635:
65:
36:
93:
504:
643:
48:
100:
72:
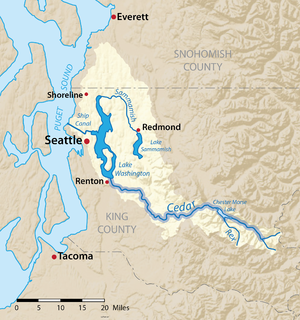
572:. The water level of Lake Washington dropped 8.8 feet (2.7 m), to the level of Lake Union. As a result, the outlet of Lake Washington became the Ship Canal instead of the Black River. The Black River dried up and no longer exists. Thus, today the Cedar River's water enters Lake Washington and then passes through the Ship Canal to Puget Sound, rather than into Elliott Bay via the Duwamish River.
561:. In 1911, there was a major flood along the lower Cedar River. This prompted the city of Renton to make a diversion canal so that the Cedar River emptied into Lake Washington instead of the Black River. The diversion was completed in 1912. The Cedar River's water, via Lake Washington, still ultimately flowed into the Black River, Duwamish River, and into Elliott Bay.
670:
discharge flowed down Boxley Creek Valley, destroying the town of
Edgewick, sawmills (owned by North Bend Lumber Company), and parts of the Milwaukee Railroad. The failure did not occur at the dam, but 6,000 feet on the moraine side of the reservoir. Initial discharge rates were estimated between 3,000 and 20,000 second-feet.
626:. The three main programs The Friends of the Cedar River Watershed managed were the Cedar River Salmon Journey, Volunteer Habitat Restoration, and Stewardship in Action. The organization disbanded in 2015, and its programs were absorbed by other entities to continue the work in advocacy and education.
685:
burned more forests in the wake of logging operations. In 1924 the City of
Seattle began the process of managing the Cedar River Watershed with a plan of ensuring water quality for the future. Logging continued, but methods were increasingly regulated and fire precautions strengthened. The 1962 Cedar
480:
Below
Chester Morse Lake, the Cedar River flows through a smaller lake called Masonry Pool. Below Masonry Pool, the Cedar River flows by two former railroad sites, Bagley Junction and Trude. The river then exits the Cedar River Watershed at Landsburg where pipelines route water to the Seattle area.
669:
to the east as natural barriers. The reservoir was known as the Cedar
Reservoir and was fed by the Cedar River Drainage. Between the hours of 12AM and 2AM on December 23, 1918 a large section of the Cedar Reservoir failed and spilled between 800,000 and 2,000,000 cubic yards of water. The
621:
The river has problems with invasive species, erosion, and pollution from adjacent properties and runoff. In 1996, the
Friends of the Cedar River Watershed was formed to organize community involvement in protection of the river and its tributaries. The organization focused on education and
665:
Another reservoir was constructed in the early 1900s by the City of
Seattle on an ancient glacial lake bed. The city constructed a ninety-foot concrete dam and used bedrock to the west and a glacial
542:
Chester Morse Lake is the main storage reservoir of the Cedar River
Watershed system. Pipelines route water to the Seattle area from Landsburg, at the western edge of the protected watershed area.
654:
Efforts to use the Cedar River as a water source began in the 1890s. A dam was built at
Landsburg and water diverted into a 29-mile (47 km) pipeline. The pipeline sent water to Seattle's
1055:
955:
531:
uses water from the Cedar River
Watershed, over 100 million US gallons (380,000 m) per day. The reservoirs and pipeline infrastructure is owned and operated by
603:
system. As a result, the Cedar River is one of the few rivers in the United States used for drinking water without requiring specially fabricated filtration.
606:
Just south of the Cedar River
Watershed is a similar protected area used for drinking water: the Green River Watershed, which supplies water to the greater
915:
469:
countyline. Several headwater streams join in the high mountains fed from glacial run-off, then the Cedar River flows generally west. It is impounded in
64:
452:
613:
The watershed also has an education center where visitors can learn about the issues that involve the region's drinking water, forest and wildlife.
