorders
8095:
8055:
8034:
8018:
7987:
7912:
7851:
7800:
7368:10.1186/1479-7364-3-3-281
6926:10.1038/s41586-018-0083-5
6224:10.1016/j.pbi.2005.07.014
5390:10.1016/j.sbi.2008.09.007
5336:10.1016/j.sbi.2004.06.005
5245:10.1016/j.sbi.2007.07.003
3495:FEMS Microbiology Letters
3118:Journal of Lipid Research
3050:Cancer Cell International
2959:10.1007/s00232-009-9200-6
2756:10.1007/s00018-003-3336-9
2627:
2509:Uptake Transporter (B12T)
2327:Transporter (SIUT) Family
2188:Cross-species subfamilies
1770:vesicular transport assay
1760:detection methodologies.
1740:10.1080/00498250701570285
1411:Schizosaccharomyces pombe
566:transmembrane regulator (
491:Agrobacterium tumefaciens
365:, drug-resistant tumors,
210:
190:
172:
167:
163:
151:
139:
127:
107:
95:
83:
71:
63:
58:
37:
32:
7741:Medical Subject Headings
7519:Research in Microbiology
7219:10.1517/17425255.4.6.721
7184:10.2174/1567201043480036
5810:10.1093/emboj/20.20.5615
5770:10.1074/jbc.274.25.17649
5721:10.1074/jbc.275.15.10962
5097:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600657
4540:10.1093/emboj/20.17.4964
4488:10.1093/emboj/19.22.5951
3457:10.1074/jbc.273.20.12466
1405:Saccharomyces cerevisiae
1061:alternating-access model
989:Methanococcus jannaschii
671:phosphatidylethanolamine
631:multiple drug resistance
607:Pseudoxanthoma elasticum
379:multiple drug resistance
7573:10.1186/1471-2180-13-98
7317:10.1073/pnas.85.10.3580
6871:10.1073/pnas.1804670115
6763:10.1126/science.1106592
6623:10.1126/science.1107733
6071:10.3389/fpls.2011.00108
5155:10.1073/pnas.93.16.8160
4747:10.1073/pnas.0709388104
4198:10.1126/science.1133488
4139:10.1126/science.1157987
3918:10.1126/science.1145950
3867:10.1126/science.1071142
3299:Journal of Bacteriology
3261:10.1073/pnas.87.17.6708
2684:Microbiological Reviews
2142:
2097:
2055:
2035:
1961:
1789:Whole cell based assays
1446:
1395:Drosophila melanogaster
1321:membrane fusion protein
48:transporter, BtuCD PDB
7663:10.1074/jbc.M409848200
7628:10.1074/jbc.M406484200
7122:10.1124/dmd.104.001669
6432:10.1074/jbc.M306226200
6254:Essays in Biochemistry
5985:10.1073/pnas.77.7.3974
5641:10.1074/jbc.M207963200
4850:10.1073/pnas.152204499
4629:10.1074/jbc.M100758200
4249:10.1074/jbc.C200228200
3672:10.1210/clinem/dgab813
3594:10.1006/smim.2001.0322
3582:Seminars in Immunology
3191:Infection and Immunity
3162:Molecular Cell Biology
3063:10.1186/1475-2867-5-30
2652:Elizabeth P. Carpenter
2207:is missing information
1706:drug-drug interactions
1581:
1526:
1505:), closed apo (
1248:
1191:Haemophilus influenzae
1172:Archaeoglobus fulgidus
1150:microorganisms lack a
1144:gram-negative bacteria
1046:Mechanism of transport
911:
883:Haemophilus influenzae
737:
719:
603:Dubin–Johnson syndrome
443:gram-negative bacteria
401:mediate the uptake of
367:Dubin–Johnson syndrome
306:adenosine triphosphate
295:transmembrane proteins
256:
237:
7452:Saier MH (Jun 2000).
7172:Current Drug Delivery
7151:Matsson, Pär (2007).
6682:(Retracted, see
6667:|...}}
6644:(Retracted, see
6579:(Retracted, see
6564:|...}}
6541:(Retracted, see
5555:10.1128/mBio.01931-19
3008:10.1085/jgp.201411164
2867:10.1128/MMBR.00031-07
2152:and no expression of
2120:fatty acid metabolism
2050:multi-drug resistance
1811:Mammalian subfamilies
1579:
1494:
1432:Staphylococcus aureus
1414:(fission yeast), and
1246:
1089:adenosine diphosphate
1050:ABC transporters are
916:catalytic core domain
899:
822:Staphylococcus aureus
725:
707:
245:Molybdate transporter
243:
231:
7685:. World Scientific.
7057:. Caister Academic.
5428:Chang G (Nov 2003).
3044:Choi CH (Oct 2005).
2799:. Caister Academic.
2112:Adrenoleukodystrophy
1627:extracellular medium
1615:multidrug-resistance
1599:multidrug resistance
1390:Arabidopsis thaliana
1348:multi-drug resistant
1274:, S-layer proteins,
860:type II ABC importer
839:binding protein (BP)
767:extracellular medium
763:phospholipid bilayer
759:phospholipid bilayer
623:macular degeneration
587:adrenoleukodystrophy
371:sideroblastic anemia
359:adrenoleukodystrophy
33:ABC Transporter, NBD
7308:1988PNAS...85.3580H
6918:2018Natur.557..196H
6862:2018PNAS..115.6834Z
6755:2005Sci...308.1023D
6615:2005Sci...308.1028R
6520:2001Sci...293.1793C
6341:2007FEBSL.581..935D
6216:2005COPB....8..494B
6117:2006FEBSL.580.1094G
5976:1980PNAS...77.3974M
5499:1995FEBSL.377..285S
5446:2003FEBSL.555..102C
5146:1996PNAS...93.8160M
4958:2006FEBSL.580.1049A
4903:2006FEBSL.580.1042R
4738:2007PNAS..10419005W
4295:1998Natur.396..703H
4131:2008Sci...321..250K
4084:10.1038/nature06264
4076:2007Natur.450..515O
4030:10.1038/nature05626
4022:2007Natur.446..213H
3974:10.1038/nature05155
3966:2006Natur.443..180D
3910:2007Sci...317.1387H
3859:2002Sci...296.1091L
3623:(11–12): 1096–102.
3252:1990PNAS...87.6708C
2046:blood–brain barrier
1210:Small ABC importers
1197:Large ABC importers
1185:transporter (MalFGK
1052:active transporters
946:ABC signature motif
928:α-helical subdomain
856:type I ABC importer
824:, are made up of a
667:phosphatidylcholine
512:lipopolysaccharides
255:complex, open state
7679:Linton KJ (2011).
6514:(5536): 1793–800.
6266:10.1042/bse0500145
3710:Shuman HA (1982).
2543:ECF uptake systems
2505:3.A.1.13 Vitamin B
2464:all uptake systems
1734:(10–11): 1135–51.
1699:Physiological role
1582:
1527:
1478:Lactococcus lactis
1465:lipopolysaccharide
1384:Plant transporters
1272:hydrolytic enzymes
1249:
1128:accessibility and
912:
828:consisting of two
738:
720:
675:phosphatidylserine
627:cone rod dystrophy
532:hydrolytic enzymes
313:translation of RNA
257:
238:
8107:
8106:
7778:Membrane proteins
7692:978-981-4280-06-8
7110:Drug Metab Dispos
7080:Drug Metab Dispos
7064:978-1-904455-49-3
6912:(7704): 196–201.
6856:(26): 6834–6839.
6715:10.1021/bi0497751
6609:(5724): 1028–31.
6392:10.1021/bi8006737
6290:The Plant Journal
6167:The Plant Journal
5856:(12): 3875–3884.
5601:10.1021/bi011211z
3904:(5843): 1387–90.
3171:978-1-4292-3413-9
2924:978-0-12-378631-9
2806:978-1-904455-49-3
2230:
2229:
1956:
1955:
1288:anticancer agents
982:MalK (E.c.MalK),
830:half transporters
591:Stargardt disease
363:Stargardt disease
226:
225:
222:
221:
217:structure summary
16:(Redirected from
8132:
8125:Protein families
7782:carrier proteins
7771:
7764:
7757:
7748:
7747:
7707:
7705:
7704:
7695:. Archived from
7675:
7665:
7656:(46): 48477–85.
7640:
7630:
7596:
7595:
7585:
7575:
7560:BMC Microbiology
7551:
7545:
7544:
7534:
7510:
7504:
7503:
7491:
7481:
7449:
7443:
7442:
7432:
7409:The FEBS Journal
7400:
7391:
7390:
7380:
7370:
7346:
7340:
7339:
7329:
7319:
7287:
7281:
7280:
7245:
7239:
7238:
7202:
7196:
7195:
7167:
7161:
7160:
7148:
7142:
7141:
7105:
7096:
7095:
7075:
7069:
7068:
7050:
7044:
7043:
7025:
7001:
6995:
6994:
6984:
6952:
6946:
6945:
6900:
6894:
6893:
6883:
6873:
6840:
6834:
6833:
6823:
6813:
6789:
6783:
6782:
6749:(5724): 1023–8.
