189:
313:(which might share common cells of origin) have better prognoses than those with mixed oligoastrocytomas, who in turn have better prognoses than patients with (pure) low-grade astrocytomas. Other factors which influence survival include age (younger the better) and performance status (ability to perform tasks of daily living). Due to the infiltrative nature of these tumors, recurrences are relatively common. Depending on the patient, radiation or chemotherapy after surgery is an option. Individuals with grade 2 astrocytoma have a 5-year survival rate of about 34% without treatment and about 70% with radiation therapy. The median survival time is 4 years.
360:
avoided. The extremely infiltrative nature of this tumor makes complete surgical removal impossible. Although radiotherapy rarely cures glioblastoma, studies show that it doubles the median survival of patients, compared to supportive care alone. The prognosis is worst for these grade 4 gliomas. Few patients survive beyond 3 years. Individuals with grade 4 astrocytoma have a median survival time of 17 weeks without treatment, 30 weeks with radiation, and 37 weeks with surgical removal of most of the tumor followed by radiation therapy. Long-term survival (at least five years) falls well under 3%.
177:
164:
405:
367:
153:
patient's brain are taken from many different directions. These are then combined by a computer, producing a cross-sectional image of the brain. For an MRI, the patient relaxes in a tunnel-like instrument while the brain is subjected to changes of magnetic field. An image is produced based on the behavior of the brain's water molecules in response to the magnetic fields. A special dye may be injected into a vein before these scans to provide contrast and make tumors easier to identify.
29:
163:
157:
surgery. Grading of the tumor sample is a method of classification that helps the doctor to determine the severity of the astrocytoma and to decide on the best treatment options. The neuropathologist grades the tumor by looking for atypical cells, the growth of new blood vessels, and for indicators of cell division called mitotic figures.
120:, arterial and venous hypoxia, competition for nutrients, release of metabolic end products (e.g., free radicals, altered electrolytes, neurotransmitters), and release and recruitment of cellular mediators (e.g., cytokines) that disrupt normal parenchymal function. Secondary clinical sequelae may be caused by elevated
152:
In the first stage of diagnosis the doctor will take a history of symptoms and perform a basic neurological exam, including an eye exam and tests of vision, balance, coordination, and mental status. The doctor will then require a CT scan and MRI of the patient's brain. During a CT scan, X-rays of the
156:
If a tumor is found, a neurosurgeon must perform a biopsy on it. This simply involves the removal of a small amount of tumor tissue, which is then sent to a neuropathologist for examination and grading. The biopsy may take place before surgical removal of the tumor or the sample may be taken during
222:
is commonly used for astrocytoma. Established in 1993 in an effort to eliminate confusion regarding diagnoses, the WHO system established a four-tiered histologic grading guideline for astrocytomas that assigns a grade from 1 to 4, with 1 being the least aggressive and 4 being the most aggressive.
132:
Homozygous deletion of CDKN2A/B is the main feature of high grade astrocytoma. In addition, a genome-wide pattern of DNA copy-number alterations (CNAs) has been uncovered, which is correlated with a patient's survival and response to treatment. This pattern identifies among lower-grade astrocytoma
359:
Consists of grade 4 astrocytoma (as of WHO 2021) that form following high-grade transformation of low-grade astrocytoma. These are more common in younger patients (mean age 45 versus 62 years). Surgical removal remains the mainstay of treatment, provided that unacceptable neurologic injury can be
418:
parenchyma. Thus, high-grade astrocytomas inevitably recur after initial surgery or therapy and are usually treated similarly to the initial tumor. Despite decades of therapeutic research, curative intervention is still nonexistent for high-grade astrocytomas; patient care ultimately focuses on
308:
Consist of relatively slow-growing astrocytomas, usually considered benign that sometimes evolve into more malignant or as higher grade tumors. They are prevalent in younger people who often present with seizures. Median survival varies with the cell type of the tumor. Grade 2 astrocytomas are
417:
are commonly indolent bodies that may permit normal neurologic function. However, left unattended, these tumors may eventually undergo neoplastic transformation. To date, complete resection of high-grade astrocytomas is impossible because of the diffuse infiltration of tumor cells into normal
107:
People can develop astrocytomas at any age. The low-grade type is more often found in children or young adults, while the high-grade type is more prevalent in adults. Astrocytomas in the base of the brain are more common in young people and account for roughly 75% of neuroepithelial tumors.