897:
741:
in the early 20th century resulted in a degraded habitat for wildlife. Starting in the late 20th century efforts began to be made to protect and
939:
690:
ceded its land in the watershed to Seattle. As a result, the city is the sole owner of the Cedar River Watershed area of the upper Cedar River.
92:
686:
River Watershed Cooperative Agreement began the process of transferring the remaining privately owned land to the City of Seattle. In 1996 the
583:
The upper Cedar River flows through a region of deep and porous glacial outwash. A large amount of water seeps into the ground, forming an
580:, which used to migrate up the Duwamish and Black rivers to reach the Cedar River, now migrate through the Ship Canal and Lake Washington.
254:
1052:
1130:
673:
By 1899 the City of Seattle had acquired ownership of most of the Cedar River Watershed. Some land remained privately owned, mainly by
1073:
698:
Due to logging in the early 20th century, only about 17%, or 14,000 acres (57 km²), of the Cedar River Watershed consists of
191:
766:
523:
is a protected area called the Cedar River Municipal Watershed. About 90,000 acres (364 km²) in size, it is owned by the
1135:
1109:
527:. The Cedar River Watershed provides drinking water for 1.4 million people in the greater Seattle area. About two-thirds of
477:. The Rex River joins the Cedar in Chester Morse Lake, as do the two forks of the Cedar River, the north and south forks.
816:
831:
749:
have been a major topic of concern, with work underway to recreate spawning channels, proper salmon habitat zones, and
1140:
1125:
1000:
659:
776:
507:
The scene at the mouth of the Cedar river where it flows into Lake Washington, as a plane comes in to land at the
856:
798:
753:. To address low counts on the river, with only 10,000 counted beyond Lake Washington by the early 2020s, the
995:
Kruckeberg, Arthur. The Natural History of Puget Sound Country. Korea: University of Washington Press, 2003.
852:
687:
550:
546:
466:
971:
440:
936:
771:
20:
655:
549:. The Black River drained the southern end of Lake Washington, flowing south then west to join the
532:
508:
485:
156:
662:. The first deliveries occurred in 1901. A second pipeline was built in 1909 and a third in 1923.
634:
528:
146:
638:
Headworks intake and wing dam on the Cedar River, 1900, part of the Seattle water supply system.
623:
573:
647:
983:
967:
923:
879:
35:
8:
742:
484:
Below the Cedar River Watershed area, the river flows west and north, past the cities of
607:
600:
588:
503:
489:
470:
409:
329:
160:
136:
1105:
996:
754:
699:
19:
This article is about the river in King County. For the river in Pacific County, see
799:
U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Cedar River (Washington)
703:
596:
592:
545:
Before 1912 the Cedar River did not empty into Lake Washington but rather into the
1040:
1059:
943:
835:
493:
417:
757:
began trucking 1,500 spawning salmon from the Ballard Locks to the Cedar River.
726:
718:
714:
554:
520:
425:
421:
1014:"Boxley Burst destroys the logging community of Edgewick on December 23, 1918"
1119:
734:
730:
458:
413:
269:
256:
206:
193:
828:
812:
565:
416:
and flows generally west and northwest, emptying into the southern end of
52:
Map of the Lake Washington drainage basin with the Cedar River highlighted
750:
722:
642:
558:
497:
436:
237:
984:
Guide to the Seattle Watershed and Pipeline Aerial Photographs 1930-1989
1013:
746:
569:
536:
462:
405:
587:. Most of this underground water eventually returns to the surface as
474:
424:
is a protected area called the Cedar River Watershed, which provides
388:
473:, a natural lake that was dammed in 1900 for use as a water storage
682:
738:
710:
678:
674:
666:
584:
524:
429:
681:. Before 1924 large sections of the forest were cut for timber.