6738:
6727:
6726:
6698:
6692:
6691:
6680:
6678:
6676:
6668:
6642:
6598:
6589:
6588:
6577:
6575:
6573:
6565:
6539:
6503:
6494:
6493:
6483:
6451:
6445:
6444:
6434:
6410:
6404:
6403:
6375:
6369:
6368:
6320:
6314:
6313:
6284:
6278:
6277:
6251:
6242:
6236:
6235:
6199:
6193:
6192:
6182:
6158:
6145:
6144:
6100:
6094:
6093:
6083:
6073:
6049:
6043:
6042:
6014:
6008:
6007:
5997:
5987:
5955:
5949:
5948:
5938:
5898:
5892:
5891:
5881:
5850:The EMBO Journal
5841:
5832:
5831:
5821:
5798:The EMBO Journal
5789:
5783:
5782:
5772:
5763:(25): 17649–54.
5748:
5742:
5741:
5723:
5705:
5696:
5690:
5689:
5678:10.1021/bi001066
5672:(46): 14183–95.
5660:
5654:
5653:
5643:
5619:
5613:
5612:
5595:(51): 15733–42.
5584:
5578:
5577:
5567:
5557:
5533:
5527:
5526:
5482:
5476:
5475:
5457:
5425:
5412:
5411:
5401:
5369:
5348:
5347:
5319:
5313:
5312:
5276:
5257:
5256:
5228:
5219:
5218:
5208:
5184:
5178:
5177:
5167:
5157:
5125:
5119:
5118:
5108:
5085:The EMBO Journal
5076:
5067:
5066:
5056:
5032:
5026:
5025:
4997:
4988:
4987:
4969:
4937:
4931:
4930:
4886:
4873:
4872:
4862:
4852:
4828:
4822:
4821:
4803:
4779:
4770:
4769:
4759:
4749:
4732:(48): 19005–10.
4717:
4702:
4701:
4691:
4659:
4642:
4641:
4631:
4622:(34): 32313–21.
4607:
4598:
4597:
4568:
4562:
4561:
4551:
4528:The EMBO Journal
4519:
4510:
4509:
4499:
4476:The EMBO Journal
4467:
4456:
4455:
4445:
4421:
4408:
4407:
4397:
4373:
4364:
4363:
4334:
4323:
4322:
4278:
4272:
4271:
4261:
4251:
4227:
4218:
4217:
4183:
4174:
4161:
4160:
4150:
4110:
4104:
4103:
4070:(7169): 515–21.
4059:
4050:
4049:
4005:
3994:
3993:
3949:
3938:
3937:
3893:
3887:
3886:
3853:(5570): 1091–8.
3844:
3835:
3824:
3823:
3813:
3781:
3742:
3741:
3731:
3707:
3701:
3700:
3674:
3665:(4): 1140–1158.
3650:
3641:
3640:
3612:
3606:
3605:
3577:
3571:
3570:
3542:
3521:
3520:
3510:
3486:
3480:
3479:
3469:
3459:
3450:(20): 12466–75.
3435:
3429:
3428:
3400:
3383:
3382:
3348:
3339:
3333:
3332:
3322:
3290:
3284:
3283:
3273:
3263:
3231:
3225:
3224:
3214:
3182:
3176:
3175:
3157:
3144:
3143:
3133:
3109:
3086:
3085:
3075:
3065:
3041:
3030:
3029:
3019:
2987:
2981:
2980:
2970:
2938:
2929:
2928:
2902:
2889:
2888:
2878:
2846:
2811:
2810:
2792:
2786:
2785:
2767:
2735:
2726:
2725:
2715:
2675:
2225:
2222:
2216:
2200:
2192:
2137:oligodendrocytes
1896:Are all used in
1818:
1817:
1759:
1650:cyclophosphamide
1544:EPR spectroscopy
1542:experiments and
1524:
1514:
1504:
1459:that transports
1400:Escherichia coli
1312:type I secretion
1228:transition state
1077:ATP-switch model
948:, also known as
909:
807:full transporter
735:
717:
683:glucosylceramide
393:across cellular
261:ABC transporters
165:
164:
53:
42:
30:
29:
21:
8140:
8139:
8135:
8134:
8133:
8131:
8130:
8129:
8110:
8109:
8108:
8103:
8091:
8051:
8030:
8014:
7983:
7908:
7847:
7796:
7789:ABC transporter
7775:
7715:
7710:
7702:
7700:
7693:
7621:(40): 41670–8.
7604:
7602:Further reading
7599:
7552:
7548:
7511:
7507:
7450:
7446:
7415:(18): 3226–45.
7401:
7394:
7347:
7343:
7288:
7284:
7269:
7246:
7242:
7203:
7199:
7168:
7164:
7149:
7145:
7106:
7099:
7086:(10): 1277–83.
7076:
7072:
7065:
7051:
7047:
7002:
6998:
6953:
6949:
6901:
6897:
6841:
6837:
6790:
6786:
6739:
6730:
6699:
6695:
6681:
6670:
6662:
6660:
6643:
6599:
6592:
6578:
6567:
6559:
6557:
6540:
6504:
6497:
6452:
6448:
6425:(37): 35193–8.
6411:
6407:
6376:
6372:
6321:
6317:
6285:
6281:
6249:
6243:
6239:
6200:
6196:
6159:
6148:
6111:(4): 1094–102.
6101:
6097:
6050:
6046:
6015:
6011:
5956:
5952:
5899:
5895:
5842:
5835:
5804:(20): 5615–25.
5790:
5786:
5749:
5745:
5714:(15): 10962–7.
5703:
5697:
5693:
5661:
5657:
5620:
5616:
5585:
5581:
5534:
5530:
5483:
5479:
5426:
5415:
5370:
5351:
5320:
5316:
5293:10.1038/nsmb836
5277:
5260:
5229:
5222:
5185:
5181:
5126:
5122:
5091:(11): 1901–10.
5077:
5070:
5033:
5029:
4998:
4991:
4938:
4934:
4887:
4876:
4843:(15): 9685–90.
4829:
4825:
4780:
4773:
4718:
4705:
4660:
4645:
4608:
4601:
4569:
4565:
4534:(17): 4964–72.
4520:
4513:
4482:(22): 5951–61.
4468:
4459:
4422:
4411:
4374:
4367:
4335:
4326:
4289:(6712): 703–7.
4279:
4275:
4242:(24): 21111–4.
4228:
4221:
4192:(5810): 373–7.
4181:
4175:
4164:
4125:(5886): 250–3.
4111:
4107:
4060:
4053:
4016:(7132): 213–6.
4006:
3997:
3960:(7108): 180–5.
3950:
3941:
3894:
3890:
3842:
3836:
3827:
3802:10.1038/nrm2646
3782:
3745:
3722:(10): 5455–61.
3708:
3704:
3651:
3644:
3613:
3609:
3578:
3574:
3543:
3524:
3487:
3483:
3436:
3432:
3401:
3386:
3357:(1–2): 88–104.
3346:
3340:
3336:
3291:
3287:
3246:(17): 6708–12.
3232:
3228:
3183:
3179:
3172:
3158:
3147:
3110:
3089:
3042:
3033:
2988:
2984:
2939:
2932:
2925:
2903:
2892:
2847:
2814:
2807:
2793:
2789:
2736:
2729:
2690:(4): 995–1017.
2676:
2665:
2661:
2638:
2630:
2625:
2584:
2508:
2330:
2226:
2220:
2217:
2210:
2201:
2190:
2180:as substrates.
2145:
2128:
2100:
2073:cystic fibrosis
2058:
2038:
1964:
1940:
1880:when deficient.
1878:cystic fibrosis
1813:
1808:
1791:
1766:
1764:Membrane assays
1714:
1701:
1679:
1654:antimetabolites
1595:
1588:
1574:
1516:
1506:
1496:
1487:
1449:
1428:
1386:
1362:
1356:
1263:
1255:
1241:
1225:
1221:
1217:
1212:
1204:
1199:
1188:
1139:
1116:-glycoprotein (
1098:
1086:
1048:
1041:
1029:
975:
901:
894:
876:
851:
818:
809:such as in the
755:plasma membrane
727:
709:
702:
595:Tangier disease
564:cystic fibrosis
560:
463:
447:polysaccharides
387:
355:cystic fibrosis
346:cystic fibrosis
254:
250:
141:OPM superfamily
54:
49:
47:
28:
23:
22:
18:ABC-transporter
15:
12:
11:
5:
8138:
8128:
8127:
8122:
8105:
8104:
8096:
8093:
8092:
8090:
8089:
8075:
8070:
8065:
8059:
8057:
8053:
8052:
8050:
8049:
8044:
8038:
8036:
8032:
8031:
8029:
8028:
8022:
8020:
8016:
8015:
8013:
8012:
8007:
8002:
7997:
7991:
7989:
7985:
7984:
7982:
7981:
7976:
7971:
7966:
7952:
7947:
7942:
7937:
7932:
7927:
7922:
7916:
7914:
7910:
7909:
7907:
7906:
7901:
7896:
7891:
7886:
7881:
7876:
7870:
7861:
7855:
7853:
7849:
7848:
7846:
7845:
7840:
7835:
7830:
7825:
7820:
7815:
7810:
7804:
7802:
7798:
7797:
7774:
7773:
7766:
7759:
7751:
7745:
7744:
7734:
7725:
7714:
7713:External links
7711:
7709:
7708:
7691:
7676:
7641:
7605:
7603:
7600:
7598:
7597:
7546:
7505:
7464:(2): 354–411.