518:
at the time of his diagnosis and vacated the title in
February 2006 after confirming the tumor was cancerous. Cappotelli underwent successful surgery and chemotherapy, but was unable to return to active wrestling work. He did return to OVW as a trainer in 2013. He died on June 29, 2018.
103:(e.g., high-grade astrocytoma), that share various features, including the ability to arise at any location in the central nervous system, but with a preference for the cerebral hemispheres; they occur usually in adults, and have an intrinsic tendency to progress to more advanced grades.
149:(MRI) scan is necessary to characterize the extent of these tumors (size, location, consistency). CT will usually show distortion of third and lateral ventricles with displacement of anterior and middle cerebral arteries. Histologic analysis is necessary for grading diagnosis.
387:
and second most frequent brain tumor after brain metastasis. Despite the low incidence of astrocytomas compared to other human cancers, mortality is significant, as the higher grades (III & IV) present high mortality rates (mainly due to late detection of the neoplasm).
412:
For low-grade astrocytomas, removal of the tumor generally allows functional survival for many years. In some reports, the 5-year survival has been over 90% with well-resected tumors. Indeed, broad intervention of low-grade conditions is a contested matter. In particular,
468:, who killed multiple people during a mass murder event in 1966, was diagnosed with astrocytoma post-mortem. The Connally Commission investigating the shooting concluded the tumor "conceivably could have contributed to his inability to control his emotions and actions".
169:
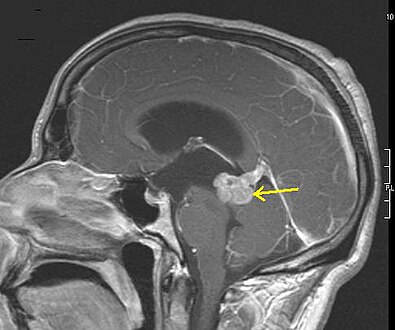
Low grade astrocytoma of the midbrain (lamina tecti), sagittal T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging after contrast medium administration: The tumor is marked with an arrow. The CSF spaces in front of the tumor are expanded due to compression-induced hydrocephalus
382:
According to the WHO data, the lowest grade astrocytomas (grade I) make up only 2% of recorded astrocytomas, grade II 8%, and the higher grade anaplastic astrocytomas (grade III) 20%. The highest graded astrocytoma (grade IV GBM) is the most common primary
330:
Consist of anaplastic astrocytomas. It is often related to seizures, neurologic deficits, headaches, or changes in mental status. The standard initial treatment is to remove as much of the tumor as possible without worsening neurologic deficits.
335:
has been shown to prolong survival and is a standard component of treatment. Individuals with grade 3 astrocytoma have a median survival time of 18 months without treatment (radiation and chemotherapy). There is no proven benefit to adjuvant
188:
1807:
1525:
1327:
1312:
1466:
96:
Narrow zones of infiltration (mostly noninvasive tumors; e.g., pilocytic astrocytoma, subependymal giant cell astrocytoma, pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma), that often are clearly outlined on diagnostic images
1907:
281:
is possible may experience total remission. Even if the surgeon is not able to remove the entire tumor, it may remain inactive or be successfully treated with radiation.
219:
277:
Consist of slow-growing astrocytomas, benign, and associated with long-term survival. Individuals with very slow-growing tumors where complete surgical removal by
309:
defined as being invasive gliomas, meaning that the tumor cells penetrate into the surrounding normal brain, making a surgical cure more difficult. People with
238:. These features reflect the malignant potential of the tumor in terms of invasion and growth rate. Various types of astrocytomas are given these WHO grades:
1342:
212:
613:"GSVD Comparison of Patient-Matched Normal and Tumor aCGH Profiles Reveals Global Copy-Number Alterations Predicting Glioblastoma Multiforme Survival"
946:
841:
Buckner, Jan C.; Brown, Paul D.; O'Neill, Brian P.; Meyer, Fredric B.; Wetmore, Cynthia J.; Uhm, Joon H. (2007). "Central
Nervous System Tumors".
1438:
488:, was diagnosed with astrocytoma in 2003. Four years to the day after winning the World Rally Championship, on 25 November 2005, Burns died in
676:"Retrospective Clinical Trial Experimentally Validates Glioblastoma Genome-Wide Pattern of DNA Copy-Number Alterations Predictor of Survival"
176:
1770:
1249:"Astrocytoma - Diagnosis and Treatment Options at Mayo Clinic." Mayo Clinic: Medical Treatment and Research Centers. Web. 07 Dec. 2009.
