36:
500:). Nonfunctional membrane and luminal proteins are extracted from the ER and degraded in the cytosol by proteasomes. Substrate retrotranslocation and extraction is assisted by the Cdc48p(Ufd1p/Npl4p) complex on the cytosolic side of the membrane. On the cytosolic side, the substrate is ubiquitinated by ER-based E2 and E3 enzymes before degradation by the 26S proteasome.
515:
standing for 'endosomal sorting complexes required for transport'). Vps4p is a AAA-type ATPase involved in this MVB sorting pathway. It had originally been identified as a ”class E” vps (vacuolar protein sorting) mutant and was subsequently shown to catalyse the dissociation of ESCRT complexes. Vps4p
392:
AAA ATPases assemble into oligomeric assemblies (often homo-hexamers) that form a ring-shaped structure with a central pore. These proteins produce a molecular motor that couples ATP binding and hydrolysis to changes in conformational states that can be propagated through the assembly in order to act
444:
in the substrate protein. In HslU, a bacterial ClpX/ClpY homologue of the HSP100 family of AAA proteins, the N- and C-terminal subdomains move towards each other when nucleotides are bound and hydrolysed. The terminal domains are most distant in the nucleotide-free state and closest in the ADP-bound
413:
on the ATP gamma-phosphate by an activated water molecule, leading to movement of the N-terminal and C-terminal AAA subdomains relative to each other. This movement allows the exertion of mechanical force, amplified by other ATPase domains within the same oligomeric structure. The additional domains
303:
AAA proteins are functionally and organizationally diverse, and vary in activity, stability, and mechanism. Members of the AAA family are found in all organisms and they are essential for many cellular functions. They are involved in processes such as
396:
The central pore may be involved in substrate processing. In the hexameric configuration, the ATP-binding site is positioned at the interface between the subunits. Upon ATP binding and hydrolysis, AAA enzymes undergo
364:
Some classes of AAA proteins have an N-terminal non-ATPase domain which is followed by either one or two AAA domains (D1 and D2). In some proteins with two AAA domains, both are evolutionarily well conserved (like in
495:
The AAA-type ATPase Cdc48p/p97 is perhaps the best-studied AAA protein. Misfolded secretory proteins are exported from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and degraded by the ER-associated degradation pathway
511:
are endosomal compartments that sort ubiquitinated membrane proteins by incorporating them into vesicles. This process involves the sequential action of three multiprotein complexes, ESCRT I to III (
384:, based on secondary structure elements included within or near the core AAA fold: clamp loader, initiator, classic, superfamily III helicase, HCLR, H2-insert, and PS-II insert.
516:
is anchored via Vps46p to the endosomal membrane. Vps4p assembly is assisted by the conserved Vta1p protein, which regulates its oligomerization status and ATPase activity.
904:
Yu RC, Hanson PI, Jahn R, Brünger AT (September 1998). "Structure of the ATP-dependent oligomerization domain of N-ethylmaleimide sensitive factor complexed with ATP".
196:
372:
While the classical AAA family was based on motifs, the family has been expanded using structural information and is now termed the AAA family.
587:
1375:
719:
635:
619:
615:
603:
599:
567:
563:
559:
555:
774:
762:
627:
607:
571:
551:
547:
369:). In others, either the D2 domain (like in Pex1p and Pex6p) or the D1 domain (in Sec18p/NSF) is better conserved in evolution.
595:
591:
583:
785:
120:
216:
947:
Koonin EV, Aravind L, Leipe DD, Iyer LM (2004). "Evolutionary history and higher order classification of AAA ATPases".
469:
dynamics, intracellular transport, transcriptional activation, protein refolding, disassembly of protein complexes and
1340:
1322:
1304:
1286:
538:
1163:
Smith DM, Benaroudj N, Goldberg A (2006). "Proteasomes and their associated ATPases: A destructive combination".
524:
AAA proteases use the energy from ATP hydrolysis to translocate a protein inside the proteasome for degradation.
1370:
340:
The AAA proteins contain two domains, an N-terminal alpha/beta domain that binds and hydrolyzes nucleotides (a
204:
329:
1318:
317:
1336:
1022:
Erzberger JP, Berger JM (2006). "Evolutionary relationships and structural mechanisms of AAA proteins".