7444:
7392:
7355:Human Genomics
7341:
7302:(10): 3580–4.
7282:
7267:
7240:
7197:
7162:
7143:
7097:
7070:
7063:
7045:
7010:The Oncologist
6996:
6947:
6895:
6835:
6784:
6728:
6709:(26): 8600–6.
6693:
6590:
6495:
6446:
6405:
6386:(35): 9300–8.
6370:
6315:
6279:
6237:
6210:(5): 494–500.
6194:
6146:
6095:
6044:
6009:
5950:
5913:(5): 793–807.
5893:
5833:
5784:
5743:
5691:
5655:
5634:(5): 3347–56.
5614:
5579:
5528:
5477:
5413:
5349:
5314:
5287:(10): 918–26.
5258:
5220:
5179:
5140:(16): 8160–6.
5120:
5068:
5027:
4989:
4952:(4): 1049–55.
4932:
4874:
4823:
4794:(7): 789–800.
4771:
4703:
4668:Molecular Cell
4643:
4599:
4563:
4511:
4457:
4430:Molecular Cell
4409:
4365:
4324:
4273:
4219:
4162:
4105:
4051:
3995:
3939:
3888:
3825:
3743:
3702:
3642:
3607:
3572:
3522:
3481:
3430:
3384:
3334:
3285:
3226:
3197:(11): 5120–5.
3177:
3170:
3145:
3124:(7): 1007–17.
3087:
3031:
2982:
2930:
2923:
2890:
2812:
2805:
2787:
2727:
2662:
2660:
2657:
2656:
2655:
2649:
2644:
2637:
2634:
2629:
2626:
2624:
2623:
2620:
2617:
2614:
2611:
2608:
2605:
2602:
2598:
2583:
2582:
2581:
2580:
2579:
2578:
2575:
2572:
2569:
2566:
2563:
2560:
2557:
2554:
2551:
2548:
2540:
2537:
2534:
2531:
2528:
2525:
2522:
2519:
2516:
2513:
2510:
2506:
2503:
2500:
2497:
2494:
2491:
2488:
2485:
2482:
2479:
2476:
2473:
2470:
2461:
2458:
2455:
2452:
2449:
2436:
2433:
2430:
2427:
2424:
2421:
2418:
2415:
2412:
2409:
2406:
2393:
2390:
2387:
2384:
2381:
2378:
2375:
2372:
2369:
2366:
2363:
2360:
2357:
2354:
2351:
2348:
2344:
2329:
2328:
2321:
2318:
2315:
2312:
2309:
2306:
2303:
2300:
2297:
2294:
2291:
2288:
2285:
2282:
2279:
2276:
2273:
2270:
2267:
2264:
2261:
2258:
2255:
2251:
2228:
2227:
2204:
2202:
2195:
2189:
2186:
2144:
2141:
2127:
2124:
2099:
2096:
2057:
2054:
2037:
2034:
2020:chromosome 17q
1963:
1960:
1954:
1953:
1945:
1942:
1938:
1935:
1931:
1930:
1917:
1914:
1911:
1907:
1906:
1901:
1894:
1891:
1887:
1886:
1881:
1874:
1871:
1867:
1866:
1861:
1858:
1855:
1851:
1850:
1842:
1839:
1836:
1832:
1831:
1828:
1825:
1822:
1812:
1809:
1807:
1804:
1790:
1787:
1765:
1762:
1713:
1710:
1700:
1697:
1678:
1675:
1658:5-fluorouracil
1623:ATP hydrolysis
1619:P-glycoprotein
1603:P-glycoprotein
1594:
1591:
1586:
1573:
1570:
1558:S. typhimurium
1485:
1448:
1445:
1427:
1424:
1385:
1382:
1366:ABCB (MDR/TAP)
1360:P-glycoprotein
1358:Main article:
1355:
1352:
1344:P-glycoprotein
1292:P-glycoprotein
1262:
1259:
1253:
1240:
1237:
1223:
1219:
1215:
1211:
1208:
1202:
1198:
1195:
1186:
1138:
1135:
1118:P-glycoprotein
1096:
1084:
1047:
1044:
1039:
1027:
974:
971:
942:Walker B motif
933:Walker A motif
893:
890:
874:
850:
847:
816:
701:
698:
635:P-glycoprotein
621:, age-related
559:
556:
462:
459:
386:
383:
252:
248:
224:
223:
220:
219:
214:
208:
207:
194:
188:
187:
177:
170:
169:
161:
160:
155:
149:
148:
143:
137:
136:
131:
125:
124:
111:
105:
104:
99:
93:
92:
87:
81:
80:
75:
69:
68:
65:
61:
60:
56:
55:
45:
43:
35:
34:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
8137:
8126:
8123:
8121:
8118:
8117:
8115:
8102:
8101:
8094:
8087:
8083:
8079:
8076:
8074:
8071:
8069:
8066:
8064:
8061:
8060:
8058:
8054:
8048:
8045:
8043:
8040:
8039:
8037:
8033:
8027:
8024:
8023:
8021:
8017:
8011:
8008:
8006:
8003:
8001:
7998:
7996:
7993:
7992:
7990:
7986:
7980:
7977:
7975:
7972:
7970:
7967:
7964:
7960:
7956:
7953:
7951:
7948:
7946:
7943:
7941:
7938:
7936:
7933:
7931:
7928:
7926:
7923:
7921:
7918:
7917:
7915:
7911:
7905:
7902:
7900:
7897:
7895:
7892:
7890:
7887:
7885:
7882:
7880:
7877:
7874:
7871:
7869:
7865:
7862:
7860:
7857:
7856:
7854:
7850:
7844:
7841:
7839:
7836:
7834:
7831:
7829:
7826:
7824:
7821:
7819:
7816:
7814:
7811:
7809:
7806:
7805:
7803:
7799:
7794:
7790:
7787:
7783:
7779:
7772:
7767:
7765:
7760:
7758:
7753:
7752:
7749:
7742:
7738:
7735:
7733:
7729:
7726:
7724:
7720:
7717:
7716:
7699:on 2012-05-11
7698:
7694:
7688:
7684:
7683:
7677:
7673:
7669:
7664:
7659:
7655:
7651:
7647:
7642:
7638:
7634:
7629:
7624:
7620:
7616:
7612:
7607:
7606:
7593:
7589:
7584:
7579:
7574:
7569:
7565:
7561:
7557:
7550:
7542:
7538:
7533:
7528:
7524:
7520:
7516:
7509:
7501:
7497:
7489:
7485:
7480:
7475:
7471:
7467:
7463:
7459:
7455:
7448:
7440:
7436:
7431:
7426:
7422:
7418:
7414:
7410:
7406:
7399:
7397:
7388:
7384:
7379:
7374:
7369:
7364:
7361:(3): 281–90.
7360:
7356:
7352:
7345:
7337:
7333:
7328:
7323:
7318:
7313:
7309:
7305:
7301:
7297:
7293:
7286:
7278:
7274:
7270:
7268:9780121821937
7264:
7260:
7256:
7252:
7244:
7236:
7232:
7228:
7224:
7220:
7216:
7213:(6): 721–32.
7212:
7208:
7201:
7193:
7189:
7185:
7181:
7177:
7173:
7166:
7158:
7154:
7147:
7139:
7135:
7131:
7127:
7123:
7119:
7116:(3): 388–94.
7115:
7111:
7104:
7102:
7093:
7089:
7085:
7081:
7074:
7066:
7060:
7056:
7049:
7041:
7037:
7033:
7029:
7024:
7019:
7016:(5): 411–24.
7015:
7011:
7007:
7000:
6992:
6988:
6983:
6978:
6974:
6970:
6966:
6962:
6958:
6951:
6943:
6939:
6935:
6931:
6927:
6923:
6919:
6915:
6911:
6907:
6899:
6891:
6887:
6882:
6877:
6872:
6867:
6863:
6859:
6855:
6851:
6847:
6839:
6831:
6827:
6822:
6817:
6812:
6807:
6803:
6799:
6795:
6788:
6780:
6776:
6772:
6768:
6764:
6760:
6756:
6752:
6748:
6744:
6737:
6735:
6733:
6724:
6720:
6716:
6712:
6708:
6704:
6697:
6689:
6685:
6674:
6666:
6659:
6655:
6651:
6647:
6640:
6636:
6632:
6628:
6624:
6620:
6616:
6612:
6608:
6604:
6597:
6595:
6586:
6582:
6571:
6563:
6556:
6552:
6548:
6544:
6537:
6533:
6529:
6525:
6521:
6517:
6513:
6509:
6502:
6500:
6491:
6487:
6482:
6477:
6473:
6469:
6465:
6461:
6457:
6450:
6442:
6438:
6433:
6428:
6424:
6420:
6416:
6409:
6401:
6397:
6393:
6389:
6385:
6381:
6374:
6366:
6362:
6358:
6354:
6350:
6346:
6342:
6338:
6334:
6330:
6326:
6319:
6311:
6307:
6303:
6299:
6296:(4): 640–54.
6295:
6291:
6283:
6275:
6271:
6267:
6263:
6260:(1): 145–60.