1288:
1005:
Waring, Thomas R., ed. "Jury Blames Tumor For
Killings: Doctor Says Whitman Unaffected"" The News and Courier 05 Aug. 1966: 9B. Print.
1266:
344:
is effective for treating recurrent anaplastic astrocytoma, its role as an adjuvant to radiation therapy has not been fully tested.
81:. This type of tumor does not usually spread outside the brain and spinal cord and it does not usually affect other organs. After
1891:
1815:
1739:
1024:
1152:
1256:"Glioblastoma Multiforme Treatment at Mayo Clinic." Mayo Clinic: Medical Treatment and Research Centers. Web. 07 Dec. 2009.
1211:
482:
1179:
1014:
Henderson, Heather (1999). "Dan
Quisenberry - In His Own Words" The 1999 Big Bad Baseball Annual. Retrieved June 24, 2013.
1577:
1431:
1353:
265:
1947:
823:
744:
1765:
436:
1264:"The new WHO Classification of Tumors affecting the Central Nervous System" by Stephen B. Tatter, M.D., Ph.D.; MGH
981:
962:
501:
was diagnosed with a grade 2/3 astrocytoma in
December 2005, scuttling plans to promote Cappottelli to the main
1424:
1572:
1138:
1113:
298:
133:
patients a subtype, where the CNA genotype is correlated with an approximately one-year survival phenotype.
1744:
1617:
515:
37:
1919:
Note: Not all brain tumors are of nervous tissue, and not all nervous tissue tumors are in the brain (see
660:
194:
146:
1829:
1049:
715:
216:
142:
124:
attributable to direct mass effect, increased blood volume, or increased cerebrospinal fluid volume.
1242:"Astrocytomas." KidsHealth - the Web's most visited site about children's health. Web. 01 May 2024.
475:
was diagnosed with grade IV astrocytoma in
January 1998. He died age 45 in 1998 in Leawood, Kansas.
1668:
1663:
1455:
1364:
896:
485:
505:
roster. Cappotelli, who won a contract with WWE through the third season of their reality program
1447:
384:
536:
1587:
1582:
1516:
495:
323:
292:
100:
492:, London, aged 34, after having been in a coma for some days as a result of his brain tumour.
1884:
1843:
1567:
1184:
940:
512:
414:
260:
121:
1283:
1942:
1848:
1658:
1263:
1109:
624:
278:
1134:
1091:
8:
1691:
1331:
1157:
967:
952:"This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License"
897:
Weller M, van den Bent M, Preusser M, Le Rhun E, Tonn JC, Minniti G; et al. (2021).
566:
489:
792:
765:
628:
1855:
1797:
1347:
923:
898:
805:
702:
675:
647:
612:
116:
Astrocytoma causes regional effects by compression, invasion, and destruction of brain
1028:
1868:
1612:
1477:
1375:
1257:
1250:
1243:
928:
858:
797:
782:
707:
652:
448:
396:
There are no precise guidelines because the exact cause of astrocytoma is not known.
332:
310:
198:
92:
Within the astrocytomas, two broad classes are recognized in literature, those with:
45:
1336:
809:
1920:
1686:
1404:
918:
910:
850:
787:
777:
697:
687:
642:
632:
506:
610:
404:
69:. Astrocytomas (also astrocytomata) originate from a specific kind of star-shaped
1760:
1604:
1369:
1270:
748:
637:
586:
498:
472:
465:
1416:
899:"EANO guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of diffuse gliomas of adulthood"
1729:
1720:
1650:
1380:
1189:
914:
50:
366:
226:
The WHO grading scheme is based on the appearance of certain characteristics:
89:
and can occur in most parts of the brain and occasionally in the spinal cord.