344:) and a C-terminal alpha-helical domain. The N-terminal domain is 200-250 amino acids long and contains
731:
401:
in the AAA-domains as well as in the N-domains. These motions can be transmitted to substrate protein.
366:
200:
1365:
278:
140:
133:
810:
Snider J, Houry WA (February 2008). "AAA proteins: diversity in function, similarity in structure".
145:
1360:
356:, substrate binding and/or regulation. These domains can lie N- or C-terminal to the AAA module.
434:
activity, for example in ClpAPS complex, which mediates protein degradation and recognition in
1035:
508:
398:
286:
352:
which includes the AAA family. Most AAA proteins have additional domains that are used for
282:
183:
20:
89:
8:
1300:
454:
427:
349:
325:
309:
271:
152:
1282:
1259:
1234:
1140:
1113:
1091:
929:
878:
835:
470:
414:
in the protein allow for regulation or direction of the force towards different goals.
1264:
1215:
1180:
1145:
1083:
1039:
999:
964:
921:
870:
865:
848:
827:
191:
125:
1095:
933:
882:
839:
64:
1254:
1246:
1207:
1172:
1135:
1125:
1075:
1031:
991:
956:
913:
860:
819:
179:
296:
to conformational changes which are transduced into mechanical force exerted on a
77:
1198:
Tucker PA, Sallai L (December 2007). "The AAA superfamily--a myriad of motions".
462:
458:
440:. The basic recognition of proteins by AAAs is thought to occur through unfolded
353:
313:
305:
157:
101:
488:, are AAA proteins which couple their ATPase activity to molecular motion along
441:
297:
293:
267:
259:
255:
1211:
1176:
1066:
Hanson PI, Whiteheart SW (July 2005). "AAA proteins: have engine, will work".
995:
960:
1354:
1235:"Communication between the AAA ring and microtubule-binding domain of dynein"
485:
345:
341:
1130:
393:
upon a target substrate, either translocating or remodelling the substrate.
1268:
1219:
1184:
1149:
1087:
1043:
1003:
968:
874:
831:
489:
925:
129:
466:
431:
410:
849:"AAA ATPases: achieving diversity of function with conserved machinery"
823:
639:
321:
263:
113:
982:
Lupas AN, Frickey T (2004). "Phylogenetic analysis of AAA proteins".
423:
1250:
1079:
758:
96:
917:
436:
108:
747:
743:
727:
715:
707:
703:
611:
579:
543:
481:
275:
211:
35:
445:
state. Thereby the opening of the central cavity is affected.
770:
766:
739:
735:
711:
679:
675:
671:
667:
663:
659:
623:
575:
512:
381:
789:
723:
699:
695:
691:
687:
683:
655:
651:
647:
643:
631:
497:
173:
84:
71:
59:
281:, which exert their activity through the energy-dependent
348:, and is shared in common with other P-loop NTPases, the
527:
1162:
1114:"The AAA superfamily of functionally diverse proteins"
946:
503:
409:
ATP hydrolysis by AAA ATPases is proposed to involve
1111:
903:
29:
ATPases associated with diverse cellular activities
1352:
1065:
292:AAA proteins couple chemical energy provided by
266:residues. This is a large, functionally diverse
254:(speak: tripple-A ATPases) are a large group of
1021:
1017:
1015:
1013:
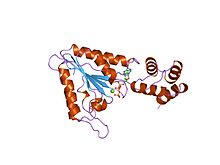
40:Structure of N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor.
375:
1197:
1107:
1105:
1061:
1059:
1057:
1055:
1053:
1010:
981:
846:
809:
532:
1232:
1156:
975:
940:
897:
380:AAA proteins are divided into seven basic
34:
1258:
1191:
1139:
1129:
1102:
1050:
864:
1036:10.1146/annurev.biophys.35.040405.101933
1112:Snider J, Thibault G, Houry WA (2008).
539:HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee (HGNC)
387:
1353:
404:
847:White SR, Lauring B (December 2007).
528:Human proteins containing this domain
426:. Prokaryotes have AAA which combine
1233:Carter AP, Vale RD (February 2010).