6259:
6255:
6248:
6241:
6233:
6229:
6225:
6221:
6217:
6213:
6209:
6205:
6198:
6190:
6186:
6181:
6176:
6173:(1): 179–91.
6172:
6168:
6164:
6157:
6155:
6153:
6151:
6142:
6138:
6134:
6130:
6126:
6122:
6118:
6114:
6110:
6106:
6099:
6091:
6087:
6082:
6077:
6072:
6067:
6063:
6059:
6055:
6048:
6040:
6036:
6032:
6028:
6024:
6020:
6013:
6005:
6001:
5996:
5991:
5986:
5981:
5977:
5973:
5970:(7): 3974–7.
5969:
5965:
5961:
5954:
5946:
5942:
5937:
5932:
5928:
5924:
5920:
5916:
5912:
5908:
5904:
5897:
5889:
5885:
5880:
5875:
5871:
5867:
5863:
5859:
5855:
5851:
5847:
5840:
5838:
5829:
5825:
5820:
5815:
5811:
5807:
5803:
5799:
5795:
5788:
5780:
5776:
5771:
5766:
5762:
5758:
5754:
5747:
5739:
5735:
5731:
5727:
5722:
5717:
5713:
5709:
5702:
5695:
5687:
5683:
5679:
5675:
5671:
5667:
5659:
5651:
5647:
5642:
5637:
5633:
5629:
5625:
5618:
5610:
5606:
5602:
5598:
5594:
5590:
5583:
5575:
5571:
5566:
5561:
5556:
5551:
5547:
5543:
5539:
5532:
5524:
5520:
5516:
5512:
5508:
5504:
5500:
5496:
5492:
5488:
5481:
5473:
5469:
5465:
5461:
5456:
5451:
5447:
5443:
5439:
5435:
5431:
5424:
5422:
5420:
5418:
5409:
5405:
5400:
5395:
5391:
5387:
5384:(6): 726–33.
5383:
5379:
5375:
5368:
5366:
5364:
5362:
5360:
5358:
5356:
5354:
5345:
5341:
5337:
5333:
5330:(4): 426–31.
5329:
5325:
5318:
5310:
5306:
5302:
5298:
5294:
5290:
5286:
5282:
5275:
5273:
5271:
5269:
5267:
5265:
5263:
5254:
5250:
5246:
5242:
5238:
5234:
5227:
5225:
5216:
5212:
5207:
5202:
5198:
5194:
5190:
5183:
5175:
5171:
5166:
5161:
5156:
5151:
5147:
5143:
5139:
5135:
5131:
5124:
5116:
5112:
5107:
5102:
5098:
5094:
5090:
5086:
5082:
5075:
5073:
5064:
5060:
5055:
5050:
5046:
5042:
5038:
5031:
5023:
5019:
5015:
5011:
5008:(9): 539–44.
5007:
5003:
4996:
4994:
4985:
4981:
4977:
4973:
4968:
4963:
4959:
4955:
4951:
4947:
4943:
4936:
4928:
4924:
4920:
4916:
4912:
4908:
4904:
4900:
4897:(4): 1042–8.
4896:
4892:
4885:
4883:
4881:
4879:
4870:
4866:
4861:
4856:
4851:
4846:
4842:
4838:
4834:
4827:
4819:
4815:
4811:
4807:
4802:
4797:
4793:
4789:
4785:
4778:
4776:
4767:
4763:
4758:
4753:
4748:
4743:
4739:
4735:
4731:
4727:
4723:
4716:
4714:
4712:
4710:
4708:
4699:
4695:
4690:
4685:
4681:
4677:
4674:(1): 139–49.
4673:
4669:
4665:
4658:
4656:
4654:
4652:
4650:
4648:
4639:
4635:
4630:
4625:
4621:
4617:
4613:
4606:
4604:
4595:
4591:
4587:
4583:
4580:(2): 333–42.
4579:
4575:
4567:
4559:
4555:
4550:
4545:
4541:
4537:
4533:
4529:
4525:
4518:
4516:
4507:
4503:
4498:
4493:
4489:
4485:
4481:
4477:
4473:
4466:
4464:
4462:
4453:
4449:
4444:
4439:
4436:(3): 651–61.
4435:
4431:
4427:
4420:
4418:
4416:
4414:
4405:
4401:
4396:
4391:
4388:(7): 571–86.
4387:
4383:
4379:
4372:
4370:
4361:
4357:
4353:
4349:
4346:(2): 343–58.
4345:
4341:
4333:
4331:
4329:
4320:
4316:
4312:
4308:
4304:
4303:10.1038/25393
4300:
4296:
4292:
4288:
4284:
4277:
4269:
4265:
4260:
4255:
4250:
4245:
4241:
4237:
4233:
4226:
4224:
4215:
4211:
4207:
4203:
4199:
4195:
4191:
4187:
4180:
4173:
4171:
4169:
4167:
4158:
4154:
4149:
4144:
4140:
4136:
4132:
4128:
4124:
4120:
4116:
4109:
4101:
4097:
4093:
4089:
4085:
4081:
4077:
4073:
4069:
4065:
4058:
4056:
4047:
4043:
4039:
4035:
4031:
4027:
4023:
4019:
4015:
4011:
4004:
4002:
4000:
3991:
3987:
3983:
3979:
3975:
3971:
3967:
3963:
3959:
3955:
3948:
3946:
3944:
3935:
3931:
3927:
3923:
3919:
3915:
3911:
3907:
3903:
3899:
3892:
3884:
3880:
3876:
3872:
3868:
3864:
3860:
3856:
3852:
3848:
3841:
3834:
3832:
3830:
3821:
3817:
3812:
3807:
3803:
3799:
3796:(3): 218–27.
3795:
3791:
3787:
3780:
3778:
3776:
3774:
3772:
3770:
3768:
3766:
3764:
3762:
3760:
3758:
3756:
3754:
3752:
3750:
3748:
3739:
3735:
3730:
3725:
3721:
3717:
3716:J. Biol. Chem
3713:
3706:
3698:
3694:
3690:
3686:
3682:
3678:
3673:
3668:
3664:
3660:
3656:
3649:
3647:
3638:
3634:
3630:
3626:
3622:
3618:
3611:
3603:
3599:
3595:
3591:
3588:(5): 267–74.
3587:
3583:
3576:
3568:
3564:
3560:
3556:
3552:
3548:
3541:
3539:
3537:
3535:
3533:
3531:
3529:
3527:
3518:
3514:
3509:
3504:
3501:(2): 217–23.
3500:
3496:
3492:
3485:
3477:
3473:
3468:
3463:
3458:
3453:
3449:
3445:
3441:
3434:
3426:
3422:
3418:
3414:
3410:
3406:
3399:
3397:
3395:
3393:
3391:
3389:
3380:
3376:
3372:
3368:
3364:
3360:
3356:
3352:
3345:
3338:
3330:
3326:
3321:
3316:
3312:
3308:
3305:(7): 2452–8.
3304:
3300:
3296:
3289:
3281:
3277:
3272:
3267:
3262:
3257:
3253:
3249:
3245:
3241:
3237:
3230:
3222:
3218:
3213:
3208:
3204:
3200:
3196:
3192:
3188:
3181:
3173:
3167:
3163:
3156:
3154:
3152:
3150:
3141:
3137:
3132:
3127:
3123:
3119:
3115:
3108:
3106:
3104:
3102:
3100:
3098:
3096:
3094:
3092:
3083:
3079:
3074:
3069:
3064:
3059:
3055:
3051:
3047:
3040:
3038:
3036:
3027:
3023:
3018:
3013:
3009:
3005:
3002:(4): 419–35.
3001:
2997:
2993:
2986:
2978:
2974:
2969:
2964:
2960:
2956:
2952:
2948:
2944:
2937:
2935:
2926:
2920:
2916:
2912:
2908:
2901:
2899:
2897:
2895:
2886:
2882:
2877:
2872:
2868:
2864:
2860:
2856:
2852:
2845:
2843:
2841:
2839:
2837:
2835:
2833:
2831:
2829:
2827:
2825:
2823:
2821:
2819:
2817:
2808:
2802:
2798:
2791:
2783:
2779:
2775:
2771:
2766:
2761:
2757:
2753:
2750:(6): 682–99.