40:
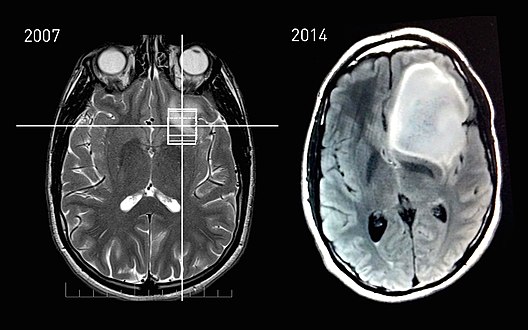
images—the upper of which shows a normal brain and the lower shows astrocytoma
1936:
1838:
1724:
1640:
478:
444:
270:
1321:
1212:"Matt Cappotelli, Former WWE Wrestler and 'Tough Enough' Winner, Dies at 38"
370:
Diagnosis of diffuse glioma, with astrocytomas mainly being diagnosed under
1875:
1863:
1592:
1535:
932:
862:
801:
711:
656:
455:
341:
337:
82:
54:
741:
215:
in use for the classification of tumor of the central nervous system, the
1734:
1696:
1530:
1482:
611:
C. H. Lee*; B. O. Alpert*; P. Sankaranarayanan; O. Alter (January 2012).
458:
440:
66:
766:"Genetic alterations and signaling pathways in the evolution of gliomas"
408:
Management of IDH-mutant gliomas, with astrocytomas at center and right.
1879:
1792:
1635:
854:
419:
117:
1304:
692:
1554:
1502:
1399:
1053:
571:
78:
443:
was diagnosed with astrocytoma after a tumor was found in his right
1784:
1627:
340:
or supplementing other treatments for this kind of tumor. Although
235:
74:
1216:
673:
231:
1358:
1712:
1545:
1316:
227:
86:
1908:
WHO classification of the tumors of the central nervous system
451:
treatment), Atwater died the following year at the age of 40.
28:
447:. After undergoing radiation therapy (including the then-new
840:
70:
1095:
985:
876:
502:
1077:
PWI Presents: 2007 Wrestling
Almanac and book of facts
182:
A pathological specimen of a gemistocytic astrocytoma
1294:
127:
759:
757:
1446:
561:
559:
557:
1934:
674:S. P. Ponnapalli, et int.; O. Alter (May 2020).
1079:. Kappa Publications. p. 17. 2007 Edition.
754:
763:
737:
735:
733:
731:
729:
727:
725:
554:
1432:
1075:Brady, Hicks. "2006: The year in wrestling".
892:
890:
581:
579:
945:: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (
1771:Embryonal tumour with multilayered rosettes
722:
1439:
1425:
1092:"Matt Cappotelli to undergo brain surgery"
887:
576:
85:, astrocytomas are the second most common
27:
922:
791:
781:
701:
691:
646:
636:
197:scans of an astrocytoma patient, showing
403:
365:
1892:Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor
1816:Primary central nervous system lymphoma
1740:Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumour
1127:
816:
764:Ohgaki, Hiroko; Kleihues, Paul (2009).
1935:
869:
834:
425:
1420:
1180:"Matt Cappotelli Beginner's Program"
1025:"Deaths England and Wales 1984–2006"
591:The Lecturio Medical Concept Library
1578:Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma
1244:KidsHealth.org - Nemours KidsHealth
1089:
266:Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma
13:
1284:Cancer.Net: Astrocytoma, Childhood
1209:
1050:"Former world champion Burns dies"
982:"Kennedy fought aggressive cancer"
111:
14:
1959:
1277:
1074:
461:(D-MA) died of malignant glioma.
234:, endothelial proliferation, and
128:Genetic and Molecular alterations
1766:Atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor
961:Brady, John (December 1, 1996).
783:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01308.x
430:
187:
175:
162:
1203:
1172:
1145:
1102:
1083:
1068:
1042:
1017:
1008:
999:
974:
955:
1860:Cranial and paraspinal nerves
1153:"Helping wrestlers get a grip"
1110:"Cappotelli undergoes surgery"
824:"Glioma - Symptoms and causes"
667:
604:
529:
437:United States Republican Party
201:over the course of seven years
1:
1573:Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma
1448:Tumours of the nervous system
1139:World Wrestling Entertainment
1114:World Wrestling Entertainment
522:
391:
299:Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma
1618:Anaplastic oligodendroglioma
1258:Glioma - Symptoms and causes
1251:Glioma - Symptoms and causes
1161:. Louisville, KY. 2013-11-12
1135:"Cappotelli recovering well"
742:mdguidelines.com Astrocytoma
638:10.1371/journal.pone.0030098
399:
136:
7:
1210:Xu, Linda (June 29, 2018).
464:University of Texas sniper
10:
1964:
915:10.1038/s41571-020-00447-z
751:Retrieved on Mars 26, 2010
206:
147:magnetic resonance imaging
1916:
1900:
1828:
1806:
1783:
1753:
1709:
1679:
1649:
1626:
1603:
1553:
1544:
1524:
1515:
1491:
1463:
1454:
1390:
1298:
1090:Dee, Louie (2007-04-06).