47:
1018:
HistoryLink.org Online Encyclopedia of Washington State History
577:
492:. At Renton, the Cedar River empties into the southern end of
401:
535:. Public access is restricted and the area is managed as a
713:
for a variety of wildlife. The river provides habitat for
412:. About 45 miles (72 km) long, it originates in the
465:, Meadow Mountain, and Yakima Pass, along the King and
79:
Location of the mouth of the Cedar River in Washington
591:, flowing mainly into the Cedar River as well as the
514:
1104:, Klingle, Matthew W., Yale University Press, 2007,
1102:Emerald City: an environmental history of Seattle
968:Guide to the Cedar River Watershed Maps 1891-1970
453:List of crossings of the Cedar River (Washington)
1117:
702:. The majority of the forest remaining today is
99:
71:
568:was finished, connecting Lake Washington and
909:
907:
880:Cedar River Watershed Environmental Overview
107:Cedar River (Washington) (the United States)
1074:"Sockeye salmon return to the Cedar River"
989:
904:
855:, Water Resource Data, Washington, 2005,
838:, The Columbia Gazetteer of North America
599:. This process acts as a kind of natural
564:In 1916 the Lake Washington Ship Canal's
553:. The Black-Green confluence created the
822:
641:
633:
502:
1043:, Friends of the Cedar River Watershed.
1036:
1034:
977:
875:
873:
871:
869:
867:
865:
767:Seattle Municipal Light and Power Plant
616:
361:10,600 cu ft/s (300 m/s)
1118:
1005:
956:Cedar River Watershed Education Center
894:Washington Road & Recreation Atlas
794:
792:
40:Cedar River in Downtown Renton in 2009
1071:
916:"Black River disappears in July 1916"
913:
848:
846:
844:
341:659 cu ft/s (18.7 m/s)
16:River in the United States of America
1072:Breda, Isabella (October 20, 2023).
1031:
961:
862:
808:
806:
500:via the Lake Washington Ship Canal.
351:30 cu ft/s (0.85 m/s)
789:
709:The Cedar River Watershed provides
539:in order to protect water quality.
13:
1095:
841:
693:
515:River modifications and management
457:The Cedar River originates in the
14:
1152:
1131:Rivers of King County, Washington
1011:
803:
307:184 sq mi (480 km)
98:
91:
70:
63:
46:
34:
1065:
1046:
914:Lange, Greg (August 25, 2000),
949:
930:
885:
496:. Its waters eventually enter
248: • coordinates
185: • coordinates
82:Show map of Washington (state)
1:
986:, Northwest Digital Archives.
782:
745:the river and its watershed.
167:Physical characteristics
110:Show map of the United States
1136:Rivers of Washington (state)
777:History of Seattle 1900–1940
688:United States Forest Service
439:via Lake Washington and the
435:The Cedar River drains into
287: • elevation
224: • elevation
7:
1062:, Seattle Public Utilities.
958:, Seattle Public Utilities.
760:
325: • location
10:
1157:
972:Northwest Digital Archives
658:and Lincoln reservoirs on
629:
450:
441:Lake Washington Ship Canal
357: • maximum
347: • minimum
337: • average
228:2,220 ft (680 m)
18:
891:General course info from
772:List of Washington rivers
446:
382:
374:
369:
365:
355:
345:
335:
323:
315:
311:
303:
295:
285:
246:
236:
232:
222:
183:
175:
171:
166:
152:
142:
132:
124:
119:
57:
45:
33:
28:
21:Cedar River (Willapa Bay)
1141:Rivers with fish ladders
1126:Cedar River (Washington)
650:bridges the Cedar River.
533:Seattle Public Utilities
509:Renton Municipal Airport
384: • left
299:45 mi (72 km)
291:17 ft (5.2 m)
651:
639:
624:ecological restoration
519:The upper Cedar River
511:
270:47.50056°N 122.21611°W
207:47.31306°N 121.52139°W
1053:Cedar River Watershed
1041:Cedar River Watershed
853:Lake Washington Basin
648:Renton Public Library
645:
637:
557:, which emptied into
506:
882:, HistoryLink Essay.