2749:
2745:
2741:
2734:
2732:
2723:
2719:
2714:
2709:
2705:
2701:
2697:
2693:
2689:
2685:
2681:
2674:
2672:
2670:
2668:
2663:
2653:
2650:
2648:
2645:
2643:
2640:
2639:
2633:
2621:
2618:
2615:
2612:
2609:
2606:
2603:
2600:
2599:
2597:
2595:
2594:
2589:
2576:
2573:
2570:
2567:
2564:
2561:
2558:
2555:
2552:
2549:
2546:
2545:
2544:
2541:
2538:
2535:
2532:
2529:
2526:
2523:
2520:
2517:
2514:
2511:
2504:
2501:
2498:
2495:
2492:
2489:
2486:
2483:
2480:
2477:
2474:
2471:
2468:
2467:
2465:
2462:
2459:
2456:
2453:
2450:
2447:
2446:
2441:
2437:
2434:
2431:
2428:
2425:
2422:
2419:
2416:
2413:
2410:
2407:
2404:
2403:
2398:
2394:
2391:
2388:
2385:
2382:
2379:
2376:
2373:
2370:
2367:
2364:
2361:
2358:
2355:
2352:
2349:
2346:
2345:
2343:
2341:
2340:
2335:
2326:
2322:
2319:
2316:
2313:
2310:
2307:
2304:
2301:
2298:
2295:
2292:
2289:
2286:
2283:
2280:
2277:
2274:
2271:
2268:
2265:
2262:
2259:
2256:
2253:
2252:
2250:
2248:
2247:
2242:
2237:
2233:
2224:
2221:December 2020
2214:
2208:
2205:This section
2203:
2199:
2194:
2193:
2185:
2183:
2179:
2175:
2171:
2167:
2166:anthracycline
2163:
2159:
2155:
2151:
2140:
2138:
2134:
2126:ABCE and ABCF
2123:
2121:
2117:
2113:
2109:
2105:
2095:
2093:
2089:
2088:sulfonylureas
2085:
2081:
2076:
2074:
2070:
2066:
2064:
2053:
2051:
2047:
2043:
2033:
2030:
2026:
2021:
2017:
2013:
2009:
2005:
2001:
1997:
1993:
1989:
1985:
1981:
1977:
1973:
1970:. These are
1969:
1959:
1952:
1949:
1946:
1943:
1936:
1933:
1932:
1929:
1925:
1921:
1918:
1915:
1912:
1909:
1908:
1905:
1902:
1899:
1895:
1892:
1889:
1888:
1885:
1882:
1879:
1875:
1872:
1869:
1868:
1865:
1862:
1859:
1856:
1853:
1852:
1849:
1846:
1843:
1840:
1837:
1834:
1833:
1829:
1826:
1823:
1820:
1819:
1816:
1803:
1800:
1795:
1786:
1784:
1778:
1774:
1771:
1761:
1757:
1753:
1749:
1745:
1741:
1737:
1733:
1729:
1724:
1720:
1709:
1707:
1696:
1693:
1688:
1684:
1674:
1671:
1667:
1663:
1659:
1655:
1651:
1645:
1643:
1639:
1634:
1632:
1628:
1624:
1620:
1616:
1610:
1606:
1604:
1600:
1590:
1578:
1569:
1567:
1563:
1559:
1555:
1550:
1545:
1541:
1540:cross-linking
1537:
1533:
1523:
1519:
1513:
1509:
1503:
1499:
1493:
1489:
1483:
1479:
1474:
1470:
1466:
1462:
1458:
1454:
1444:
1441:
1437:
1433:
1423:
1421:
1417:
1413:
1412:
1407:
1406:
1401:
1397:
1396:
1391:
1381:
1379:
1375:
1371:
1367:
1361:
1351:
1349:
1345:
1339:
1336:
1332:
1328:
1324:
1322:
1317:
1313:
1307:
1305:
1301:
1297:
1293:
1289:
1285:
1281:
1277:
1273:
1269:
1261:ABC exporters
1258:
1245:
1236:
1234:
1229:
1207:
1194:
1192:
1184:
1181:
1177:
1173:
1169:
1165:
1164:x-ray crystal
1161:
1160:cell membrane
1157:
1153:
1149:
1148:Gram-positive
1145:
1137:ABC importers
1134:
1131:
1127:
1123:
1122:Spectroscopic
1119:
1115:
1111:
1105:
1101:
1092:
1090:
1082:
1078:
1074:
1070:
1066:
1062:
1057:
1053:
1043:
1037:
1033:
1025:
1019:
1016:
1012:
1009:and backbone
1008:
1003:
997:
995:
990:
985:
981:
970:
967:
963:
959:
955:
951:
947:
943:
939:
935:
934:
929:
925:
921:
917:
908:
904:
898:
889:
886:
884:
879:
872:
867:
865:
861:
857:
846:
844:
840:
835:
831:
827:
823:
819:
812:
808:
803:
801:
797:
793:
789:
785:
784:alpha helices
781:
780:
775:
770:
768:
764:
760:
756:
752:
748:
744:
734:
730:
724:
716:
712:
706:
697:
695:
691:
686:
684:
680:
679:sphingomyelin
676:
672:
668:
664:
660:
657:, but not of
656:
655:dexamethasone
652:
648:
644:
640:
636:
632:
628:
624:
620:
616:
612:
609:, persistent
608:
604:
600:
596:
592:
588:
584:
580:
579:polymorphisms
575:
573:
570:) and in the
569:
565:
555:
553:
549:
545:
541:
537:
533:
529:
525:
521:
517:
516:teichoic acid
513:
508:
505:
500:
496:
492:
488:
484:
480:
476:
472:
468:
458:
456:
452:
448:
444:
440:
436:
432:
428:
424:
420:
416:
412:
408:
404:
400:
396:
392:
382:
380:
376:
372:
368:
364:
360:
356:
350:
347:
343:
339:
335:
331:
326:
322:
318:
314:
309:
307:
303:
300:
296:
291:
289:
285:
281:
277:
274:
270:
269:gene families
266:
262:
246:
242:
235:
230:
218:
215:
213:
209:
206:
202:
198:
195:
193:
189:
185:
181:
178:
175:
171:
166:
162:
159:
156:
154:
150:
147:
144:
142:
138:
135:
132:
130:
126:
123:
119:
115:
112:
110:
106:
103:
100:
98:
94:
91:
88:
86:
82:
79:
76:
74:
70:
66:
62:
57:
52:
41:
36:
31:
19:
8097:
7788:
7701:. Retrieved
7697:the original
7681:
7653:
7649:
7618:
7614:
7563:
7559:
7549:
7525:(2): 270–7.
7522:
7518:
7508:
7499:
7461:
7457:
7447:
7412:
7408:
7358:
7354:
7344:
7299:
7295:
7285:
7250:
7243:
7210:
7206:
7200:
7178:(1): 27–42.
7175:
7171:
7165:
7156:
7146:
7113:
7109:
7083:
7079:
7073:
7054:
7048:
7013:
7009:
6999:
6967:(1): 36–42.
6964:
6960:
6950:
6909:
6905:
6898:
6853:
6849:
6838:
6804:(10): e271.
6801:
6798:PLOS Biology
6797:
6787:
6746:
6742:
6706:
6703:Biochemistry
6702:
6696:
6671:{{
6663:{{
6606:
6602:
6568:{{
6560:{{
6511:
6507:
6463:
6459:
6449:
6422:
6418:
6408:
6383:
6380:Biochemistry
6379:
6373:
6335:(5): 935–8.
6332:
6329:FEBS Letters
6328:
6318:
6293:
6289:
6282:
6257:
6253:
6240:
6207:
6203:
6197:
6170:
6166:
6108:
6105:FEBS Letters
6104:
6098:
6061:
6057:
6047:
6022:
6018:
6012:
5967:
5963:
5953:
5910:
5906:
5896:
5853:
5849:
5801:
5797:
5787:
5760:
5756:
5746:
5711:
5707:
5694:
5669:
5666:Biochemistry
5665:
5658:
5631:
5627:
5617:
5592:
5589:Biochemistry
5588:
5582:
5545:
5541:
5531:
5493:(3): 285–9.
5490:
5487:FEBS Letters
5486:
5480:
5440:(1): 102–5.
5437:
5434:FEBS Letters
5433:
5381:
5377:
5327:
5323:
5317:
5284:
5280:
5239:(4): 412–8.
5236:
5232:
5199:(4): 413–9.
5196:
5192:
5182:
5137:
5133:
5123:
5088:
5084:
5044:
5040:
5030:
5005:
5001:
4949:
4946:FEBS Letters
4945:
4935:
4894:
4891:FEBS Letters
4890:
4840:
4836:
4826:
4791:
4787:
4729:
4725:
4671:
4667:
4619:
4615:
4577:
4573:
4566:
4531:
4527:
4479:
4475:
4433:
4429:
4385:
4381:
4343:
4339:
4286:
4282:
4276:
4239:
4235:
4189:
4185:
4122:
4118:
4108:
4067:
4063:
4013:
4009:
3957:
3953:
3901:
3897:
3891:
3850:
3846:
3793:
3789:
3719:
3715:
3705:
3662:
3658:
3620:
3616:
3610:
3585:
3581:
3575:
3553:(1): 29–52.
3550:
3546:
3498:
3494:
3484:
3447:
3443:
3433:
3408:
3404:
3354:
3350:
3337:
3302:
3298:
3288:
3243:
3239:
3229:
3194:
3190:
3180:
3161:
3121:
3117:
3053:
3049:
2999:
2995:
2985:
2950:
2946:
2906:
2858:
2854:
2796:
2790:
2747:
2743:
2687:
2683:
2631:
2591:
2585:
2542:
2463:
2443:
2400:
2337:
2331:
2324:
2244:
2238:
2234:
2231:
2218:
2206:
2174:mitoxantrone
2150:mitoxantrone
2146:
2129:
2101:
2077:
2067:
2059:
2039:
1965:
1957:
1814:
1796:
1792:
1779:
1775:
1769:
1767:
1731:
1727:
1722:
1719:ATPase assay
1715:
1702:
1680:
1646:
1635:
1611:
1607:
1596:
1583:
1566:fluorescence
1561:
1557:
1553:
1548:
1535:
1531:
1528:
1481:
1480:. MsbA from
1477:
1450:
1431:
1429:
1409:
1403:
1399:
1393:
1389:
1387:
1373:
1369:
1365:
1363:
1340:
1334:
1333:(HlyA) from
1326:
1319:
1316:ABC exporter
1315:
1311:
1308:
1280:bacteriocins
1276:lantibiotics
1264:
1250:
1213:
1200:
1190:
1179:
1175:
1171:
1140:
1130:crosslinking
1106:
1102:
1093:
1076:
1072:
1068:
1064:
1060:
1055:
1049:
1020:
998:
988:
984:T. litoralis
983:
979:
976:
961:
953:
949:
945:
941:
937:
931:
927:
922:-like motor
915:
913:
887:
882:
880:
868:
864:ABC exporter
863:
859:
855:
852:
842:
838:
829:
821:
810:
806:
804:
802:resistance.