217:World Health Organization
143:X-ray computed tomography
44:
35:
26:
21:
1948:Nervous system neoplasia
1745:Lhermitte–Duclos disease
1669:Choroid plexus carcinoma
1664:Choroid plexus papilloma
486:World Rally Championship
971:, retrieved 2010-04-11.
963:"I'm Still Lee Atwater"
843:Mayo Clinic Proceedings
1588:Anaplastic astrocytoma
1583:Fibrillary astrocytoma
537:"What Is Astrocytoma?"
415:pilocytic astrocytomas
409:
379:
324:Anaplastic astrocytoma
303:Mixed oligoastrocytoma
1844:Esthesioneuroblastoma
1568:Pilocytic astrocytoma
1185:Ohio Valley Wrestling
513:Ohio Valley Wrestling
496:Professional wrestler
471:Major League pitcher
439:political strategist
407:
385:nervous system cancer
369:
261:Pilocytic astrocytoma
122:intracranial pressure
1849:Ganglioneuroblastoma
1754:CNS embryonal tumors
1659:Choroid plexus tumor
516:Heavyweight Champion
279:stereotactic surgery
220:(WHO) grading system
1692:Gliomatosis cerebri
1289:Imaging Astrocytoma
1158:The Courier-Journal
968:The Washington Post
629:2012PLoSO...730098L
426:Society and culture
354:Grade 4 Astrocytoma
1856:Nerve sheath tumor
1798:Hemangiopericytoma
1391:External resources
1269:2012-01-30 at the
1056:. 26 November 2005
903:Nat Rev Clin Oncol
855:10.4065/82.10.1271
747:2017-11-30 at the
680:APL Bioengineering
410:
380:
311:oligodendrogliomas
1930:
1929:
1869:Neurofibromatosis
1824:
1823:
1779:
1778:
1705:
1704:
1613:Oligodendroglioma
1511:
1510:
1478:Craniopharyngioma
1414:
1413:
1291:MR, CT, Pathology
988:. August 26, 2009
877:"CBTRUS - CBTRUS"
693:10.1063/1.5142559
449:implant radiation
376:nuclear ATRX lost
364:
363:
333:Radiation therapy
199:tumor progression
99:Diffuse zones of
60:
59:
16:Medical condition
1955:
1921:brain metastasis
1885:Acoustic neuroma
1687:Oligoastrocytoma
1680:Multiple/unknown
1551:
1550:
1542:
1541:
1522:
1521:
1496:
1471:
1461:
1460:
1441:
1434:
1427:
1418:
1417:
1296:
1295:
1229:
1228:
1226:
1224:
1207:
1201:
1200:
1198:
1197:
1188:. Archived from
1176:
1170:
1169:
1167:
1166:
1149:
1143:
1142:
1131:
1125:
1124:
1122:
1121:
1106:
1100:
1099:
1087:
1081:
1080:
1072:
1066:
1065:
1063:
1061:
1046:
1040:
1039:
1037:
1036:
1027:. Archived from
1021:
1015:
1012:
1006:
1003:
997:
996:
994:
993:
978:
972:
959:
953:
950:
944:
936:
926:
894:
885:
884:
873:
867:
866:
838:
832:
831:
820:
814:
813:
795:
785:
761:
752:
739:
720:
719:
705:
695:
671:
665:
664:
650:
640:
608:
602:
601:
599:
597:
583:
574:
563:
552:
551:
549:
547:
533:
481:, winner of the
241:
240:
191:
179:
166:
31:
19:
18:
1963:
1962:
1958:
1957:
1956:
1954:
1953:
1952:
1933:
1932:
1931:
1926:
1925:
1912:
1896:
1820:
1802:
1775:
1761:Medulloblastoma
1749:
1711:
1701:
1675:
1645:
1622:
1605:Oligodendrocyte
1599:
1534:
1528:
1526:Neuroepithelial
1507:
1492:
1487:
1464:
1450:
1445:
1415:
1410:
1409:
1386:
1385:
1307:
1280:
1275:
1271:Wayback Machine
1233:
1232:
1222:
1220:
1208:
1204:
1195:
1193:
1178:
1177:
1173:
1164:
1162:
1151:
1150:
1146:
1133:
1132:
1128:
1119:
1117:
1108:
1107:
1103:
1088:
1084:
1073:
1069:
1059:
1057:
1048:
1047:
1043:
1034:
1032:
1023:
1022:
1018:
1013:
1009:
1004:
1000:
991:
989:
980:
979:
975:
960:
956:
951:
938:
937:
895:
888:
875:
874:
870:
849:(10): 1271–86.