704:second growth forest
617:Environmental issues
275:47.50056; -122.21611
212:47.31306; -121.52139
370:Basin features
266: /
203: /
1058:2007-09-30 at the
942:2007-09-28 at the
834:2004-11-29 at the
652:
640:
512:
471:Chester Morse Lake
1110:978-0-300-11641-0
1078:The Seattle Times
937:Source Protection
755:Muckleshoot Tribe
700:old growth forest
394:
393:
1148:
1089:
1088:
1086:
1084:
1069:
1063:
1050:
1044:
1038:
1029:
1028:
1026:
1024:
1009:
1003:
993:
987:
981:
975:
965:
959:
953:
947:
934:
928:
927:
926:on June 21, 2011
922:, archived from
911:
902:
901:
889:
883:
877:
860:
850:
839:
826:
820:
810:
801:
796:
601:water filtration
597:Rattlesnake Lake
593:Snoqualmie River
428:for the greater
385:
358:
348:
338:
326:
281:
280:
278:
277:
276:
271:
267:
264:
263:
262:
259:
225:
218:
217:
215:
214:
213:
208:
204:
201:
200:
199:
196:
186:
111:
102:
101:
95:
83:
74:
73:
67:
50:
38:
26:
25:
1156:
1155:
1151:
1150:
1149:
1147:
1146:
1145:
1116:
1115:
1098:
1096:Further reading
1093:
1092:
1082:
1080:
1070:
1066:
1060:Wayback Machine
1051:
1047:
1039:
1032:
1022:
1020:
1012:Stein, Alan J.
1010:
1006:
994:
990:
982:
978:
966:
962:
954:
950:
946:, Tacoma Water.
944:Wayback Machine
935:
931:
912:
905:
892:
890:
886:
878:
863:
851:
842:
836:Wayback Machine
827:
823:
811:
804:
797:
790:
785:
763:
737:and associated
731:Steelhead trout
717:fish including
696:
694:Natural history
632:
619:
525:City of Seattle
517:
494:Lake Washington
455:
449:
418:Lake Washington
383:
356:
346:
336:
324:
288:
274:
272:
268:
265:
260:
257:
255:
253:
252:
249:
242:Lake Washington
223:
211:
209:
205:
202:
197:
194:
192:
190:
189:
184:
115:
114:
113:
112:
109:
108:
105:
104:
103:
86:
85:
84:
81:
80:
77:
76:
75:
53:
41:
24:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1154:
1144:
1143:
1138:
1133:
1128:
1114:
1113:
1097:
1094:
1091:
1090:
1064:
1045:
1030:
1004:
988:
976:
960:
948:
929:
903:
898:Benchmark Maps
884:
861:
840:
821:
815:elevation for
802:
787:
786:
784:
781:
780:
779:
774:
769:
762:
759:
727:Sockeye salmon
719:Chinook salmon
695:
692:
677:companies and
656:Volunteer Park
631:
628:
618:
615:
576:fish, such as
555:Duwamish River
516:
513:
448:
445:
426:drinking water
392:
391:
386:
380:
379:
376:
372:
371:
367:
366:
363:
362:
359:
353:
352:
349:
343:
342:
339:
333:
332:
327:
321:
320:
317:
313:
312:
309:
308:
305:
301:
300:
297:
293:
292:
289:
286:
283:
282:
250:
247:
244:
243:
240:
234:
233:
230:
229:
226:
220:
219:
187:
181:
180:
177:
173:
172:
169:
168:
164:
163:
154:
150:
149:
144:
140:
139:
134:
130:
129:
126:
122:
121:
117:
116:
106:
97:
96:
90:
89:
88:
87:
78:
69:
68:
62:
61:
60:
59:
58:
55:
54:
51:
43:
42:
39:
31:
30:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1153:
1142:
1139:
1137:
1134:
1132:
1129:
1127:
1124:
1123:
1121:
1111:
1107:
1103:
1100:
1099:
1079:
1075:
1068:
1061:
1057:
1054:
1049:
1042:
1037:
1035:
1019:
1015:
1008:
1002:
1001:0-295-97477-X
998:
992:
985:
980:
973:
969:
964:
957:
952:
945:
941:
938:
933:
925:
921:
917:
910:
908:
899:
895:
888:
881:
876:
874:
872:
870:
868:
866:
858:
854:
849:
847:
845:
837:
833:
830:
825:
818:
814:
809:
807:
800:
795:
793:
788:
778:
775:
773:
770:
768:
765:
764:
758:
756:
752:
748:
744:
740:
736:
735:Deforestation
732:
728:
724:
720:
716:
712:
707:
705:
701:
691:
689:
684:
680:
676:
671:
668:
663:
661:
657:
649:
644:
636:
627:
625:
614:
611:
609:
604:
602:
598:
594:
590:
586:
581:
579:
575:
571:
567:
562:
560:
556:
552:
548:
543:
540:
538:
534:
530:
526:
522:
510:
505:
501:
499:
495:
491:
487:
482:
478:
476:
472:
468:
464:
460:
459:Cascade Range
454:
444:
442:
438:
433:
431:
427:
423:
419:
415:
414:Cascade Range
411:
407:
403:
399:
390:
387:
381:
377:
373:
368:
364:
360:
354:
350:
344:
340:
334:
331:
328:
322:
318:
314:
310:
306:
302:
298:
294:
290:
284:
279:
251:
245:
241:
239:
235:
231:
227:
221:
216:
188:
182:
179:Cascade Range
178:
174:
170:
165:
162:
158:
155:
151:
148:
145:
141:
138:
135:
131:
128:United States
127:
123:
118:
94:
66:
56:
49:
44:
37:
32:
27:
22:
1101:
1081:. Retrieved
1077:
1067:
1048:
1021:. Retrieved
1017:
1007:
991:
979:
963:
951:
932:
924:the original
919:
893:
887:
824:
819:coordinates.
813:Google Earth
751:fish ladders
708:
697:
672:
664:
660:Capitol Hill
653:
620:
612:
605:
582:
566:Montlake Cut
563:
544:
541:
518:
486:Maple Valley
483:
479:
456:
434:
420:. Its upper
397:
395:
157:Maple Valley
1083:October 20,
1023:28 December
920:HistoryLink
829:Cedar River
747:Salmon runs
723:Coho salmon
559:Elliott Bay
551:Green River
547:Black River
529:King County
498:Puget Sound
437:Puget Sound
398:Cedar River
375:Tributaries
273: /
261:122°12′58″W
210: /
198:121°31′17″W
29:Cedar River
1120:Categories
783:References
715:anadromous
574:Anadromous
570:Lake Union
537:wilderness
463:Abiel Peak
451:See also:
410:Washington
406:U.S. state
304:Basin size
195:47°18′47″N
137:Washington
683:Wildfires
521:watershed
475:reservoir
422:watershed
389:Rex River
316:Discharge
258:47°30′2″N
1056:Archived
940:Archived
832:Archived
761:See also
679:sawmills
467:Kittitas
120:Location
900:. 2000.
743:restore
739:erosion
711:habitat
675:logging
667:moraine
630:History
589:springs
585:aquifer
430:Seattle
404:in the
125:Country
1108:
999:
729:, and
610:area.
608:Tacoma
578:salmon
490:Renton
447:Course
432:area.
378:
330:Renton
319:
296:Length
176:Source
161:Renton
153:Cities
143:County
461:near
402:river
400:is a
238:Mouth
133:State
1106:ISBN
1085:2023
1025:2016
997:ISBN
857:USGS
817:GNIS
646:The
595:and
488:and
396:The
147:King
408:of
1122::
1076:.
1033:^
1016:.
970:,
918:,
906:^
896:.
864:^
843:^
805:^
791:^
733:.
725:,
721:,
706:.
443:.
159:,
1112:.
1087:.
1027:.
974:.
859:.
23:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.