795:
791:
777:
773:
771:
751:polypeptides
747:polypeptides
739:
687:
659:progesterone
576:
572:sulfonylurea
561:
554:biogenesis.
544:bacteriocins
509:
490:
483:erythrocytes
479:Enterobactin
475:siderophores
464:
438:
434:
398:
388:
351:
310:
292:
288:translocases
264:
260:
258:
6466:: 295–329.
5047:(1): 1–18.
3467:2434/611267
2953:(1): 1–10.
2178:doxorubicin
2164:can export
1968:chromosomes
1898:peroxisomes
1806:Subfamilies
1728:Xenobiotica
1683:Prokaryotic
1666:doxorubicin
1640:(MRP1) and
1631:vinblastine
1549:V. cholerae
1455:. It is an
1440:vinblastine
1436:doxorubicin
1284:antibiotics
1156:lipoprotein
1112:binding to
1110:vinblastine
950:LSGGQ motif
918:similar to
694:xenobiotics
663:cholesterol
639:aldosterone
617:, X-linked
615:hyperplasia
599:cholestasis
548:antibiotics
540:antibiotics
461:Prokaryotic
423:hydrophilic
411:amino acids
280:prokaryotes
153:OPM protein
59:Identifiers
27:Gene family
8114:Categories
7703:2012-05-16
6025:: 347–75.
3411:: 241–68.
2659:References
2104:peroxisome
2063:N terminus
1687:eukaryotic
1168:molybdenum
1013:groups of
958:hydrolysis
788:N-terminal
681:(SM), and
558:Eukaryotic
552:cytochrome
546:, peptide
477:, such as
431:Eukaryotes
391:substrates
317:DNA repair
180:structures
8098:see also
6673:retracted
6665:retracted
6570:retracted
6562:retracted
5927:1381-6128
5870:0261-4189
5193:Structure
4382:Structure
4319:204996524
3697:243863723
3681:1945-7197
2704:0146-0749
2593:IPR003838
2445:IPR005495
2402:IPR010390
2339:IPR000412
2246:IPR036640
2213:talk page
2170:topotecan
2092:diazoxide
1910:ABCE/ABCF
1830:Examples
1670:substrate
1662:annamycin
1473:mutations
1469:endotoxin
1331:hemolysin
1325:, and an
1152:periplasm
1081:phosphate
1036:glutamine
1032:glutamate
1024:aspartate
994:catalysis
966:histidine
871:molybdate
826:homodimer
815:vitamin B
800:macrolide
700:Structure
643:dendritic
583:Mendelian
530:), heme,
520:hemolysis
499:galactose
471:Pathogens
467:virulence
455:periplasm
451:cytoplasm
449:from the
439:effluxers
435:Exporters
403:nutrients
399:importers
395:membranes
102:PDOC00185
90:IPR003439
44:Vitamin B
8078:Sterolin
7672:15347662
7637:15252017
7592:23647830
7541:15748994
7488:10839820
7439:21740521
7387:19403462
7235:86198612
7227:18611113
7192:16305368
7130:15608134
7092:11560870
7032:14530494
6991:19819701
6942:13660653
6934:29720648
6890:29735709
6830:17927448
6771:15890883
6723:15222771
6658:17185584
6639:37250061
6631:15890884
6555:17185584
6536:11546864
6490:17362200
6441:12842882
6400:18690712
6365:19960736
6357:17303126
6310:21992190
6274:21967056
6232:16054428
6189:19309458
6141:23368914
6133:16359667
6090:22639627
6039:17263663
5945:23688078
5828:11598005
5779:10364203
5738:33274934
5730:10753896
5686:11087367
5650:12424247
5609:11747450
5574:31431556
5523:20395778
5472:24228062
5464:14630327
5408:18948194
5344:15313236
5309:23058653
5301:15452563
5253:17723295
5115:15889153
5063:15511523
5022:11551790
4984:20550226
4976:16412422
4927:34114828
4919:16337944
4869:12093921
4818:18850076
4810:10892749
4766:18024585
4698:12150914
4638:11402022
4594:12823972
4558:11532960
4506:11080142
4452:14527411
4404:11470432
4360:12823973
4268:11964392
4214:10531462
4206:17158291
4157:18621668
4092:18033289
4038:17322901
3990:27132450
3982:16943773
3934:37232959
3926:17673622
3875:12004122
3820:19234479
3689:34748636
3637:16460798
3617:Placenta
3602:11502161
3567:15749056
3425:15189142
3379:21763870
3371:15519310
3140:11441126
3082:16202168
3026:24638992
2977:19806386
2885:18535149
2782:21422822
2774:15052411
2765:11138499
2636:See also
2588:InterPro
2440:InterPro
2397:InterPro
2334:InterPro
2241:InterPro
1827:Function
1756:25944548
1748:17968740
1525:)
1453:flippase
1374:MDR1 Pgp
1126:protease
1114:permease
1065:outward-
834:monomers
776:and the
736:)
718:)
690:placenta
651:cortisol
528:protease
493:encodes
415:peptides
385:Function
330:vitamins
321:cassette
234:flippase
197:RCSB PDB
85:InterPro
67:ABC_tran
7583:3654945
7430:3168698
7378:2752038
7336:3368466
7304:Bibcode
7277:9711542
7138:7063502
7040:2780630
6982:4608440
6914:Bibcode
6881:6042065
6858:Bibcode
6821:2001213
6779:1308350
6751:Bibcode
6743:Science
6611:Bibcode
6603:Science
6516:Bibcode
6508:Science
6481:2569861
6337:Bibcode
6212:Bibcode
6113:Bibcode
6081:3355715
6064:: 108.
6004:7001450
5972:Bibcode
5936:6341993
5888:2249654
5565:6703430
5515:8549739
5495:Bibcode
5442:Bibcode
5399:2643341
5215:9562560
5174:8710841
5142:Bibcode
5106:1142601
4954:Bibcode
4899:Bibcode
4757:2141898
4734:Bibcode
4689:3516284
4311:9872322
4291:Bibcode
4259:3516282
4186:Science
4148:2527972
4127:Bibcode
4119:Science
4100:4384771
4072:Bibcode
4046:4417002
4018:Bibcode
3962:Bibcode
3906:Bibcode
3898:Science
3855:Bibcode
3847:Science
3811:2830722
3738:7040366
3517:8181727
3476:9575204
3329:9079938
3280:2118656
3248:Bibcode
3221:7927795
3073:1277830
3017:3971661
2968:2760711
2876:2415747
2722:8302219
2590::
2442::
2399::
2336::
2243::
1824:Members
1799:calcein
1723:in vivo
1532:E. coli
1482:E. coli
1461:lipid A
1426:Sav1866
1335:E. coli
1302:), and
1183:maltose
1180:E. coli
1178:BtuCD,
1176:E. coli
1018:motif.
1015:glycine
980:E. coli
962:H motif
924:ATPases
811:E. coli
796:E. coli
792:E. coli
504:osmotic
495:glucose
453:to the
427:bilayer
338:sterols
302:ATPases
278:, from
97:PROSITE
78:PF00005
7793:TC 3A1
7743:(MeSH)
7689:
7670:
7635:
7590:
7580:
7566:: 98.
7539:
7486:
7476:
7437:
7427:
7385:
7375:
7334:
7327:280257
7324:
7275:
7265:
7233:
7225:
7190:
7136:
7128:
7090:
7061:
7038:
7030:
6989:
6979:
6940:
6932:
6906:Nature
6888:
6878:
6828:
6818:
6777:
6769:
6721:
6656:
6652:,
6637:
6629:
6553:
6549:,
6534:
6488:
6478:
6439:
6398:
6363:
6355:
6308:
6272:
6230:
6187:
6139:
6131:
6088:
6078:
6037:
6002:
5995:349750
5992:
5943:
5933:
5925:
5886:
5879:552155
5876:
5868:
5826:
5819:125677
5816:
5777:
5736:
5728:
5684:
5648:
5607:
5572:
5562:
5521:
5513:
5470:
5462:
5406:
5396:
5342:
5307:
5299:
5251:
5213:
5172:
5162:
5113:
5103:
5061:
5020:
4982:
4974:
4925:
4917:
4867:
4860:124977
4857:
4816:
4808:
4764:
4754:
4696:
4686:
4636:
4592:
4556:
4549:125601
4546:
4504:
4497:305842
4494:
4450:
4402:
4358:
4317:
4309:
4283:Nature
4266:
4256:
4212:
4204:
4155:
4145:
4098:
4090:
4064:Nature
4044:
4036:
4010:Nature
3988:
3980:
3954:Nature
3932:
3924:
3883:906489
3881:
3873:
3818:
3808:
3736:
3695:
3687:
3679:
3635:
3600:
3565:
3515:
3474:
3423:
3377:
3369:
3327:
3320:178989
3317:
3278:
3268:
3219:
3212:303233
3209:
3168:
3138:
3080:
3070:
3056:: 30.