484:, one of the three major classes of
476:
422:AAA proteins are not restricted to
417:
13:
1376:Single-pass transmembrane proteins
1024:Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct
803:
519:
504:Targeting to multivesicular bodies
14:
1387:
359:
1341:HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee
1323:HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee
1305:HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee
1287:HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee
1283:"Gene group: AAA ATPases (ATAD)"
866:10.1111/j.1600-0854.2007.00642.x
1329:
1311:
1293:
1275:
242:ssociated with diverse cellular
1226:
795:
1:
890:
453:AAA proteins are involved in
330:regulation of gene expression
168:Available protein structures:
448:
346:Walker A and Walker B motifs
335:
7:
1337:"Symbol report for AFG3L1P"
1301:"Gene group: Torsins (TOR)"
10:
1392:
753:
536:
376:Evolutionary relationships
18:
1212:10.1016/j.sbi.2007.09.012
1177:10.1016/j.jsb.2006.04.012
996:10.1016/j.jsb.2003.11.020
961:10.1016/j.jsb.2003.10.010
210:
190:
172:
167:
163:
151:
139:
119:
107:
95:
83:
70:
58:
50:
45:
33:
28:
1200:Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol
1068:Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol
780:
533:AAA ATPase family (HGNC)
1319:"Symbol report for AK6"
1131:10.1186/gb-2008-9-4-216
399:conformational changes
270:belonging to the AAA+
1371:Protein superfamilies
509:Multivesicular bodies
322:peroxisome biogenesis
262:of approximately 230
388:Quaternary structure
318:microtubule severing
21:AAA (disambiguation)
19:For other uses, see
812:Biochem. Soc. Trans
455:protein degradation
411:nucleophilic attack
405:Molecular mechanism
326:signal transduction
310:protein degradation
289:of macromolecules.
272:protein superfamily
824:10.1042/BST0360072
471:protein aggregates
1239:Biochem Cell Biol
906:Nat. Struct. Biol
666:(Nbla10058);
258:sharing a common
226:
225:
222:
221:
217:structure summary
1383:
1366:Protein families
1345:
1344:
1333:
1327:
1326:
1315:
1309:
1308:
1297:
1291:
1290:
1279:
1273:
1272:
1262:
1230:
1224:
1223:
1195:
1189:
1188:
1160:
1154:
1153:
1143:
1133:
1109:
1100:
1099:
1063:
1048:
1047:
1019:
1008:
1007:
979:
973:
972:
944:
938:
937:
901:
886:
868:
843:
477:Molecular motion
418:Prokaryotic AAAs
260:conserved module
165:
164:
38:
26:
25:
1391:
1390:
1386:
1385:
1384:
1382:
1381:
1380:
1361:Protein domains
1351:
1350:
1349:
1348:
1335:
1334:
1330:
1317:
1316:
1312:
1299:
1298:
1294:
1281:
1280:
1276:
1251:10.1139/o09-127
1231:
1227:
1196:
1192:
1165:J. Struct. Biol
1161:
1157:
1110:
1103:
1080:10.1038/nrm1684
1064:
1051:
1020:
1011:
984:J. Struct. Biol
980:
976:
949:J. Struct. Biol
945:
941:
902:
898:
893:
859:(12): 1657–67.
806:
804:Further reading
798:
783:
756:
541:
535:
530:
522:
520:Other functions
506:
479:
463:DNA replication
459:membrane fusion
451:
442:protein domains
420:
407:
390:
378:
362:
354:oligomerization
338:
314:membrane fusion
306:DNA replication
274:of ring-shaped
41:
24:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1389:
1379:
1378:
1373:
1368:
1363:
1347:
1346:
1328:
1310:
1292:
1274:
1225:
1190:
1155:
1101:
1049:
1009:
974:
955:(1–2): 11–31.
939:
895:
894:
892:
889:
888:
887:
844:
818:(Pt 1): 72–7.