839:
835:
822:
821:
817:
776:(12): 2235–41.
762:
755:
749:Wayback Machine
740:
723:
672:
668:
609:
605:
595:
593:
585:
584:
577:
564:
555:
545:
543:
535:
534:
530:
525:
499:Matt Cappotelli
473:Dan Quisenberry
466:Charles Whitman
435:In March 1990,
433:
428:
402:
394:
213:grading systems
209:
202:
192:
183:
180:
171:
167:
139:
130:
114:
112:Pathophysiology
17:
12:
11:
5:
1961:
1951:
1950:
1945:
1928:
1927:
1917:
1914:
1913:
1911:
1910:
1904:
1902:
1898:
1897:
1895:
1894:
1889:
1888:
1887:
1873:
1872:
1871:
1866:
1858:
1853:
1852:
1851:
1846:
1835:
1833:
1826:
1825:
1822:
1821:
1819:
1818:
1812:
1810:
1804:
1803:
1801:
1800:
1795:
1789:
1787:
1781:
1780:
1777:
1776:
1774:
1773:
1768:
1763:
1757:
1755:
1751:
1750:
1748:
1747:
1742:
1737:
1732:
1730:Retinoblastoma
1727:
1721:Ganglioneuroma
1717:
1715:
1707:
1706:
1703:
1702:
1700:
1699:
1694:
1689:
1683:
1681:
1677:
1676:
1674:
1673:
1672:
1671:
1666:
1655:
1653:
1651:Choroid plexus
1647:
1646:
1644:
1643:
1638:
1632:
1630:
1624:
1623:
1621:
1620:
1615:
1609:
1607:
1601:
1600:
1598:
1597:
1596:
1595:
1590:
1585:
1580:
1575:
1570:
1559:
1557:
1548:
1539:
1519:
1513:
1512:
1509:
1508:
1506:
1505:
1499:
1497:
1489:
1488:
1486:
1485:
1480:
1474:
1472:
1458:
1452:
1451:
1444:
1443:
1436:
1429:
1421:
1412:
1411:
1408:
1407:
1395:
1394:
1392:
1388:
1387:
1384:
1383:
1372:
1361:
1350:
1339:
1324:
1308:
1303:
1302:
1300:
1299:Classification
1293:
1292:
1286:
1279:
1278:External links
1276:
1274:
1273:
1261:
1254:
1247:
1239:
1231:
1230:
1202:
1171:
1144:
1126:
1101:
1082:
1067:
1041:
1016:
1007:
998:
973:
954:
909:(3): 170–186.
886:
868:
833:
815:
770:Cancer Science
753:
721:
666:
603:
575:
553:
527:
526:
524:
521:
432:
429:
427:
424:
401:
398:
393:
390:
362:
361:
357:
356:
355:
350:
346:
345:
328:
327:
326:
319:
315:
314:
306:
305:
304:
301:
296:
287:
283:
282:
275:
274:
273:
268:
263:
256:
252:
251:
248:
245:
208:
205:
204:
203:
193:
186:
184:
181:
174:
172:
168:
161:
138:
135:
129:
126:
113:
110:
105:
104:
97:
58:
57:
51:Neuro-oncology
48:
42:
41:
33:
32:
24:
23:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1960:
1949:
1946:
1944:
1941:
1940:
1938:
1924:
1922:
1915:
1909:
1906:
1905:
1903:
1899:
1893:
1890:
1886:
1883:
1882:
1881:
1877:
1874:
1870:
1867:
1865:
1862:
1861:
1859:
1857:
1854:
1850:
1847:
1845:
1842:
1841:
1840:
1839:Neuroblastoma
1837:
1836:
1834:
1831:
1827:
1817:
1814:
1813:
1811:
1809:
1808:Hematopoietic
1805:
1799:
1796:
1794:
1791:
1790:
1788:
1786:
1782:
1772:
1769:
1767:
1764:
1762:
1759:
1758:
1756:
1752:
1746:
1743:
1741:
1738:
1736:
1733:
1731:
1728:
1726:
1725:Ganglioglioma
1722:
1719:
1718:
1716:
1714:
1708:
1698:
1695:
1693:
1690:
1688:
1685:
1684:
1682:
1678:
1670:
1667:
1665:
1662:
1661:
1660:
1657:
1656:
1654:
1652:
1648:
1642:
1641:Subependymoma
1639:
1637:
1634:
1633:
1631:
1629:
1625:
1619:
1616:
1614:
1611:
1610:
1608:
1606:
1602:
1594:
1591:
1589:
1586:
1584:
1581:
1579:
1576:
1574:
1571:
1569:
1566:
1565:
1564:
1561:
1560:
1558:
1556:
1552:
1549:
1547:
1543:
1540:
1537:
1536:spinal tumors
1532:
1527:
1523:
1520:
1518:
1514:
1504:
1501:
1500:
1498:
1495:
1490:
1484:
1481:
1479:
1476:
1475:
1473:
1470:
1468:
1462:
1459:
1457:
1453:
1449:
1442:
1437:
1435:
1430:
1428:
1423:
1422:
1419:
1406:
1402:
1401:
1397:
1396:
1393:
1389:
1382:
1378:
1377:
1373:
1371:
1367:
1366:
1362:
1360:
1356:
1355:
1351:
1349:
1345:
1344:
1340:
1338:
1334:
1333:
1329:
1325:
1323:
1319:
1318:
1314:
1310:
1309:
1306:
1301:
1297:
1290:
1287:
1285:
1282:
1281:
1272:
1268:
1265:
1262:
1259:
1255:
1252:
1248:
1245:
1241:
1240:
1238:
1237:
1219:
1218:
1213:
1206:
1192:on 2015-08-20
1191:
1187:
1186:
1181:
1175:
1160:
1159:
1154:
1148:
1141:. 2007-05-09.
1140:
1136:
1130:
1115:
1111:
1105:
1097:
1093:
1086:
1078:
1071:
1055:
1051:
1045:
1031:on 2009-08-31
1030:
1026:
1020:
1011:
1002:
987:
983:
977:
970:
969:
964:
958:
948:
942:
934:
930:
925:
920:
916:
912:
908:
904:
900:
893:
891:
882:
878:
872:
864:
860:
856:
852:
848:
844:
837:
829:
825:
819:
811:
807:
803:
799:
794:
789:
784:
779:
775:
771:
767:
760:
758:
750:
746:
743:
738:
736:
734:
732:
730:
728:
726:
717:
716:Press Release
713:
709:
704:
699:
694:
689:
686:(2): 026106.
685:
681:
677:
670:
662:
658:
654:
649:
644:
639:
634:
630:
626:
623:(1): e30098.
622:
618:
614:
607:
592:
588:
587:"Astrocytoma"
582:
580:
573:
569:
568:
562:
560:
558:
542:
538:
532:
528:
520:
517:
514:
510:
509:
504:
500:
497:
493:
491:
487:
484:
480:
479:Richard Burns
476:
474:
469:
467:
462:
460:
457:
452:
450:
446:
445:parietal lobe
442:
438:
431:Notable cases
423:
421:
416:
406:
397:
389:
386:
377:
373:
368:
358:
353:
352:
351:
348:
347:
343:
339:
334:
329:
325:
322:
321:
320:
317:
316:
312:
307:
302:
300:
297:
295:) astrocytoma
294:
290:
289:
288:
285:
284:
280:
276:
272:
271:Subependymoma
269:
267:
264:
262:
259:
258:
257:
254:
253:
249:
247:Astrocytomas
246:
243:
242:
239:
237:
233:
229:
224:
221:
218:
214:
200:
196:
190:
185:
178:
173:
165:
160:
159:
158:
154:
150:
148:
144:
134:
125:
123:
119:
109:
102:
98:
95:
94:
93:
90:
88:
84:
83:glioblastomas
80:
76:
72:
68:
65:is a type of
64:
56:
52:
49:
47:
43:
39:
34:
30:
25:
20:
1918:
1876:Neurilemmoma
1864:Neurofibroma
1593:Glioblastoma
1562:
1531:brain tumors
1493:
1465:
1398:
1374:
1363:
1352:
1341:
1326:
1311:
1236:Bibliography
1235:
1234:
1221:. Retrieved
1215:
1205:
1194:. Retrieved
1190:the original
1183:
1174:
1163:. Retrieved
1156:
1147:
1129:
1118:. Retrieved
1116:. 2007-05-01
1104:
1085:
1076:
1070:
1058:. Retrieved
1044:
1033:. Retrieved
1029:the original
1019:
1010:
1001:
990:. Retrieved
976:
966:
957:
941:cite journal
906:
902:
880:
871:
846:
842:
836:
827:
818:
773:
769:
683:
679:
669:
620:
616:
606:
594:. Retrieved
590:
565:
544:. Retrieved
540:
531:
508:Tough Enough
507:
494:
477:
470:
463:
456:U.S. Senator
453:
434:
422:management.