3024:
3014:
2975:
2965:
2921:
2883:
2873:
2803:
2780:
2772:
2762:
2720:
2713:372944
2710:
2702:
2628:Images
2586:ABC3 (
2332:ABC2 (
2325:Uptake
2239:ABC1 (
2016:ABCA10
1996:ABCA13
1994:, and
1992:ABCA12
1982:, and
1845:ABCA12
1821:Family
1754:
1746:
1457:ATPase
1268:toxins
1233:ATPase
1087:) and
1007:serine
1002:lysine
954:Q loop
938:P-loop
677:(PS),
673:(PE),
669:(PC),
536:toxins
514:, and
419:sugars
375:ataxia
334:lipids
284:humans
273:extant
232:Lipid
212:PDBsum
186:
176:
122:SUPFAM
64:Symbol
7732:ABCdb
7728:ABCdb
7479:98997
7231:S2CID
7134:S2CID
7036:S2CID
6938:S2CID
6775:S2CID
6669:with
6635:S2CID
6566:with
6361:S2CID
6250:(PDF)
6137:S2CID
5734:S2CID
5704:(PDF)
5519:S2CID
5468:S2CID
5305:S2CID
5165:38640
4980:S2CID
4923:S2CID
4814:S2CID
4315:S2CID
4210:S2CID
4182:(PDF)
4096:S2CID
4042:S2CID
3986:S2CID
3930:S2CID
3879:S2CID
3843:(PDF)
3693:S2CID
3375:S2CID
3347:(PDF)
3271:54606
2778:S2CID
2176:, or
2162:ABCG2
2158:ABCC1
2154:ABCB1
2133:ABCE1
2116:ABCD1
2108:ABCD1
2042:ABCB1
2029:ABCA4
2025:ABCA1
2012:ABCA9
2008:ABCA8
2004:ABCA6
2000:ABCA5
1988:ABCA7
1984:ABCA4
1980:ABCA3
1976:ABCA2
1972:ABCA1
1951:ABCG1
1948:ABCG2
1928:ABCF2
1924:ABCF1
1920:ABCE1
1904:ABCD1
1884:ABCC6
1864:ABCB5
1848:ABCA1
1752:S2CID
1642:ABCG2
1638:ABCC1
1420:auxin
1370:ABCB1
1323:(MFP)
1300:ABCC1
1011:amide
342:drugs
276:phyla
134:3.A.1
118:SCOPe
109:SCOP2
7955:C8-9
7864:B2-3
7723:TCDB
7687:ISBN
7668:PMID
7633:PMID
7588:PMID
7537:PMID
7484:PMID
7435:PMID
7383:PMID
7332:PMID
7273:PMID
7263:ISBN
7223:PMID
7188:PMID
7157:Diva
7126:PMID
7088:PMID
7059:ISBN
7028:PMID
6987:PMID
6930:PMID
6886:PMID
6826:PMID
6767:PMID
6719:PMID
6654:PMID
6627:PMID
6551:PMID
6532:PMID
6486:PMID
6437:PMID
6396:PMID
6353:PMID
6306:PMID
6270:PMID
6228:PMID
6185:PMID
6129:PMID
6086:PMID
6035:PMID
6000:PMID
5941:PMID
5923:ISSN
5884:PMID
5866:ISSN
5824:PMID
5775:PMID
5726:PMID
5682:PMID
5646:PMID
5605:PMID
5570:PMID
5542:mBio
5511:PMID
5460:PMID
5404:PMID
5340:PMID
5297:PMID
5249:PMID
5211:PMID
5170:PMID
5111:PMID
5059:PMID
5045:1659
5018:PMID
4972:PMID
4915:PMID
4865:PMID
4806:PMID
4788:Cell
4762:PMID
4694:PMID
4634:PMID
4590:PMID
4554:PMID
4502:PMID
4448:PMID
4400:PMID
4356:PMID
4307:PMID
4264:PMID
4202:PMID
4153:PMID
4088:PMID
4034:PMID
3978:PMID
3922:PMID
3871:PMID
3816:PMID
3734:PMID
3685:PMID
3677:ISSN
3633:PMID
3598:PMID
3563:PMID
3551:1733
3513:PMID
3472:PMID
3421:PMID
3367:PMID
3355:1666
3325:PMID
3276:PMID
3217:PMID
3166:ISBN
3136:PMID
3078:PMID
3022:PMID
2973:PMID
2919:ISBN
2881:PMID
2801:ISBN
2770:PMID
2718:PMID
2700:ISSN
2143:ABCG
2098:ABCD
2078:The
2069:CFTR
2056:ABCC
2036:ABCB
2014:and
2006:and
2002:and
1962:ABCA
1934:ABCG
1890:ABCD
1870:ABCC
1854:ABCB
1835:ABCA
1783:BSEP
1768:The
1744:PMID
1692:RNAi
1685:and
1664:and
1522:3b60
1512:3b5x
1502:3b5w
1447:MsbA
1416:HeLa
1318:, a
1296:MRP1
1286:and
1067:and
940:and
920:RecA
907:2onj
862:and
733:2onj
715:2qi9
653:and
568:CFTR
524:heme
497:and
487:gene
473:use
407:ions
315:and
259:The
236:MsbA
205:PDBj
201:PDBe
184:ECOD
174:Pfam
158:3g5u
129:TCDB
114:1b0u
73:Pfam
51:1l7v
7979:C13
7974:C11
7969:C10
7904:B11
7843:A13
7838:A12
7721:in
7658:doi
7654:279
7623:doi
7619:279
7578:PMC
7568:doi
7527:doi
7523:156
7474:PMC
7466:doi
7425:PMC
7417:doi
7413:278
7373:PMC
7363:doi
7322:PMC
7312:doi
7255:doi
7215:doi
7180:doi
7118:doi
7018:doi
6977:PMC
6969:doi
6922:doi
6910:557
6876:PMC
6866:doi
6854:115
6816:PMC
6806:doi
6759:doi
6747:308
6711:doi
6684:doi
6646:doi
6619:doi
6607:308
6581:doi
6543:doi
6524:doi
6512:293
6476:PMC
6468:doi
6427:doi
6423:278
6388:doi
6345:doi
6333:581
6298:doi
6262:doi
6220:doi
6175:doi
6121:doi
6109:580
6076:PMC
6066:doi
6027:doi
5990:PMC
5980:doi
5931:PMC
5915:doi
5874:PMC
5858:doi
5814:PMC
5806:doi
5765:doi
5761:274
5716:doi
5712:275
5674:doi
5636:doi
5632:278
5597:doi
5560:PMC
5550:doi
5503:doi
5491:377
5450:doi
5438:555
5394:PMC
5386:doi
5332:doi
5289:doi
5241:doi
5201:doi
5160:PMC
5150:doi
5101:PMC
5093:doi
5049:doi
5010:doi
4962:doi
4950:580
4907:doi
4895:580
4855:PMC
4845:doi
4796:doi
4792:101
4752:PMC
4742:doi
4730:104
4684:PMC
4676:doi
4624:doi
4620:276
4582:doi
4578:330
4544:PMC
4536:doi
4492:PMC
4484:doi
4438:doi
4390:doi
4348:doi
4344:330
4299:doi
4287:396
4254:PMC
4244:doi
4240:277
4194:doi
4190:315
4143:PMC
4135:doi
4123:321
4080:doi
4068:450
4026:doi
4014:446
3970:doi
3958:443
3914:doi
3902:317
3863:doi
3851:296
3806:PMC
3798:doi
3724:doi
3720:257
3667:doi
3663:107
3625:doi
3590:doi
3555:doi
3503:doi
3499:117
3462:hdl
3452:doi
3448:273
3413:doi
3359:doi
3315:PMC
3307:doi
3303:179
3266:PMC
3256:doi
3207:PMC
3199:doi
3126:doi
3068:PMC
3058:doi
3012:PMC
3004:doi
3000:143
2963:PMC
2955:doi
2951:231
2911:doi
2871:PMC
2863:doi
2760:PMC
2752:doi
2708:PMC
2692:doi
2596:):
2342:):
2249:):
2156:or
2106:.
1785:).
1736:doi
1652:),
1518:PDB
1508:PDB
1498:PDB
1372:or
903:PDB
832:or
743:ATP
729:PDB
711:PDB
489:in
437:or
299:AAA
282:to
192:PDB
8116::
8086:G8
8084:,
8082:G5
8073:G4
8068:G2
8063:G1
8047:F2
8042:F1
8026:E1
8010:D4
8005:D3
8000:D2
7995:D1
7963:C9
7961:,
7959:C8
7950:C7
7945:C6
7940:C5
7935:C4
7930:C3
7925:C2
7920:C1
7899:B9
7894:B7
7889:B6
7884:B5
7879:B4
7873:B3
7868:B2
7859:B1
7833:A8
7828:A7
7823:A4
7818:A3
7813:A2
7808:A1
7784::
7780:,
7666:.