805:
802:
797:
794:
782:
779:
755:
752:
534:
531:
529:
526:
521:
518:
505:
502:
478:
475:
450:
447:
419:
416:
406:
403:
389:
386:
377:
374:
361:
360:Classification
358:
337:
334:
298:macromolecular
294:ATP hydrolysis
268:protein family
256:protein family
224:
223:
220:
219:
214:
208:
207:
194:
188:
187:
177:
170:
169:
161:
160:
155:
149:
148:
143:
137:
136:
123:
117:
116:
111:
105:
104:
99:
93:
92:
87:
81:
80:
75:
68:
67:
62:
56:
55:
52:
48:
47:
43:
42:
39:
31:
30:
16:Protein family
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1388:
1377:
1374:
1372:
1369:
1367:
1364:
1362:
1359:
1358:
1356:
1342:
1338:
1332:
1324:
1320:
1314:
1306:
1302:
1296:
1288:
1284:
1278:
1270:
1266:
1261:
1256:
1252:
1248:
1244:
1240:
1236:
1229:
1221:
1217:
1213:
1209:
1206:(6): 641–52.
1205:
1201:
1194:
1186:
1182:
1178:
1174:
1170:
1166:
1159:
1151:
1147:
1142:
1137:
1132:
1127:
1123:
1119:
1115:
1108:
1106:
1097:
1093:
1089:
1085:
1081:
1077:
1074:(7): 519–29.
1073:
1069:
1062:
1060:
1058:
1056:
1054:
1045:
1041:
1037:
1033:
1029:
1025:
1018:
1016:
1014:
1005:
1001:
997:
993:
990:(1–2): 2–10.
989:
985:
978:
970:
966:
962:
958:
954:
950:
943:
935:
931:
927:
923:
919:
915:
912:(9): 803–11.
911:
907:
900:
896:
884:
880:
876:
872:
867:
862:
858:
854:
850:
845:
841:
837:
833:
829:
825:
821:
817:
813:
808:
807:
801:
793:
791:
787:
778:
776:
772:
768:
764:
760:
751:
749:
745:
741:
737:
733:
729:
725:
721:
717:
713:
709:
705:
701:
697:
693:
689:
685:
681:
677:
673:
669:
665:
661:
657:
653:
649:
645:
641:
637:
633:
629:
625:
621:
617:
613:
609:
605:
601:
597:
593:
589:
585:
581:
577:
573:
569:
565:
561:
557:
553:
549:
545:
540:
525:
517:
514:
510:
501:
499:
493:
491:
487:
486:motor protein
483:
474:
472:
468:
464:
460:
456:
446:
443:
439:
438:
433:
429:
425:
415:
412:
402:
400:
394:
385:
383:
373:
370:
368:
357:
355:
351:
347:
343:
342:Rossmann fold
333:
331:
327:
323:
319:
315:
311:
307:
301:
299:
295:
290:
288:
287:translocation
284:
280:
277:
273:
269:
265:
261:
257:
253:
249:
247:
243:
241:
237:
235:
230:
218:
215:
213:
209:
206:
202:
198:
195:
193:
189:
185:
181:
178:
175:
171:
166:
162:
159:
156:
154:
150:
147:
144:
142:
138:
135:
131:
127:
124:
122:
118:
115:
112:
110:
106:
103:
100:
98:
94:
91:
88:
86:
82:
79:
76:
73:
69:
66:
63:
61:
57:
53:
49:
44:
37:
32:
27:
22:
1331:
1313:
1295:
1277:
1245:(1): 15–21.
1242:
1238:
1228:
1203:
1199:
1193:
1171:(1): 72–83.
1168:
1164:
1158:
1121:
1117:
1071:
1067:
1027:
1023:
987:
983:
977:
952:
948:
942:
918:10.1038/1843
909:
905:
899:
856:
852:
815:
811:
799:
784:
757:
542:
523:
507:
494:
490:microtubules
480:
452:
435:
421:
408:
395:
391:
379:
371:
363:
339:
302:
291:
251:
245:
244:
239:
238:
233:
232:
228:
227:
1118:Genome Biol
796:Pseudogenes
467:microtubule
432:proteolytic
350:superfamily
300:substrate.
46:Identifiers
1355:Categories
1124:(4): 216.
1030:: 93–114.