411:
395:
381:
375:
371:
342:temozolomide
338:chemotherapy
250:Description
225:
211:Of numerous
210:
155:
151:
140:
131:
115:
106:
101:infiltration
91:
73:cell in the
62:
61:
55:neurosurgery
1943:Brain tumor
1735:Neurocytoma
1697:Gliosarcoma
1563:Astrocytoma
1483:Pituicytoma
1060:25 February
828:Mayo Clinic
567:Astrocytoma
490:Westminster
459:Ted Kennedy
441:Lee Atwater
291:Low-grade (
67:brain tumor
63:Astrocytoma
22:Astrocytoma
1937:Categories
1880:Schwannoma
1793:Meningioma
1636:Ependymoma
1376:DiseasesDB
1196:2015-08-26
1165:2015-08-26
1120:2015-08-26
1035:2015-11-25
992:2010-02-27
523:References
511:, was the
454:Long-time
420:palliative
392:Prevention
372:IDH mutant
293:fibrillary
244:WHO grade
118:parenchyma
77:called an
1555:Astrocyte
1503:Pinealoma
1456:Endocrine
1400:eMedicine
1054:bbc.co.uk
661:Highlight
572:eMedicine
400:Treatment
170:internus.
137:Diagnosis
79:astrocyte
46:Specialty
1785:Meninges
1628:Ependyma
1405:med/2693
1267:Archived
1223:June 29,
933:33293629
863:17908533
810:16742915
802:19737147
793:11159448
745:Archived
712:32478280
657:22291905
617:PLOS ONE
236:necrosis
145:(CT) or
75:cerebrum
1370:D001254
1348:M9400/3
1217:TheWrap
924:7904519
703:7229984
648:3264559
625:Bibcode
232:mitosis
207:Grading
1713:neuron
1710:Mature
1546:Glioma
1494:Other:
1467:Sellar
1359:137800
931:
921:
881:CBTRUS
861:
808:
800:
790:
710:
700:
655:
645:
596:1 July
546:1 July
228:atypia
87:glioma
1901:Other
1381:29449
1343:ICD-O
806:S2CID
541:WebMD
71:glial
1365:MeSH
1354:OMIM
1332:9-CM
1225:2018
1062:2008
947:link
929:PMID
859:PMID
798:PMID
708:PMID
653:PMID
598:2021
548:2021
483:2001
374:and
318:III
36:Two
1830:PNS
1517:CNS
1337:191
1328:ICD
1322:C71
1313:ICD
1096:WWE
986:CNN
919:PMC
911:doi
851:doi
788:PMC
778:doi
774:100
698:PMC
688:doi
643:PMC
633:doi
570:at
503:WWE
349:IV
286:II
195:MRI
141:An
38:PET
1939::
1923:).
1723::
1403::
1379::
1368::
1357::
1346::
1335::
1320::
1317:10
1214:.
1182:.
1155:.
1137:.
1112:.
1094:.
1052:.
984:.
965:,
943:}}
939:{{
927:.
917:.
907:18
905:.
901:.
889:^
879:.
857:.
847:82
845:.
826:.
804:.
796:.
786:.
772:.
768:.
756:^
724:^
714:.
706:.
696:.
682:.
678:.
659:.
651:.
641:.
631:.
619:.
615:.
589:.
578:^
556:^
539:.
255:I
230:,
53:,
1878:/
1832::
1538:)
1533:,
1529:(
1469::
1440:e
1433:t
1426:v
1330:-
1315:-
1305:D
1260:.
1253:.
1246:.
1227:.
1199:.
1168:.
1123:.
1098:.
1064:.
1038:.
995:.
949:)
935:.
913::
883:.
865:.
853::
830:.
812:.
780::
718:.
690::
684:4
663:.
635::
627::
621:7
600:.
550:.
378:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.