7652:.
7648:.
7631:.
7617:.
7613:.
7586:.
7576:.
7564:13
7562:.
7558:.
7535:.
7521:.
7517:.
7498:.
7492:;
7482:.
7472:.
7462:64
7460:.
7456:.
7433:.
7423:.
7411:.
7407:.
7395:^
7381:.
7371:.
7357:.
7353:.
7330:.
7320:.
7310:.
7300:85
7298:.
7294:.
7271:.
7261:.
7229:.
7221:.
7209:.
7186:.
7174:.
7155:.
7132:.
7124:.
7114:33
7112:.
7100:^
7084:29
7082:.
7034:.
7026:.
7012:.
7008:.
6985:.
6975:.
6965:35
6963:.
6959:.
6936:.
6928:.
6920:.
6908:.
6884:.
6874:.
6864:.
6852:.
6848:.
6824:.
6814:.
6800:.
6796:.
6773:.
6765:.
6757:.
6745:.
6731:^
6717:.
6707:43
6705:.
6633:.
6625:.
6617:.
6605:.
6593:^
6530:.
6522:.
6510:.
6498:^
6484:.
6474:.
6464:76
6462:.
6458:.
6435:.
6421:.
6417:.
6394:.
6384:47
6382:.
6359:.
6351:.
6343:.
6331:.
6327:.
6304:.
6294:69
6292:.
6268:.
6258:50
6256:.
6252:.
6226:.
6218:.
6206:.
6183:.
6171:59
6169:.
6165:.
6149:^
6135:.
6127:.
6119:.
6107:.
6084:.
6074:.
6060:.
6056:.
6033:.
6023:58
6021:.
5998:.
5988:.
5978:.
5968:77
5966:.
5962:.
5939:.
5929:.
5921:.
5911:20
5909:.
5905:.
5882:.
5872:.
5864:.
5852:.
5848:.
5836:^
5822:.
5812:.
5802:20
5800:.
5796:.
5773:.
5759:.
5755:.
5732:.
5724:.
5710:.
5706:.
5680:.
5670:39
5668:.
5644:.
5630:.
5626:.
5603:.
5593:40
5591:.
5568:.
5558:.
5546:10
5544:.
5540:.
5517:.
5509:.
5501:.
5489:.
5466:.
5458:.
5448:.
5436:.
5432:.
5416:^
5402:.
5392:.
5382:18
5380:.
5376:.
5352:^
5338:.
5328:14
5326:.
5303:.
5295:.
5285:11
5283:.
5261:^
5247:.
5237:17
5235:.
5223:^
5209:.
5195:.
5191:.
5168:.
5158:.
5148:.
5138:93
5136:.
5132:.
5109:.
5099:.
5089:24
5087:.
5083:.
5071:^
5057:.
5043:.
5039:.
5016:.
5006:26
5004:.
4992:^
4978:.
4970:.
4960:.
4948:.
4944:.
4921:.
4913:.
4905:.
4893:.
4877:^
4863:.
4853:.
4841:99
4839:.
4835:.
4812:.
4804:.
4790:.
4786:.
4774:^
4760:.
4750:.
4740:.
4728:.
4724:.
4706:^
4692:.
4682:.
4672:10
4670:.
4666:.
4646:^
4632:.
4618:.
4614:.
4602:^
4588:.
4576:.
4552:.
4542:.
4532:20
4530:.
4526:.
4514:^
4500:.
4490:.
4480:19
4478:.
4474:.
4460:^
4446:.
4434:12
4432:.
4428:.
4412:^
4398:.
4384:.
4380:.
4368:^
4354:.
4342:.
4327:^
4313:.
4305:.
4297:.
4285:.
4262:.
4252:.
4238:.
4234:.
4222:^
4208:.
4200:.
4188:.
4184:.
4165:^
4151:.
4141:.
4133:.
4121:.
4117:.
4094:.
4086:.
4078:.
4066:.
4054:^
4040:.
4032:.
4024:.
4012:.
3998:^
3984:.
3976:.
3968:.
3956:.
3942:^
3928:.
3920:.
3912:.
3900:.
3877:.
3869:.
3861:.
3849:.
3845:.
3828:^
3814:.
3804:.
3794:10
3792:.
3788:.
3746:^
3732:.
3718:.
3714:.
3691:.
3683:.
3675:.
3661:.
3657:.
3645:^
3631:.
3621:27
3619:.
3596:.
3586:13
3584:.
3561:.
3549:.
3525:^
3511:.
3497:.
3493:.
3470:.
3460:.
3446:.
3442:.
3419:.
3409:73
3407:.
3387:^
3373:.
3365:.
3353:.
3349:.
3323:.
3313:.
3301:.
3297:.
3274:.
3264:.
3254:.
3244:87
3242:.
3238:.
3215:.
3205:.
3195:62
3193:.
3189:.
3148:^
3134:.
3122:42
3120:.
3116:.
3090:^
3076:.
3066:.
3052:.
3048:.
3034:^
3020:.
3010:.
2998:.
2994:.
2971:.
2961:.
2949:.
2945:.
2933:^
2917:.
2893:^
2879:.
2869:.
2859:72
2857:.
2853:.
2815:^
2776:.
2768:.
2758:.
2748:61
2746:.
2742:.
2730:^
2716:.
2706:.
2698:.
2688:57
2686:.
2682:.
2666:^
2507:12
2172:,
2160:.
2122:.
2094:.
2065:.
2052:.
2010:,
1990:,
1986:,
1978:,
1974:,
1926:,
1922:,
1750:.
1742:.
1732:37
1730:.
1520::
1510::
1500::
1438:,
1408:,
1402:,
1278:,
1270:,
1203:12
1146:.
1124:,
1083:(P
996:.
905::
858:,
817:12
769:.
731::
713::
605:,
601:,
593:,
589:,
542:,
538:,
522:,
417:,
413:,
409:,
373:,
361:,
357:,
340:,
336:,
290:.
263:,
247:AB
203:;
199:;
182:/
146:17
120:/
116:/
46:12
8088:)
8080:(
8056:G
8035:F
8019:E
7988:D
7965:)
7957:(
7913:C
7875:)
7866:(
7852:B
7801:A
7795:)
7791:(
7770:e
7763:t
7756:v
7706:.
7674:.
7660::
7639:.
7625::
7594:.
7570::
7543:.
7529::
7490:.
7468::
7441:.
7419::
7389:.
7365::
7359:3
7338:.
7314::
7306::
7279:.
7257::
7237:.
7217::
7211:4
7194:.
7182::
7176:1
7159:.
7140:.
7120::
7094:.
7067:.
7042:.
7020::
7014:8
6993:.
6971::
6944:.
6924::
6916::
6892:.
6868::
6860::
6832:.
6808::
6802:5
6781:.
6761::
6753::
6725:.
6713::
6690:)
6686::
6679:)
6677:.
6648::
6641:.
6621::
6613::
6587:)
6583::
6576:)
6574:.
6545::
6538:.
6526::
6518::
6492:.
6470::
6443:.
6429::
6402:.
6390::
6367:.
6347::
6339::
6312:.
6300::
6276:.
6264::
6234:.
6222::
6214::
6208:8
6191:.
6177::
6143:.
6123::
6115::
6092:.
6068::
6062:2
6041:.
6029::
6006:.
5982::
5974::
5947:.
5917::
5890:.
5860::
5854:9
5830:.
5808::
5781:.
5767::
5740:.
5718::
5688:.
5676::
5652:.
5638::
5611:.
5599::
5576:.
5552::
5525:.
5505::
5497::
5474:.
5452::
5444::
5410:.
5388::
5346:.
5334::
5311:.
5291::
5255:.
5243::
5217:.
5203::
5197:6
5176:.
5152::
5144::
5117:.
5095::
5065:.
5051::
5024:.
5012::
4986:.
4964::
4956::
4929:.
4909::
4901::
4871:.
4847::
4820:.
4798::
4768:.
4744::
4736::
4700:.
4678::
4640:.
4626::
4596:.
4584::
4560:.
4538::
4508:.
4486::
4454:.
4440::
4406:.
4392::
4386:9
4362:.
4350::
4321:.
4301::
4293::
4270:.
4246::
4216:.
4196::
4159:.
4137::
4129::
4102:.
4082::
4074::
4048:.
4028::
4020::
3992:.
3972::
3964::
3936:.
3916::
3908::
3885:.
3865::
3857::
3822:.
3800::
3740:.
3726::
3699:.
3669::
3639:.
3627::
3604:.
3592::
3569:.
3557::
3519:.
3505::
3478:.
3464::
3454::
3427:.
3415::
3381:.
3361::
3331:.
3309::
3282:.
3258::
3250::
3223:.
3201::
3174:.
3142:.
3128::
3084:.
3060::
3054:5
3028:.
3006::
2979:.
2957::
2927:.
2913::
2887:.
2865::
2809:.
2784:.
2754::
2724:.
2694::
2448:)
2405:)
2223:)
2219:(
2215:.
1939:3
1900:.
1758:.
1738::
1656:(
1587:i
1486:2
1298:/
1254:i
1224:2
1220:2
1216:2
1187:2
1097:i
1085:i
1040:2
1028:2
875:2
253:2
251:C
249:2
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.