891:References
718:(SPAF);
537:See also:
424:eukaryotes
283:remodeling
264:amino acid
180:structures
153:Membranome
800:AFG3L1P;
788:(CINAP);
449:Functions
428:chaperone
367:Cdc48/p97
336:Structure
248:ctivities
114:PDOC00572
102:IPR003959
1269:20130675
1220:18023171
1185:16919475
1150:18466635
1096:27830342
1088:16072036
1044:16689629
1004:15037233
969:15037234
934:13261575
883:29221806
875:17897320
840:13407283
832:18208389
750:(FTSH);
734:;
720:SPATA5L1
638:;
328:and the
252:proteins
197:RCSB PDB
97:InterPro
90:2004.1.1
1260:2894566
1141:2643927
926:9731775
853:Traffic
754:Torsins
702:;
698:;
686:;
658:;
654:;
620:KATNAL2
616:KATNAL1
610:;
598:;
482:Dyneins
437:E. coli
279:NTPases
146:cd00009
109:PROSITE
65:PF00004
1267:
1257:
1218:
1183:
1148:
1138:
1094:
1086:
1042:
1002:
967:
932:
924:
881:
873:
838:
830:
748:YME1L1
744:WRNIP1
738:;
728:TRIP13
716:SPATA5
708:RUVBL2
704:RUVBL1
682:;
678:;
670:;
662:;
630:;
626:;
612:KATNA1
604:FIGNL2
600:FIGNL1
580:CHTF18
578:;
568:ATAD3C
564:ATAD3B
560:ATAD3A
556:ATAD2B
554:;
550:;
544:AFG3L2
382:clades
276:P-loop
236:TPases
212:PDBsum
186:
176:
134:SUPFAM
78:CL0023
51:Symbol
1092:S2CID
930:S2CID
879:S2CID
836:S2CID
781:Other
775:TOR4A
771:TOR3A
767:TOR2A
763:TOR1B
759:TOR1A
746:;
740:VPS4B
736:VPS4A
730:;
712:SPAST
706:;
694:;
680:PSMC6
676:PSMC5
672:PSMC4
668:PSMC3
664:PSMC2
660:PSMC1
650:;
628:LONP2
624:LONP1
614:;
608:IQCA1
594:;
576:BCS1L
574:;
572:ATAD5
562:;
558:;
552:ATAD2
548:ATAD1
546:;
513:ESCRT
430:with
130:SCOPe
121:SCOP2
1265:PMID
1216:PMID
1181:PMID
1146:PMID
1084:PMID
1040:PMID
1000:PMID
965:PMID
922:PMID
871:PMID
828:PMID
790:CDC6
724:SPG7
714:;
700:RFC5
696:RFC4
692:RFC3
688:RFC2
684:RFC1
656:PEX6
652:PEX1
648:ORC4
644:ORC1
632:MDN1
622:;
618:;
596:FIGN
592:CLPX
588:CLPP
584:CLBP
498:ERAD
205:PDBj
201:PDBe
184:ECOD
174:Pfam
126:1nsf
85:ECOD
74:clan
72:Pfam
60:Pfam
1255:PMC
1247:doi
1208:doi
1173:doi
1169:156
1136:PMC
1126:doi
1076:doi
1032:doi
992:doi
988:146
957:doi
953:146
914:doi
861:doi
820:doi
792:;
786:AK6
773:;
769:;
732:VCP
722:;
690:;
646:;
640:NVL
636:NSF
285:or
229:AAA
192:PDB
141:CDD
54:AAA
1357::
1339:.
1321:.
1303:.
1285:.
1263:.
1253:.
1243:88
1241:.
1237:.
1214:.
1204:17
1202:.
1179:.
1167:.
1144:.
1134:.
1120:.
1116:.
1104:^
1090:.
1082:.
1070:.
1052:^
1038:.
1028:35
1026:.
1012:^
998:.
986:.
963:.
951:.
928:.
920:.
908:.
877:.
869:.
855:.
851:.
834:.
826:.
816:36
814:.
777:;
765:;
761:;
742:;
726:;
710:;
674:;
642:;
634:;
606:;
602:;
590:;
586:;
582:;
570:;
566:;
492:.
473:.
465:,
461:,
457:,
332:.
324:,
320:,
316:,
312:,
308:,
250:)
203:;
199:;
182:/
158:74
132:/
128:/
1343:.
1325:.
1307:.
1289:.
1271:.
1249::
1222:.
1210::
1187:.
1175::
1152:.
1128::
1122:9
1098:.
1078::
1072:6
1046:.
1034::
1006:.
994::
971:.
959::
936:.
916::
910:5
885:.
863::
857:8
842:.
822::
496:(
246:A
240:A
234:A
231:(
23:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.